Professional Documents
Culture Documents
51% Attack - Definition, Who Is at Risk, Example, and Cost
51% Attack - Definition, Who Is at Risk, Example, and Cost
Uploaded by
Shaina BustosCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cypherium Whitepaper v1.0Document19 pagesCypherium Whitepaper v1.0WaleedNo ratings yet
- 51% Attack: What Is A 51% Attack?Document2 pages51% Attack: What Is A 51% Attack?Gna OngNo ratings yet
- What Is A 51% Attack On Blockchain? How Does A 51% Attack Work?Document3 pagesWhat Is A 51% Attack On Blockchain? How Does A 51% Attack Work?Farhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Difinition Attack 51%Document1 pageDifinition Attack 51%mask.smileNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.0 - Attacks On BlockchainsDocument29 pagesLecture 3.2.0 - Attacks On BlockchainsSenior GamingNo ratings yet
- Guarding The BlockchainDocument5 pagesGuarding The Blockchainnajam.ecomNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of A 51% Attack and How You Can Prevent OneDocument8 pagesThe Anatomy of A 51% Attack and How You Can Prevent OneGilmar AraujoNo ratings yet
- Blockchain AnswerDocument35 pagesBlockchain AnswerGaurav ShankarNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument2 pagesBlockchainSeun OgunlaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesBlockchain TechnologydhoniNo ratings yet
- NTCCDocument11 pagesNTCCAditya OberaiNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Architecture Design-1Document21 pagesBlock Chain Architecture Design-1Mayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Consensus Attacks, Alt CoinsDocument15 pagesConsensus Attacks, Alt CoinsGaja LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Architecture DesignDocument18 pagesBlock Chain Architecture DesignMayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain ImportantDocument10 pagesBlockchain Importantshuklaanshul312No ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document13 pagesWa0000.AnuNo ratings yet
- Blockchain ArchitectureDocument2 pagesBlockchain Architecturenagham abuwarda0% (1)
- A Novel Approach For Computer Worm Control Using Decentralized Data StructuresDocument4 pagesA Novel Approach For Computer Worm Control Using Decentralized Data Structuresneedmoney90100% (1)
- Black Yellow Dark Simple Digital Technology in Education Technology Presen - 20240229 - 094520 - 0000Document10 pagesBlack Yellow Dark Simple Digital Technology in Education Technology Presen - 20240229 - 094520 - 0000Esha ChavanNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentamandubeyNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument1 pageBlockchainPushpendra gourNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentamandubeyNo ratings yet
- Blockchain and Cryptocuurency AttacksDocument14 pagesBlockchain and Cryptocuurency AttacksAhsan RamzanNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: The Distributed LedgerDocument5 pagesBlockchain: The Distributed LedgerKSHITIJ PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Pros and ConsDocument2 pagesBlockchain Pros and ConsAnkita BhadanaNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument38 pagesUnit Isyednashita786No ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument18 pagesBlockchainChauhan 07No ratings yet
- CSC200 ProjectDocument16 pagesCSC200 ProjectolatunjiemioluwaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Sarfirey GamersNo ratings yet
- Minima Whitepaper v11Document13 pagesMinima Whitepaper v11Agus SetiawanNo ratings yet
- LImitations PoWDocument8 pagesLImitations PoWMeenakshi RajputNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Block-Chain TechnologyDocument4 pagesDefinition:: Block-Chain TechnologyHypersting GamingNo ratings yet
- Bootstrapping BlockchainsDocument6 pagesBootstrapping Blockchainszero 1No ratings yet
- BCT MaterialDocument10 pagesBCT Materialrocky2003rajkumarNo ratings yet
- Loopring WhitepaperDocument15 pagesLoopring WhitepaperСергей БуркатовскийNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument4 pagesBlockchainMichele VaselliNo ratings yet
- Part E-16 Block Chain TechnologyDocument6 pagesPart E-16 Block Chain TechnologyIfra ReNo ratings yet
- Understanding Blockchain ConsensusDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Blockchain Consensusishikaroy607No ratings yet
- Bahirdar University: DistributedDocument7 pagesBahirdar University: DistributedAmen AbatemameNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology Unit I II III NotesDocument43 pagesBlockchain Technology Unit I II III Noteshapiness1131No ratings yet
- (Kit061) Blockchain QuestionbankDocument36 pages(Kit061) Blockchain Questionbankranjeet2213005-dNo ratings yet
- Unlock The Power of Blockchain - DigitalOceanDocument14 pagesUnlock The Power of Blockchain - DigitalOceanMihai TiberiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BlockchainDocument7 pagesChapter 2 BlockchainFarheen AkramNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Assignment 1Document4 pagesE-Commerce Assignment 1Hypersting GamingNo ratings yet
- Tendermint: Consensus Without MiningDocument11 pagesTendermint: Consensus Without MiningRod MarchNo ratings yet
- BCT Notes For Unit-1Document47 pagesBCT Notes For Unit-1MayankNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument23 pagesBlockchainRudra JhaNo ratings yet
- Cypherium: A Scalable and Permissionless Smart Contract PlatformDocument19 pagesCypherium: A Scalable and Permissionless Smart Contract PlatformChakravartthi UrsNo ratings yet
- DEF CON Safe Mode - Blockchain Village - Rastogi Gokul - Verifiable Delay Functions For Preventing DDoS Attacks On Ethereum 2.0Document82 pagesDEF CON Safe Mode - Blockchain Village - Rastogi Gokul - Verifiable Delay Functions For Preventing DDoS Attacks On Ethereum 2.0MitchNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Document6 pagesBlockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Amen AbatemameNo ratings yet
- What Is A Block Chain ?Document2 pagesWhat Is A Block Chain ?Anshul TembhareNo ratings yet
- What Are Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies?Document2 pagesWhat Are Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies?MD S Raju IslamNo ratings yet
- KUS Whitepaper: Open The Hash Castle, Enjoy The Encrypted WorldDocument44 pagesKUS Whitepaper: Open The Hash Castle, Enjoy The Encrypted WorldtheodsNo ratings yet
- RapidChain - A Fast Blockchain Protocol Via Full ShardingDocument31 pagesRapidChain - A Fast Blockchain Protocol Via Full ShardingJexiaNo ratings yet
- QB Answers Ia 1 18ai733Document11 pagesQB Answers Ia 1 18ai733Sahithi BhashyamNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Permissioned Blockchain ProsDocument2 pagesPros and Cons of Permissioned Blockchain ProsAlexandrew charle RimocalNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technologyriley zeroNo ratings yet
- ConsensusDocument19 pagesConsensusfrgegtbgNo ratings yet
- CryptoDocument37 pagesCryptoHARSH GAIKWAD100% (1)
- Blockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1From EverandBlockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1No ratings yet
- 1 UpdatesDocument37 pages1 UpdatesShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Keltner Channel - Definition, How It Works, and How To UseDocument1 pageKeltner Channel - Definition, How It Works, and How To UseShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Kaizen - Understanding The Japanese Business PhilosophyDocument1 pageKaizen - Understanding The Japanese Business PhilosophyShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Understanding KaizenDocument1 pageUnderstanding KaizenShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Keltner Channel MethodsDocument2 pagesKeltner Channel MethodsShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Types of Letters of CreditDocument1 pageTypes of Letters of CreditShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument1 pageFrequently Asked QuestionsShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Example of A Letter of CreditDocument1 pageExample of A Letter of CreditShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Karen Claire F. Palarca BSAC 2-1 Country Comparison Between Singapore and United Arab EmiratesDocument3 pagesKaren Claire F. Palarca BSAC 2-1 Country Comparison Between Singapore and United Arab EmiratesShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Letter of Credit - What It Is, Examples, and How One Is UsedDocument1 pageLetter of Credit - What It Is, Examples, and How One Is UsedShaina BustosNo ratings yet
51% Attack - Definition, Who Is at Risk, Example, and Cost
51% Attack - Definition, Who Is at Risk, Example, and Cost
Uploaded by
Shaina BustosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
51% Attack - Definition, Who Is at Risk, Example, and Cost
51% Attack - Definition, Who Is at Risk, Example, and Cost
Uploaded by
Shaina BustosCopyright:
Available Formats
51% Attack: Definition, Who Is At Risk,
Example, and Cost
Reviewed by ERIKA RASURE
Fact checked by SUZANNE KVILHAUG
What Is a 51% Attack?
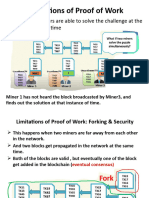
A 51% attack is an attack on a cryptocurrency blockchain by a group of
miners who control more than 50% of the network's mining hash rate.
Owning 51% of the nodes on the network theoretically gives the controlling
parties the power to alter the blockchain.
The attackers would be able to prevent new transactions from gaining
confirmations, allowing them to halt payments between some or all users.
They would also be able to reverse transactions that were completed while
they were in control. Reversing transactions could allow them to
double-spend coins, one of the issues consensus mechanisms like
proof-of-work were created to prevent.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
● Blockchains are distributed ledgers that record every transaction
made on a cryptocurrency's network.
● A 51% attack is an attack on a blockchain by a group of miners who
control more than 50% of the network's mining hash rate.
● Attackers with majority network control can interrupt the recording of
new blocks by preventing other miners from completing blocks.
● Changing historical blocks is impossible due to the chain of
information stored in Bitcoin's blockchain.
● Although a successful attack on Bitcoin or Ethereum is unlikely,
smaller networks are frequent targets for 51% attacks.
You might also like
- Cypherium Whitepaper v1.0Document19 pagesCypherium Whitepaper v1.0WaleedNo ratings yet
- 51% Attack: What Is A 51% Attack?Document2 pages51% Attack: What Is A 51% Attack?Gna OngNo ratings yet
- What Is A 51% Attack On Blockchain? How Does A 51% Attack Work?Document3 pagesWhat Is A 51% Attack On Blockchain? How Does A 51% Attack Work?Farhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Difinition Attack 51%Document1 pageDifinition Attack 51%mask.smileNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.0 - Attacks On BlockchainsDocument29 pagesLecture 3.2.0 - Attacks On BlockchainsSenior GamingNo ratings yet
- Guarding The BlockchainDocument5 pagesGuarding The Blockchainnajam.ecomNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of A 51% Attack and How You Can Prevent OneDocument8 pagesThe Anatomy of A 51% Attack and How You Can Prevent OneGilmar AraujoNo ratings yet
- Blockchain AnswerDocument35 pagesBlockchain AnswerGaurav ShankarNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument2 pagesBlockchainSeun OgunlaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesBlockchain TechnologydhoniNo ratings yet
- NTCCDocument11 pagesNTCCAditya OberaiNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Architecture Design-1Document21 pagesBlock Chain Architecture Design-1Mayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Consensus Attacks, Alt CoinsDocument15 pagesConsensus Attacks, Alt CoinsGaja LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Architecture DesignDocument18 pagesBlock Chain Architecture DesignMayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Blockchain ImportantDocument10 pagesBlockchain Importantshuklaanshul312No ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document13 pagesWa0000.AnuNo ratings yet
- Blockchain ArchitectureDocument2 pagesBlockchain Architecturenagham abuwarda0% (1)
- A Novel Approach For Computer Worm Control Using Decentralized Data StructuresDocument4 pagesA Novel Approach For Computer Worm Control Using Decentralized Data Structuresneedmoney90100% (1)
- Black Yellow Dark Simple Digital Technology in Education Technology Presen - 20240229 - 094520 - 0000Document10 pagesBlack Yellow Dark Simple Digital Technology in Education Technology Presen - 20240229 - 094520 - 0000Esha ChavanNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentamandubeyNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument1 pageBlockchainPushpendra gourNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled DocumentamandubeyNo ratings yet
- Blockchain and Cryptocuurency AttacksDocument14 pagesBlockchain and Cryptocuurency AttacksAhsan RamzanNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: The Distributed LedgerDocument5 pagesBlockchain: The Distributed LedgerKSHITIJ PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Pros and ConsDocument2 pagesBlockchain Pros and ConsAnkita BhadanaNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument38 pagesUnit Isyednashita786No ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument18 pagesBlockchainChauhan 07No ratings yet
- CSC200 ProjectDocument16 pagesCSC200 ProjectolatunjiemioluwaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document9 pagesAssignment 1Sarfirey GamersNo ratings yet
- Minima Whitepaper v11Document13 pagesMinima Whitepaper v11Agus SetiawanNo ratings yet
- LImitations PoWDocument8 pagesLImitations PoWMeenakshi RajputNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Block-Chain TechnologyDocument4 pagesDefinition:: Block-Chain TechnologyHypersting GamingNo ratings yet
- Bootstrapping BlockchainsDocument6 pagesBootstrapping Blockchainszero 1No ratings yet
- BCT MaterialDocument10 pagesBCT Materialrocky2003rajkumarNo ratings yet
- Loopring WhitepaperDocument15 pagesLoopring WhitepaperСергей БуркатовскийNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument4 pagesBlockchainMichele VaselliNo ratings yet
- Part E-16 Block Chain TechnologyDocument6 pagesPart E-16 Block Chain TechnologyIfra ReNo ratings yet
- Understanding Blockchain ConsensusDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Blockchain Consensusishikaroy607No ratings yet
- Bahirdar University: DistributedDocument7 pagesBahirdar University: DistributedAmen AbatemameNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Technology Unit I II III NotesDocument43 pagesBlockchain Technology Unit I II III Noteshapiness1131No ratings yet
- (Kit061) Blockchain QuestionbankDocument36 pages(Kit061) Blockchain Questionbankranjeet2213005-dNo ratings yet
- Unlock The Power of Blockchain - DigitalOceanDocument14 pagesUnlock The Power of Blockchain - DigitalOceanMihai TiberiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BlockchainDocument7 pagesChapter 2 BlockchainFarheen AkramNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Assignment 1Document4 pagesE-Commerce Assignment 1Hypersting GamingNo ratings yet
- Tendermint: Consensus Without MiningDocument11 pagesTendermint: Consensus Without MiningRod MarchNo ratings yet
- BCT Notes For Unit-1Document47 pagesBCT Notes For Unit-1MayankNo ratings yet
- BlockchainDocument23 pagesBlockchainRudra JhaNo ratings yet
- Cypherium: A Scalable and Permissionless Smart Contract PlatformDocument19 pagesCypherium: A Scalable and Permissionless Smart Contract PlatformChakravartthi UrsNo ratings yet
- DEF CON Safe Mode - Blockchain Village - Rastogi Gokul - Verifiable Delay Functions For Preventing DDoS Attacks On Ethereum 2.0Document82 pagesDEF CON Safe Mode - Blockchain Village - Rastogi Gokul - Verifiable Delay Functions For Preventing DDoS Attacks On Ethereum 2.0MitchNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Document6 pagesBlockchain: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)Amen AbatemameNo ratings yet
- What Is A Block Chain ?Document2 pagesWhat Is A Block Chain ?Anshul TembhareNo ratings yet
- What Are Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies?Document2 pagesWhat Are Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies?MD S Raju IslamNo ratings yet
- KUS Whitepaper: Open The Hash Castle, Enjoy The Encrypted WorldDocument44 pagesKUS Whitepaper: Open The Hash Castle, Enjoy The Encrypted WorldtheodsNo ratings yet
- RapidChain - A Fast Blockchain Protocol Via Full ShardingDocument31 pagesRapidChain - A Fast Blockchain Protocol Via Full ShardingJexiaNo ratings yet
- QB Answers Ia 1 18ai733Document11 pagesQB Answers Ia 1 18ai733Sahithi BhashyamNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Permissioned Blockchain ProsDocument2 pagesPros and Cons of Permissioned Blockchain ProsAlexandrew charle RimocalNo ratings yet
- Blockchain TechnologyDocument2 pagesBlockchain Technologyriley zeroNo ratings yet
- ConsensusDocument19 pagesConsensusfrgegtbgNo ratings yet
- CryptoDocument37 pagesCryptoHARSH GAIKWAD100% (1)
- Blockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1From EverandBlockchain: A Guide To Blockchain, The Technology Behind Bitcoin, Ethereum And Other Cryptocurrency: Blockchain, #1No ratings yet
- 1 UpdatesDocument37 pages1 UpdatesShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Keltner Channel - Definition, How It Works, and How To UseDocument1 pageKeltner Channel - Definition, How It Works, and How To UseShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Kaizen - Understanding The Japanese Business PhilosophyDocument1 pageKaizen - Understanding The Japanese Business PhilosophyShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Understanding KaizenDocument1 pageUnderstanding KaizenShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Keltner Channel MethodsDocument2 pagesKeltner Channel MethodsShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Types of Letters of CreditDocument1 pageTypes of Letters of CreditShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument1 pageFrequently Asked QuestionsShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Example of A Letter of CreditDocument1 pageExample of A Letter of CreditShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Karen Claire F. Palarca BSAC 2-1 Country Comparison Between Singapore and United Arab EmiratesDocument3 pagesKaren Claire F. Palarca BSAC 2-1 Country Comparison Between Singapore and United Arab EmiratesShaina BustosNo ratings yet
- Letter of Credit - What It Is, Examples, and How One Is UsedDocument1 pageLetter of Credit - What It Is, Examples, and How One Is UsedShaina BustosNo ratings yet