Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Demo Slides and Drawing
Demo Slides and Drawing
Uploaded by
Mark Lorenz NaldozaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aerobic Gram Negative Rods Flowchart 508Document1 pageAerobic Gram Negative Rods Flowchart 508Issa AlejoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ID FlowchartDocument6 pagesBacterial ID FlowchartTom Tsou50% (2)
- Mycology SimplifiedDocument8 pagesMycology Simplifiedvishuvishu8648No ratings yet
- Fungi NotesDocument5 pagesFungi NotesAmber PeakeNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative CocciDocument4 pagesGram Negative CoccirefuapalackyNo ratings yet
- Nonsporeforming Gram Pos - AngelesDocument1 pageNonsporeforming Gram Pos - AngelesLiterally NoOneNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Gram Negative Rods FlowchartDocument1 pageAerobic Gram Negative Rods FlowchartKeithNo ratings yet
- Week 3 PPT Characteristics and Classification FA MADocument47 pagesWeek 3 PPT Characteristics and Classification FA MAMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- 3.-Helminthes 2Document17 pages3.-Helminthes 2Sherwin BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - MycologyDocument7 pagesMicrobiology - Mycologytdci.franceskorineganzaNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument18 pagesFUNGILei Ann PunlaNo ratings yet
- 2023skill - MKK KtiDocument18 pages2023skill - MKK KtiLILIANA DEWINo ratings yet
- 64b2bc7c3de5b60018322afb - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 07)Document6 pages64b2bc7c3de5b60018322afb - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 07)sourajeetsahoo2610No ratings yet
- Parasitology Study GuideDocument35 pagesParasitology Study GuidesamkennedybusinessNo ratings yet
- HelminthsDocument6 pagesHelminthsJericho TumamaoNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument104 pagesUntitled Notebooksaisri943877No ratings yet
- 12 ResizedDocument68 pages12 Resizedsurojitroy47911No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: The Fungi: Presented By:Dr. Maryam MukhtarDocument12 pagesChapter 9: The Fungi: Presented By:Dr. Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerNo ratings yet
- Mycology For UGDocument24 pagesMycology For UGRishabh Dev KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFDocument18 pages2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFSean SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- Intro Medical Mycology Part 5Document1 pageIntro Medical Mycology Part 5pammcakeghzNo ratings yet
- Zoonosis (Plu - ZoonosessDocument8 pagesZoonosis (Plu - Zoonosess6wcdwfcfydNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotes Fungi+parasites +helminthDocument43 pagesEukaryotes Fungi+parasites +helmintheyadballas35No ratings yet
- L-2 Bot 7 JuneDocument41 pagesL-2 Bot 7 Junedeekshitha 212521No ratings yet
- gramPosOrganisms PDFDocument1 pagegramPosOrganisms PDFPurple basket100% (1)
- Gram Positive CocciDocument27 pagesGram Positive Coccishekhar JhaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument6 pagesGram Positive CoccirefuapalackyNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Helminthic Infection 3Document13 pagesIntestinal Helminthic Infection 3gf5kxqgnx9No ratings yet
- Sporozoa TableDocument2 pagesSporozoa TableJoshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Mycology 1 PrelimDocument4 pagesMycology 1 PrelimKaye Angel VillonNo ratings yet
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAEDocument12 pagesENTEROBACTERIACEAECeline AyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Protista and Fungi-1Document5 pagesChapter 7 Protista and Fungi-1muhammad shoaibNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification Bcom 1Document5 pagesBiological Classification Bcom 1monikakansal213No ratings yet
- Microb B1 CompileDocument13 pagesMicrob B1 CompileEarn chiNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument38 pagesFungiMeong MeongNo ratings yet
- Strongyloides Stercoralis: Faecal Like CylinderDocument18 pagesStrongyloides Stercoralis: Faecal Like CylinderAyop KhNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium: AVI SIDDocument3 pagesPlasmodium: AVI SIDMon DoceNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic MycosesDocument3 pagesOpportunistic MycosesMary100% (1)
- PlasmodiumDocument92 pagesPlasmodiumnitesh rawat100% (2)
- Chapter 8 TransDocument3 pagesChapter 8 Transchayiezen0301No ratings yet
- Gram PositiveDocument7 pagesGram Positiveomprkashkumawat178No ratings yet
- Fluoroquinolones and QuinolonesDocument4 pagesFluoroquinolones and Quinoloneskrithik.2k3No ratings yet
- 01 Virology Eggs Complete PDFDocument27 pages01 Virology Eggs Complete PDFXher Faixal100% (1)
- BotanyDocument25 pagesBotanynaagin12300No ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Gram Positive Non Spore Forming BacilliDocument26 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of Gram Positive Non Spore Forming BacillialmlalyNo ratings yet
- How To Identify Bacteria by Chart .Document30 pagesHow To Identify Bacteria by Chart .hawkar omerNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology RevisionDocument4 pagesBacteriology RevisionVenkat TNo ratings yet
- The Nematodes TabulatedDocument29 pagesThe Nematodes TabulatedAdrienn MangilitNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus-Midterm - 2ND SemDocument6 pagesStreptococcus-Midterm - 2ND Semrhenzyl ganoNo ratings yet
- 06 Parasitoid InsectsDocument23 pages06 Parasitoid InsectsvioindahNo ratings yet
- MBTE2010 Lec 4Document81 pagesMBTE2010 Lec 4makabigail7No ratings yet
- Para SorozoansDocument19 pagesPara Sorozoansandrea.gabrielNo ratings yet
- Identification Identification: Escheria Coli Salmonella TyphimuriumDocument2 pagesIdentification Identification: Escheria Coli Salmonella TyphimuriumMadiNo ratings yet
- Based On Belizario:: Fasciolopsis BuskiDocument6 pagesBased On Belizario:: Fasciolopsis BuskimaqmmNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument18 pagesMicrobiologyAnimesh GiriNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diversity Gram-Negative Strategies For Survival: NitrosomonasDocument30 pagesMicrobial Diversity Gram-Negative Strategies For Survival: NitrosomonasZarlmein TiongsonNo ratings yet
- E Paths Hal A File 801642429049Document9 pagesE Paths Hal A File 801642429049Aijaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Intro To MycoDocument5 pagesIntro To MycoPatricia Marie M. AgnesNo ratings yet
- All You Need to Know About Neck Threadworms and Your Itchy HorseFrom EverandAll You Need to Know About Neck Threadworms and Your Itchy HorseNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- The Nest Is Empty - The Hindu Folio On AgingDocument6 pagesThe Nest Is Empty - The Hindu Folio On AgingebooksufiNo ratings yet
- E Mannual Temperate Fruits 1Document44 pagesE Mannual Temperate Fruits 1gamerrr.mahiNo ratings yet
- Psychosexual Theory - Sigmund Freud: Neurologist PsychoanalysisDocument4 pagesPsychosexual Theory - Sigmund Freud: Neurologist PsychoanalysisEmmajean'Ricky GustiloNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesExercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratespikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- SZ Sales ProgramDocument28 pagesSZ Sales ProgramrossifrancescoNo ratings yet
- Vaux CimreplacmentDocument28 pagesVaux CimreplacmentmanutecNo ratings yet
- Women EmpowermentDocument7 pagesWomen EmpowermentJessica Glenn100% (1)
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document13 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768maquinariakypcon100% (2)
- Leister Plastic-Welding BR Plastic-Fabrication EN PDFDocument48 pagesLeister Plastic-Welding BR Plastic-Fabrication EN PDFDuong DoanNo ratings yet
- Basic Facts About ESOPs2Document20 pagesBasic Facts About ESOPs2Quant TradingNo ratings yet
- Datasheet DD2603Document3 pagesDatasheet DD2603RONALD TERRAZASNo ratings yet
- Printable Cosmetology LawbookDocument42 pagesPrintable Cosmetology LawbookCaro TNo ratings yet
- MYCOSESDocument41 pagesMYCOSESDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Sample ReviewDocument5 pagesSample Reviewdawit gebreyohansNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Five Stages of Grief - Class 6 DocumentDocument2 pagesBeyond The Five Stages of Grief - Class 6 DocumentoksanaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Among High School StudentsDocument21 pagesAnxiety Among High School StudentsFr. Joseph KattakayamNo ratings yet
- (MED II) 1.05 Emergencies in Cancer PatientsDocument17 pages(MED II) 1.05 Emergencies in Cancer PatientsJearwin AngelesNo ratings yet
- Improving Fast-Food Restaurants' Method of Operation: Automated Drive-Through Ordering SystemDocument12 pagesImproving Fast-Food Restaurants' Method of Operation: Automated Drive-Through Ordering SystemAllin John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- ERBEJETDocument8 pagesERBEJETHossain TanjilaaNo ratings yet
- Seal Gas FlowDocument2 pagesSeal Gas FlowoluwasolNo ratings yet
- JuvenilleDocument5 pagesJuvenilleelviemjmontemayorNo ratings yet
- Last Six Months Current AffairsDocument102 pagesLast Six Months Current Affairschoudharysiya8580409398No ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument11 pagesChapter - 10: Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDestroy YtNo ratings yet
- Atumo Thesis TESSDocument58 pagesAtumo Thesis TESStessemaNo ratings yet
- 3 Manufacture of ConcreteDocument13 pages3 Manufacture of Concretekiran sreekumarNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Formulating Sensiva SC 50 Into EmulsionsDocument16 pagesGuidelines For Formulating Sensiva SC 50 Into EmulsionsLogdi JamesNo ratings yet
- Acronyms and Its Meaning: S/N Acronyms Stand For Explainationa & Meaning Examples TLVDocument2 pagesAcronyms and Its Meaning: S/N Acronyms Stand For Explainationa & Meaning Examples TLVshamroz khanNo ratings yet
- GENERAL 5pgDocument5 pagesGENERAL 5pgeee beeNo ratings yet
- Simulation Study of LPG Cooking BurnerDocument3 pagesSimulation Study of LPG Cooking BurnerBensinghdhas Sathiya Dhas100% (1)
- 2020 Proposal Online CarolingDocument2 pages2020 Proposal Online CarolingPel Vincent CruzNo ratings yet
Demo Slides and Drawing
Demo Slides and Drawing
Uploaded by
Mark Lorenz NaldozaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Demo Slides and Drawing
Demo Slides and Drawing
Uploaded by
Mark Lorenz NaldozaCopyright:
Available Formats
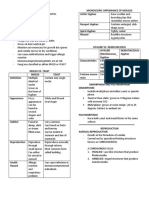
Acid Fast Stain
↳ acid fast organisms
↳ Mycobacterium Spp .
Acidfastnes
e
long-chain ,
multiply-crosslinked
fatty acids in cell wall
↳inMycobacteriane
Ziehl-Neelen staining
by
Positive
: "Red /Pink"
↳ presence of acid-fast bacteria
"Blue"
Negative :
unfertilized
OVA
-
Other Demo Slides :
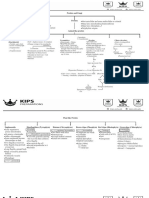
Hookworm
Gram
positive cocci in tetrads Rhabditiform Larva
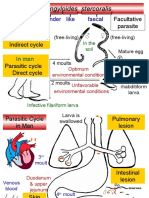
Adult worms live in the lumen of the small intestine. A female may produce
approximately 200,000 eggs per day, which are passed with the feces.
Unfertilized eggs may be ingested but are not infective. Larvae develop to AFB positive
infectivity within fertile eggs after 18 days to several weeks , depending on the
Gram negative bacilli in chain
environmental conditions (optimum: moist, warm, shaded soil). After infective Strongyloides Filariform Larva
eggs are swallowed, the larvae hatch, invade the intestinal mucosa, and are
carried via the portal, then systemic circulation to the lungs. The larvae mature
further in the lungs (10 to 14 days), penetrate the alveolar walls, ascend the
bronchial tree to the throat, and are swallowed. Upon reaching the small intestine,
they develop into adult worms. Between 2 and 3 months are required from
ingestion of the infective eggs to oviposition by the adult female. Adult worms can
live 1 to 2 years.
Hosts
Humans and swine are the major hosts for Ascaris; see Causal Agents for
discussion on species status of Ascaris from both hosts. Natural infections with
A. lumbricoides sometimes occur in monkeys and apes. Adult worms live in the
lumen of the small intestine. A female may produce approximately 200,000 eggs
per day, which are passed with the feces . Unfertilized eggs may be ingested but
are not infective. Larvae develop to infectivity within fertile eggs after 18 days to
several weeks , depending on the environmental conditions (optimum: moist,
warm, shaded soil). After infective eggs are swallowed , the larvae hatch , invade
the intestinal mucosa, and are carried via the portal, then systemic circulation to
the lungs . The larvae mature further in the lungs (10 to 14 days), penetrate the
alveolar walls, ascend the bronchial tree to the throat, and are swallowed . Upon
reaching the small intestine, they develop into adult worms. Between 2 and 3
months are required from ingestion of the infective eggs to oviposition by the
adult female. Adult worms can live 1 to 2 years.
Hosts
Humans and swine are the major hosts for Ascaris; see Causal Agents for
discussion on species status of Ascaris from both hosts. Natural infections with
A. lumbricoides sometimes occur in monkeys and apes.
You might also like
- Aerobic Gram Negative Rods Flowchart 508Document1 pageAerobic Gram Negative Rods Flowchart 508Issa AlejoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ID FlowchartDocument6 pagesBacterial ID FlowchartTom Tsou50% (2)
- Mycology SimplifiedDocument8 pagesMycology Simplifiedvishuvishu8648No ratings yet
- Fungi NotesDocument5 pagesFungi NotesAmber PeakeNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative CocciDocument4 pagesGram Negative CoccirefuapalackyNo ratings yet
- Nonsporeforming Gram Pos - AngelesDocument1 pageNonsporeforming Gram Pos - AngelesLiterally NoOneNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Gram Negative Rods FlowchartDocument1 pageAerobic Gram Negative Rods FlowchartKeithNo ratings yet
- Week 3 PPT Characteristics and Classification FA MADocument47 pagesWeek 3 PPT Characteristics and Classification FA MAMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- 3.-Helminthes 2Document17 pages3.-Helminthes 2Sherwin BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - MycologyDocument7 pagesMicrobiology - Mycologytdci.franceskorineganzaNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument18 pagesFUNGILei Ann PunlaNo ratings yet
- 2023skill - MKK KtiDocument18 pages2023skill - MKK KtiLILIANA DEWINo ratings yet
- 64b2bc7c3de5b60018322afb - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 07)Document6 pages64b2bc7c3de5b60018322afb - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 07)sourajeetsahoo2610No ratings yet
- Parasitology Study GuideDocument35 pagesParasitology Study GuidesamkennedybusinessNo ratings yet
- HelminthsDocument6 pagesHelminthsJericho TumamaoNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument104 pagesUntitled Notebooksaisri943877No ratings yet
- 12 ResizedDocument68 pages12 Resizedsurojitroy47911No ratings yet
- Chapter 9: The Fungi: Presented By:Dr. Maryam MukhtarDocument12 pagesChapter 9: The Fungi: Presented By:Dr. Maryam MukhtarMaryyum UmerNo ratings yet
- Mycology For UGDocument24 pagesMycology For UGRishabh Dev KushwahaNo ratings yet
- 2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFDocument18 pages2A-Sarigumba - 10 MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA PDFSean SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- Intro Medical Mycology Part 5Document1 pageIntro Medical Mycology Part 5pammcakeghzNo ratings yet
- Zoonosis (Plu - ZoonosessDocument8 pagesZoonosis (Plu - Zoonosess6wcdwfcfydNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotes Fungi+parasites +helminthDocument43 pagesEukaryotes Fungi+parasites +helmintheyadballas35No ratings yet
- L-2 Bot 7 JuneDocument41 pagesL-2 Bot 7 Junedeekshitha 212521No ratings yet
- gramPosOrganisms PDFDocument1 pagegramPosOrganisms PDFPurple basket100% (1)
- Gram Positive CocciDocument27 pagesGram Positive Coccishekhar JhaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive CocciDocument6 pagesGram Positive CoccirefuapalackyNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Helminthic Infection 3Document13 pagesIntestinal Helminthic Infection 3gf5kxqgnx9No ratings yet
- Sporozoa TableDocument2 pagesSporozoa TableJoshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Mycology 1 PrelimDocument4 pagesMycology 1 PrelimKaye Angel VillonNo ratings yet
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAEDocument12 pagesENTEROBACTERIACEAECeline AyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Protista and Fungi-1Document5 pagesChapter 7 Protista and Fungi-1muhammad shoaibNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification Bcom 1Document5 pagesBiological Classification Bcom 1monikakansal213No ratings yet
- Microb B1 CompileDocument13 pagesMicrob B1 CompileEarn chiNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument38 pagesFungiMeong MeongNo ratings yet
- Strongyloides Stercoralis: Faecal Like CylinderDocument18 pagesStrongyloides Stercoralis: Faecal Like CylinderAyop KhNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium: AVI SIDDocument3 pagesPlasmodium: AVI SIDMon DoceNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic MycosesDocument3 pagesOpportunistic MycosesMary100% (1)
- PlasmodiumDocument92 pagesPlasmodiumnitesh rawat100% (2)
- Chapter 8 TransDocument3 pagesChapter 8 Transchayiezen0301No ratings yet
- Gram PositiveDocument7 pagesGram Positiveomprkashkumawat178No ratings yet
- Fluoroquinolones and QuinolonesDocument4 pagesFluoroquinolones and Quinoloneskrithik.2k3No ratings yet
- 01 Virology Eggs Complete PDFDocument27 pages01 Virology Eggs Complete PDFXher Faixal100% (1)
- BotanyDocument25 pagesBotanynaagin12300No ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Gram Positive Non Spore Forming BacilliDocument26 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of Gram Positive Non Spore Forming BacillialmlalyNo ratings yet
- How To Identify Bacteria by Chart .Document30 pagesHow To Identify Bacteria by Chart .hawkar omerNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology RevisionDocument4 pagesBacteriology RevisionVenkat TNo ratings yet
- The Nematodes TabulatedDocument29 pagesThe Nematodes TabulatedAdrienn MangilitNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus-Midterm - 2ND SemDocument6 pagesStreptococcus-Midterm - 2ND Semrhenzyl ganoNo ratings yet
- 06 Parasitoid InsectsDocument23 pages06 Parasitoid InsectsvioindahNo ratings yet
- MBTE2010 Lec 4Document81 pagesMBTE2010 Lec 4makabigail7No ratings yet
- Para SorozoansDocument19 pagesPara Sorozoansandrea.gabrielNo ratings yet
- Identification Identification: Escheria Coli Salmonella TyphimuriumDocument2 pagesIdentification Identification: Escheria Coli Salmonella TyphimuriumMadiNo ratings yet
- Based On Belizario:: Fasciolopsis BuskiDocument6 pagesBased On Belizario:: Fasciolopsis BuskimaqmmNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument18 pagesMicrobiologyAnimesh GiriNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diversity Gram-Negative Strategies For Survival: NitrosomonasDocument30 pagesMicrobial Diversity Gram-Negative Strategies For Survival: NitrosomonasZarlmein TiongsonNo ratings yet
- E Paths Hal A File 801642429049Document9 pagesE Paths Hal A File 801642429049Aijaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Intro To MycoDocument5 pagesIntro To MycoPatricia Marie M. AgnesNo ratings yet
- All You Need to Know About Neck Threadworms and Your Itchy HorseFrom EverandAll You Need to Know About Neck Threadworms and Your Itchy HorseNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- The Nest Is Empty - The Hindu Folio On AgingDocument6 pagesThe Nest Is Empty - The Hindu Folio On AgingebooksufiNo ratings yet
- E Mannual Temperate Fruits 1Document44 pagesE Mannual Temperate Fruits 1gamerrr.mahiNo ratings yet
- Psychosexual Theory - Sigmund Freud: Neurologist PsychoanalysisDocument4 pagesPsychosexual Theory - Sigmund Freud: Neurologist PsychoanalysisEmmajean'Ricky GustiloNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesExercise 4:: Organic Components: CarbohydratespikachuzingungaNo ratings yet
- SZ Sales ProgramDocument28 pagesSZ Sales ProgramrossifrancescoNo ratings yet
- Vaux CimreplacmentDocument28 pagesVaux CimreplacmentmanutecNo ratings yet
- Women EmpowermentDocument7 pagesWomen EmpowermentJessica Glenn100% (1)
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document13 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768maquinariakypcon100% (2)
- Leister Plastic-Welding BR Plastic-Fabrication EN PDFDocument48 pagesLeister Plastic-Welding BR Plastic-Fabrication EN PDFDuong DoanNo ratings yet
- Basic Facts About ESOPs2Document20 pagesBasic Facts About ESOPs2Quant TradingNo ratings yet
- Datasheet DD2603Document3 pagesDatasheet DD2603RONALD TERRAZASNo ratings yet
- Printable Cosmetology LawbookDocument42 pagesPrintable Cosmetology LawbookCaro TNo ratings yet
- MYCOSESDocument41 pagesMYCOSESDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Sample ReviewDocument5 pagesSample Reviewdawit gebreyohansNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Five Stages of Grief - Class 6 DocumentDocument2 pagesBeyond The Five Stages of Grief - Class 6 DocumentoksanaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Among High School StudentsDocument21 pagesAnxiety Among High School StudentsFr. Joseph KattakayamNo ratings yet
- (MED II) 1.05 Emergencies in Cancer PatientsDocument17 pages(MED II) 1.05 Emergencies in Cancer PatientsJearwin AngelesNo ratings yet
- Improving Fast-Food Restaurants' Method of Operation: Automated Drive-Through Ordering SystemDocument12 pagesImproving Fast-Food Restaurants' Method of Operation: Automated Drive-Through Ordering SystemAllin John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- ERBEJETDocument8 pagesERBEJETHossain TanjilaaNo ratings yet
- Seal Gas FlowDocument2 pagesSeal Gas FlowoluwasolNo ratings yet
- JuvenilleDocument5 pagesJuvenilleelviemjmontemayorNo ratings yet
- Last Six Months Current AffairsDocument102 pagesLast Six Months Current Affairschoudharysiya8580409398No ratings yet
- Chapter - 10: Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument11 pagesChapter - 10: Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDestroy YtNo ratings yet
- Atumo Thesis TESSDocument58 pagesAtumo Thesis TESStessemaNo ratings yet
- 3 Manufacture of ConcreteDocument13 pages3 Manufacture of Concretekiran sreekumarNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Formulating Sensiva SC 50 Into EmulsionsDocument16 pagesGuidelines For Formulating Sensiva SC 50 Into EmulsionsLogdi JamesNo ratings yet
- Acronyms and Its Meaning: S/N Acronyms Stand For Explainationa & Meaning Examples TLVDocument2 pagesAcronyms and Its Meaning: S/N Acronyms Stand For Explainationa & Meaning Examples TLVshamroz khanNo ratings yet
- GENERAL 5pgDocument5 pagesGENERAL 5pgeee beeNo ratings yet
- Simulation Study of LPG Cooking BurnerDocument3 pagesSimulation Study of LPG Cooking BurnerBensinghdhas Sathiya Dhas100% (1)
- 2020 Proposal Online CarolingDocument2 pages2020 Proposal Online CarolingPel Vincent CruzNo ratings yet