Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth Science Student Book - CPO Focus On-94-97
Earth Science Student Book - CPO Focus On-94-97
Uploaded by
jhonatanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earth Science Student Book - CPO Focus On-94-97
Earth Science Student Book - CPO Focus On-94-97
Uploaded by
jhonatanCopyright:
Available Formats
4.2 How Does Heat Move?
Ice cream will melt when it comes in contact with warm air molecules. How does this convection - transfer of heat
happen? This section describes how heat is transferred. through the motion of liquids and
gases.
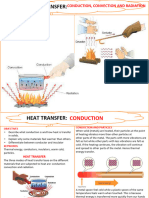
Heat transfer by convection
What is Convection is the transfer of heat through the motion of gases and
convection? liquids such as air and water. Warm air tends to rise and cold air
tends to sink. Convection occurs naturally in Earth’s atmosphere.
Convection also occurs in homes. To understand convection, let’s
think of how a room gets heated.
Convection is A radiator is a device used to heat a room. Heat from a radiator
used to heat warms nearby air atoms. The warmed atoms move quickly and
rooms carry heat energy as they rise above the radiator. A curtain above
the radiator flutters as fast-moving atoms collide with it.
Eventually, heat from the radiator and convection of the air make
the room comfortably warm.
Figure 4.6: Hawks use convection to
soar. They are lifted higher in the sky by
rising warm air.
Convection is Air near Earth’s surface gets warm and rises. Hawks make use of
used to fly convection to soar in the sky. Rising warm air provides lift so that
hawks can soar. Eventually, the rising warm air cools down and
sinks back to the ground where it may get reheated.
82 UNIT 2 ENERGY IN EARTH’S SYSTEMS
CHAPTER 4: HEAT
Heat transfer by conduction
What is Conduction is the transfer of heat by the direct contact of atoms
conduction? and molecules in solids. Heat is transferred from atom to atom by
direct contact. If you hold an ice cube in your hand, warmer hand
atoms will transfer heat by conduction to the cooler ice cube atoms.
Example of heat Unlike the atoms in liquids and gases, the atoms in solids are conduction - transfer of heat by
transfer by anchored in place. They can wiggle and push each other, but they direct contact of atoms and
molecules.
conduction do not move freely. If you place a cold spoon into a mug of hot cocoa,
you may notice that the handle of the spoon becomes warm. If solid
atoms can’t move freely, how does the handle of a spoon resting in a
mug of hot cocoa get warm? Imagine the spoon handle as a long line
of atoms. At first, all of the atoms are moving at similar speeds.
You know this because the whole handle is at the same
temperature. Soon the part of the handle closest to the surface of
the cocoa heats up. This means that the handle’s atoms close to the
surface of the cocoa are now wiggling and pushing at a higher
speed. As these atoms push other atoms further along the handle,
these more distant atoms speed up in turn. In a similar fashion, the Where is conduction in your
atoms are sped up all along the handle. Transferring heat this way house? Walk through your house.
is an example of conduction. In each room, observe whether or
not there are objects that are
involved in conduction. Based on
your observations, make a list of
as many examples of heat transfer
by conduction as you can.
Remember, heat transfer by
conduction works in solids,
because direct contact of atoms
and molecules must occur.
4.2 HOW DOES HEAT MOVE?
83
Heat transfer by radiation
What is The warmth of the Sun on your face feels good on a cool day.
radiation? The heat from the Sun is necessary for life to exist on Earth radiation - heat transfer that
(Figure 4.7). This heat is not transferred to Earth by conduction or involves energy waves and no
direct contact or movement by
convection. Instead, the Sun’s heat reaches Earth by a heat atoms.
transfer process called radiation. Radiation is heat transfer
through empty space. Heat transfer by radiation occurs without
direct contact or movement of atoms.
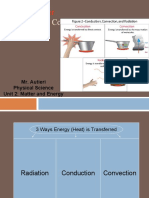
Summary of All three forms of heat transfer are often working at the same time
convection, to transfer energy from warmer objects to cooler objects. A pot of
conduction, and water being heated by a campfire is warmed through the process
radiation of conduction, convection, and radiation!
Figure 4.7: The Sun’s heat is the
product of nuclear reactions between
atoms in the Sun. The Sun’s heat
reaches Earth by radiation.
84 UNIT 2 ENERGY IN EARTH’S SYSTEMS
CHAPTER 4: HEAT
4.2 Section Review
Another type of power plant
1. Why does an ice cube melt in your hand?
You have probably heard of
2. State the type of heat transfer that is occurring in each nuclear power plants. These
situation: power plants produce heat using
a. Warm air rises. radioactivity. When unstable atoms
undergo radioactive decay, they
b. You feel the heat on your feet as you walk barefoot across a also happen to produce heat. This
driveway in the summertime. heat can be used to heat water. As
c. You feel the warmth of the Sun on your face. with power plants that use fossil
fuels, nuclear power plants work
3. A hawk gets some help while flying by using convection
by using the steam from heated
currents (air currents created by rising warm air). How is the water to turn a turbine. The turbine
Sun involved in creating convection currents? converts the energy from the
4. How would heat transfer occur in the following substances or steam into energy that turns a
objects? generator. The generator then
converts this kinetic energy into
a. The atmosphere electricity.
b. A metal rod
c. Water in a pot
d. An empty pot on a hot stove
e. The air inside a hot-air balloon
5. You mom is cooking a pot of spaghetti on the stove. You observe
that the spaghetti moves all around the pot even though she
isn’t stirring. What makes the spaghetti move?
6. How is radiation different from heat transfer by convection and
conduction?
7. A thermostat controls the switches on a furnace or air
conditioner by sensing room temperature. Explain, using
conduction, convection, and radiation, where you would place
the thermostat in your classroom. Consider windows, outside
and inside walls, and the locations of heating and cooling ducts.
4.2 HOW DOES HEAT MOVE?
85
You might also like
- Microscale Inorganic Chemistry - A Comprehensive Laboratory Experience - Szafran, ZviDocument392 pagesMicroscale Inorganic Chemistry - A Comprehensive Laboratory Experience - Szafran, ZviJade Fromage79% (14)
- MetallurgyDocument19 pagesMetallurgyShubh RamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy ReadingDocument5 pagesThermal Energy Readingapi-189616674No ratings yet
- NGSS3D MSPS ThermalEnergyTransfer EXPLAIN STEMscopediaDocument7 pagesNGSS3D MSPS ThermalEnergyTransfer EXPLAIN STEMscopediaSivekiNo ratings yet
- 0 BooksDocument16 pages0 BooksRameen FatimaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Temperatu-ReDocument11 pagesHeat and Temperatu-ReFedora MefiaNo ratings yet
- ثرموDocument9 pagesثرموasmaaabdelkreem71No ratings yet
- Las 7 Q3 Week 6Document2 pagesLas 7 Q3 Week 6Darven Cinchez100% (1)
- ScE7.2.3 Booklet 2019 - ANSWERSDocument7 pagesScE7.2.3 Booklet 2019 - ANSWERSBackup UserNo ratings yet
- ENGI 273 Lec 2 - IspringDocument22 pagesENGI 273 Lec 2 - IspringHaidy T. SakrNo ratings yet
- B.7-3 Thermal Energy TransferDocument22 pagesB.7-3 Thermal Energy TransferajinnorabahurNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment 8Document1 pageFormative Assessment 8bashadelacruz7No ratings yet
- HE BackDocument2 pagesHE BackJoshua BrightNo ratings yet
- Sci Oly 2.0Document12 pagesSci Oly 2.0arinaitwejoshua24No ratings yet
- Difference Between Conduction Convection and Radiation Gr. VDocument2 pagesDifference Between Conduction Convection and Radiation Gr. Vm.kadarfi26No ratings yet
- HeatDocument12 pagesHeatMayukh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy (GZ) 2017Document20 pagesHeat Energy (GZ) 2017kaviNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferSquidward TentaclesNo ratings yet
- Detailed PrintneDocument9 pagesDetailed PrintneAiza GenanibanNo ratings yet
- Energy TransferDocument6 pagesEnergy TransferSamin YasarNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument35 pagesHeat TransferUbaid Khan100% (2)
- S2Phy Unit 6-Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument56 pagesS2Phy Unit 6-Transfer of Thermal EnergyAung Ye HtetNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer - G6 Lesson NotesDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer - G6 Lesson NotesJung Ahn HongNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat Week6Document28 pagesTemperature and Heat Week6Marc Jenley MarqhitesNo ratings yet
- Fill-In-The-Blank-Heat TransferDocument1 pageFill-In-The-Blank-Heat TransferPrecious ChirangareNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Heat Transfer Learning Activity Sheets 6Document3 pagesScience 7 Heat Transfer Learning Activity Sheets 6fitz zamoraNo ratings yet
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument9 pagesHeat Transfersattyams93No ratings yet
- G-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3Document9 pagesG-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3AbebechNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Student HandoutDocument39 pagesHeat Exchanger Student HandoutkotiNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Thermal ProcessesDocument6 pages2.3 Thermal ProcesseshaiderNo ratings yet
- PhysicssDocument5 pagesPhysicsschionumaraliaNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Heat and TemperatureDocument32 pagesCH 13 Heat and TemperaturetuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Heat 7.1 Heat As A Form of Energy (Haba Sebagai Bentuk Tenaga)Document4 pagesChapter 7: Heat 7.1 Heat As A Form of Energy (Haba Sebagai Bentuk Tenaga)Siti Norahimmah MbiaNo ratings yet
- Review of Past Terms:: - Define "Energy"Document26 pagesReview of Past Terms:: - Define "Energy"vinooDS100% (1)
- David Physics s3Document12 pagesDavid Physics s3RUKUNDO OliveNo ratings yet
- 4 Fundamentals of Heat TransferDocument36 pages4 Fundamentals of Heat TransferShaurya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 8 Class PhysicsDocument269 pages8 Class PhysicsDauren KamshybekovNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer ConductionconvectionradiationDocument14 pagesEnergy Transfer ConductionconvectionradiationalongsilatNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer ConductionconvectionradiationDocument14 pagesEnergy Transfer Conductionconvectionradiationkumpul tugasNo ratings yet
- II. A. TemperatureDocument7 pagesII. A. TemperatureWă ÎłNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection Radiation CusmsDocument26 pagesConduction Convection Radiation CusmsMitanshu ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 1Document75 pagesLecture No 1Raza AnsariNo ratings yet
- Modes of Heat TransferDocument6 pagesModes of Heat TransferfaisalNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Unit 10: Transfer of Thermal Energy: Non-Metals MetalsDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Unit 10: Transfer of Thermal Energy: Non-Metals MetalsJawad hossainNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Unit 10: Transfer of Thermal Energy: Non-Metals MetalsDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Unit 10: Transfer of Thermal Energy: Non-Metals MetalsHush PereraNo ratings yet
- Answer in Earth's Internal HeatDocument16 pagesAnswer in Earth's Internal HeatShadz Dhan100% (2)
- 11-Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument46 pages11-Transfer of Thermal Energyrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- 10SCIO - Conduction Convection and Radiation - Theory & Quiz - 160319Document8 pages10SCIO - Conduction Convection and Radiation - Theory & Quiz - 160319Danny TNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection and Radiation: Heat TransferDocument14 pagesConduction, Convection and Radiation: Heat Transferlucky asliNo ratings yet
- THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT (LESSON (PlanDocument7 pagesTHERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT (LESSON (Planarjie cajoconNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Thermal ProcessesDocument21 pages3.5 Thermal ProcessesEkaitz SantamariaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy and Heat: Jennefer CardenasDocument14 pagesThermal Energy and Heat: Jennefer CardenasMinduliNo ratings yet
- Comprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementDocument33 pagesComprendre Les Différents Modes de Transferts de Chaleur, Conduction, Convection Et RayonnementAhmed MobarkiNo ratings yet
- Physics Thermal Equilibrium LessonDocument24 pagesPhysics Thermal Equilibrium LessonRufat IsmayilovNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat TransferDocument7 pagesTemperature and Heat TransferAhmed HashkarNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TransesDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer TransesERICKA MAE CANTOSNo ratings yet
- UNIDAD10 Sources of EnergyDocument10 pagesUNIDAD10 Sources of EnergyPedro MIRANDA FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection and Radiation Lesson 2Document9 pagesConduction Convection and Radiation Lesson 2Ajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument3 pagesHeatmantwin_88No ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument24 pagesHeat TransferABEGAIL SOLIMANNo ratings yet
- Effects of Fruit Coatings, Fungicide, and Storage Temperature On Fruit Shelf-Life and Qualities of California' PapayaDocument8 pagesEffects of Fruit Coatings, Fungicide, and Storage Temperature On Fruit Shelf-Life and Qualities of California' PapayaRahmidamiliyntNo ratings yet
- Cspe Xlpe Uhdpe CpeDocument34 pagesCspe Xlpe Uhdpe Cpesuranjana26No ratings yet
- B1e 004Document40 pagesB1e 004Ganesh BabuNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of The Chemical Composition and Bioactive Ingredients of The Chinese Medicinal Mushroom DongChongXiaCao, Its Counterfeit and Mimic, and Fermented Mycelium of Cordyceps SinensisDocument7 pagesA Comparison of The Chemical Composition and Bioactive Ingredients of The Chinese Medicinal Mushroom DongChongXiaCao, Its Counterfeit and Mimic, and Fermented Mycelium of Cordyceps SinensisHoang IceNo ratings yet
- Tecatron Gf40 Black en All 201711Document2 pagesTecatron Gf40 Black en All 201711JorgeMariscalNo ratings yet
- Manual Kit Reagen Kreatinin HumanDocument1 pageManual Kit Reagen Kreatinin HumanZayyyanNo ratings yet
- Introduction SaponificationDocument2 pagesIntroduction SaponificationMUHAMMAD NUR KHAIRINo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and EthersDocument5 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and Ethersyeet buoyNo ratings yet
- Ionpure® VNX High Flow Continuous Electrodeionization (CEDI) ModulesDocument2 pagesIonpure® VNX High Flow Continuous Electrodeionization (CEDI) ModulesEdwinNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument17 pagesHydrocarbonlalitkumarNo ratings yet
- Ammónia Nyomás-Entalpia Diagramja, Logaritmikus LéptékezésselDocument1 pageAmmónia Nyomás-Entalpia Diagramja, Logaritmikus LéptékezésselNHI TRẦN TUYẾTNo ratings yet
- Astm E999Document5 pagesAstm E999amein kaidNo ratings yet
- Determination of Colorant Type in Yellow Tofu Using Vis - NIR and SW - NIRDocument20 pagesDetermination of Colorant Type in Yellow Tofu Using Vis - NIR and SW - NIRsrihartiNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration ReviewDocument24 pagesMedication Administration ReviewReignallienn Inocencio MartinNo ratings yet
- A Method For Optimizing Jet-Mill-Bit Hydraulics in Horizontal DrillingDocument7 pagesA Method For Optimizing Jet-Mill-Bit Hydraulics in Horizontal DrillingAgungRizkyNo ratings yet
- Proportional Pressure Reducing Valve, Direct Operated, Increasing Characteristic Curve FTDRE 2 KDocument12 pagesProportional Pressure Reducing Valve, Direct Operated, Increasing Characteristic Curve FTDRE 2 KsnsnagarajanNo ratings yet
- CrosswordDocument2 pagesCrosswordPaula Larios AguilarNo ratings yet
- Monthly Report: Pt. Rainbow Indah Carpet Finishing DepartmentDocument34 pagesMonthly Report: Pt. Rainbow Indah Carpet Finishing DepartmentDwinanto RahmatNo ratings yet
- Radiographer - 2013 - Currie - Radionuclide ProductionDocument7 pagesRadiographer - 2013 - Currie - Radionuclide Productionmemeththikadimagi2001No ratings yet
- BRB 1288-Be-EghsDocument11 pagesBRB 1288-Be-EghsSofiNo ratings yet
- FRAP Tutorial EMBO DebrecenDocument55 pagesFRAP Tutorial EMBO DebrecenYunonNo ratings yet
- LPG Vs Vs DA-1Document18 pagesLPG Vs Vs DA-1GitanjaliNo ratings yet
- Biomimetic Approaches and Materials in Restorative and Regenerative Dentistry: Review ArticleDocument14 pagesBiomimetic Approaches and Materials in Restorative and Regenerative Dentistry: Review ArticleAtisha BansalNo ratings yet
- Journal Polyphenols SugarcaneDocument11 pagesJournal Polyphenols SugarcaneMarkNo ratings yet
- Solubility Curve WorksheetDocument5 pagesSolubility Curve WorksheetRohanee Hafsa KapusanNo ratings yet
- Rockland Community College BIO 107 Honors Review For Lab Practical IDocument2 pagesRockland Community College BIO 107 Honors Review For Lab Practical IkuriiriNo ratings yet
- 31.12.23 SR - Star Co-Sc (Model A, B&C) Jee Main Gtm-4 - QPDocument18 pages31.12.23 SR - Star Co-Sc (Model A, B&C) Jee Main Gtm-4 - QPReddyNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Edexcel (9-1) Student Book Answers: Download NowDocument1 pageCHEMISTRY Edexcel (9-1) Student Book Answers: Download NowTiannaNo ratings yet