Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Training Exercises
Lab Training Exercises
Uploaded by
Helena Pascual PérezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mini Vet Guide Preview 1Document28 pagesMini Vet Guide Preview 1Mariana HiginoNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology-McqDocument2 pagesHuman Physiology-Mcqaryan kothambiaNo ratings yet
- Components of Nursing Health HistoryDocument3 pagesComponents of Nursing Health Historyrenz_redoblado77% (13)
- Ancient Primer For Practical Godhead: The Deer Exercise For MenDocument25 pagesAncient Primer For Practical Godhead: The Deer Exercise For MenAnirudh100% (4)
- Lipid Metabolism 2023Document36 pagesLipid Metabolism 2023Moses MutsikwiNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument38 pagesFatty Acid SynthesisEmm NomanNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis by Prof DR Abdalla Jarari 2nd Year For VIDEOSDocument66 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis by Prof DR Abdalla Jarari 2nd Year For VIDEOSnoran alfaitoryNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument37 pagesFatty Acid MetabolismEniola abdullahi AduagbaNo ratings yet
- + F.R.Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument28 pages+ F.R.Fatty Acid SynthesisAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- BCH 1212 Lipid Metabolism 1Document44 pagesBCH 1212 Lipid Metabolism 1Hamirie JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Lipogenesis & Fatty Acid BiosynthesisDocument42 pagesLipogenesis & Fatty Acid BiosynthesisSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Document18 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Sanreet Randhawa100% (1)
- De Novo Synthesis of Fatty AcidsDocument40 pagesDe Novo Synthesis of Fatty Acidsangela marie abadillaNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 2019Document26 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis 2019Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument30 pagesFatty Acid Synthesisabdullah zaheerNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Breakdown: Coa-Sh +Document12 pagesFatty Acid Breakdown: Coa-Sh +Ika DewiNo ratings yet
- BIOSINTESISDocument34 pagesBIOSINTESISAyodia RanggiNo ratings yet
- Z (H) IV Biochemistry 2Document28 pagesZ (H) IV Biochemistry 2hariom.hospitalNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids SynthesisDocument25 pagesFatty Acids Synthesisjuveriyamehreen611No ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis: Molecular Biochemistry IIDocument31 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis: Molecular Biochemistry IIDozdiNo ratings yet
- 2.2 TCA CycleDocument14 pages2.2 TCA Cyclesabirinaly30No ratings yet
- Fatty Acid BiossynthesisDocument30 pagesFatty Acid Biossynthesisbrayan felipe de hoyos jimenezNo ratings yet
- 2 Aula 21.22 Síntese de Ácidos GordosDocument42 pages2 Aula 21.22 Síntese de Ácidos GordosFilipa MendesNo ratings yet
- 2021 BCH313 Lipids Biosynthesis Word NotesDocument18 pages2021 BCH313 Lipids Biosynthesis Word NotesApheleleNo ratings yet
- Lipid BiosynthesisDocument187 pagesLipid BiosynthesisThanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- TCA Cycle by J. BoyeDocument20 pagesTCA Cycle by J. Boyegen. wadayioo samejoNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument28 pagesFatty Acid MetabolismPrakash KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Four Days Session - Day 3 Updated - PresentationDocument597 pagesFour Days Session - Day 3 Updated - PresentationKALI ANIRUDH GNo ratings yet
- Sintesis LemakDocument35 pagesSintesis LemakAndriati RahayuNo ratings yet
- The Krebs Cycle: Removal of Hydrogens and Electrons, and The Release of CODocument24 pagesThe Krebs Cycle: Removal of Hydrogens and Electrons, and The Release of COLeann RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument20 pagesCitric Acid CycleAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- N Acetyl-Coa: Overview: Lipids To SucroseDocument1 pageN Acetyl-Coa: Overview: Lipids To SucroseLuke ShantiNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument28 pagesFatty Acid Synthesishassanainshahi13No ratings yet
- 12 Fatty Acid and TAG Biosynthesis 20141115Document15 pages12 Fatty Acid and TAG Biosynthesis 20141115Chui WaiNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid BiosynthesisDocument7 pagesFatty Acid BiosynthesisJeremiah Eyo AmanamNo ratings yet
- Digestion of Triacylglycerols Beta-Oxidation of Fatty Acids ATP and Fatty Acid OxidationDocument31 pagesDigestion of Triacylglycerols Beta-Oxidation of Fatty Acids ATP and Fatty Acid OxidationNICHAEL MARIA CELINA UYNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathways For Lipids and Amino AcidsDocument17 pagesMetabolic Pathways For Lipids and Amino AcidsLa Ode RinaldiNo ratings yet
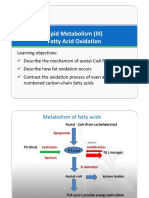
- Lipid Metabolism (III) - Fatty Acid OxidationDocument28 pagesLipid Metabolism (III) - Fatty Acid Oxidationlightning proNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Fatty AcidsDocument3 pagesBiosynthesis of Fatty AcidsAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Lipids (2) NewDocument64 pagesMetabolism of Lipids (2) NewLyra Get100% (1)
- Biochemistry Ii: Lipid BiosynthesisDocument13 pagesBiochemistry Ii: Lipid BiosynthesisPrem Sagar MishraNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Body ProductionDocument4 pagesRegulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Body ProductionJireh Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Oxidation and Synthesis of Ketone BodyDocument58 pagesFatty Acid Oxidation and Synthesis of Ketone BodyCeciliaNo ratings yet
- Biokim Fatty AcidDocument4 pagesBiokim Fatty AcidSepti Darlia PutriNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Lipids - 2. Lipogenesis. Metabolism of Cholesterol. Regulation and Pathology of Lipid Metabolism: Obesity, AtherosclerosisDocument70 pagesMetabolism of Lipids - 2. Lipogenesis. Metabolism of Cholesterol. Regulation and Pathology of Lipid Metabolism: Obesity, AtherosclerosisdrjanggeumNo ratings yet
- 2 - Lipid BiosynthesisDocument44 pages2 - Lipid BiosynthesisAhmed HamarnehNo ratings yet
- FA Synthesis Part One Illustration AtfDocument1 pageFA Synthesis Part One Illustration Atfnofov45585No ratings yet
- The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. GrishamDocument60 pagesThe Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grishamaabolton21No ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis: 28.1 Stages of FA SynthesisDocument13 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis: 28.1 Stages of FA SynthesisrJNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids SynthesisDocument30 pagesFatty Acids SynthesisGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- L15 Oxidation of Fatty Acids and KetogenesisDocument50 pagesL15 Oxidation of Fatty Acids and Ketogenesisyebadem228No ratings yet
- B-Oxidation of Fatty AcidDocument41 pagesB-Oxidation of Fatty AcidSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis Fatty AcidsDocument59 pagesBiosynthesis Fatty AcidsKate Alyssa Caton100% (1)
- Fatty Acid OxidationDocument28 pagesFatty Acid OxidationEmm NomanNo ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument41 pagesBeta Oxidationguna sundariNo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids 1Document22 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty Acids 1ShaikafridNo ratings yet
- Fattyacidsynthesis Dr. Balakrishna Biochemistry 08.05.2020Document30 pagesFattyacidsynthesis Dr. Balakrishna Biochemistry 08.05.2020scurvy foxNo ratings yet
- Gandham RajeevDocument41 pagesGandham RajeevAlok PatraNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and TCA Cycle ActivityDocument6 pagesGlycolysis and TCA Cycle ActivityYannis ZoldenbergNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Lipid Biosynthesis (4pp) PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 21 Lipid Biosynthesis (4pp) PDFAfdal AdhaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument15 pagesOxidation of Fatty AcidsMomena SafdarNo ratings yet
- M - 29 Lipid MetabolismDocument5 pagesM - 29 Lipid MetabolismDr. Tapan Kr. DuttaNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceDocument4 pagesCitric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceBiochemistry DenNo ratings yet
- DM Type 2Document13 pagesDM Type 2Yssah Moira HamacNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA Prof EvaDocument3 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA Prof EvaElsy Pramitha SariNo ratings yet
- Determining Canine Estrus Stage Via Vaginal Cytology: TheriogenologyDocument3 pagesDetermining Canine Estrus Stage Via Vaginal Cytology: TheriogenologyGissele ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Cold Hip BathDocument8 pagesCold Hip BathahalyaNo ratings yet
- Hormons: A. B. C. D. EDocument12 pagesHormons: A. B. C. D. ERashri SharmaNo ratings yet
- Heroes Come in Every SizeDocument8 pagesHeroes Come in Every SizeIrul MelonNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology ReviewerDocument57 pagesMedical Technology ReviewerOng Christopher100% (2)
- CC 2 Lec-CompreDocument105 pagesCC 2 Lec-CompreLyra Dennise Llido100% (2)
- Neonatal Hyperglycemia: Irina Franciucirina FranciucDocument11 pagesNeonatal Hyperglycemia: Irina Franciucirina FranciucAnaNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsDocument47 pagesAnticoagulantsMARK VINCENT BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn Care: Fluid (Green Amniotic Fluid) ) To Prevent AspirationDocument17 pagesEssential Newborn Care: Fluid (Green Amniotic Fluid) ) To Prevent AspirationthadzamingNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Versi InggDocument18 pagesJurnal Versi InggAtika NajlaNo ratings yet
- Applied Biology - Mod 12-Csir Net: Suman BhattacharjeeDocument50 pagesApplied Biology - Mod 12-Csir Net: Suman BhattacharjeeGeorge Kishore DasNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument18 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistsKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Disorders in The Critically Ill PatientDocument11 pagesAcid-Base Disorders in The Critically Ill PatientAriel Pinares La ONo ratings yet
- Amphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-6Document4 pagesAmphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-6Vh TRNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument50 pagesObesityKetan JainNo ratings yet
- Anindra Nallapat (33Y/M) Diabetc Profle - Advanced New: Report For Tests AskedDocument28 pagesAnindra Nallapat (33Y/M) Diabetc Profle - Advanced New: Report For Tests AskedAnindra NallapatiNo ratings yet
- Disoreder Sex of DevelopmentDocument37 pagesDisoreder Sex of DevelopmentBesth To Frynce HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition IGCSE BiologyDocument20 pagesPlant Nutrition IGCSE BiologyHarnoor KaurNo ratings yet
- Drug Clearance: Dr. Rajib Bhattacharjee Asstt. Professor Dept of Pharmacy, NSUDocument11 pagesDrug Clearance: Dr. Rajib Bhattacharjee Asstt. Professor Dept of Pharmacy, NSUMohannad AlfadhalNo ratings yet
- TSH LiaisonDocument6 pagesTSH Liaisonsorayafathi90No ratings yet
- MODULE 7-11 Notes PrefiDocument7 pagesMODULE 7-11 Notes PrefiPASCUAL, ALJON R.No ratings yet
- Gynae T and D Expl - 1Document44 pagesGynae T and D Expl - 1vivekanurag97No ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3Document188 pagesScience 10 Q3mariacayeneNo ratings yet
Lab Training Exercises
Lab Training Exercises
Uploaded by
Helena Pascual PérezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Training Exercises
Lab Training Exercises
Uploaded by
Helena Pascual PérezCopyright:
Available Formats
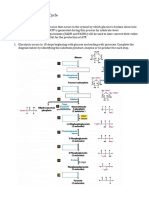
1.
Draw structural formulas and name (using both the Δ and ω nomenclatures) :
a) 18-carbon chain length fatty acid with two double bonds at ω6 and ω9 positions;
b) 20-carbon chain length fatty acid with three double bonds at Δ5, Δ8, and Δ11 positions.
c) Which of these fatty acids must be included in the diet and why?
2. Explain how carbohydrate catabolism is related to fatty acid synthesis.
Carbohydrate catabolism and fatty acid synthesis are linked through the shared intermediate
acetyl-CoA. Carbohydrate breakdown produces acetyl-CoA, a key substrate for both energy
production (via the citric acid cycle) and fatty acid synthesis. Additionally, NADPH, essential
for fatty acid synthesis, is generated through pathways like the pentose phosphate pathway,
branching from glycolysis. This integration allows cells to balance energy production and
storage based on nutrient availability and metabolic demands.
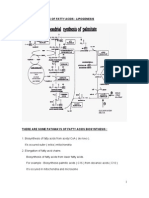
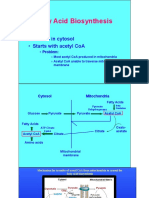
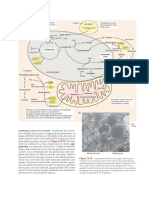
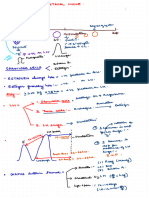
3. Explain how carbons for fatty acid synthesis are transported from mitochondria into the cytosol.
Draw a schematic depiction of this process.
Cytosce
Mitochondria
e
↓
Citrate shuttle
kC < Citrate D
I
Oxalacetate
- -
Azety-CoA +
rate
L
Barty (OA
+ Oxal.
I p-citram
Lyase
↓ ---
Acety COA
·eavage
↓ ↓
Fatty Acids oxalantall
syn
ratty
.
Acids Syn
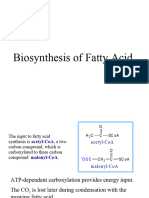
4. What is the preparatory reaction of fatty acid synthesis? Which enzyme catalyzes this
reaction? Briefly describe the catalytic activity(-es) of this enzyme and indicate coenzyme.
HCO3-QDMUCONCoA
Acet ye-CoA + ATP + +
ADP
ACC utilizes the coenzyme biotin to transfer a carboxyl group from bicarbonate to acetyl-
CoA, forming malonyl-CoA. This step is crucial for the regulation and initiation of fatty acid
synthesis.
5. What is the enzyme complex that catalyzes synthesis of palmitic acid? Briefly explain the
enzymatic activity(-ies) of this complex. Indicate coenzymes necessary for this complex
The enzyme complex responsible for synthesizing palmitic acid is fatty acid synthase (FAS).
FAS carries out a series of enzymatic activities, including acetyl and malonyl transfers,
condensation, reduction, dehydration, and enoyl reduction. These activities, repeated in cycles,
add two-carbon units to the growing fatty acid chain until palmitic acid is formed (C16:0). The
coenzymes involved are NADPH and the carrier protein ACP (Acyl Carrier Protein).
You might also like
- Mini Vet Guide Preview 1Document28 pagesMini Vet Guide Preview 1Mariana HiginoNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology-McqDocument2 pagesHuman Physiology-Mcqaryan kothambiaNo ratings yet
- Components of Nursing Health HistoryDocument3 pagesComponents of Nursing Health Historyrenz_redoblado77% (13)
- Ancient Primer For Practical Godhead: The Deer Exercise For MenDocument25 pagesAncient Primer For Practical Godhead: The Deer Exercise For MenAnirudh100% (4)
- Lipid Metabolism 2023Document36 pagesLipid Metabolism 2023Moses MutsikwiNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument38 pagesFatty Acid SynthesisEmm NomanNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis by Prof DR Abdalla Jarari 2nd Year For VIDEOSDocument66 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis by Prof DR Abdalla Jarari 2nd Year For VIDEOSnoran alfaitoryNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument37 pagesFatty Acid MetabolismEniola abdullahi AduagbaNo ratings yet
- + F.R.Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument28 pages+ F.R.Fatty Acid SynthesisAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- BCH 1212 Lipid Metabolism 1Document44 pagesBCH 1212 Lipid Metabolism 1Hamirie JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Lipogenesis & Fatty Acid BiosynthesisDocument42 pagesLipogenesis & Fatty Acid BiosynthesisSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Document18 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis 11.12.19Sanreet Randhawa100% (1)
- De Novo Synthesis of Fatty AcidsDocument40 pagesDe Novo Synthesis of Fatty Acidsangela marie abadillaNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis 2019Document26 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis 2019Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument30 pagesFatty Acid Synthesisabdullah zaheerNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Breakdown: Coa-Sh +Document12 pagesFatty Acid Breakdown: Coa-Sh +Ika DewiNo ratings yet
- BIOSINTESISDocument34 pagesBIOSINTESISAyodia RanggiNo ratings yet
- Z (H) IV Biochemistry 2Document28 pagesZ (H) IV Biochemistry 2hariom.hospitalNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids SynthesisDocument25 pagesFatty Acids Synthesisjuveriyamehreen611No ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis: Molecular Biochemistry IIDocument31 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis: Molecular Biochemistry IIDozdiNo ratings yet
- 2.2 TCA CycleDocument14 pages2.2 TCA Cyclesabirinaly30No ratings yet
- Fatty Acid BiossynthesisDocument30 pagesFatty Acid Biossynthesisbrayan felipe de hoyos jimenezNo ratings yet
- 2 Aula 21.22 Síntese de Ácidos GordosDocument42 pages2 Aula 21.22 Síntese de Ácidos GordosFilipa MendesNo ratings yet
- 2021 BCH313 Lipids Biosynthesis Word NotesDocument18 pages2021 BCH313 Lipids Biosynthesis Word NotesApheleleNo ratings yet
- Lipid BiosynthesisDocument187 pagesLipid BiosynthesisThanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- TCA Cycle by J. BoyeDocument20 pagesTCA Cycle by J. Boyegen. wadayioo samejoNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument28 pagesFatty Acid MetabolismPrakash KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Four Days Session - Day 3 Updated - PresentationDocument597 pagesFour Days Session - Day 3 Updated - PresentationKALI ANIRUDH GNo ratings yet
- Sintesis LemakDocument35 pagesSintesis LemakAndriati RahayuNo ratings yet
- The Krebs Cycle: Removal of Hydrogens and Electrons, and The Release of CODocument24 pagesThe Krebs Cycle: Removal of Hydrogens and Electrons, and The Release of COLeann RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument20 pagesCitric Acid CycleAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- N Acetyl-Coa: Overview: Lipids To SucroseDocument1 pageN Acetyl-Coa: Overview: Lipids To SucroseLuke ShantiNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument28 pagesFatty Acid Synthesishassanainshahi13No ratings yet
- 12 Fatty Acid and TAG Biosynthesis 20141115Document15 pages12 Fatty Acid and TAG Biosynthesis 20141115Chui WaiNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid BiosynthesisDocument7 pagesFatty Acid BiosynthesisJeremiah Eyo AmanamNo ratings yet
- Digestion of Triacylglycerols Beta-Oxidation of Fatty Acids ATP and Fatty Acid OxidationDocument31 pagesDigestion of Triacylglycerols Beta-Oxidation of Fatty Acids ATP and Fatty Acid OxidationNICHAEL MARIA CELINA UYNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathways For Lipids and Amino AcidsDocument17 pagesMetabolic Pathways For Lipids and Amino AcidsLa Ode RinaldiNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism (III) - Fatty Acid OxidationDocument28 pagesLipid Metabolism (III) - Fatty Acid Oxidationlightning proNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Fatty AcidsDocument3 pagesBiosynthesis of Fatty AcidsAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Lipids (2) NewDocument64 pagesMetabolism of Lipids (2) NewLyra Get100% (1)
- Biochemistry Ii: Lipid BiosynthesisDocument13 pagesBiochemistry Ii: Lipid BiosynthesisPrem Sagar MishraNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Body ProductionDocument4 pagesRegulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Body ProductionJireh Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Oxidation and Synthesis of Ketone BodyDocument58 pagesFatty Acid Oxidation and Synthesis of Ketone BodyCeciliaNo ratings yet
- Biokim Fatty AcidDocument4 pagesBiokim Fatty AcidSepti Darlia PutriNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Lipids - 2. Lipogenesis. Metabolism of Cholesterol. Regulation and Pathology of Lipid Metabolism: Obesity, AtherosclerosisDocument70 pagesMetabolism of Lipids - 2. Lipogenesis. Metabolism of Cholesterol. Regulation and Pathology of Lipid Metabolism: Obesity, AtherosclerosisdrjanggeumNo ratings yet
- 2 - Lipid BiosynthesisDocument44 pages2 - Lipid BiosynthesisAhmed HamarnehNo ratings yet
- FA Synthesis Part One Illustration AtfDocument1 pageFA Synthesis Part One Illustration Atfnofov45585No ratings yet
- The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. GrishamDocument60 pagesThe Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: Reginald H. Garrett Charles M. Grishamaabolton21No ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Synthesis: 28.1 Stages of FA SynthesisDocument13 pagesFatty Acid Synthesis: 28.1 Stages of FA SynthesisrJNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids SynthesisDocument30 pagesFatty Acids SynthesisGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- L15 Oxidation of Fatty Acids and KetogenesisDocument50 pagesL15 Oxidation of Fatty Acids and Ketogenesisyebadem228No ratings yet
- B-Oxidation of Fatty AcidDocument41 pagesB-Oxidation of Fatty AcidSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis Fatty AcidsDocument59 pagesBiosynthesis Fatty AcidsKate Alyssa Caton100% (1)
- Fatty Acid OxidationDocument28 pagesFatty Acid OxidationEmm NomanNo ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument41 pagesBeta Oxidationguna sundariNo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids 1Document22 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty Acids 1ShaikafridNo ratings yet
- Fattyacidsynthesis Dr. Balakrishna Biochemistry 08.05.2020Document30 pagesFattyacidsynthesis Dr. Balakrishna Biochemistry 08.05.2020scurvy foxNo ratings yet
- Gandham RajeevDocument41 pagesGandham RajeevAlok PatraNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and TCA Cycle ActivityDocument6 pagesGlycolysis and TCA Cycle ActivityYannis ZoldenbergNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Lipid Biosynthesis (4pp) PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 21 Lipid Biosynthesis (4pp) PDFAfdal AdhaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument15 pagesOxidation of Fatty AcidsMomena SafdarNo ratings yet
- M - 29 Lipid MetabolismDocument5 pagesM - 29 Lipid MetabolismDr. Tapan Kr. DuttaNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceDocument4 pagesCitric Acid Cycle: Central Metabolic Cycle and Its SignificanceBiochemistry DenNo ratings yet
- DM Type 2Document13 pagesDM Type 2Yssah Moira HamacNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA Prof EvaDocument3 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA Prof EvaElsy Pramitha SariNo ratings yet
- Determining Canine Estrus Stage Via Vaginal Cytology: TheriogenologyDocument3 pagesDetermining Canine Estrus Stage Via Vaginal Cytology: TheriogenologyGissele ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Cold Hip BathDocument8 pagesCold Hip BathahalyaNo ratings yet
- Hormons: A. B. C. D. EDocument12 pagesHormons: A. B. C. D. ERashri SharmaNo ratings yet
- Heroes Come in Every SizeDocument8 pagesHeroes Come in Every SizeIrul MelonNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology ReviewerDocument57 pagesMedical Technology ReviewerOng Christopher100% (2)
- CC 2 Lec-CompreDocument105 pagesCC 2 Lec-CompreLyra Dennise Llido100% (2)
- Neonatal Hyperglycemia: Irina Franciucirina FranciucDocument11 pagesNeonatal Hyperglycemia: Irina Franciucirina FranciucAnaNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsDocument47 pagesAnticoagulantsMARK VINCENT BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn Care: Fluid (Green Amniotic Fluid) ) To Prevent AspirationDocument17 pagesEssential Newborn Care: Fluid (Green Amniotic Fluid) ) To Prevent AspirationthadzamingNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Versi InggDocument18 pagesJurnal Versi InggAtika NajlaNo ratings yet
- Applied Biology - Mod 12-Csir Net: Suman BhattacharjeeDocument50 pagesApplied Biology - Mod 12-Csir Net: Suman BhattacharjeeGeorge Kishore DasNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument18 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistsKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Disorders in The Critically Ill PatientDocument11 pagesAcid-Base Disorders in The Critically Ill PatientAriel Pinares La ONo ratings yet
- Amphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-6Document4 pagesAmphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-6Vh TRNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument50 pagesObesityKetan JainNo ratings yet
- Anindra Nallapat (33Y/M) Diabetc Profle - Advanced New: Report For Tests AskedDocument28 pagesAnindra Nallapat (33Y/M) Diabetc Profle - Advanced New: Report For Tests AskedAnindra NallapatiNo ratings yet
- Disoreder Sex of DevelopmentDocument37 pagesDisoreder Sex of DevelopmentBesth To Frynce HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition IGCSE BiologyDocument20 pagesPlant Nutrition IGCSE BiologyHarnoor KaurNo ratings yet
- Drug Clearance: Dr. Rajib Bhattacharjee Asstt. Professor Dept of Pharmacy, NSUDocument11 pagesDrug Clearance: Dr. Rajib Bhattacharjee Asstt. Professor Dept of Pharmacy, NSUMohannad AlfadhalNo ratings yet
- TSH LiaisonDocument6 pagesTSH Liaisonsorayafathi90No ratings yet
- MODULE 7-11 Notes PrefiDocument7 pagesMODULE 7-11 Notes PrefiPASCUAL, ALJON R.No ratings yet
- Gynae T and D Expl - 1Document44 pagesGynae T and D Expl - 1vivekanurag97No ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3Document188 pagesScience 10 Q3mariacayeneNo ratings yet