Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CMT Definitions
CMT Definitions
Uploaded by
CHARLES LEJANOCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 3-D WheelDocument24 pages3-D WheelKim Ciudadano29% (7)
- QA-QC PlanDocument18 pagesQA-QC PlanSen IMO67% (3)
- Quality ControlDocument30 pagesQuality Controlpandey_baibhav100% (2)
- CMATS 11nov2019 PDFDocument352 pagesCMATS 11nov2019 PDFJICA DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Qa & QC Manual - DraftDocument15 pagesQa & QC Manual - DraftNayla Shafea Azzahra100% (1)
- Unified BSR Rural Road PMGSY Rajasthan 20 December 2019Document103 pagesUnified BSR Rural Road PMGSY Rajasthan 20 December 2019Roopesh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Friction Coefficient For Concrete Cast On SoilDocument2 pagesFriction Coefficient For Concrete Cast On SoilBogdanB100% (2)
- HQ (M+W) (HQ+E) S: Duties of A Materials EngineerDocument20 pagesHQ (M+W) (HQ+E) S: Duties of A Materials Engineerjoren calzadoNo ratings yet
- Material Testing Quality ControlDocument22 pagesMaterial Testing Quality Controlsarbjeet singhNo ratings yet
- OVERVIEW Materials QualityDocument14 pagesOVERVIEW Materials QualityRomeo Beding Densen Jr.No ratings yet
- PQMDocument32 pagesPQMJun KhoNo ratings yet
- Material Testing & Quality ControlDocument22 pagesMaterial Testing & Quality ControlJun Michael100% (1)
- CMT Merged-2 1Document7 pagesCMT Merged-2 1MerickNo ratings yet
- Matls - Engr. Accr. ReviewDocument352 pagesMatls - Engr. Accr. ReviewJun Kho100% (1)
- Qa QC ProgrammeDocument6 pagesQa QC ProgrammesrisetNo ratings yet
- Minimum Testing Requirement: Quality ControlDocument4 pagesMinimum Testing Requirement: Quality Controlaybi pearlNo ratings yet
- C. Manufactured: 2. Handling and Storage of MaterialsDocument1 pageC. Manufactured: 2. Handling and Storage of MaterialsCiv PaesNo ratings yet
- QAQCDocument56 pagesQAQCRavindra Babu Sivapu100% (1)
- Sop 03Document29 pagesSop 03kamatgauravNo ratings yet
- Quality Requirements TA1056 MBI Sampang Agung Brewery Extension 014000 - 1Document10 pagesQuality Requirements TA1056 MBI Sampang Agung Brewery Extension 014000 - 1ery achjariNo ratings yet
- Introduction Importance of Materials TestingDocument61 pagesIntroduction Importance of Materials TestingJIENNY LOU TENGCONo ratings yet
- Quality ControlDocument37 pagesQuality ControlMark Anthony Limbo67% (3)
- A Study of Quality Control and Quality Assurance at Construction SiteDocument19 pagesA Study of Quality Control and Quality Assurance at Construction Sitetapan12345100% (14)
- Qaqcsuk LatestDocument126 pagesQaqcsuk LatestNajimieItachiIINo ratings yet
- Road Construction Essentials QA/QC PlanDocument10 pagesRoad Construction Essentials QA/QC Planrafiullah amireeNo ratings yet
- Quality Control PlanDocument13 pagesQuality Control PlanMohammad Taqi HamidiNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Policy: Project Special ProvisionsDocument4 pagesPurpose and Policy: Project Special Provisionsraditanka aobakweNo ratings yet
- Quality ManualDocument4 pagesQuality ManualAli IrvaliNo ratings yet
- Quality ControlDocument30 pagesQuality ControlkhanNo ratings yet
- 01 40 00 FL Quality RequirementsDocument11 pages01 40 00 FL Quality RequirementssbunNo ratings yet
- 23sampling Methods and Quality Assurance PlanDocument34 pages23sampling Methods and Quality Assurance PlanSumit Rathi100% (1)
- Quality ControlDocument30 pagesQuality ControlMohammedNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance and Quality Control PlanDocument6 pagesQuality Assurance and Quality Control PlanTia KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Section 014500 Quality Control and Testing - Rev1Document5 pagesSection 014500 Quality Control and Testing - Rev1Al LopezNo ratings yet
- 6 QualityDocument6 pages6 QualityAhmed GamalNo ratings yet
- Construction Specification 494-Contractor Quality Control: 1. ScopeDocument3 pagesConstruction Specification 494-Contractor Quality Control: 1. Scopedarlene zaraNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification 3Document2 pagesTechnical Specification 3Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- (05727) - Precast Concrete Technician Study GuideDocument37 pages(05727) - Precast Concrete Technician Study GuideTharach JanesuapasaereeNo ratings yet
- PQP EpldtDocument8 pagesPQP Epldtmartin leeNo ratings yet
- Number Three Wind Farm Lewis County, New York Case 16-F-0328 May 2018 1 Project InformationDocument6 pagesNumber Three Wind Farm Lewis County, New York Case 16-F-0328 May 2018 1 Project Informationblackberry7130gNo ratings yet
- 560-S27 QUALITY CONTROL PROGRAM Rev.4Document27 pages560-S27 QUALITY CONTROL PROGRAM Rev.4AbdelmuneimNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification 2Document2 pagesTechnical Specification 2Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Section 014000 Quality Requirements - Rev1Document6 pagesSection 014000 Quality Requirements - Rev1Al LopezNo ratings yet
- Tip QC PlanDocument14 pagesTip QC PlanTC Nihal AlcansoyNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument25 pagesReportSHAIK HUMAYUNNo ratings yet
- 12 Project Quality Plan 7.11.20 (Final)Document81 pages12 Project Quality Plan 7.11.20 (Final)Michael Patungan100% (1)
- Quality Control of BuildingDocument7 pagesQuality Control of BuildingsrikanthNo ratings yet
- MQCH Orientation Project Engineers3Document42 pagesMQCH Orientation Project Engineers3engr rangNo ratings yet
- QC ProgramDocument7 pagesQC ProgramHerbert HernandezNo ratings yet
- Project Quality Management-1Document9 pagesProject Quality Management-1Abdelaziz sharafNo ratings yet
- GPPM 22 PDFDocument64 pagesGPPM 22 PDFKirti Ambastha100% (1)
- Quality Management in Construction ProjectDocument36 pagesQuality Management in Construction ProjectPravin MindeNo ratings yet
- Typical Job Description For Inspection/Quality AssuranceDocument20 pagesTypical Job Description For Inspection/Quality AssuranceMahfoz KazolNo ratings yet
- Project Qulaity Plan DraftDocument9 pagesProject Qulaity Plan DraftAhmad CheemaNo ratings yet
- Quality Control of High Way MaterialsDocument41 pagesQuality Control of High Way MaterialsPearl UnarineNo ratings yet
- Lecture On-Importance of Materials TestingDocument61 pagesLecture On-Importance of Materials TestingLovely Luna100% (3)
- Method Statement For BlockworksMasonry - WelcomeDocument1 pageMethod Statement For BlockworksMasonry - WelcomeChristopher PantojaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 QUALITY MANAGEMENTDocument17 pagesModule 3 QUALITY MANAGEMENTThippesh GNNo ratings yet
- Solid Concrete Brick and Block QC-QA Program Manual - 2014Document19 pagesSolid Concrete Brick and Block QC-QA Program Manual - 2014velmurug_balaNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document5 pagesWa0000.oguaputaezijNo ratings yet
- QC MANUAL (Project Quality Plan) WisnuDocument10 pagesQC MANUAL (Project Quality Plan) WisnuNovie DwiyantiNo ratings yet
- Expansive PDFDocument6 pagesExpansive PDFAlê Fabiano CavalcanteNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions Paper I: ASME Awareness and Section VIII Code. 1Document4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions Paper I: ASME Awareness and Section VIII Code. 1RahulNo ratings yet
- Pressure Method - AASHTO T 152 (ASTM C231)Document5 pagesPressure Method - AASHTO T 152 (ASTM C231)Einstein JeboneNo ratings yet
- Magma 150 and 230 Owner Operator ManualDocument48 pagesMagma 150 and 230 Owner Operator ManualAwatef BahloulNo ratings yet
- Plastic Heater - PT - Bella Prima Perkasa-Model CORE BUNDDLEDocument1 pagePlastic Heater - PT - Bella Prima Perkasa-Model CORE BUNDDLETopik Budi OetomoNo ratings yet
- PFRS 15 - DayagDocument105 pagesPFRS 15 - DayagASHERAH ENGKONGNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document25 pagesLab Report 1Cherif Chokeir60% (5)
- Terracotta Tile 2019 Company EditionDocument8 pagesTerracotta Tile 2019 Company EditionSiti ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Masina Gheata ArkticDocument160 pagesMasina Gheata ArkticPetre IonNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Directional DrillingDocument7 pagesHorizontal Directional DrillingDebasis SahaNo ratings yet
- Vit MeDocument1 pageVit MeBo Cau GaiNo ratings yet
- Swell-Shrink Behavior of Expansive Soils, Damage and Control PDFDocument10 pagesSwell-Shrink Behavior of Expansive Soils, Damage and Control PDFbela_medeiros-1No ratings yet
- Instructions: Page 1 of 5 Instruction Sheet NumberDocument5 pagesInstructions: Page 1 of 5 Instruction Sheet NumberOnofreNo ratings yet
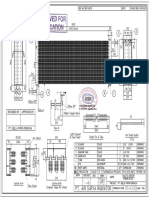
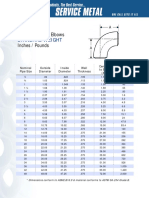
- Long Radius 90° Elbows Inches / Pounds: Standard WeightDocument1 pageLong Radius 90° Elbows Inches / Pounds: Standard WeightezhiljananiNo ratings yet
- Aircrete Blocks Technical Manual: Sub Head Hanson Building ProductsDocument56 pagesAircrete Blocks Technical Manual: Sub Head Hanson Building ProductseaNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin Trucks: Companion Flange, ReplacementDocument8 pagesService Bulletin Trucks: Companion Flange, ReplacementZulmary Pirela azuajeNo ratings yet
- Design of Connections: Fig 4.1: Typical Connections: (A) Beam To Column (B) Beam To BeamDocument16 pagesDesign of Connections: Fig 4.1: Typical Connections: (A) Beam To Column (B) Beam To BeamMuriungi RicharsNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Fibers..Document14 pagesBamboo Fibers..vinese.althearNo ratings yet
- Cept Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesCept Literature ReviewAmaan Jahangir AlamNo ratings yet
- Comparison Cda Ancold GuidelinesDocument1 pageComparison Cda Ancold Guidelinesjosafa_engNo ratings yet
- Op-3-60. Checklist For Supervision of Earthworks: Work Instructions For EngineersDocument4 pagesOp-3-60. Checklist For Supervision of Earthworks: Work Instructions For Engineersjinwook75No ratings yet
- Apl Apollo Tubes Limited Unit-Iii: Works-Vill-Kudavali Plot No-M-1, Murbad, 421401, Thane (MS)Document1 pageApl Apollo Tubes Limited Unit-Iii: Works-Vill-Kudavali Plot No-M-1, Murbad, 421401, Thane (MS)devanshbhuvansht.823No ratings yet
- Hexalobular (6 Lobe) Socket Pan Head Machine Screws: Article# d1 d2 Max. K Max. T Max. A LDocument3 pagesHexalobular (6 Lobe) Socket Pan Head Machine Screws: Article# d1 d2 Max. K Max. T Max. A LRavindra ErabattiNo ratings yet
- 2018-SAC-LATAM-SPEC60Hz - AM040MXMKKC - EA CONDENSADORADocument3 pages2018-SAC-LATAM-SPEC60Hz - AM040MXMKKC - EA CONDENSADORAFabian HernandezNo ratings yet
- Ra 544 Civil Engineering Law 11321Document7 pagesRa 544 Civil Engineering Law 11321JHON MARK YANONGNo ratings yet
- Street Light Pole Specification MS 16112021Document3 pagesStreet Light Pole Specification MS 16112021Mahmudul Hasan TanuNo ratings yet
- MS-02-Method Statement For Surface Excavation WorksDocument22 pagesMS-02-Method Statement For Surface Excavation WorksAmila Priyadarshana DissanayakeNo ratings yet
CMT Definitions
CMT Definitions
Uploaded by
CHARLES LEJANOCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CMT Definitions
CMT Definitions
Uploaded by
CHARLES LEJANOCopyright:
Available Formats
CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS AND TESTING
Materials Quality Control and Its Significance
A. Definitions
QUALITY - is a judgment by the costumers or users of a product or service, it is the
extent which the costumes or users feel the product or service passes their needs and
expectations.
The term QUALITY is that characteristic of a product that provides a level of
performance in terms of service and life. “Quality” does not mean “perfect”.
Quality Control Work is the responsibility of contractor
Quality control work consists of all work elements carried out by the manager or by those
in his organization, which contribute to the quality of the output of the organization
Quality Assurance Work
Quality assurance work consists of all work elements carried out by the manager or by
those in his organization, which contribute to the quality of the output of some other
organization.
-J.R. Taylor
Quality Control System
B. Purpose
The purpose of materials quality control is to insure the highest quality of work and
extend the service life of any structure by constructing according to the prescribed plans
and specifications. The plans indicate the specific type of the structure and the
specifications present the characteristic in which it is to be built, as well as the materials
that are to be incorporated into the work.
Other purposes are to check and regulate the use of construction materials, and to
economize on the cost of construction. Fulfilling these, requires adequate control of
materials prior to and after placing to their final position in the structure. The extent of
controlling the required materials depends on the nature and limits of the work, the
specification requirements and local conditions. Normally, every material should be
subjected to testing, inspection and verification before acceptance.
C. Quality Control Procedures
1. Selection of Materials
Information regarding the location of materials sources that will be
incorporated into the work may be represented by the following:
a. Raw materials such as soil, sand and bank or river gravel (with little or no
processing).
b. Materials that are processed without basically changing their properties, such
as washed/ manufactured sand, crushed rock and gravel, and etc.
c. Manufactured materials such as bituminous materials, cement, paint,
structural and reinforcing steel.
d. Combination of materials that may be partly or totally manufactured, such as
bituminous and Portland cement concrete.
Materials to be postured or obtained from selected portions of any are of
materials sources such as mentioned above should be known in advance so
that the required tests can be made or arrangement for testing the materials
involved may be done to avoid unnecessary delays in construction due to
rejection of unacceptable quality of materials.
2. Handling and storage of materials
Handling and storage of delivered construction materials should be carefully
and properly planned to avoid damage and maintain the desired quality. It should
be placed or deposited in a safe place protected from contamination or the action
of weather. The proposed source of materials to be used should be accessible to
the project.
Conditions for Acceptance of Materials
a. No materials shall be incorporated into the work until tested and found
satisfactory.
b. The approval of preliminary samples shall not be considered as a guarantee
of acceptance of all materials from the same source, as to the quality and
quantity of such materials.
c. Any materials which had been sampled and passed as satisfactory may be
resampled and retested any time before, during and after incorporation into
the work.
3. Sampling and Testing of Materials
Quality control is checking for conformity to the requirements. That is,
conformance to materials specifications and methods of construction, or
workmanship. Quality control therefore, includes all procedures which are
necessary to insure that the materials used and workmanship employed conform
to the standard of quality specified.
a. Quality control program (QCP)
To facilitate quality control, a program of quality control works to be
complied by the contractor is prepared by the DPWH. The plan include
provisions on how the work and materials should be inspected and the
nature and amount of testing to be done. An example of a quality control
program is shown in Annex A.
Likewise, the DPWH provides a team to monitor the quality control
activities in the project, like: sampling, testing, laboratory procedures,
equipment calibration and quality control reporting
b. Minimum Testing Requirements- are prescribed in each project based on
estimated quantities. The requirements specify the kind and number of tests
for each item of work.
Testing is done as the materials are being incorporated into the work.
It should be emphasized that what are specified are the minimum number of
testing only. The owner can therefore, can require more test if he is in doubt
of the quality of materials or the finished structure.
c. Pretesting of manufactured materials such as cement, asphalt, and steel bar.
Samples are obtained at the factory and tested at the laboratories. Upon
verification, the pretested materials are ready for use upon delivery at the
jobsite.
4. Proper Construction methods/procedures
a. Establish a working quality control organization with responsibility for
supervision and inspection at all levels of work.
b. Construction method should be done according to each item of work
indicated in the design.
c. To see to it that materials used pass the required specification prior to
incorporation to the project
You might also like
- 3-D WheelDocument24 pages3-D WheelKim Ciudadano29% (7)
- QA-QC PlanDocument18 pagesQA-QC PlanSen IMO67% (3)
- Quality ControlDocument30 pagesQuality Controlpandey_baibhav100% (2)
- CMATS 11nov2019 PDFDocument352 pagesCMATS 11nov2019 PDFJICA DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Qa & QC Manual - DraftDocument15 pagesQa & QC Manual - DraftNayla Shafea Azzahra100% (1)
- Unified BSR Rural Road PMGSY Rajasthan 20 December 2019Document103 pagesUnified BSR Rural Road PMGSY Rajasthan 20 December 2019Roopesh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Friction Coefficient For Concrete Cast On SoilDocument2 pagesFriction Coefficient For Concrete Cast On SoilBogdanB100% (2)
- HQ (M+W) (HQ+E) S: Duties of A Materials EngineerDocument20 pagesHQ (M+W) (HQ+E) S: Duties of A Materials Engineerjoren calzadoNo ratings yet
- Material Testing Quality ControlDocument22 pagesMaterial Testing Quality Controlsarbjeet singhNo ratings yet
- OVERVIEW Materials QualityDocument14 pagesOVERVIEW Materials QualityRomeo Beding Densen Jr.No ratings yet
- PQMDocument32 pagesPQMJun KhoNo ratings yet
- Material Testing & Quality ControlDocument22 pagesMaterial Testing & Quality ControlJun Michael100% (1)
- CMT Merged-2 1Document7 pagesCMT Merged-2 1MerickNo ratings yet
- Matls - Engr. Accr. ReviewDocument352 pagesMatls - Engr. Accr. ReviewJun Kho100% (1)
- Qa QC ProgrammeDocument6 pagesQa QC ProgrammesrisetNo ratings yet
- Minimum Testing Requirement: Quality ControlDocument4 pagesMinimum Testing Requirement: Quality Controlaybi pearlNo ratings yet
- C. Manufactured: 2. Handling and Storage of MaterialsDocument1 pageC. Manufactured: 2. Handling and Storage of MaterialsCiv PaesNo ratings yet
- QAQCDocument56 pagesQAQCRavindra Babu Sivapu100% (1)
- Sop 03Document29 pagesSop 03kamatgauravNo ratings yet
- Quality Requirements TA1056 MBI Sampang Agung Brewery Extension 014000 - 1Document10 pagesQuality Requirements TA1056 MBI Sampang Agung Brewery Extension 014000 - 1ery achjariNo ratings yet
- Introduction Importance of Materials TestingDocument61 pagesIntroduction Importance of Materials TestingJIENNY LOU TENGCONo ratings yet
- Quality ControlDocument37 pagesQuality ControlMark Anthony Limbo67% (3)
- A Study of Quality Control and Quality Assurance at Construction SiteDocument19 pagesA Study of Quality Control and Quality Assurance at Construction Sitetapan12345100% (14)
- Qaqcsuk LatestDocument126 pagesQaqcsuk LatestNajimieItachiIINo ratings yet
- Road Construction Essentials QA/QC PlanDocument10 pagesRoad Construction Essentials QA/QC Planrafiullah amireeNo ratings yet
- Quality Control PlanDocument13 pagesQuality Control PlanMohammad Taqi HamidiNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Policy: Project Special ProvisionsDocument4 pagesPurpose and Policy: Project Special Provisionsraditanka aobakweNo ratings yet
- Quality ManualDocument4 pagesQuality ManualAli IrvaliNo ratings yet
- Quality ControlDocument30 pagesQuality ControlkhanNo ratings yet
- 01 40 00 FL Quality RequirementsDocument11 pages01 40 00 FL Quality RequirementssbunNo ratings yet
- 23sampling Methods and Quality Assurance PlanDocument34 pages23sampling Methods and Quality Assurance PlanSumit Rathi100% (1)
- Quality ControlDocument30 pagesQuality ControlMohammedNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance and Quality Control PlanDocument6 pagesQuality Assurance and Quality Control PlanTia KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Section 014500 Quality Control and Testing - Rev1Document5 pagesSection 014500 Quality Control and Testing - Rev1Al LopezNo ratings yet
- 6 QualityDocument6 pages6 QualityAhmed GamalNo ratings yet
- Construction Specification 494-Contractor Quality Control: 1. ScopeDocument3 pagesConstruction Specification 494-Contractor Quality Control: 1. Scopedarlene zaraNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification 3Document2 pagesTechnical Specification 3Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- (05727) - Precast Concrete Technician Study GuideDocument37 pages(05727) - Precast Concrete Technician Study GuideTharach JanesuapasaereeNo ratings yet
- PQP EpldtDocument8 pagesPQP Epldtmartin leeNo ratings yet
- Number Three Wind Farm Lewis County, New York Case 16-F-0328 May 2018 1 Project InformationDocument6 pagesNumber Three Wind Farm Lewis County, New York Case 16-F-0328 May 2018 1 Project Informationblackberry7130gNo ratings yet
- 560-S27 QUALITY CONTROL PROGRAM Rev.4Document27 pages560-S27 QUALITY CONTROL PROGRAM Rev.4AbdelmuneimNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification 2Document2 pagesTechnical Specification 2Buliga MarianNo ratings yet
- Section 014000 Quality Requirements - Rev1Document6 pagesSection 014000 Quality Requirements - Rev1Al LopezNo ratings yet
- Tip QC PlanDocument14 pagesTip QC PlanTC Nihal AlcansoyNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument25 pagesReportSHAIK HUMAYUNNo ratings yet
- 12 Project Quality Plan 7.11.20 (Final)Document81 pages12 Project Quality Plan 7.11.20 (Final)Michael Patungan100% (1)
- Quality Control of BuildingDocument7 pagesQuality Control of BuildingsrikanthNo ratings yet
- MQCH Orientation Project Engineers3Document42 pagesMQCH Orientation Project Engineers3engr rangNo ratings yet
- QC ProgramDocument7 pagesQC ProgramHerbert HernandezNo ratings yet
- Project Quality Management-1Document9 pagesProject Quality Management-1Abdelaziz sharafNo ratings yet
- GPPM 22 PDFDocument64 pagesGPPM 22 PDFKirti Ambastha100% (1)
- Quality Management in Construction ProjectDocument36 pagesQuality Management in Construction ProjectPravin MindeNo ratings yet
- Typical Job Description For Inspection/Quality AssuranceDocument20 pagesTypical Job Description For Inspection/Quality AssuranceMahfoz KazolNo ratings yet
- Project Qulaity Plan DraftDocument9 pagesProject Qulaity Plan DraftAhmad CheemaNo ratings yet
- Quality Control of High Way MaterialsDocument41 pagesQuality Control of High Way MaterialsPearl UnarineNo ratings yet
- Lecture On-Importance of Materials TestingDocument61 pagesLecture On-Importance of Materials TestingLovely Luna100% (3)
- Method Statement For BlockworksMasonry - WelcomeDocument1 pageMethod Statement For BlockworksMasonry - WelcomeChristopher PantojaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 QUALITY MANAGEMENTDocument17 pagesModule 3 QUALITY MANAGEMENTThippesh GNNo ratings yet
- Solid Concrete Brick and Block QC-QA Program Manual - 2014Document19 pagesSolid Concrete Brick and Block QC-QA Program Manual - 2014velmurug_balaNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document5 pagesWa0000.oguaputaezijNo ratings yet
- QC MANUAL (Project Quality Plan) WisnuDocument10 pagesQC MANUAL (Project Quality Plan) WisnuNovie DwiyantiNo ratings yet
- Expansive PDFDocument6 pagesExpansive PDFAlê Fabiano CavalcanteNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions Paper I: ASME Awareness and Section VIII Code. 1Document4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions Paper I: ASME Awareness and Section VIII Code. 1RahulNo ratings yet
- Pressure Method - AASHTO T 152 (ASTM C231)Document5 pagesPressure Method - AASHTO T 152 (ASTM C231)Einstein JeboneNo ratings yet
- Magma 150 and 230 Owner Operator ManualDocument48 pagesMagma 150 and 230 Owner Operator ManualAwatef BahloulNo ratings yet
- Plastic Heater - PT - Bella Prima Perkasa-Model CORE BUNDDLEDocument1 pagePlastic Heater - PT - Bella Prima Perkasa-Model CORE BUNDDLETopik Budi OetomoNo ratings yet
- PFRS 15 - DayagDocument105 pagesPFRS 15 - DayagASHERAH ENGKONGNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document25 pagesLab Report 1Cherif Chokeir60% (5)
- Terracotta Tile 2019 Company EditionDocument8 pagesTerracotta Tile 2019 Company EditionSiti ZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Masina Gheata ArkticDocument160 pagesMasina Gheata ArkticPetre IonNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Directional DrillingDocument7 pagesHorizontal Directional DrillingDebasis SahaNo ratings yet
- Vit MeDocument1 pageVit MeBo Cau GaiNo ratings yet
- Swell-Shrink Behavior of Expansive Soils, Damage and Control PDFDocument10 pagesSwell-Shrink Behavior of Expansive Soils, Damage and Control PDFbela_medeiros-1No ratings yet
- Instructions: Page 1 of 5 Instruction Sheet NumberDocument5 pagesInstructions: Page 1 of 5 Instruction Sheet NumberOnofreNo ratings yet
- Long Radius 90° Elbows Inches / Pounds: Standard WeightDocument1 pageLong Radius 90° Elbows Inches / Pounds: Standard WeightezhiljananiNo ratings yet
- Aircrete Blocks Technical Manual: Sub Head Hanson Building ProductsDocument56 pagesAircrete Blocks Technical Manual: Sub Head Hanson Building ProductseaNo ratings yet
- Service Bulletin Trucks: Companion Flange, ReplacementDocument8 pagesService Bulletin Trucks: Companion Flange, ReplacementZulmary Pirela azuajeNo ratings yet
- Design of Connections: Fig 4.1: Typical Connections: (A) Beam To Column (B) Beam To BeamDocument16 pagesDesign of Connections: Fig 4.1: Typical Connections: (A) Beam To Column (B) Beam To BeamMuriungi RicharsNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Fibers..Document14 pagesBamboo Fibers..vinese.althearNo ratings yet
- Cept Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesCept Literature ReviewAmaan Jahangir AlamNo ratings yet
- Comparison Cda Ancold GuidelinesDocument1 pageComparison Cda Ancold Guidelinesjosafa_engNo ratings yet
- Op-3-60. Checklist For Supervision of Earthworks: Work Instructions For EngineersDocument4 pagesOp-3-60. Checklist For Supervision of Earthworks: Work Instructions For Engineersjinwook75No ratings yet
- Apl Apollo Tubes Limited Unit-Iii: Works-Vill-Kudavali Plot No-M-1, Murbad, 421401, Thane (MS)Document1 pageApl Apollo Tubes Limited Unit-Iii: Works-Vill-Kudavali Plot No-M-1, Murbad, 421401, Thane (MS)devanshbhuvansht.823No ratings yet
- Hexalobular (6 Lobe) Socket Pan Head Machine Screws: Article# d1 d2 Max. K Max. T Max. A LDocument3 pagesHexalobular (6 Lobe) Socket Pan Head Machine Screws: Article# d1 d2 Max. K Max. T Max. A LRavindra ErabattiNo ratings yet
- 2018-SAC-LATAM-SPEC60Hz - AM040MXMKKC - EA CONDENSADORADocument3 pages2018-SAC-LATAM-SPEC60Hz - AM040MXMKKC - EA CONDENSADORAFabian HernandezNo ratings yet
- Ra 544 Civil Engineering Law 11321Document7 pagesRa 544 Civil Engineering Law 11321JHON MARK YANONGNo ratings yet
- Street Light Pole Specification MS 16112021Document3 pagesStreet Light Pole Specification MS 16112021Mahmudul Hasan TanuNo ratings yet
- MS-02-Method Statement For Surface Excavation WorksDocument22 pagesMS-02-Method Statement For Surface Excavation WorksAmila Priyadarshana DissanayakeNo ratings yet