Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost Sheet
Cost Sheet
Uploaded by
Ankit YadavCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Research MethodologyDocument46 pagesResearch Methodologyنور شهبره فانوت100% (6)
- Engineering Economy 3Document37 pagesEngineering Economy 3Steven SengNo ratings yet
- 74749bos60489 cp6Document34 pages74749bos60489 cp6tempNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument19 pagesCost SheetpraphullmadaneNo ratings yet
- COST ACCOUNTING I Module VDocument4 pagesCOST ACCOUNTING I Module VEmil E. ANo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet: Learning OutcomesDocument26 pagesCost Sheet: Learning OutcomesSusovan SirNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument26 pagesCost SheetPankaj SahaniNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument5 pagesCost Sheetgaurav gauravNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet: Learning OutcomesDocument15 pagesCost Sheet: Learning OutcomesshubNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet SummaryDocument8 pagesCost Sheet SummaryBahi Khata CommerceNo ratings yet
- CHP 6. Cost Sheet - CapranavDocument14 pagesCHP 6. Cost Sheet - CapranavMonikaNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-2Document14 pagesCourse Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-2Tanvir Ahmed ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- RR Cost SheetDocument4 pagesRR Cost SheetRamiz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Dr. (CA) Ankita Jain: Unit - IiiDocument11 pagesDr. (CA) Ankita Jain: Unit - IiiBHAVYA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Costs - Concepts and ClassificationsDocument5 pagesCosts - Concepts and ClassificationsCarlo B CagampangNo ratings yet
- 103 Sample Chapter PDFDocument28 pages103 Sample Chapter PDFKomal MusaleNo ratings yet
- 103 Sample ChapterDocument28 pages103 Sample ChapterRithik VisuNo ratings yet
- 110-W2-3-Cost concept-chp02-STDocument85 pages110-W2-3-Cost concept-chp02-STmargaret mariaNo ratings yet
- COST Lesson 2Document4 pagesCOST Lesson 2Christian Clyde Zacal Ching0% (1)
- 1 Introduction To Cost Accounting (2017)Document62 pages1 Introduction To Cost Accounting (2017)kilogek124No ratings yet
- Session 3 - MAC - ConceptsDocument18 pagesSession 3 - MAC - ConceptsABHASH JHANo ratings yet
- Cost ClassificationDocument6 pagesCost ClassificationAnonymous yy8In96j0r100% (1)
- Cost Accounting With More Illustrations-2Document21 pagesCost Accounting With More Illustrations-2Rohit KashyapNo ratings yet
- Classification of CostsDocument84 pagesClassification of CostsRoyal ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Cost Classification Theory and Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesCost Classification Theory and Practice QuestionsBilal Rauf100% (1)
- Manufacturing AccountsDocument10 pagesManufacturing Accountsamosoundo59No ratings yet
- Cost 1 CH-twoDocument10 pagesCost 1 CH-twoDebela AbidhuNo ratings yet
- Cost ManagementDocument23 pagesCost ManagementEswara ReddyNo ratings yet
- Overheads - Absorption Costing Method: Learning OutcomesDocument89 pagesOverheads - Absorption Costing Method: Learning Outcomessamyak bafnaNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet P&SDocument41 pagesCost Sheet P&SJishnuPatilNo ratings yet
- Full Download Managerial Accounting Creating Value in A Dynamic Business Environment Hilton 10th Edition Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Managerial Accounting Creating Value in A Dynamic Business Environment Hilton 10th Edition Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterdrearingpuncheonrpeal100% (21)
- Costing Formulae Topic WiseDocument81 pagesCosting Formulae Topic WiseSuresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Accounting 2Document5 pagesAccounting 2jessicaong2403No ratings yet
- Notes in Strategic Cost Management (SLPO)Document7 pagesNotes in Strategic Cost Management (SLPO)Laila OlpindoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Cost Sheet or Statement of CostDocument16 pagesChapter 12 Cost Sheet or Statement of CostNeelesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Basic Cost Term and Concepts - An Inrodution 13.12.22Document36 pagesBasic Cost Term and Concepts - An Inrodution 13.12.22JayaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cost Management ConceptsDocument7 pagesBasic Cost Management ConceptsImadNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts: Solutions To QuestionsDocument13 pagesManagerial Accounting and Cost Concepts: Solutions To QuestionsGera MatsNo ratings yet
- A.3. Cost ClassificationsDocument57 pagesA.3. Cost ClassificationsTiyas KurniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument33 pagesChapter TwoTerefe DubeNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management Accounting and Quandative TechniqueDocument86 pagesCost and Management Accounting and Quandative TechniquesaiyuvatechNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Creating Value in A Dynamic Business Environment Hilton 10th Edition Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesManagerial Accounting Creating Value in A Dynamic Business Environment Hilton 10th Edition Solutions Manualbarrenlywale1ibn8No ratings yet
- Costing Formulae Topic WiseDocument83 pagesCosting Formulae Topic WiseViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- CostingDocument10 pagesCostingd.pagkatoytoyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Account-Ref - Material: SyllabusDocument5 pagesManufacturing Account-Ref - Material: SyllabusMohamed MuizNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Wastes Stream: Toyota Production System Lean Principles and ValuesFrom EverandManufacturing Wastes Stream: Toyota Production System Lean Principles and ValuesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Creating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowFrom EverandCreating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]From EverandPractical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Lean-based Production Management: Practical Lean ManufacturingFrom EverandLean-based Production Management: Practical Lean ManufacturingNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Kanban the Toyota Way: An Inventory Buffering System to Eliminate InventoryFrom EverandKanban the Toyota Way: An Inventory Buffering System to Eliminate InventoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsFrom EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Total Plant Performance Management:: A Profit-Building Plan to Promote, Implement, and Maintain Optimum Performance Throughout Your PlantFrom EverandTotal Plant Performance Management:: A Profit-Building Plan to Promote, Implement, and Maintain Optimum Performance Throughout Your PlantNo ratings yet
- Identifying Mura-Muri-Muda in the Manufacturing Stream: Toyota Production System ConceptsFrom EverandIdentifying Mura-Muri-Muda in the Manufacturing Stream: Toyota Production System ConceptsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Integrated Design and Construction - Single Responsibility: A Code of PracticeFrom EverandIntegrated Design and Construction - Single Responsibility: A Code of PracticeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction - IE 112Document12 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction - IE 112leojhunNo ratings yet
- (Economy) Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), Marginal Standing Facility (MSF), Repo, Reverse Repo, SLR, CRR, NEFT, RTGS, NDTL: Meaning ExplainedDocument14 pages(Economy) Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), Marginal Standing Facility (MSF), Repo, Reverse Repo, SLR, CRR, NEFT, RTGS, NDTL: Meaning Explainedsameer bakshiNo ratings yet
- O Uco Bank: Rnictj/Date: 19.08.2019Document3 pagesO Uco Bank: Rnictj/Date: 19.08.2019Satya KarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 MC QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 4 MC QuestionsjessicaNo ratings yet
- B&K Wealth Management Introduction & CapabilitiesDocument18 pagesB&K Wealth Management Introduction & Capabilitiesiifl dataNo ratings yet
- Cornerstone Exercises Cornerstone Exercise 17.1Document30 pagesCornerstone Exercises Cornerstone Exercise 17.1Nirwana PuriNo ratings yet
- Admas University School of Postgraduate Studies MBA Financial Management AssignmentDocument17 pagesAdmas University School of Postgraduate Studies MBA Financial Management AssignmentAbnet BeleteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Test Bank - Static - Version1Document26 pagesChapter 06 Test Bank - Static - Version1Veronica MargotNo ratings yet
- Accelerating Capital Markets Development in Emerging EconomiesDocument26 pagesAccelerating Capital Markets Development in Emerging EconomiesIchbin BinNo ratings yet
- EconDocument4 pagesEconKianna SabalaNo ratings yet
- STR Op BB OkDocument18 pagesSTR Op BB OkriddhmarketingNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Executive CompensationDocument2 pagesCase Study On Executive CompensationanathomsanNo ratings yet
- MBA 530 GROW ModelDocument5 pagesMBA 530 GROW ModelSchool Purposes OnlyNo ratings yet
- Flat No. 2 Iesco BillDocument1 pageFlat No. 2 Iesco BillGamers CrewNo ratings yet
- Ch6.Strategy in Global EnvironmentDocument17 pagesCh6.Strategy in Global EnvironmentDian MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Tata Steel 2015 16 PDFDocument300 pagesTata Steel 2015 16 PDFAman PrasasdNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP TÀI CHÍNH QUỐC TẾDocument2 pagesBÀI TẬP TÀI CHÍNH QUỐC TẾXuan KimNo ratings yet
- TAPMI Placement Brochure 2010-11Document48 pagesTAPMI Placement Brochure 2010-11tapmiblogsNo ratings yet
- MastekDocument27 pagesMastekcsheth3650No ratings yet
- HO Inventory-EstimationDocument1 pageHO Inventory-EstimationAl Francis GuillermoNo ratings yet
- NABARD ESI Summary SheetsDocument692 pagesNABARD ESI Summary SheetsGoutham RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Amendment in Itb and GCC: Amend - ITBGCC 1Document2 pagesAmendment in Itb and GCC: Amend - ITBGCC 1Mayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Framework of Sustainable Supply Chain Management - Moving Toward New TheoryDocument78 pagesA Framework of Sustainable Supply Chain Management - Moving Toward New TheoryjulienfolquetNo ratings yet
- 2) Instructions For Playing The GameDocument7 pages2) Instructions For Playing The GameAna MariaNo ratings yet
- Lego StudentDocument7 pagesLego StudentPookguy100% (1)
- Struktur Organisasi: Organization StructureDocument2 pagesStruktur Organisasi: Organization StructureRalila SejahteraNo ratings yet
- Social Structure TheoryDocument16 pagesSocial Structure TheorySalman AtherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 36Document14 pagesLecture 36praneix100% (1)
Cost Sheet
Cost Sheet
Uploaded by
Ankit YadavOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cost Sheet
Cost Sheet
Uploaded by
Ankit YadavCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter
COST SHEET
I. Introduction
One of the objectives of cost accounting system is ascertainment of cost for a cost object. The cost objects
may be a product, service or any cost centre. Ascertainment of cost includes elementwise collection of costs,
accumulation of the costs so collected for a certain volume or period and then arrange all these accumulated
costs into a sheet to calculate total cost for the cost object.
A Cost Sheet or Cost Statement is “a document which provides a detailed cost information. In a typical cost
sheet, cost information are presented on the basis of functional classification. However, other classification
may also be adopted as per the requirements of users of the information.
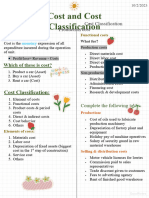
II. Functional Classification of Elements of Cost
Under this classification, costs are divided according to the function for which they have been incurred. The
following are the classification of costs based on functions:
i. Direct Material Cost
ii. Direct Employee (labour) Cost
iii. Direct Expenses
iv. Production/ Manufacturing Overheads
v. Administration Overheads
vi. Selling Overheads
vii. Distribution Overheads
viii. Research and Development costs etc.
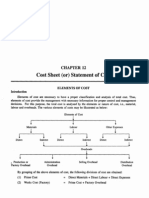
III. Cost Heads in a Cost Sheet
The costs as classified on the basis of functions are grouped into the following cost heads in a cost sheet:
i. Prime Cost - Prime cost represents the total of direct materials costs, direct employee (labour) costs
and direct expenses.
ii. Cost of Production - It is the total of prime cost and factory related costs and overheads.
iii. Cost of Goods Sold - It is the cost of production for goods sold.
iv. Cost of Sales - It is the total cost of a product incurred to make the product available to the customer
or consumer.
Prepared by: Raman Luthra
Chartered Accountant
IV. Cost Sheet/Statement
Total Cost per
Particulars
Cost Unit
1. Direct Material Consumed:
Opening Stock of Raw Material xxx
Add: Additions/ Purchases xxx
Less: Closing stock of Raw Material xxx
xxx
2. Direct employee (labour) cost xxx
3. Direct expenses xxx
4. Prime Cost (1+2+3) xxx
5. Add: Works/ Factory Overheads xxx
6. Gross Works Cost (4+5) xxx
7. Add: Opening Work in Process xxx
8. Less: Closing Work in Process (xxx)
9. Works/ Factory Cost (6+7-8) xxx
Add: Administrative Overheads (relating to
10. xxx
production activity)
Cost of Production/ Cost of Goods Manufactured
11. xxx
(9+10)
12. Add: Opening stock of finished goods xxx
13. Less: Closing stock of finished goods (xxx)
14. Cost of Goods Sold (11+12-13) xxx
15. Add: Administrative Overheads (General) xxx
16. Add: Marketing Overheads:
Selling Overheads xxx
Distribution Overheads xxx
17. Cost of Sales (14+15+16) xxx
Prepared by: Raman Luthra
Chartered Accountant
• Factory Overheads: It is also known as works/production/manufacturing overheads. It includes the
following indirect costs:
i. Consumable stores and spares;
ii. Depreciation of plant and machinery, factory building etc.
iii. Lease rent of production assets;
iv. Repair and maintenance of plant and machinery, factory building etc.
v. Indirect employees cost related with production activities;
vi. Drawing and Designing department cost;
vii. Insurance of plant and machinery, factory building, stock of raw material & WIP etc.
viii. Amortized cost of jigs, fixtures, tooling etc.
ix. Service department cost such as Tool Room, Engineering & Maintenance, Pollution Control
etc.
• Administrative Overheads(Factory): It includes only those administration overheads which are
related to production. The general administration overhead is not included in production cost.
• Administrative Overheads(General): It is the cost related with general administration of the entity.
It includes the followings:
i. Depreciation and maintenance of, building, furniture etc. of corporate or general
management.
ii. Salary of administrative employees, accountants, directors, secretaries etc
iii. Rent, rates & taxes, insurance, lighting, office expenses etc.
iv. Indirect materials- printing and stationery, office supplies etc.
v. Legal charges, audit fees, corporate office expenses like directors’ sitting fees, remuneration
and commission, meeting expenses etc.
• Selling Overheads: It is the cost related with sale of products or services. It includes the following
costs:
i. Salary and wages related with sales department and employees directly related with selling
of goods.
ii. Rent, depreciation, maintenance and other cost related with sales department.
iii. Cost of advertisement, maintenance of website for online sales, market research etc.
• Distribution Overheads: It includes the cost related with making the goods available to the
customers. The costs are
i. Salary and wages of employees engaged in distribution of goods.
ii. Transportation and insurance costs related with distribution.
iii. Depreciation, hire charges, maintenance and other operating costs related with distribution
vehicles etc.
• Cost of Sales: It is the total cost of a product incurred to make the product available to the customer
or consumer. It is the aggregate of cost of goods sold, administrative costs, marketing costs and other
separate line items of cost which could not form part of cost of production.
Prepared by: Raman Luthra
Chartered Accountant
Multiple Choice Questions
1. [Question] Generally, for the purpose of cost sheet preparation, costs are classified on the basis of?
a) Functions
b) Variability
c) Relevance
d) Nature
e) Controllability
Answer: a.
2. [Question] Which of the following does not form part of prime cost:
a) Cost of packing
b) Cost of transportation paid to bring materials to factory
c) GST paid on raw materials (input credit cannot be claimed)
d) Overtime premium paid to workers.
e) Royalties paid on production of each unit.
Answer: a.
3. A Ltd. received an order, for which it purchased a special frame for manufacturing, it is a part of:
a) Direct Materials
b) Direct expenses
c) Factory Overhead
d) Administration Overheads
e) Factory overhead
Answer: b.
4. Salary paid to plant supervisor is a part of
a) Direct expenses
b) Factory overheads
c) Quality control cost
d) Administration cost(Factory)
e) Administration cost(General)
Answer: b.
5. Depreciation of director’s laptop is treated as a part of:
a) Administration Overheads
b) Factory Overheads
c) Direct Expenses
d) Research & Development cost.
e) Selling and Distribution cost.
Answer: a.
Prepared by: Raman Luthra
Chartered Accountant
6. Which of the following items is not included in preparation of cost sheet?
a) Carriage inward
b) Purchase returns
c) Sales commission
d) Interest paid
e) Depreciation on plant and Machinery
Answer: d.
7. Which of the following items is not excluded while preparing a cost sheet?
a) Goodwill written off
b) Provision for taxation
c) Property tax on Factory building
d) Transfer to reserves
e) Interest paid
Answer: c.
8. As costing team member, calculate the Cost of sales if; Sales Rs. 1,00,000; opening stock Rs. 5,000; purchases
Rs. 80,000; Closing stock Rs. 15,000; and office rent Rs. 10,000?
a) 70,000
b) 75,000
c) 80,000
d) 85,000
e) 90,000
Answer: c.
Prepared by: Raman Luthra
Chartered Accountant
You might also like
- Research MethodologyDocument46 pagesResearch Methodologyنور شهبره فانوت100% (6)
- Engineering Economy 3Document37 pagesEngineering Economy 3Steven SengNo ratings yet
- 74749bos60489 cp6Document34 pages74749bos60489 cp6tempNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument19 pagesCost SheetpraphullmadaneNo ratings yet
- COST ACCOUNTING I Module VDocument4 pagesCOST ACCOUNTING I Module VEmil E. ANo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet: Learning OutcomesDocument26 pagesCost Sheet: Learning OutcomesSusovan SirNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument26 pagesCost SheetPankaj SahaniNo ratings yet
- Cost SheetDocument5 pagesCost Sheetgaurav gauravNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet: Learning OutcomesDocument15 pagesCost Sheet: Learning OutcomesshubNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet SummaryDocument8 pagesCost Sheet SummaryBahi Khata CommerceNo ratings yet
- CHP 6. Cost Sheet - CapranavDocument14 pagesCHP 6. Cost Sheet - CapranavMonikaNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-2Document14 pagesCourse Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-2Tanvir Ahmed ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- RR Cost SheetDocument4 pagesRR Cost SheetRamiz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Dr. (CA) Ankita Jain: Unit - IiiDocument11 pagesDr. (CA) Ankita Jain: Unit - IiiBHAVYA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Costs - Concepts and ClassificationsDocument5 pagesCosts - Concepts and ClassificationsCarlo B CagampangNo ratings yet
- 103 Sample Chapter PDFDocument28 pages103 Sample Chapter PDFKomal MusaleNo ratings yet
- 103 Sample ChapterDocument28 pages103 Sample ChapterRithik VisuNo ratings yet
- 110-W2-3-Cost concept-chp02-STDocument85 pages110-W2-3-Cost concept-chp02-STmargaret mariaNo ratings yet
- COST Lesson 2Document4 pagesCOST Lesson 2Christian Clyde Zacal Ching0% (1)
- 1 Introduction To Cost Accounting (2017)Document62 pages1 Introduction To Cost Accounting (2017)kilogek124No ratings yet
- Session 3 - MAC - ConceptsDocument18 pagesSession 3 - MAC - ConceptsABHASH JHANo ratings yet
- Cost ClassificationDocument6 pagesCost ClassificationAnonymous yy8In96j0r100% (1)
- Cost Accounting With More Illustrations-2Document21 pagesCost Accounting With More Illustrations-2Rohit KashyapNo ratings yet
- Classification of CostsDocument84 pagesClassification of CostsRoyal ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Cost Classification Theory and Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesCost Classification Theory and Practice QuestionsBilal Rauf100% (1)
- Manufacturing AccountsDocument10 pagesManufacturing Accountsamosoundo59No ratings yet
- Cost 1 CH-twoDocument10 pagesCost 1 CH-twoDebela AbidhuNo ratings yet
- Cost ManagementDocument23 pagesCost ManagementEswara ReddyNo ratings yet
- Overheads - Absorption Costing Method: Learning OutcomesDocument89 pagesOverheads - Absorption Costing Method: Learning Outcomessamyak bafnaNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet P&SDocument41 pagesCost Sheet P&SJishnuPatilNo ratings yet
- Full Download Managerial Accounting Creating Value in A Dynamic Business Environment Hilton 10th Edition Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Managerial Accounting Creating Value in A Dynamic Business Environment Hilton 10th Edition Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterdrearingpuncheonrpeal100% (21)
- Costing Formulae Topic WiseDocument81 pagesCosting Formulae Topic WiseSuresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Accounting 2Document5 pagesAccounting 2jessicaong2403No ratings yet
- Notes in Strategic Cost Management (SLPO)Document7 pagesNotes in Strategic Cost Management (SLPO)Laila OlpindoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Cost Sheet or Statement of CostDocument16 pagesChapter 12 Cost Sheet or Statement of CostNeelesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Basic Cost Term and Concepts - An Inrodution 13.12.22Document36 pagesBasic Cost Term and Concepts - An Inrodution 13.12.22JayaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cost Management ConceptsDocument7 pagesBasic Cost Management ConceptsImadNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting and Cost Concepts: Solutions To QuestionsDocument13 pagesManagerial Accounting and Cost Concepts: Solutions To QuestionsGera MatsNo ratings yet
- A.3. Cost ClassificationsDocument57 pagesA.3. Cost ClassificationsTiyas KurniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument33 pagesChapter TwoTerefe DubeNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management Accounting and Quandative TechniqueDocument86 pagesCost and Management Accounting and Quandative TechniquesaiyuvatechNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Creating Value in A Dynamic Business Environment Hilton 10th Edition Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesManagerial Accounting Creating Value in A Dynamic Business Environment Hilton 10th Edition Solutions Manualbarrenlywale1ibn8No ratings yet
- Costing Formulae Topic WiseDocument83 pagesCosting Formulae Topic WiseViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- CostingDocument10 pagesCostingd.pagkatoytoyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Account-Ref - Material: SyllabusDocument5 pagesManufacturing Account-Ref - Material: SyllabusMohamed MuizNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Wastes Stream: Toyota Production System Lean Principles and ValuesFrom EverandManufacturing Wastes Stream: Toyota Production System Lean Principles and ValuesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Creating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowFrom EverandCreating a One-Piece Flow and Production Cell: Just-in-time Production with Toyota’s Single Piece FlowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]From EverandPractical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Lean-based Production Management: Practical Lean ManufacturingFrom EverandLean-based Production Management: Practical Lean ManufacturingNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Kanban the Toyota Way: An Inventory Buffering System to Eliminate InventoryFrom EverandKanban the Toyota Way: An Inventory Buffering System to Eliminate InventoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsFrom EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Total Plant Performance Management:: A Profit-Building Plan to Promote, Implement, and Maintain Optimum Performance Throughout Your PlantFrom EverandTotal Plant Performance Management:: A Profit-Building Plan to Promote, Implement, and Maintain Optimum Performance Throughout Your PlantNo ratings yet
- Identifying Mura-Muri-Muda in the Manufacturing Stream: Toyota Production System ConceptsFrom EverandIdentifying Mura-Muri-Muda in the Manufacturing Stream: Toyota Production System ConceptsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Integrated Design and Construction - Single Responsibility: A Code of PracticeFrom EverandIntegrated Design and Construction - Single Responsibility: A Code of PracticeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction - IE 112Document12 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction - IE 112leojhunNo ratings yet
- (Economy) Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), Marginal Standing Facility (MSF), Repo, Reverse Repo, SLR, CRR, NEFT, RTGS, NDTL: Meaning ExplainedDocument14 pages(Economy) Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), Marginal Standing Facility (MSF), Repo, Reverse Repo, SLR, CRR, NEFT, RTGS, NDTL: Meaning Explainedsameer bakshiNo ratings yet
- O Uco Bank: Rnictj/Date: 19.08.2019Document3 pagesO Uco Bank: Rnictj/Date: 19.08.2019Satya KarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 MC QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 4 MC QuestionsjessicaNo ratings yet
- B&K Wealth Management Introduction & CapabilitiesDocument18 pagesB&K Wealth Management Introduction & Capabilitiesiifl dataNo ratings yet
- Cornerstone Exercises Cornerstone Exercise 17.1Document30 pagesCornerstone Exercises Cornerstone Exercise 17.1Nirwana PuriNo ratings yet
- Admas University School of Postgraduate Studies MBA Financial Management AssignmentDocument17 pagesAdmas University School of Postgraduate Studies MBA Financial Management AssignmentAbnet BeleteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Test Bank - Static - Version1Document26 pagesChapter 06 Test Bank - Static - Version1Veronica MargotNo ratings yet
- Accelerating Capital Markets Development in Emerging EconomiesDocument26 pagesAccelerating Capital Markets Development in Emerging EconomiesIchbin BinNo ratings yet
- EconDocument4 pagesEconKianna SabalaNo ratings yet
- STR Op BB OkDocument18 pagesSTR Op BB OkriddhmarketingNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Executive CompensationDocument2 pagesCase Study On Executive CompensationanathomsanNo ratings yet
- MBA 530 GROW ModelDocument5 pagesMBA 530 GROW ModelSchool Purposes OnlyNo ratings yet
- Flat No. 2 Iesco BillDocument1 pageFlat No. 2 Iesco BillGamers CrewNo ratings yet
- Ch6.Strategy in Global EnvironmentDocument17 pagesCh6.Strategy in Global EnvironmentDian MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Tata Steel 2015 16 PDFDocument300 pagesTata Steel 2015 16 PDFAman PrasasdNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP TÀI CHÍNH QUỐC TẾDocument2 pagesBÀI TẬP TÀI CHÍNH QUỐC TẾXuan KimNo ratings yet
- TAPMI Placement Brochure 2010-11Document48 pagesTAPMI Placement Brochure 2010-11tapmiblogsNo ratings yet
- MastekDocument27 pagesMastekcsheth3650No ratings yet
- HO Inventory-EstimationDocument1 pageHO Inventory-EstimationAl Francis GuillermoNo ratings yet
- NABARD ESI Summary SheetsDocument692 pagesNABARD ESI Summary SheetsGoutham RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Amendment in Itb and GCC: Amend - ITBGCC 1Document2 pagesAmendment in Itb and GCC: Amend - ITBGCC 1Mayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Framework of Sustainable Supply Chain Management - Moving Toward New TheoryDocument78 pagesA Framework of Sustainable Supply Chain Management - Moving Toward New TheoryjulienfolquetNo ratings yet
- 2) Instructions For Playing The GameDocument7 pages2) Instructions For Playing The GameAna MariaNo ratings yet
- Lego StudentDocument7 pagesLego StudentPookguy100% (1)
- Struktur Organisasi: Organization StructureDocument2 pagesStruktur Organisasi: Organization StructureRalila SejahteraNo ratings yet
- Social Structure TheoryDocument16 pagesSocial Structure TheorySalman AtherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 36Document14 pagesLecture 36praneix100% (1)


















































![Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/235162742/149x198/2a816df8c8/1709920378?v=1)