Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA Replication
DNA Replication
Uploaded by
jeonginCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- General Biology 2: Quarter 3: Module 4Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 3: Module 4Ann Lorraine Montealto Sadora100% (1)
- Detailed AnswersDocument5 pagesDetailed Answersuk207581No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument218 pagesGenetic EngineeringSrramNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Question Molecular BiologyDocument112 pagesConceptual Question Molecular BiologykoyewubrhanuNo ratings yet
- DNADocument1 pageDNAmailNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesBiomolecules - Nucleic AcidsRyan S. CutamoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Nucleic Acids 2023Document35 pagesLecture 4 Nucleic Acids 2023PPNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance _d45a3eb5-9198-4355-a27a-b51ba566e126Document55 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance _d45a3eb5-9198-4355-a27a-b51ba566e126PRAVEENKUMARJADHAVNo ratings yet
- Bio 206 Tutorial - 02 & 03Document26 pagesBio 206 Tutorial - 02 & 03Brian HowardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document57 pagesChapter 2Mamila TadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Molecular GeneticsDocument53 pagesUnit 2. Molecular GeneticsRuben Ruiz MartinNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture #3: Cell Biology Is An Interesting Subject So EnjoyDocument15 pagesCell Biology Lecture #3: Cell Biology Is An Interesting Subject So EnjoySaleh HalasahNo ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 8th EditionDocument9 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 8th Editionyegigo4129No ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument48 pagesNucleic AcidsompurahardiNo ratings yet
- GENETICS DNADocument4 pagesGENETICS DNAtasmiahjethwa14No ratings yet
- Name - Honors Anatomy and Physiology Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesName - Honors Anatomy and Physiology Nucleic AcidsthehourofarrivalNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument7 pagesNucleic AciddearbhupiNo ratings yet
- 5.1DNA and RNADocument26 pages5.1DNA and RNAserficasoNo ratings yet
- Notes C22 121Document20 pagesNotes C22 121Gopi NathNo ratings yet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis - Chapter Notes: "Life Is A Three Letter Word!"Document13 pagesDNA and Protein Synthesis - Chapter Notes: "Life Is A Three Letter Word!"Chan Karlok100% (1)
- Learning Outcomes: Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument23 pagesLearning Outcomes: Molecular Basis of InheritanceCrystal A-hahaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Report HanaDocument6 pagesSummary of Report HanaWalid BacundoNo ratings yet
- Module 6-Composition, Structure and Functions of The Major Types of Nucleic AcidDocument36 pagesModule 6-Composition, Structure and Functions of The Major Types of Nucleic AcidSusana N peNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: The Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument19 pagesLecture 5: The Chemical Basis of HeredityShigrid Ann DocilNo ratings yet
- Dna & RnaDocument70 pagesDna & RnaEvette dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids PPT (B)Document43 pagesNucleic Acids PPT (B)welfred indinoNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument7 pagesDNA Replicationlubuto TuntepeNo ratings yet
- Packaging of DNA Into A ChromosomeDocument4 pagesPackaging of DNA Into A ChromosomeBugmenot05100% (1)
- Nucleic acidsLECTUREDocument116 pagesNucleic acidsLECTUREKesha Marie TalloNo ratings yet
- Xeroderma Pigmentosum Is Inherited Human Skin Diseases That Causes A Variety of Phenotype Change in Skin Cell Exposed To SunlighDocument1 pageXeroderma Pigmentosum Is Inherited Human Skin Diseases That Causes A Variety of Phenotype Change in Skin Cell Exposed To Sunlighסנאבל מוסאNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Lubuguin OpinionDocument12 pagesChapter 8: Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Lubuguin OpinionCarla LubuguinNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Nukleotida (Purin Dan Pirimidin)Document92 pagesStruktur Dan Fungsi Nukleotida (Purin Dan Pirimidin)hafidaNo ratings yet
- Am S Dna TopologyDocument33 pagesAm S Dna TopologyParijat BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids RevisionDocument15 pagesNucleic Acids RevisionGilbert ossullivanNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Tzuyu ChouNo ratings yet
- Biology Genetics PresentationDocument68 pagesBiology Genetics PresentationDAN DNANo ratings yet
- 8 - Genetic MaterialDocument22 pages8 - Genetic MaterialCrisha LimNo ratings yet
- DNA - Level 1 18 Jan 2010Document4 pagesDNA - Level 1 18 Jan 2010safemindNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1 On Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesAssignment No.1 On Nucleic AcidsRuel John RanayNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance.Document24 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance.Harsha AntonyNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationDocument15 pagesCentral Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationCristina RocheNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument48 pagesInstant Download PDF Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full Chapterahwazylanre100% (7)
- Full download Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfDocument44 pagesFull download Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfocijomsztuka57100% (7)
- Anatomy of Eukaryotes: J.Daphne Joy Kiruba B.SC Microbiology 1 YearDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Eukaryotes: J.Daphne Joy Kiruba B.SC Microbiology 1 YearDaphne joy kiruba.J Micro INo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Project Complete FileDocument14 pagesNucleic Acid Project Complete FilekrushangNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Document29 pagesNucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Arslan AliNo ratings yet
- (Unit II) Chapter 6: The Structure of DNADocument24 pages(Unit II) Chapter 6: The Structure of DNAswagNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Nucleic AcidDocument28 pages1.5 Nucleic AcidLak Judin IINo ratings yet
- 1-Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument46 pages1-Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsFair PisuttisarunNo ratings yet
- Nucleiuc AcidDocument18 pagesNucleiuc AcidJunelle Ramos AquinoNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Genetic Control My NotesDocument51 pagesTopic 4 Genetic Control My NotesrukashablessingNo ratings yet
- 5.nucleic AcidDocument24 pages5.nucleic AcidAzizi ZainodinNo ratings yet
- Notes - Dna Protein Synthesis - Student 2000Document14 pagesNotes - Dna Protein Synthesis - Student 2000api-270403367No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT HIGHLIGHT by SEEP PahujaDocument31 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT HIGHLIGHT by SEEP Pahujasafeerjavaid8No ratings yet
- Nucleic ProjectDocument27 pagesNucleic ProjectKartikey ShuklaNo ratings yet
- TM 03 Asam Nukleat (Biologi Molekuler 2014)Document23 pagesTM 03 Asam Nukleat (Biologi Molekuler 2014)himawarumNo ratings yet
- 637605951536919459classxiibiologych 6PPT 1Document11 pages637605951536919459classxiibiologych 6PPT 1Kamla RathiNo ratings yet
- DNA in Supramolecular Chemistry and NanotechnologyFrom EverandDNA in Supramolecular Chemistry and NanotechnologyEugen StulzNo ratings yet
- Novel Nanoscale Hybrid MaterialsFrom EverandNovel Nanoscale Hybrid MaterialsBhanu P. S. ChauhanNo ratings yet
DNA Replication
DNA Replication
Uploaded by
jeonginOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DNA Replication
DNA Replication
Uploaded by
jeonginCopyright:
Available Formats
This learning guide provides a detailed overview of DNA replication, emphasizing its importance in
ensuring genetic continuity. Let's break down the key points:
1. **Introduction:** The guide begins by drawing an analogy between a photocopier and DNA
replication, highlighting Chester Carlson's invention of the photocopier in 1938 and Xerox's
introduction of the first commercial office photocopier in the late 1950s.
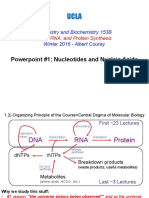
2. **Nucleic Acids:** It explains the structure of nucleic acids, emphasizing the role of nucleotides,
which consist of a sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous bases. It distinguishes between DNA
and RNA in terms of structure, composition, and function.
3. **Central Dogma:** The guide introduces the central dogma of molecular biology, which
encompasses DNA replication, transcription, and translation, focusing on DNA replication for this
lesson.
4. **DNA Replication Process:**
- **Initiation:** The separation of DNA strands by helicase, stabilization by single-stranded binding
proteins, and synthesis of RNA primers by primase.
- **Elongation:** Addition of nucleotides by DNA Polymerase III, leading strand synthesis, and
lagging strand synthesis with Okazaki fragments.
- **Termination:** Removal of RNA primers by DNA Polymerase I, sealing of nicks by ligase, and
dissociation of protein complexes.
5. **Conclusion:** The guide summarizes the DNA replication process, emphasizing the phases of
initiation, elongation, and termination. It underscores the importance of DNA polymerases in
proofreading and repairing errors.
Overall, this learning guide provides a comprehensive understanding of DNA replication, from its
molecular mechanisms to its significance in genetic inheritance and cellular processes.
You might also like
- General Biology 2: Quarter 3: Module 4Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 3: Module 4Ann Lorraine Montealto Sadora100% (1)
- Detailed AnswersDocument5 pagesDetailed Answersuk207581No ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument218 pagesGenetic EngineeringSrramNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Question Molecular BiologyDocument112 pagesConceptual Question Molecular BiologykoyewubrhanuNo ratings yet
- DNADocument1 pageDNAmailNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules - Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesBiomolecules - Nucleic AcidsRyan S. CutamoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Nucleic Acids 2023Document35 pagesLecture 4 Nucleic Acids 2023PPNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance _d45a3eb5-9198-4355-a27a-b51ba566e126Document55 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance _d45a3eb5-9198-4355-a27a-b51ba566e126PRAVEENKUMARJADHAVNo ratings yet
- Bio 206 Tutorial - 02 & 03Document26 pagesBio 206 Tutorial - 02 & 03Brian HowardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document57 pagesChapter 2Mamila TadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Molecular GeneticsDocument53 pagesUnit 2. Molecular GeneticsRuben Ruiz MartinNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture #3: Cell Biology Is An Interesting Subject So EnjoyDocument15 pagesCell Biology Lecture #3: Cell Biology Is An Interesting Subject So EnjoySaleh HalasahNo ratings yet
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 8th EditionDocument9 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 8th Editionyegigo4129No ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument48 pagesNucleic AcidsompurahardiNo ratings yet
- GENETICS DNADocument4 pagesGENETICS DNAtasmiahjethwa14No ratings yet
- Name - Honors Anatomy and Physiology Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesName - Honors Anatomy and Physiology Nucleic AcidsthehourofarrivalNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument7 pagesNucleic AciddearbhupiNo ratings yet
- 5.1DNA and RNADocument26 pages5.1DNA and RNAserficasoNo ratings yet
- Notes C22 121Document20 pagesNotes C22 121Gopi NathNo ratings yet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis - Chapter Notes: "Life Is A Three Letter Word!"Document13 pagesDNA and Protein Synthesis - Chapter Notes: "Life Is A Three Letter Word!"Chan Karlok100% (1)
- Learning Outcomes: Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument23 pagesLearning Outcomes: Molecular Basis of InheritanceCrystal A-hahaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Report HanaDocument6 pagesSummary of Report HanaWalid BacundoNo ratings yet
- Module 6-Composition, Structure and Functions of The Major Types of Nucleic AcidDocument36 pagesModule 6-Composition, Structure and Functions of The Major Types of Nucleic AcidSusana N peNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: The Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument19 pagesLecture 5: The Chemical Basis of HeredityShigrid Ann DocilNo ratings yet
- Dna & RnaDocument70 pagesDna & RnaEvette dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids PPT (B)Document43 pagesNucleic Acids PPT (B)welfred indinoNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument7 pagesDNA Replicationlubuto TuntepeNo ratings yet
- Packaging of DNA Into A ChromosomeDocument4 pagesPackaging of DNA Into A ChromosomeBugmenot05100% (1)
- Nucleic acidsLECTUREDocument116 pagesNucleic acidsLECTUREKesha Marie TalloNo ratings yet
- Xeroderma Pigmentosum Is Inherited Human Skin Diseases That Causes A Variety of Phenotype Change in Skin Cell Exposed To SunlighDocument1 pageXeroderma Pigmentosum Is Inherited Human Skin Diseases That Causes A Variety of Phenotype Change in Skin Cell Exposed To Sunlighסנאבל מוסאNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Lubuguin OpinionDocument12 pagesChapter 8: Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Lubuguin OpinionCarla LubuguinNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Nukleotida (Purin Dan Pirimidin)Document92 pagesStruktur Dan Fungsi Nukleotida (Purin Dan Pirimidin)hafidaNo ratings yet
- Am S Dna TopologyDocument33 pagesAm S Dna TopologyParijat BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids RevisionDocument15 pagesNucleic Acids RevisionGilbert ossullivanNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Tzuyu ChouNo ratings yet
- Biology Genetics PresentationDocument68 pagesBiology Genetics PresentationDAN DNANo ratings yet
- 8 - Genetic MaterialDocument22 pages8 - Genetic MaterialCrisha LimNo ratings yet
- DNA - Level 1 18 Jan 2010Document4 pagesDNA - Level 1 18 Jan 2010safemindNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1 On Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesAssignment No.1 On Nucleic AcidsRuel John RanayNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance.Document24 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance.Harsha AntonyNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationDocument15 pagesCentral Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationCristina RocheNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument48 pagesInstant Download PDF Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual Full Chapterahwazylanre100% (7)
- Full download Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfDocument44 pagesFull download Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manual all chapter 2024 pdfocijomsztuka57100% (7)
- Anatomy of Eukaryotes: J.Daphne Joy Kiruba B.SC Microbiology 1 YearDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Eukaryotes: J.Daphne Joy Kiruba B.SC Microbiology 1 YearDaphne joy kiruba.J Micro INo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Project Complete FileDocument14 pagesNucleic Acid Project Complete FilekrushangNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Document29 pagesNucleic Acids: Assignment Biochem-700Arslan AliNo ratings yet
- (Unit II) Chapter 6: The Structure of DNADocument24 pages(Unit II) Chapter 6: The Structure of DNAswagNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Nucleic AcidDocument28 pages1.5 Nucleic AcidLak Judin IINo ratings yet
- 1-Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument46 pages1-Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsFair PisuttisarunNo ratings yet
- Nucleiuc AcidDocument18 pagesNucleiuc AcidJunelle Ramos AquinoNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Genetic Control My NotesDocument51 pagesTopic 4 Genetic Control My NotesrukashablessingNo ratings yet
- 5.nucleic AcidDocument24 pages5.nucleic AcidAzizi ZainodinNo ratings yet
- Notes - Dna Protein Synthesis - Student 2000Document14 pagesNotes - Dna Protein Synthesis - Student 2000api-270403367No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT HIGHLIGHT by SEEP PahujaDocument31 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT HIGHLIGHT by SEEP Pahujasafeerjavaid8No ratings yet
- Nucleic ProjectDocument27 pagesNucleic ProjectKartikey ShuklaNo ratings yet
- TM 03 Asam Nukleat (Biologi Molekuler 2014)Document23 pagesTM 03 Asam Nukleat (Biologi Molekuler 2014)himawarumNo ratings yet
- 637605951536919459classxiibiologych 6PPT 1Document11 pages637605951536919459classxiibiologych 6PPT 1Kamla RathiNo ratings yet
- DNA in Supramolecular Chemistry and NanotechnologyFrom EverandDNA in Supramolecular Chemistry and NanotechnologyEugen StulzNo ratings yet
- Novel Nanoscale Hybrid MaterialsFrom EverandNovel Nanoscale Hybrid MaterialsBhanu P. S. ChauhanNo ratings yet