Professional Documents
Culture Documents
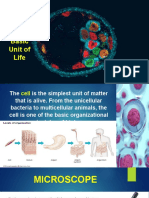
Biology Cells
Biology Cells
Uploaded by
sarmientoangelica6720 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesOriginal Title
biology cells
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesBiology Cells
Biology Cells
Uploaded by
sarmientoangelica672Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
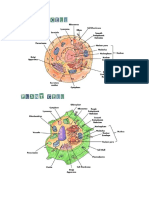
1. Cell Membrane (Plasma 5.
Endoplasmic Reticulum - Where
membrane) – Serves as the proteins and other molecules are
boundary between the cell and its being transported. Also known as
external environment. the (Manufacturer and shippers of
2. Cell Wall – is a rigid the cell).
structure that surrounds the cell 6.Golgi Apparatus – Site of
membrane and provides support sorting, packaging and distribution
and protection. of lipids and proteins.
3. Nucleus – A spherical
7. Chloroplast – Plant cell
structure usually located near the
organelles that carry out
center of the cell. “Control center
photosynthesis.
of the cell.”
4. Nucleolus – It manufactures 8.Mitochondria – Rod-shaped,
cells’ protein producing double membrane bodies that vary
structures and ribosomes. in number and shape. Also referred
as the “Powerhouse of the cell.”
9.Vacuole – Stores food, enzymes
12.Amyloplast – Is a colorless
and other materials needed by the
plant plastid that forms and stores
cell. “Storage tank of the cell.”
starch. It is responsible for the
10.Ribosomes – They are the synthesis and storage of starch,
smallest membrane-bound which is an important energy
organelles which comprise RNA reserve in plants.
and protein. They are the sites for
13.Cytoplasm – Forms the largest
protein synthesis, hence, also
part of the cell, where most life
referred to as the protein factories
processes occur. Structure where
of the cell.
the membrane bound organelles
11.Peroxisome – Organelles that are located.
sequester diverse oxidative
reactions and play important roles
in metabolism, reactive oxygen
species detoxification, and
signaling.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
1. Lysosome – It breaks down cellular waste products and
debris from outside the cell into simple compounds which
N
are transferred to the cytoplasm as new cell-building.
2. Cytoplasm – It maintain the cell’s shape.
3. Ribosomes – is the cellular machinery responsible for
making proteins.
4. Cell Membrane – Separates the interior of the cell from
the outside environment.
5. Nucleus – It controls and regulates the activities of the
cell ( growth and metabolism ) and carries genes,
structures that contain the hereditary information.
6. Nucleolus – Is to produce and assemble the cell’s
ribosomes.
7. Endoplasmic Reticulum – is the “bakery” of the cell,
because it makes proteins.
8. Golgi Body – It helps process and package proteins and
lipid molecules, especially proteins destined to be
exported from the cell.
9. Secretory Vesicles – stores molecules and proteins from
the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus until the
cell is ready to release them.
10. Centrosomes – it organize the microtubules so it’s
called as the microtubules organizing center.
11. Mitochondrion – Responsible for producing the
majority of cellular energy through the process of
oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), and are found in
nearly all eukaryotic cells.
You might also like
- LAB REPORT 1 Wet Mount PreparationDocument7 pagesLAB REPORT 1 Wet Mount PreparationKoreen Bayani100% (1)
- Worksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleDocument3 pagesWorksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Cellular Basis of LifeDocument4 pagesCellular Basis of Lifemarc7victor7salesNo ratings yet
- Genetics - FunctionsDocument4 pagesGenetics - Functionsrhonamalupa216No ratings yet
- Animal & Plant CellDocument4 pagesAnimal & Plant CellKaren PangilinanNo ratings yet
- XOXOXDocument7 pagesXOXOXVazima QtNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment 1Document6 pagesBio Assignment 1ditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- Plant Cell EmeDocument1 pagePlant Cell EmeErica LeysonNo ratings yet
- Major-Parts-Of-The-Cell - ReviewerDocument5 pagesMajor-Parts-Of-The-Cell - Reviewerjadenn busiaNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- Cells Basic Function & StructureDocument2 pagesCells Basic Function & StructureEzel MayNo ratings yet
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAliyah ZalzosNo ratings yet
- Parts & Function of CellsDocument25 pagesParts & Function of CellsHariet ObieNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LectureDocument13 pagesModule 2 LectureJeal NochefrancaNo ratings yet
- PACHECO - EXERCISE NO.1-The CellDocument3 pagesPACHECO - EXERCISE NO.1-The CellMaria Brooklyn PachecoNo ratings yet
- Cells PDFDocument107 pagesCells PDFida hadiNo ratings yet
- Cell AnalogyDocument17 pagesCell AnalogyJianne CabildoNo ratings yet
- Structure of An Animal CellDocument1 pageStructure of An Animal CellNEBRIAGA, MARY S. 3-2No ratings yet
- Ch.4 Cell StructureDocument31 pagesCh.4 Cell StructureEmma WisemanNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Organelles: Prepared By: SAPANA JHADocument14 pagesEukaryotic Cell Organelles: Prepared By: SAPANA JHAAppu JhaNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCell OrganellesMark Kenneth CastilloNo ratings yet
- Diagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteDocument4 pagesDiagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteAdriana Santiago RoaNo ratings yet
- Module For Anaphy CellDocument11 pagesModule For Anaphy CellBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document12 pagesGeneral Biology 1Samariah Nicole AbajeroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - OrganellesDocument34 pagesLesson 2 - OrganellesArvin Jay Lamberte100% (1)
- Science 9 - Edible Cell ActivityDocument9 pagesScience 9 - Edible Cell ActivitySheena Mar dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Biology Sem1 - Chap1Document78 pagesBiology Sem1 - Chap1kotaknotaku100% (1)
- Membrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesMembrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemFarah Jaye Verde CayayanNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- Genbio I ReviewerDocument12 pagesGenbio I Reviewerjustanony92No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and StructuresDocument18 pagesCell Parts and StructuresEmma LoreinNo ratings yet
- ALEXIS JEAN BARREDO - Plant CellsDocument4 pagesALEXIS JEAN BARREDO - Plant CellsAlexis Jean Calinisan BarredoNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 REVIEWDocument16 pagesUnit 4 REVIEWJuliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellskrmalbunagNo ratings yet
- Basic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsDocument18 pagesBasic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsRikki Mae BuenoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Structure and Function Worksheetcheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Quiz#1 GenBioDocument1 pageQuiz#1 GenBioHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Document6 pagesExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- Lesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions FunctionsDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions Functionskruyll vlogsNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesProkaryotic CellsalyssaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Draw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellDocument3 pagesDraw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellPratik SagarNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellscalustre2016No ratings yet
- 1.) Cell Wall - Provides Structural Support and To Control The Amount of Water Entering TheDocument3 pages1.) Cell Wall - Provides Structural Support and To Control The Amount of Water Entering TheKate MontenegroNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellPrincess MillanNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewerabijaneee11No ratings yet
- BIOCHEM CellDocument11 pagesBIOCHEM CellErnesto Dasalla IIINo ratings yet
- GenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesGenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2The GreatNo ratings yet
- Biology REVIEW FOR CMDocument12 pagesBiology REVIEW FOR CMyangyang804574No ratings yet
- Cell Theory, Cell Structure and Function VocabularyDocument2 pagesCell Theory, Cell Structure and Function VocabularyjennymabilenNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animals Cells Moving TestDocument6 pagesPlant and Animals Cells Moving TestWELFREDO YUNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12-General Biology (Cells)Document11 pagesGrade 12-General Biology (Cells)angeliaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 4thq Hypothesis Testing 1Document22 pages4thq Hypothesis Testing 1sarmientoangelica672No ratings yet
- ECigarette SmokingDocument6 pagesECigarette Smokingsarmientoangelica672No ratings yet
- Science 10 NotesDocument1 pageScience 10 Notessarmientoangelica672No ratings yet
- POINTERS TO REVIEW in MAPEH 10Document2 pagesPOINTERS TO REVIEW in MAPEH 10sarmientoangelica672No ratings yet
- Roan L. Rodriguez: Strategic Intervention Material FOR Grade 7 Students S.Y 2016-2017Document30 pagesRoan L. Rodriguez: Strategic Intervention Material FOR Grade 7 Students S.Y 2016-2017roan rodriguez67% (3)
- Study Island Life Science Assignment 1 Classification CellsDocument13 pagesStudy Island Life Science Assignment 1 Classification Cellsapi-243882603No ratings yet
- Final MC1 Laboratory ManualDocument18 pagesFinal MC1 Laboratory ManualKrison Jake ArticuloNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Introduction To BiochemistryDocument8 pagesChapter - 1: Introduction To Biochemistrysantosh s uNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of CellsDocument53 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of CellsMika ForwardNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of Life (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)Document2 pagesCell As A Unit of Life (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)jrpyroNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 Form 1Document23 pagesScience Chapter 2 Form 1Kelvin0% (1)
- 8 TH C V Raman English Notes1Document25 pages8 TH C V Raman English Notes1malaisamy43235No ratings yet
- Cells The Basic Unit of LifeDocument17 pagesCells The Basic Unit of LifePrecious FacinalNo ratings yet
- Transes Zoology Lec LabDocument29 pagesTranses Zoology Lec LabPrincess Jamella BaltNo ratings yet
- Sci 7 2nd Quarter Module 1Document16 pagesSci 7 2nd Quarter Module 1DisgraceNo ratings yet
- Cell 1Document2 pagesCell 1Trilochan TripathyNo ratings yet
- Cell Type Cell Shape Cell Parts Visible FunctionDocument5 pagesCell Type Cell Shape Cell Parts Visible FunctionAgnesRicardoNo ratings yet
- Ftre 2023 Sample Paper Class Ix p1 At+pcbmDocument23 pagesFtre 2023 Sample Paper Class Ix p1 At+pcbmjirokol164No ratings yet
- Full Download Human Heredity Principles and Issues 10th Edition Michael Cummings Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Human Heredity Principles and Issues 10th Edition Michael Cummings Solutions Manualwalmmidgetoin38o100% (31)
- Sample Questions in ScienceDocument6 pagesSample Questions in ScienceshasvinaNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument12 pagesBiology ReviewerAngela SernatNo ratings yet
- Cells PowerpointDocument4 pagesCells Powerpointlu.justina100% (2)
- ANAPHY LEC PRELIMS NOTES by NOVERO KEN BMLS2 1Document55 pagesANAPHY LEC PRELIMS NOTES by NOVERO KEN BMLS2 1Marcus Randielle FloresNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument2 pagesCytoskeletonastro paculanNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal CellHera Lopez100% (1)
- Mitosis and Meiosis ExamDocument13 pagesMitosis and Meiosis ExamCearra Mae EbronaNo ratings yet
- The Istanbul Consensus Workshop On Embryo Assessment: Proceedings of An Expert MeetingDocument13 pagesThe Istanbul Consensus Workshop On Embryo Assessment: Proceedings of An Expert MeetingchristopherNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Their Functions - RS' ScienceDocument1 pageCell Organelles and Their Functions - RS' ScienceMishaNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument5 pagesAnswersHavila Saafi100% (1)
- Cytoplasmic InheritanceDocument13 pagesCytoplasmic Inheritanceanay_379100% (1)
- 1st Sec. - Biology Full SummaryDocument108 pages1st Sec. - Biology Full Summaryali SaidNo ratings yet
- Cell PartsDocument2 pagesCell PartsZarahbeth Claire G. ArcederaNo ratings yet