Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ARUP - Tải trọng tác động
ARUP - Tải trọng tác động
Uploaded by
Thành Vương XuânCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ARUP - Tải trọng tác động
ARUP - Tải trọng tác động
Uploaded by
Thành Vương XuânCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
Loads (1/4)
3. LOADS
Rev A. 22 Feb 1999, units for load at the end of 3.4 corrected.
3.1 DENSITY OF MATERIALS1,2
Material Density Material Density
(kN/m3) (kN/m3)
Aluminium 27.2 Marble 25.5 - 27.8
Asphalt, paving 22.6 Mastic 11.0
Blockwork Lightweight 12.6 Mortar, cement 18.9 - 20.4
Standard 21.2 Mud 16.5 - 18.8
Brickwork Concrete 22.8 Oils In bulk 8.8
Facing 19.7 In barrels 5.7
Cement 14.1 In drums 7.1
Chalk, in lumps 11.0 - 12.6 Plaster 13.3
Clay (in lumps) 11.0 Plasterboard 8.6
Clay (dry) 18.8 - 22.0 Sand Dry 15.7 - 18.8
Clay (moist) 20.4 - 25.1 Moist 18.1 - 19.6
Clay (wet) 20.4 - 25.1 Wet 18.1 - 20.4
Concrete Normal 24.0 Sandstones 12.6 - 18.8
Lightweight 18 - 20 Shale 14.1 - 18.8
Crushed brick 12.6 - 15.7 Slate, Welsh 28.2
Crushed stone 17.3 - 20.4 Snow Wet compact 3.1
Foamed blocks 13.0 Fresh 0.9
Glass 27.4 Steel 78.5
Gravel, clean 14.1 - 17.3 Timber C18 - 3.8
Iron Cast 70.7 (Softwoods) C24 - 4.2
Wrought 75.4 C30 - 4.6
Lead, cast or rolled 111.1 Water 9.8
Limestone 25.1
3.2 DEAD LOADING
3.2.1 General1,3
C In the absence of specific details, use the following:
Floor finish (screed) 75mm 1.2 kN/m2 on plan
Ceiling boards 0.4 kN/m2 on plan
False ceiling 0.25kN/m2
Services: nominal 0.25kN/m2
HVAC 0.4kN/m2
Demountable lightweight partitions 1.0 kN/m2 on plan
Blockwork partitions 2.5 kN/m2 on plan
External walling:
curtain walling and glazing 0.5 kN/m2 on elevation
cavity walls (lightweight block/brick) 3.5 kN/m2 on elevation
THIS DOCUMENT IS COPYRIGHT AND IS PUBLISHED FOR DISTRIBUTION
ONLY WITHIN THE OVE ARUP PARTNERSHIP. IT IS NOT INTENDED FOR
AND SHOULD NOT BE RELIED UPON BY ANY THIRD PARTY.
Ver 3.1/Feb 99
3. Loads (2/4)
3.2.2 Specific dead loading
C Composite construction4
Layer Typical Thickness Typical Dead Load
(mm) on plan kN/m2
Screed Normal 50 1.2
Lightweight 0.9
Slab Normal 130 2.8 - 3.3 *
Lightweight 2.3 - 2.6 *
The lower value is for a trapezoidal deck (Ribdeck AL), the higher value is for a re-entrant profile (Holorib).
C Cladding1
Cladding Arrangement Load on Elevation
(kN/m2)
Cladding sheeting and fixings 0.5
Steel wall framing only 0.25 - 0.4
Framing + brick panels and windows 2.4
Framing + steel sheeting 0.75
Windows, industrial type 0.25
Patent glazing: single 0.3
double 0.55
Doors - industrial wood 0.4
Lath + plaster + studding 0.5
Plate glass / 25mm thick 0.65
Lead plywood
C Walls
Wall type Composition Dead load on elevation (kN/m2)
Concrete walls 225 wall 5.4
12mm plaster each face 0.2
Masonry wall (280 cavity) 102.5 brick 2.25
100 lightweight block and plaster 1.15
Party wall Cavity wall two 102.5 brick leaves plastered 5.0
both sides
Internal wall 100mm lightweight block plastered both sides 1.4
102.5mm brick plastered both sides 2.75
225mm thick plastered both sides 4.4
Curtain wall Glazing + spandrel 1.0
Acoustic wall 265 brick and block 2.5
Partition Demountable 1 on plan
Stud with lath & plaster 0.76
THIS DOCUMENT IS COPYRIGHT AND IS PUBLISHED FOR DISTRIBUTION
ONLY WITHIN THE OVE ARUP PARTNERSHIP. IT IS NOT INTENDED FOR
AND SHOULD NOT BE RELIED UPON BY ANY THIRD PARTY.
Ver 3.1/Feb 99
3. Loads (3/4)
Roofs1,5
Description Dead load on plan (kN/m2)
(Assuming flat)
Bituman roofing felts (3 layers including chipping) 0.29
Ceiling tray/panels 0.25
Asphalt (19mm, 25mm) 0.41, 0.58
Tiles (clay laid to 100mm gauge) 0.62 - 0.70
Concrete tiles interlocking 0.48 - 0.55
3.3 TYPICAL IMPOSED LOADING2
C Be generous at scheme design stage
C Allow for change of use and flexibility of building.
C Make no allowance for imposed load reductions during the scheme design except when
assessing the load on foundations.
Use of structure Intensity of distributed Concentrated load
loading (kN/m2)
Assembly areas 5.0 3.6
Banking hall 3.0 2.7
Bedrooms (hotels, hospitals) 2.0 1.8
Book stores 2.4 for each metre of 7.0
storage height (min 6.5)
Churches 3.0 2.7
Classrooms 3.0 2.7
Communal kitchens 3.0 4.5
Corridors 4.0 4.5
Domestic, floor 1.5 1.4
Factories (general industrial) 5.0 4.5
File rooms in offices 5.0 4.5
- compactus † 7.5
Garages (cars and light vans) 2.5 9.0
Grandstands (fixed seats) 5.0 3.6
Gymnasia 5.0 3.6
Libraries
- reading rooms 4.0 4.5
- mobile racking 4.8 for each metre of 7.0
storage height (min 9.6)
Plant / motor rooms etc. 7.5 4.5
Museum floors 4.0 4.5
Rooms with mainframe computers 3.5 4.5
Offices, general 2.5 * 2.7
Shops (not stock rooms) 4.0 3.6
* This may increase up to 5.0 kN/m depending on the clients requirements, add 1.0 kN/m for lightweight
2 2
demountable partitions.
† Compact filing system (usually over a small proportion of the floor area e.g. adjacent to cores).
THIS DOCUMENT IS COPYRIGHT AND IS PUBLISHED FOR DISTRIBUTION
ONLY WITHIN THE OVE ARUP PARTNERSHIP. IT IS NOT INTENDED FOR
AND SHOULD NOT BE RELIED UPON BY ANY THIRD PARTY.
Ver 3.1/Feb 99
3. Loads (4/4)
3.4 IMPOSED LOADS ON BARRIERS
3.4.1 The horizontal force F (in kN), normal to and uniformly distributed over any length of 1.5m of a
barrier for a car park, required to withstand the impact of a vehicle is given by:
0.5mv 2
F'
*c%*b
where m Is the gross mass of the vehicle (in kg);
v is the velocity of the vehicle (in m/s) normal to the barrier;
δ c is the ceformation of the vehicle (in mm);
δ b is the deflection of the barrier (in mm).
Variables Mass of vehicles <2500 kg Mass of vehicles >2500 kg
m 1500 mass of vehicles
v 4.5 4.5
δ
c 10 100
Note : where δ
b = 0 use F = 150 kN for mass of vehicle = 2500 kg.
3.5 REFERENCES
1. SCI, Steelwork Design Guide to BS 5950 (Vol. 4) (1991)
2. OVE ARUP & PARTNERS, Metric Handbook (1970)
3. IStructE & ICE, Manual for the design of reinforced concrete building structures ("Green
Book") (1985)
4. RICHARD LEES Ltd, Steel Deck Flooring Systems
5. BS 6399 - Parts 1 & 2
THIS DOCUMENT IS COPYRIGHT AND IS PUBLISHED FOR DISTRIBUTION
ONLY WITHIN THE OVE ARUP PARTNERSHIP. IT IS NOT INTENDED FOR
AND SHOULD NOT BE RELIED UPON BY ANY THIRD PARTY.
Ver 3.1/Feb 99
You might also like
- Pottery Analysis, Second Edition: A SourcebookFrom EverandPottery Analysis, Second Edition: A SourcebookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Weekly Report EMAARDocument20 pagesWeekly Report EMAARMohamed FathyNo ratings yet
- Labor and Equipment RatesDocument26 pagesLabor and Equipment RatesAljon Jardeleza SebastianNo ratings yet
- ACI 305R - Hot Weather Concreting (1999 - ERRATA 2006)Document20 pagesACI 305R - Hot Weather Concreting (1999 - ERRATA 2006)tariqkhanNo ratings yet
- Database of Embodied Energy and Water Values For MaterialsDocument3 pagesDatabase of Embodied Energy and Water Values For MaterialsMax Yanac TelleriaNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Metallic BookshelfDocument15 pagesDesign and Construction of Metallic BookshelfKenneth Iyahen100% (2)
- Bill of Quntity Ato Alem Meles As CorrectedDocument194 pagesBill of Quntity Ato Alem Meles As Correctedhabtamu tadesseNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2 Structural TheoryDocument12 pagesLecture Notes 2 Structural TheoryDevieNo ratings yet
- DSR Analizer Ver.16Document5 pagesDSR Analizer Ver.16Anoop GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document47 pagesBook 2rulakhaled1969No ratings yet
- Sample Hypothesis For Structural Analysis of A BuildingDocument4 pagesSample Hypothesis For Structural Analysis of A BuildingTyong AlvesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument35 pagesChapter 2 PDFJeisther Timothy Galano0% (1)
- Load Calculation DDDocument8 pagesLoad Calculation DDMohammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Most Common Materials Unit WeightDocument7 pagesMost Common Materials Unit WeightYvoj Oñisac100% (1)
- 01,44 Cfriuk C13,9 PC+: 2013 Ec 1St Quarter Consi:Rucdon WorksDocument48 pages01,44 Cfriuk C13,9 PC+: 2013 Ec 1St Quarter Consi:Rucdon WorksmohammednasruNo ratings yet
- Tebal Dinding 100 MM Tebal Dinding 75 MMDocument2 pagesTebal Dinding 100 MM Tebal Dinding 75 MMGandhi WidiarnokoNo ratings yet
- Final Boq - Ali HussainDocument3 pagesFinal Boq - Ali Hussainesramergani2No ratings yet
- PRIMA Flex Technical Manual 2Document28 pagesPRIMA Flex Technical Manual 2Charles Vladimir SolvaskyNo ratings yet
- 3 Part 3Document1 page3 Part 3ajay thakulNo ratings yet
- Material Description Weight in kN/m2 U.N.O.: Most Common MaterialsDocument7 pagesMaterial Description Weight in kN/m2 U.N.O.: Most Common Materialssongyanxin_dlutNo ratings yet
- STAAD - Pro & STAAD Advanced Concrete Designer: Reinforced-Concrete Building Project UsingDocument1 pageSTAAD - Pro & STAAD Advanced Concrete Designer: Reinforced-Concrete Building Project UsingHolly WestNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Fundamentals - InfiltracionesDocument1 pageAshrae Fundamentals - InfiltracionesJesus David Lizarazo MartinezNo ratings yet
- RAIC Field Review ChecklistsDocument38 pagesRAIC Field Review ChecklistsDemetrius CioncaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Manpower and Equipment Productivity RateDocument10 pagesPhilippine Manpower and Equipment Productivity RateRonald Klint Marquinez AlcarazNo ratings yet
- G2 - 12S1871 - 22s17137 - 32j19180 - Ahmed Al AmriDocument34 pagesG2 - 12S1871 - 22s17137 - 32j19180 - Ahmed Al AmriMaram AbduallahNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Rate MG NREGA 2020Document145 pagesSchedule of Rate MG NREGA 2020AnkushDhimanNo ratings yet
- Unit Rate Analysis of AdisuDocument8 pagesUnit Rate Analysis of AdisuAbiyot HordofaNo ratings yet
- 282 29loadfoorcemomentDocument60 pages282 29loadfoorcemomentNur MaishaNo ratings yet
- Loading PDFDocument5 pagesLoading PDFOeng BunhakNo ratings yet
- LoadsDocument2 pagesLoadsfatha abdulNo ratings yet
- Tables For Quiz 1Document16 pagesTables For Quiz 1Patricia Kayla SeroteNo ratings yet
- 50m3 Elwevated RCC RsDocument4 pages50m3 Elwevated RCC RsMaulidNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of ClayDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of ClayLourabel Joy Salinas MejiaNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Basis Report FinalDocument50 pagesStructural Design Basis Report FinalJagdish MallickNo ratings yet
- Annex A - Material DensitiesDocument4 pagesAnnex A - Material DensitiesArul SujinNo ratings yet
- Unprised PSF BoQsDocument6 pagesUnprised PSF BoQsyamanta_rajNo ratings yet
- Structural CalcsDocument48 pagesStructural CalcsNasir Ullah100% (1)
- Rajesh Thirumala EstimationDocument27 pagesRajesh Thirumala Estimationdeepak tom babuNo ratings yet
- BOQ BID MaintaDocument5 pagesBOQ BID MaintaNahomNo ratings yet
- Brick CalculationsDocument13 pagesBrick CalculationsMirza Mustansir BaigNo ratings yet
- National Structural Code of The Philippines - Section 204205Document7 pagesNational Structural Code of The Philippines - Section 204205ADRIAN EMMANUEL CLEMENTENo ratings yet
- Weights of Building MaterialsDocument3 pagesWeights of Building MaterialsMizan RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit Price Check Sheet: Formwork For ConcretingDocument3 pagesUnit Price Check Sheet: Formwork For ConcretingAbenezerNo ratings yet
- A) Dead Load Considered: SL - No.Load Contributorlength (M) Width (M) Height (M) Unit Weight (Kn/M3) Udl (KN/M)Document4 pagesA) Dead Load Considered: SL - No.Load Contributorlength (M) Width (M) Height (M) Unit Weight (Kn/M3) Udl (KN/M)Noor MohdNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis and Design Report OF Residential Building of Client Name, 8'Ka'Manahari MakwanpurDocument29 pagesStructural Analysis and Design Report OF Residential Building of Client Name, 8'Ka'Manahari MakwanpurSudip ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Asce 7-22 CH 03com - For PCDocument16 pagesAsce 7-22 CH 03com - For PCsharethefilesNo ratings yet
- Conception Analysis and Design of A 3d Steel BuildingDocument87 pagesConception Analysis and Design of A 3d Steel BuildinggunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Estimation and CostingDocument11 pagesEstimation and CostingVictor OuruNo ratings yet
- Low Energy Building MaterialsDocument27 pagesLow Energy Building MaterialsKamalBhatia100% (2)
- Table 1: Initial SDL and LLDocument2 pagesTable 1: Initial SDL and LLMuhamad Amirul Md. RazdiNo ratings yet
- MembraneDocument3 pagesMembraneer.sanjaysah2020No ratings yet
- Live Load and Dead Load CalculationsDocument2 pagesLive Load and Dead Load CalculationsKrijan MaliNo ratings yet
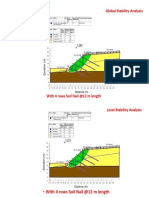
- Slope 4m 12 Soil NailDocument2 pagesSlope 4m 12 Soil NailHauzhiNo ratings yet
- Grade 20 N PDFDocument1 pageGrade 20 N PDFSujithNo ratings yet
- Norms: Coefficient of Friction For The Investigation of Penstock SupportsDocument11 pagesNorms: Coefficient of Friction For The Investigation of Penstock SupportsAsmita KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Khani AB No. 05Document11 pagesKhani AB No. 05Asmita KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Estimates: Rough Estimate (M / M) (Based On Plinth Area Basis)Document14 pagesEstimates: Rough Estimate (M / M) (Based On Plinth Area Basis)visharam100% (1)
- Materials For Miscellaneous Work in TRJM & GRNBDocument26 pagesMaterials For Miscellaneous Work in TRJM & GRNByafhanNo ratings yet
- Loading For Structural Analysis - ManilaDocument30 pagesLoading For Structural Analysis - ManilajayNo ratings yet
- The Detailed and Abstract Estimate For The Proposed R.C.C Toilet Block in Little Kanchipuram Co-Operative Urban Bank Complex, KanchipuramDocument12 pagesThe Detailed and Abstract Estimate For The Proposed R.C.C Toilet Block in Little Kanchipuram Co-Operative Urban Bank Complex, KanchipurampraveenNo ratings yet
- BSEN 10025 2000 New EditionDocument68 pagesBSEN 10025 2000 New Editionpbp2956No ratings yet
- 04 MASONRY HandoutDocument9 pages04 MASONRY HandoutZabeth villalonNo ratings yet
- New Generation Polycarboxylate Hyperplasticiser: Meets The Israeli Standards # 896Document2 pagesNew Generation Polycarboxylate Hyperplasticiser: Meets The Israeli Standards # 896weamNo ratings yet
- All Fastenal Bolt Torque Chart-2Document9 pagesAll Fastenal Bolt Torque Chart-2rizman123786No ratings yet
- Concrete Mix DesignDocument21 pagesConcrete Mix DesignfaheemqcNo ratings yet
- Rokn Al Najom موجنلا نكر: Series Description Qty. Unit Cost Total CostDocument2 pagesRokn Al Najom موجنلا نكر: Series Description Qty. Unit Cost Total CostJOHN basaNo ratings yet
- Haylu - B+G+4 Apartment - FD - BoQ - Priced - 1911181Document80 pagesHaylu - B+G+4 Apartment - FD - BoQ - Priced - 1911181YosefNo ratings yet
- Seismic Retrofitting Guidlines of Buildings in NepalDocument444 pagesSeismic Retrofitting Guidlines of Buildings in NepalÖzgür BozdağNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Foil Polyester Tape For CableDocument4 pagesAluminium Foil Polyester Tape For CableHemendra JasaparaNo ratings yet
- Metallic Coatings For Corrosion PreventionDocument9 pagesMetallic Coatings For Corrosion PreventionDevashish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Design Code: Asme B31.3 Process Piping - For Straight Pipe Under Internal PressureDocument10 pagesDesign Code: Asme B31.3 Process Piping - For Straight Pipe Under Internal Pressurefaisman100% (1)
- 27.) Daguioman Stone MasonryDocument69 pages27.) Daguioman Stone MasonryErnest Belmes100% (1)
- YA VA Catalogue 2Document53 pagesYA VA Catalogue 2bandara123100% (1)
- ASTM A106-A106M-04bDocument8 pagesASTM A106-A106M-04bNadhiraNo ratings yet
- Mineral Casting As Material For Machine Base Frames of Precision MachinesDocument4 pagesMineral Casting As Material For Machine Base Frames of Precision MachinesrahulkumbharkarNo ratings yet
- Piping FabricationDocument36 pagesPiping Fabricationbvenky991100% (5)
- Rate Analysis-All ActivitiesDocument25 pagesRate Analysis-All ActivitiesmuraliNo ratings yet
- IsolcomerDocument8 pagesIsolcomerToth HelgaNo ratings yet
- C-CAN12 SimpsonDocument224 pagesC-CAN12 SimpsonIsaac NooryNo ratings yet
- Australian Standard: Inspection of Buildings Part 1: Pre-Purchase Inspections - Residential BuildingsDocument37 pagesAustralian Standard: Inspection of Buildings Part 1: Pre-Purchase Inspections - Residential BuildingswestozzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - AggregateDocument33 pagesChapter 2 - AggregateHadi Iz'aanNo ratings yet
- Balbach DSC Carbon enDocument12 pagesBalbach DSC Carbon encachoNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolt M16 - M16 Countersunk & Wedge Anchor Bolt M16 ManufacturersDocument9 pagesAnchor Bolt M16 - M16 Countersunk & Wedge Anchor Bolt M16 ManufacturersBashir AliNo ratings yet
- Breakup RMC (13.06.2019)Document9 pagesBreakup RMC (13.06.2019)Swaraj BPNo ratings yet
- Abecia - PT#2 - Minerals in ActionDocument6 pagesAbecia - PT#2 - Minerals in ActionJAN JENIS NICOLE ABECIANo ratings yet
- API-1000-11 Rev 0 PDFDocument3 pagesAPI-1000-11 Rev 0 PDF213eknoNo ratings yet
- Deyu Cai: Duct Schedule, Seaming & SupportsDocument1 pageDeyu Cai: Duct Schedule, Seaming & SupportsSKYLERNo ratings yet