Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Life Science Chapter 5 - Cellular Respiration
Life Science Chapter 5 - Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
carlosgoh246Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingIbai BiNo ratings yet
- AVCL - 1-Physical-and-Chemical-Properties-of-CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesAVCL - 1-Physical-and-Chemical-Properties-of-CarbohydratesMichelle Rose Orozco0% (1)
- Module 2: Polymer Reactions Step-Growth Polymerization KineticsDocument35 pagesModule 2: Polymer Reactions Step-Growth Polymerization KineticsYu An Shih100% (1)
- Biology - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 2023Document5 pagesBiology - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 2023witness vurayayiNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument16 pagesRespirationlayalirsNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAIQdrJat36J9RtnPUAS9sOmcsu9yLAFerEbaweE0U2K4PAtc8viRq9P9-mZEGIbJ9oaVu5ASblSTXUEe5mPmw8jWZr4 Vn5QSBTLLuo3sGyGO-NAMBcoaKpu NNHBFSN j6xd6tq 7VZFgDocument17 pagesACFrOgAIQdrJat36J9RtnPUAS9sOmcsu9yLAFerEbaweE0U2K4PAtc8viRq9P9-mZEGIbJ9oaVu5ASblSTXUEe5mPmw8jWZr4 Vn5QSBTLLuo3sGyGO-NAMBcoaKpu NNHBFSN j6xd6tq 7VZFgThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Respiration 1Document30 pagesRespiration 1tshireletso.kodisangNo ratings yet
- Class ViiDocument5 pagesClass Viirachna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Notes Respiration Handout 1Document3 pagesNotes Respiration Handout 1Imran IjazNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 Energy of LifeDocument29 pagesLec 9 Energy of LifeFahim AbidNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and Fermentation PPTDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration and Fermentation PPTSaif ElkhatibNo ratings yet
- B6 - Respiration 6.1 - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration: BrewingDocument2 pagesB6 - Respiration 6.1 - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration: BrewingCherish KausaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic - Anaerobic - Importance: of RespirationDocument22 pagesAerobic - Anaerobic - Importance: of RespirationLizzy AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Chap7F4 Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesChap7F4 Cellular RespirationSyahir NajmiNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesCellular Respirationsk0561.kklNo ratings yet
- Basis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationDocument3 pagesBasis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationLia JeonNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Ms. A. BantonDocument18 pagesTeacher: Ms. A. BantonCxsh TvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cellular RespirationDocument17 pagesChapter 7 Cellular RespirationbubabozN aOIDHao8nxNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument24 pagesCellular RespirationTrinity BenjaminNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument4 pagesRESPIRATIONTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cellular RespirationDocument47 pagesChapter 7 Cellular Respirationwickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Respiration HandoutDocument3 pagesRespiration HandoutfaadelaaliNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Pearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationDocument77 pagesPearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationMetaknight360 LiveNo ratings yet
- Reflex ActionDocument220 pagesReflex ActionEmaan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration: or The Making of Energy With Out OxygenDocument10 pagesAnaerobic Respiration: or The Making of Energy With Out OxygenRhie Gie100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration Notes 2012Document18 pagesCellular Respiration Notes 2012Sean SolemNo ratings yet
- Group4 BIology Presentation 1Document13 pagesGroup4 BIology Presentation 1Junjun GwapoNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespiDocument3 pagesCellular Respif l o u n d e rNo ratings yet
- Respiration PowerpointDocument14 pagesRespiration Powerpointmmpanjwani4No ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument13 pagesAnaerobic RespirationmarkNo ratings yet
- Bio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Document17 pagesBio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Gillion lordNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- ANSWER Chapter 7 BIO F4Document3 pagesANSWER Chapter 7 BIO F4Izeliwani Haji IsmailNo ratings yet
- DLP Biology F4 Answers Chap 7 (Final)Document3 pagesDLP Biology F4 Answers Chap 7 (Final)deathangel88 GtNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument52 pagesCellular RespirationVinz Arvhil MatagayNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration Genbio g3Document13 pagesAnaerobic Respiration Genbio g3leeyaonde123No ratings yet
- Bio C7 NotesDocument6 pagesBio C7 NotesTHEN YUE PINGNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument7 pagesRespirationmandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesRESPIRATIONMishingo BatuNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION Notes 2ADocument9 pagesRESPIRATION Notes 2AGeorginah NjambiNo ratings yet
- Bio Respiration Chapter SummaryDocument2 pagesBio Respiration Chapter SummaryYoussef Abdurrahman WeinmanNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics (4.4) : Key TermsDocument8 pagesBioenergetics (4.4) : Key Termsv2jj5qfhjpNo ratings yet
- 8-C1.2 Cell RespirationDocument47 pages8-C1.2 Cell Respirationmakaya02No ratings yet
- Topic 10 Respiration 2023Document8 pagesTopic 10 Respiration 2023nizaizzatiNo ratings yet
- # Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)Document7 pages# Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)VELLAMMAH A/P NARAYANASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument3 pagesRespiration in PlantsaarushpancholiNo ratings yet
- ResperationDocument5 pagesResperationaishabroNo ratings yet
- GR 11 LS Cellular Respiration NotesDocument5 pagesGR 11 LS Cellular Respiration Notestshidinaomi5No ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument21 pagesAnaerobic RespirationMr H BioNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiration: by Ana Nurnasuha & Irina KesumaDocument15 pages7.1 Respiration: by Ana Nurnasuha & Irina KesumaLyana AhmadNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesDocument11 pagesCH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesEvannaCoronaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument6 pagesRespirationfaithdanielleyNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Document18 pagesCellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Clarisse De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Biology Section 2 Lesson 4Document73 pagesBiology Section 2 Lesson 4Andeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow Through Living ThingsDocument8 pagesEnergy Flow Through Living ThingsKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 7 - Chapter 04Document16 pagesExp SC 7 - Chapter 04megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Int Esws at 8ce3 Comparing RespirationDocument1 pageInt Esws at 8ce3 Comparing RespirationThe PassionNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - 19012023Document12 pagesRespiratory System - 19012023Tripti AhujaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Lesson 3 AnaerobicDocument8 pagesChapter 12 Lesson 3 AnaerobicTHE FALCON STRIKE GAMERZNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 RespirationDocument33 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 RespirationPau Siew LingNo ratings yet
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Ch01-Introduction To Materials ScienceDocument42 pagesCh01-Introduction To Materials ScienceSaleem MoussaNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids Chemistry, Synthesis, and Applications Edited by Moghis U. AhmadDocument28 pagesFatty Acids Chemistry, Synthesis, and Applications Edited by Moghis U. AhmaddsdsdNo ratings yet
- FAO Emamectin Benzoate PDFDocument15 pagesFAO Emamectin Benzoate PDFmercuriusNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics - 1Document41 pagesPharmacokinetics - 1SristeeNo ratings yet
- Cables and Wires CatalogueDocument16 pagesCables and Wires CatalogueVENITHA KNo ratings yet
- Xanthoproteic Acid TestDocument2 pagesXanthoproteic Acid TestJhona Mae CortesNo ratings yet
- Control ValvesDocument32 pagesControl ValvesParmeshwar Nath Tripathi100% (1)
- Hi Pon 50 01 Polyurethane Top Coat Ver 12.0Document4 pagesHi Pon 50 01 Polyurethane Top Coat Ver 12.0kominthitsar7474No ratings yet
- Suncare Formulation Zero Mark Sun Stick spf50Document2 pagesSuncare Formulation Zero Mark Sun Stick spf50Mart Allen BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1background of The StudyDocument32 pagesChapter One 1.1background of The StudyChinwuba Samuel EbukaNo ratings yet
- Limestone and Phosphogypsum Effects On Soil FertilityDocument19 pagesLimestone and Phosphogypsum Effects On Soil FertilityEloi Carlos GoveNo ratings yet
- Flue Gas Carbon Capture Plants.: by Linde and BASFDocument4 pagesFlue Gas Carbon Capture Plants.: by Linde and BASFUmar Ijaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Dna/Rna Prep Na: User ManualDocument6 pagesDna/Rna Prep Na: User ManualHarun GanićNo ratings yet
- QS Rovabio® Advance L2 - APAC ONLY (En)Document3 pagesQS Rovabio® Advance L2 - APAC ONLY (En)embahNo ratings yet
- ADS 19 - Environmental Specification For Soil ContaminationDocument13 pagesADS 19 - Environmental Specification For Soil ContaminationAzi GNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Fatty AcidsDocument2 pagesPost Lab Fatty AcidsBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Installation With Mortar - Umlauf 2015 PDFDocument18 pagesInstallation With Mortar - Umlauf 2015 PDFvũ minh tâmNo ratings yet
- TDS - Adekanol Uh-450 VF PDFDocument6 pagesTDS - Adekanol Uh-450 VF PDFAPEX SONNo ratings yet
- Conbextra GPDocument69 pagesConbextra GPGavriel NgNo ratings yet
- VESTA Exercise SheetsDocument5 pagesVESTA Exercise SheetsMarcos BHNo ratings yet
- Adhesion and Dentin Bonding AgentsDocument50 pagesAdhesion and Dentin Bonding AgentsFatema86100% (2)
- Marathon 500: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesMarathon 500: Technical Data Sheetalfad maulaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture and Sequestration An OverviewDocument7 pagesCarbon Capture and Sequestration An OverviewIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics Chapter 7 Novel Drug Delivery System NotesDocument10 pagesPharmaceutics Chapter 7 Novel Drug Delivery System NotesBhuvnesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet For Sakaphen Si 14EG - 20231025Document1 pageProduct Data Sheet For Sakaphen Si 14EG - 20231025이선엽No ratings yet
- Wbi11 01 Rms 20240307Document25 pagesWbi11 01 Rms 20240307ashfairfan30No ratings yet
- Palatihan ISCC 2023Document15 pagesPalatihan ISCC 2023imran.teknikkimiaNo ratings yet
Life Science Chapter 5 - Cellular Respiration
Life Science Chapter 5 - Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
carlosgoh246Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Life Science Chapter 5 - Cellular Respiration
Life Science Chapter 5 - Cellular Respiration
Uploaded by
carlosgoh246Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5 – Cellular Respiration
living things need energy
energy such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is stored in food substances
the process releases energy for cellular activities
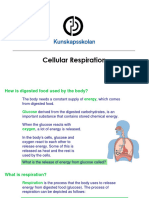
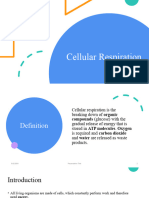
What is cellular respiration ?
the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting ( turn from one course
to another ) the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste
products carbon dioxide and water
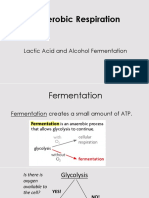
organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation
There are two types of cellular respiration :
aerobic respiration
the main source of energy for living organisms that take in oxygen
example :
- marathon runners use aerobic respiration as their source of energy for running
the presence of oxygen
certain conditions
- raw materials ( oxygen and glucose )
- mitochondria
anaerobic respiration
the absence of oxygen
Ethanol fermentation
- occurs in yeast
- used to brew alcohol
beer, wines, and hard liquor
- as an organic solvent and disinfectant
- a biofuel for cars
- renewable energy
can be produced from plants ( corn and potato )
- carbon dioxide product
to make bread rise
- word equation :
Lactic acid fermentation
- found in our muscles
- word equation :
certain conditions
- raw materials ( glucose )
when there is insufficient or no oxygen
certain organisms prefer anaerobic respiration to aerobic respiration
- baker’s yeast
- certain bacteria
when more energy is needed than the body is able to produce by aerobic respiration
- sprinters use both aerobic and anaerobic respiration for running as this provides them with more
energy in a short period of time with their limited oxygen intake
process by which sugar is broken down to release energy in the absence of oxygen
Aerobic respiration is sufficient to power you across the finish line for leisurely running. It uses oxygen as its main
energy source and doesn’t result in a significant buildup of lactic acid.
High-intensity training force your body to produce instant energy through the immediate breakdown of glycogen
stores. It is harder for the heart and muscles to perform anaerobic respiration if they could perform aerobic
respiration.
Glycogen : a form of energy storage in the body
carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is the main source of energy for cells.
glucose then converts to glycogen
Aerobic vs Anaerobic Respiration :
Aerobic Anaerobic Anaerobic
( ethanol ) ( lactic acid )
Raw materials glucose as raw material
requires oxygen does not require oxygen
Products produces carbon dioxide does not produce carbon
dioxide
produces water produces ethanol produces lactic acid
produces energy produces energy
- more energy per unit of food - less energy per unit of food than aerobic
than anaerobic
Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration :
Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration
Word equation
Products glucose and oxygen carbon dioxide and water
raw materials for cellular raw materials of
respiration photosynthesis
Energy transformed into glucose during released from glucose during
photosynthesis cellular respiration
You might also like
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingIbai BiNo ratings yet
- AVCL - 1-Physical-and-Chemical-Properties-of-CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesAVCL - 1-Physical-and-Chemical-Properties-of-CarbohydratesMichelle Rose Orozco0% (1)
- Module 2: Polymer Reactions Step-Growth Polymerization KineticsDocument35 pagesModule 2: Polymer Reactions Step-Growth Polymerization KineticsYu An Shih100% (1)
- Biology - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 2023Document5 pagesBiology - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 2023witness vurayayiNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument16 pagesRespirationlayalirsNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAIQdrJat36J9RtnPUAS9sOmcsu9yLAFerEbaweE0U2K4PAtc8viRq9P9-mZEGIbJ9oaVu5ASblSTXUEe5mPmw8jWZr4 Vn5QSBTLLuo3sGyGO-NAMBcoaKpu NNHBFSN j6xd6tq 7VZFgDocument17 pagesACFrOgAIQdrJat36J9RtnPUAS9sOmcsu9yLAFerEbaweE0U2K4PAtc8viRq9P9-mZEGIbJ9oaVu5ASblSTXUEe5mPmw8jWZr4 Vn5QSBTLLuo3sGyGO-NAMBcoaKpu NNHBFSN j6xd6tq 7VZFgThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Respiration 1Document30 pagesRespiration 1tshireletso.kodisangNo ratings yet
- Class ViiDocument5 pagesClass Viirachna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Notes Respiration Handout 1Document3 pagesNotes Respiration Handout 1Imran IjazNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 Energy of LifeDocument29 pagesLec 9 Energy of LifeFahim AbidNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and Fermentation PPTDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration and Fermentation PPTSaif ElkhatibNo ratings yet
- B6 - Respiration 6.1 - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration: BrewingDocument2 pagesB6 - Respiration 6.1 - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration: BrewingCherish KausaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic - Anaerobic - Importance: of RespirationDocument22 pagesAerobic - Anaerobic - Importance: of RespirationLizzy AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Chap7F4 Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesChap7F4 Cellular RespirationSyahir NajmiNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesCellular Respirationsk0561.kklNo ratings yet
- Basis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationDocument3 pagesBasis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationLia JeonNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Ms. A. BantonDocument18 pagesTeacher: Ms. A. BantonCxsh TvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cellular RespirationDocument17 pagesChapter 7 Cellular RespirationbubabozN aOIDHao8nxNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument24 pagesCellular RespirationTrinity BenjaminNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument4 pagesRESPIRATIONTumisang PitiroseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cellular RespirationDocument47 pagesChapter 7 Cellular Respirationwickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Respiration HandoutDocument3 pagesRespiration HandoutfaadelaaliNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Pearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationDocument77 pagesPearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationMetaknight360 LiveNo ratings yet
- Reflex ActionDocument220 pagesReflex ActionEmaan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration: or The Making of Energy With Out OxygenDocument10 pagesAnaerobic Respiration: or The Making of Energy With Out OxygenRhie Gie100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration Notes 2012Document18 pagesCellular Respiration Notes 2012Sean SolemNo ratings yet
- Group4 BIology Presentation 1Document13 pagesGroup4 BIology Presentation 1Junjun GwapoNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespiDocument3 pagesCellular Respif l o u n d e rNo ratings yet
- Respiration PowerpointDocument14 pagesRespiration Powerpointmmpanjwani4No ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument13 pagesAnaerobic RespirationmarkNo ratings yet
- Bio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Document17 pagesBio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Gillion lordNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- ANSWER Chapter 7 BIO F4Document3 pagesANSWER Chapter 7 BIO F4Izeliwani Haji IsmailNo ratings yet
- DLP Biology F4 Answers Chap 7 (Final)Document3 pagesDLP Biology F4 Answers Chap 7 (Final)deathangel88 GtNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument52 pagesCellular RespirationVinz Arvhil MatagayNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration Genbio g3Document13 pagesAnaerobic Respiration Genbio g3leeyaonde123No ratings yet
- Bio C7 NotesDocument6 pagesBio C7 NotesTHEN YUE PINGNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument7 pagesRespirationmandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesRESPIRATIONMishingo BatuNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION Notes 2ADocument9 pagesRESPIRATION Notes 2AGeorginah NjambiNo ratings yet
- Bio Respiration Chapter SummaryDocument2 pagesBio Respiration Chapter SummaryYoussef Abdurrahman WeinmanNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics (4.4) : Key TermsDocument8 pagesBioenergetics (4.4) : Key Termsv2jj5qfhjpNo ratings yet
- 8-C1.2 Cell RespirationDocument47 pages8-C1.2 Cell Respirationmakaya02No ratings yet
- Topic 10 Respiration 2023Document8 pagesTopic 10 Respiration 2023nizaizzatiNo ratings yet
- # Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)Document7 pages# Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)VELLAMMAH A/P NARAYANASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument3 pagesRespiration in PlantsaarushpancholiNo ratings yet
- ResperationDocument5 pagesResperationaishabroNo ratings yet
- GR 11 LS Cellular Respiration NotesDocument5 pagesGR 11 LS Cellular Respiration Notestshidinaomi5No ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument21 pagesAnaerobic RespirationMr H BioNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiration: by Ana Nurnasuha & Irina KesumaDocument15 pages7.1 Respiration: by Ana Nurnasuha & Irina KesumaLyana AhmadNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesDocument11 pagesCH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation NotesEvannaCoronaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument6 pagesRespirationfaithdanielleyNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Document18 pagesCellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Clarisse De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Biology Section 2 Lesson 4Document73 pagesBiology Section 2 Lesson 4Andeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow Through Living ThingsDocument8 pagesEnergy Flow Through Living ThingsKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 7 - Chapter 04Document16 pagesExp SC 7 - Chapter 04megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Int Esws at 8ce3 Comparing RespirationDocument1 pageInt Esws at 8ce3 Comparing RespirationThe PassionNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - 19012023Document12 pagesRespiratory System - 19012023Tripti AhujaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Lesson 3 AnaerobicDocument8 pagesChapter 12 Lesson 3 AnaerobicTHE FALCON STRIKE GAMERZNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 RespirationDocument33 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 RespirationPau Siew LingNo ratings yet
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Ch01-Introduction To Materials ScienceDocument42 pagesCh01-Introduction To Materials ScienceSaleem MoussaNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids Chemistry, Synthesis, and Applications Edited by Moghis U. AhmadDocument28 pagesFatty Acids Chemistry, Synthesis, and Applications Edited by Moghis U. AhmaddsdsdNo ratings yet
- FAO Emamectin Benzoate PDFDocument15 pagesFAO Emamectin Benzoate PDFmercuriusNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics - 1Document41 pagesPharmacokinetics - 1SristeeNo ratings yet
- Cables and Wires CatalogueDocument16 pagesCables and Wires CatalogueVENITHA KNo ratings yet
- Xanthoproteic Acid TestDocument2 pagesXanthoproteic Acid TestJhona Mae CortesNo ratings yet
- Control ValvesDocument32 pagesControl ValvesParmeshwar Nath Tripathi100% (1)
- Hi Pon 50 01 Polyurethane Top Coat Ver 12.0Document4 pagesHi Pon 50 01 Polyurethane Top Coat Ver 12.0kominthitsar7474No ratings yet
- Suncare Formulation Zero Mark Sun Stick spf50Document2 pagesSuncare Formulation Zero Mark Sun Stick spf50Mart Allen BautistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1background of The StudyDocument32 pagesChapter One 1.1background of The StudyChinwuba Samuel EbukaNo ratings yet
- Limestone and Phosphogypsum Effects On Soil FertilityDocument19 pagesLimestone and Phosphogypsum Effects On Soil FertilityEloi Carlos GoveNo ratings yet
- Flue Gas Carbon Capture Plants.: by Linde and BASFDocument4 pagesFlue Gas Carbon Capture Plants.: by Linde and BASFUmar Ijaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Dna/Rna Prep Na: User ManualDocument6 pagesDna/Rna Prep Na: User ManualHarun GanićNo ratings yet
- QS Rovabio® Advance L2 - APAC ONLY (En)Document3 pagesQS Rovabio® Advance L2 - APAC ONLY (En)embahNo ratings yet
- ADS 19 - Environmental Specification For Soil ContaminationDocument13 pagesADS 19 - Environmental Specification For Soil ContaminationAzi GNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Fatty AcidsDocument2 pagesPost Lab Fatty AcidsBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Installation With Mortar - Umlauf 2015 PDFDocument18 pagesInstallation With Mortar - Umlauf 2015 PDFvũ minh tâmNo ratings yet
- TDS - Adekanol Uh-450 VF PDFDocument6 pagesTDS - Adekanol Uh-450 VF PDFAPEX SONNo ratings yet
- Conbextra GPDocument69 pagesConbextra GPGavriel NgNo ratings yet
- VESTA Exercise SheetsDocument5 pagesVESTA Exercise SheetsMarcos BHNo ratings yet
- Adhesion and Dentin Bonding AgentsDocument50 pagesAdhesion and Dentin Bonding AgentsFatema86100% (2)
- Marathon 500: Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesMarathon 500: Technical Data Sheetalfad maulaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture and Sequestration An OverviewDocument7 pagesCarbon Capture and Sequestration An OverviewIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutics Chapter 7 Novel Drug Delivery System NotesDocument10 pagesPharmaceutics Chapter 7 Novel Drug Delivery System NotesBhuvnesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet For Sakaphen Si 14EG - 20231025Document1 pageProduct Data Sheet For Sakaphen Si 14EG - 20231025이선엽No ratings yet
- Wbi11 01 Rms 20240307Document25 pagesWbi11 01 Rms 20240307ashfairfan30No ratings yet
- Palatihan ISCC 2023Document15 pagesPalatihan ISCC 2023imran.teknikkimiaNo ratings yet