Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Memory and Programmable Logic
Memory and Programmable Logic
Uploaded by
kschauhan8007Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Memory and Programmable Logic
Memory and Programmable Logic
Uploaded by
kschauhan8007Copyright:
Available Formats
Memory and programmable logic
READ-ONLY MEMORY (ROM)
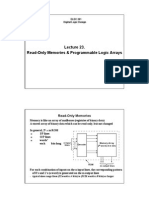
A read-only memory (ROM) is a device that includes both the decoder and the OR gates within
a single IC package. The connections between the outputs of the decoder and the inputs of the
OR gates can be specified for each particular configuration.
A ROM is essentially a memory (or storage) device in which permanent binary information is
stored. The binary information must be specified by the designer and is then embedded in the
unit to form the required interconnection pattern. ROMs come with special internal electronic
fuses that can be "programmed" for a specific configuration. Once the pattern is established, it
stays within the unit even when power is turned off and on again.
It consists of n input lines and m output lines. Each bit combination of the input variables is
called an address. Each bit combination that comes out of the output lines is called a word. The
number of bits per word is equal to the number of output lines, m. An address is essentially a
binary number that denotes one of the min terms of n variables. The number of distinct
addresses possible with n input variables is 2n
. An output word can be selected by a unique
address, and since there are 2n distinct addresses in a ROM, there are 2n distinct wordsthat are
said to be stored in the unit.
The word available on the output lines at any given time depends on the address value applied
to the input lines. A ROM is characterized by the number of words 2n
and the number of bits
per word m.
You might also like
- Lecture-1.2.5 UEC612 CombCircuits PLDs-4Document55 pagesLecture-1.2.5 UEC612 CombCircuits PLDs-4Harry PotterNo ratings yet
- Module-4 Memory and Programmable Logic: Read-Only Memory (Rom)Document32 pagesModule-4 Memory and Programmable Logic: Read-Only Memory (Rom)Yogiraj TiwariNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Memory and Programmable LogicDocument17 pagesUNIT 4 Memory and Programmable LogicSanthosh KundeNo ratings yet
- Memory Devices: Prepared by Rajesh Paul - (Electronics) ADC-AMPDocument17 pagesMemory Devices: Prepared by Rajesh Paul - (Electronics) ADC-AMPSubrahmanyam GuduruNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument22 pagesUnit VSmarty SohamNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I CPLD & FPGA ArchitecturesDocument22 pagesUNIT - I CPLD & FPGA Architecturesyayavaram100% (2)
- CPLD Fpga Notes FOR VLSI BACKGROUNDDocument16 pagesCPLD Fpga Notes FOR VLSI BACKGROUNDadi_risingsunNo ratings yet
- Memories-V - Ldic Digital NotesDocument22 pagesMemories-V - Ldic Digital NotesbasambhagyarekhaNo ratings yet
- UNIT V Notes 1Document7 pagesUNIT V Notes 1N. ANSGAR MARY ITNo ratings yet
- UNIT V NotesDocument22 pagesUNIT V NotesN. ANSGAR MARY ITNo ratings yet
- Memory and Programmable LogicDocument17 pagesMemory and Programmable LogicAjay GahlotNo ratings yet
- Digital MemoriesDocument59 pagesDigital MemoriesAnkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 CPLD & Fpga Architecture & Applications Introduction: The Need of Programmable Devices Was Realized in Early 70s Itself With TheDocument21 pagesUnit-1 CPLD & Fpga Architecture & Applications Introduction: The Need of Programmable Devices Was Realized in Early 70s Itself With TheGoutham DevisettyNo ratings yet
- Cse231 Memory DesignDocument30 pagesCse231 Memory Designsrktemp2023No ratings yet
- Memory Unit 5Document8 pagesMemory Unit 5G.LAKSHIMIPRIYA Dept Of Computer ScienceNo ratings yet
- Binary Decoder: Binary Decoders Are Another Type of Digital Logic Device That Has Inputs of 2-Bit, 3-Bit or 4-BitDocument7 pagesBinary Decoder: Binary Decoders Are Another Type of Digital Logic Device That Has Inputs of 2-Bit, 3-Bit or 4-BitJohn Brix BalisterosNo ratings yet
- DSD MemoryDocument37 pagesDSD MemoryibiiuoujNo ratings yet
- Binary Decoder - DocxkenDocument11 pagesBinary Decoder - DocxkenLiezel JuarezNo ratings yet
- DAY-15 Programmable Logic Devices PLD: Programmable Read Only Memory PROMDocument11 pagesDAY-15 Programmable Logic Devices PLD: Programmable Read Only Memory PROMAnusha SagiNo ratings yet
- Department of Ece Subject Code: Ec1203 Digital Electronics (For Third Semester Ece) Two Mark Questions-AnswersDocument12 pagesDepartment of Ece Subject Code: Ec1203 Digital Electronics (For Third Semester Ece) Two Mark Questions-AnswersSurendar PNo ratings yet
- DD Slides 7Document61 pagesDD Slides 7tanay.s1No ratings yet
- Semiconductor MemoriesDocument61 pagesSemiconductor Memoriesnavikaundal49No ratings yet
- Programmable Logic and Storage DevicesDocument63 pagesProgrammable Logic and Storage DevicesHectorLopezNo ratings yet
- Cam Module 5 RomDocument28 pagesCam Module 5 Romnamitha rNo ratings yet
- Rohini 37988195242Document4 pagesRohini 37988195242saran2732006sNo ratings yet
- Binary DecoderDocument7 pagesBinary DecoderAlinChanNo ratings yet
- Rohini College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument5 pagesRohini College of Engineering & TechnologyDarshan BysaniNo ratings yet
- Module - II BDocument48 pagesModule - II BPamusainagaharshavardhanNo ratings yet
- Inside RAM: Two-Level AddressingDocument12 pagesInside RAM: Two-Level AddressingdoomachaleyNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Combinational Logic by Standard Ics and Programmable Rom MemoriesDocument5 pagesImplementation of Combinational Logic by Standard Ics and Programmable Rom MemoriesJohn KirubaNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - DIO Module & InterfacesDocument94 pagesSession 3 - DIO Module & InterfacesMerihan Mohammad MeriNo ratings yet
- The Central Processing Unit (CPU) : Bayan University For Science & TechnologyDocument56 pagesThe Central Processing Unit (CPU) : Bayan University For Science & TechnologyAltayeb AbdulhameedNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem CA NotesDocument176 pages2nd Sem CA NotesKaen SenpaiNo ratings yet
- Memory Address DecodingDocument28 pagesMemory Address DecodingKokohAliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document10 pagesLecture 6Elmustafa Sayed Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ch6 Memory&Progm LogicDocument8 pagesCh6 Memory&Progm LogicAbishek SahNo ratings yet
- Sequential N CombinationDocument13 pagesSequential N CombinationManikandan ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Digital Integrated Circuits: Designing Memory and Array StructuresDocument70 pagesDigital Integrated Circuits: Designing Memory and Array StructuresShubham GargNo ratings yet
- DecoderDocument1 pageDecoderparassuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital System-Digital TermsDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Digital System-Digital Termsdanilopangatungan8No ratings yet
- Microprocessor (P) (Mpu) : Μ A Pisacpuonasinglechip. Components Of CpuDocument24 pagesMicroprocessor (P) (Mpu) : Μ A Pisacpuonasinglechip. Components Of CpuKashif HussainNo ratings yet
- Selection of Registers: Recall The R-Type MIPS InstructionsDocument20 pagesSelection of Registers: Recall The R-Type MIPS Instructionsahmed qaziNo ratings yet
- Memory and Programmable LogicDocument47 pagesMemory and Programmable Logicdewantosatrio50% (2)
- Unit 13: Chapter 3 - Combinational Logic DesignDocument40 pagesUnit 13: Chapter 3 - Combinational Logic DesignVani YamaniNo ratings yet
- Mpmc-3 Concept Oriented NotesDocument47 pagesMpmc-3 Concept Oriented NotesNimmagadda Chandra PaulNo ratings yet
- 1.1 IntroDocument49 pages1.1 IntroKarl Martin AlduesoNo ratings yet
- 8051Document69 pages8051Raffi SkNo ratings yet
- EMISY Second Test Exemplary Questions Solved-3Document15 pagesEMISY Second Test Exemplary Questions Solved-3YANG LIUNo ratings yet
- Rom, PlaDocument7 pagesRom, PlaShaik IrfanNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorsDocument4 pagesMicroprocessorsleoNo ratings yet
- LectEPE1301 3 RegistersRAMMemory AddressMappingAndDecoding1Document25 pagesLectEPE1301 3 RegistersRAMMemory AddressMappingAndDecoding1Bryan KekNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics (Physics)Document8 pagesDigital Electronics (Physics)joyalsaju319No ratings yet
- Mpin TDocument55 pagesMpin Tzinabuhaile26No ratings yet
- ArchitectureDocument10 pagesArchitecturedineshe.eceNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Lecture 1Document17 pagesModule 3 - Lecture 1AQeNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document20 pagesCH 7Gcross NGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document22 pagesChapter 3Gemechis GurmesaNo ratings yet
- Memory SystemsDocument29 pagesMemory SystemsAbha HameedNo ratings yet
- Two Mark Questions For DSDDocument17 pagesTwo Mark Questions For DSDvnirmalacseNo ratings yet