Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Establish Quality Standard
Establish Quality Standard
Uploaded by
mahad mohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- EHQMS Process MatrixDocument2 pagesEHQMS Process MatrixAbdullahKhan100% (6)
- Audit Program Accounts PayableDocument20 pagesAudit Program Accounts PayableSarang SinghNo ratings yet
- OP 1106 Audit Report Processing To Be Used On or After 31-Oct-2021Document11 pagesOP 1106 Audit Report Processing To Be Used On or After 31-Oct-2021Vijay YadavNo ratings yet
- Financial Accountability at Schools Challenges and ImplicationsDocument22 pagesFinancial Accountability at Schools Challenges and Implicationsmurti51No ratings yet
- Quality Management PlanDocument10 pagesQuality Management PlanAudrey Owens100% (2)
- 4 5832618050993524747Document13 pages4 5832618050993524747Alazer Tesfaye Ersasu TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Yangon Technological University Department of Civil Engineering Construction ManagementDocument18 pagesYangon Technological University Department of Civil Engineering Construction Managementthan zawNo ratings yet
- Software Project: Quality ManagementDocument17 pagesSoftware Project: Quality ManagementImran AhmedNo ratings yet
- DMPM 1104 Project Quality Management Lecture Notes 1Document12 pagesDMPM 1104 Project Quality Management Lecture Notes 1edwinchirchir6130No ratings yet
- Essentials of PM - 10-12Document60 pagesEssentials of PM - 10-12Muhammad Aman Azam100% (1)
- Unit 5 Quality ManagementDocument7 pagesUnit 5 Quality ManagementKezzy KayNo ratings yet
- BSBPMG532 v1.0 Student Workbook and Learning ActivitiesDocument58 pagesBSBPMG532 v1.0 Student Workbook and Learning ActivitiesmiantariqpervazNo ratings yet
- Lecture Qualtiy ManagementDocument103 pagesLecture Qualtiy ManagementAiman ChouhdaryNo ratings yet
- PRINCE2® Theme: QualityDocument3 pagesPRINCE2® Theme: QualitySocrates KontosNo ratings yet
- Online Education Portal Project: Uality Anagement LANDocument10 pagesOnline Education Portal Project: Uality Anagement LANHehe HoNo ratings yet
- Updated Quality Management PlanDocument3 pagesUpdated Quality Management PlanLok SewaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Project ScheduleDocument14 pagesModule 4 - Project ScheduleDenmark WilsonNo ratings yet
- 34 BotaDocument6 pages34 BotaprofbruceNo ratings yet
- Project MGMTDocument32 pagesProject MGMTHussien AliyiNo ratings yet
- 16 Establish Quality StandardsDocument10 pages16 Establish Quality StandardsSamuel AdamuNo ratings yet
- Quality Planning Management - Summary NotesDocument13 pagesQuality Planning Management - Summary NotesGeorge NjolomaNo ratings yet
- P M P Chapter 8Document17 pagesP M P Chapter 8Khaled KhanNo ratings yet
- A PQP Mandarory or NotDocument3 pagesA PQP Mandarory or NotkhaledhaddadNo ratings yet
- TbsmqualitymanagementplanDocument22 pagesTbsmqualitymanagementplanapi-338883409No ratings yet
- Project Management3Document12 pagesProject Management3Veronica Cretu-IonascuNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument63 pagesProject Quality ManagementEljay VinsonNo ratings yet
- Quality Management ProcessDocument13 pagesQuality Management ProcessSukumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Plan Guide: Document NameDocument3 pagesQuality Management Plan Guide: Document NameisolongNo ratings yet
- .Quality - ManagamentDocument31 pages.Quality - Managamentp comNo ratings yet
- Project Quality Management ClaireDocument34 pagesProject Quality Management ClaireDerrick KazoobaNo ratings yet
- CDC UP Quality Management Practices GuideDocument5 pagesCDC UP Quality Management Practices GuideRavi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Management 05Document28 pagesSoftware Quality Management 05tesfanesh 65tgNo ratings yet
- Project Work: Prepare A Quality Plan Document (25%)Document90 pagesProject Work: Prepare A Quality Plan Document (25%)eyerusalem tesfayeNo ratings yet
- PQMT SyllabusDocument44 pagesPQMT Syllabusnjeri njorogeNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 PresentationDocument43 pagesWEEK 6 Presentationyuvrajsinhgohel15No ratings yet
- Cover Page and Declaration: Master of Business Administration (M.B.A.)Document48 pagesCover Page and Declaration: Master of Business Administration (M.B.A.)Hind ImadNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1Document4 pagesAssignment No. 1saddam walandkarNo ratings yet
- Qlty MGMT in ProjectsDocument5 pagesQlty MGMT in Projectssweet16barbiesNo ratings yet
- Quality PlanDocument3 pagesQuality PlanblackcoutureconsultationsNo ratings yet
- PM 333 Lecture 13 Project Quality ManagementDocument16 pagesPM 333 Lecture 13 Project Quality ManagementJesse TungarazaNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance Statement of Work (Version 2.0)Document21 pagesQuality Assurance Statement of Work (Version 2.0)KomalNo ratings yet
- PM - Lecture 7 Project Quality ManagementDocument43 pagesPM - Lecture 7 Project Quality ManagementMariam MansourNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument32 pagesProject Quality ManagementLemark R.0% (1)
- What Is A Quality Management Process?: 1.1 InstructionsDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Quality Management Process?: 1.1 Instructionsksamanta23No ratings yet
- Project Quality PlanDocument15 pagesProject Quality PlankumaraguruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Project Quality ManagementDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Project Quality ManagementHussen MossaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal 2Document5 pagesReflective Journal 2suhasana0305No ratings yet
- Construction Quality, Safety and Human ValuesDocument56 pagesConstruction Quality, Safety and Human ValuesGireesh Gowda GiriNo ratings yet
- Sample Project ManagementDocument25 pagesSample Project ManagementVishwa VichuNo ratings yet
- Bsbpmg411 Task 1Document11 pagesBsbpmg411 Task 1Tanmay JhulkaNo ratings yet
- SQA ImportantDocument8 pagesSQA ImportantMuhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument8 pagesProject Quality ManagementJoereane LlarenaNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Process Checklists 3.2. Benchmarking 3.3. Quality (Project) Audit 3.4. The PCDA (Plan, Do, Check, and Act) CycleDocument32 pages3.1. Process Checklists 3.2. Benchmarking 3.3. Quality (Project) Audit 3.4. The PCDA (Plan, Do, Check, and Act) CycleAnonymous Jo79oINo ratings yet
- DPPM Qly Note3Document21 pagesDPPM Qly Note3OJOK APOLLONo ratings yet
- Group Project Project Quality Management 24-06-2021Document59 pagesGroup Project Project Quality Management 24-06-2021Ubaid ur RehmanNo ratings yet
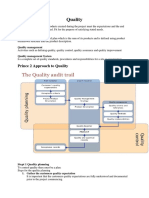
- Quality: Prince 2 Approach To QualityDocument3 pagesQuality: Prince 2 Approach To Qualityquree25No ratings yet
- Quality Management PlanDocument9 pagesQuality Management PlanDhetzz Alvin Sevenfoldism100% (1)
- GSLC IspmDocument2 pagesGSLC IspmaniieendyazhrNo ratings yet
- PQPDocument1 pagePQPislam0207No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Project Quality ManagementDocument7 pagesLesson 6 - Project Quality Managementsandaru malindaNo ratings yet
- Project Quality Management Derrick NewDocument35 pagesProject Quality Management Derrick NewDerrick KazoobaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Project Management Knowledge AreasDocument38 pagesChapter Two: Project Management Knowledge AreasRobel HabtamuNo ratings yet
- IT Audit Domain 1 - v3Document81 pagesIT Audit Domain 1 - v3rewNo ratings yet
- Manpower Audit BackgroundDocument6 pagesManpower Audit Backgroundmagayaprincess169No ratings yet
- The Impact of Information Technology On The Audit Process Session 1Document35 pagesThe Impact of Information Technology On The Audit Process Session 1Nathalia TriandiniNo ratings yet
- Cbo Credit Manual Jul 21Document295 pagesCbo Credit Manual Jul 21prashanth100% (1)
- Guidelines For The Implementation of A Quality Management System in Industrial CompaniesDocument8 pagesGuidelines For The Implementation of A Quality Management System in Industrial CompaniesMilagros MontesinosNo ratings yet
- Auditing For Managers - The Ultimate Risk Management ToolDocument369 pagesAuditing For Managers - The Ultimate Risk Management Toolthenneberry61No ratings yet
- The Effect of Competence, Objectivity, Independence On The Effectiveness of Internal Audit With Management Support As Moderating VariableDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Competence, Objectivity, Independence On The Effectiveness of Internal Audit With Management Support As Moderating VariableInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ethical Matters PDFDocument13 pagesEthical Matters PDFCathyNo ratings yet
- Aau ModelDocument34 pagesAau ModelTayech TayuNo ratings yet
- Psa 530: Audit Sampling and Other Selective TestingDocument49 pagesPsa 530: Audit Sampling and Other Selective TestingJeric IsraelNo ratings yet
- MBA I - 428 Business Ethics Unit - Iv: Corporate Governance MeaningDocument6 pagesMBA I - 428 Business Ethics Unit - Iv: Corporate Governance MeaningJebin JamesNo ratings yet
- BW ResourcesDocument8 pagesBW ResourcesHazel Canoy100% (3)
- Office Performance Commitment and Review Form: Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDocument13 pagesOffice Performance Commitment and Review Form: Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDENNIS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Afm Exam Essentials-2023Document3 pagesAfm Exam Essentials-2023sakhiahmadyarNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditing (Online) - Syllabus - ConcourseDocument15 pagesInternal Auditing (Online) - Syllabus - Concoursebislig water districtNo ratings yet
- Computerized AuditingDocument29 pagesComputerized AuditingpalpitopitooNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Mr. Gaurav RanaDocument36 pagesProject Report: Mr. Gaurav RanaBIKASH BHASKARNo ratings yet
- AIS Complete Testbank QuizDocument74 pagesAIS Complete Testbank QuizRomiline Umayam100% (5)
- Dictionar Conta FinanteDocument27 pagesDictionar Conta FinanteEmilia VasileNo ratings yet
- Client AcceptanceDocument26 pagesClient AcceptanceSaiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Boundries of Management ControlDocument14 pagesBoundries of Management ControlRamesh Rasik PaudelNo ratings yet
- Attachment - FSMS Process Interaction (Rev 0) - 210901Document1 pageAttachment - FSMS Process Interaction (Rev 0) - 210901QA HBTNo ratings yet
- Senthil Kumar Sundaresan: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesSenthil Kumar Sundaresan: ObjectiveAnanthan VijayanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Financial Accounting An Integrated Approach 5th Edition by TrotmanDocument21 pagesSolution Manual For Financial Accounting An Integrated Approach 5th Edition by Trotmana540142314No ratings yet
- ZTE SOC Solutions To Usability and Scalability Guidelines For The DesignDocument4 pagesZTE SOC Solutions To Usability and Scalability Guidelines For The Designinformationsecret0% (1)
- Chapter 2Document30 pagesChapter 2Justin ForondaNo ratings yet
Establish Quality Standard
Establish Quality Standard
Uploaded by
mahad mohamedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Establish Quality Standard
Establish Quality Standard
Uploaded by
mahad mohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
Establish Quality Standards Training, Teaching and
Learning Materials Development Lo-2
JIGJIGA POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE
WATER WORKS SITE CONSTRUCTION
MANAGEMENT LEVEL-IV Level IV
LEARNING GUIDE # 2
Unit of Competence: Establish Quality Standards
Module Title: Establish Quality Standards
LG Code: WRS SCM4 06 0413
TTLM Code: WRS SCM4 TTLM062 24
LO2: Assist in planning of quality assurance procedures and
Implement quality assurance procedures
INTRODUCTIO
Learning Guide # 2
N
This learning guide is developed to provide you the necessary information regarding the following
content coverage and topics –
Assist in planning of quality assurance procedures and Implement quality assurance
procedures
Quality Assurance, Quality planning and Quality of the Deliverables
Quality of the Process and Creating a Strategy for Quality
Implementing Quality Assurance, The Project Triangle and Quality Assurance Outputs
This guide will also assist you to attain the learning outcome stated in the cover page.
Specifically, upon completion of this Learning Guide, you will be able to –
Collected & prepared by: WSSC Page 1
Establish Quality Standards Training, Teaching and
Learning Materials Development Lo-2
Assist in planning of quality assurance procedures and Implement quality assurance
procedures
Identify and confirm Quality Assurance, Quality planning and Quality of the Deliverables
Identify and confirm Quality of the Process and Creating a Strategy for Quality
Identify and confirm Implementing Quality Assurance, The Project Triangle and Quality
Assurance Outputs
Learning Activities
1. Read the specific objectives of this Learning Guide.
2. Read the information written in the “Information Sheets 1” in pages 3-8.
3. Accomplish the “Self-check” in page 9.
4. If you earned a satisfactory evaluation proceed to “formative exam”. However, if your rating is
unsatisfactory, see your teacher for further instructions or go back to Learning Activity # 1. But if
satisfactory you can proceed to Learning Guide 3.
Your teacher will evaluate your output either satisfactory or unsatisfactory. If unsatisfactory, your
teacher shall advice you on additional work. But if satisfactory you can proceed to the next topic.
Assist in planning of quality assurance procedures and
Information Sheet 1 Implement quality assurance procedures
Quality Assurance
The specification of quality related features is an essential component of defining the end-
product of a project. If a project aims to deliver a complex end-product, the quality aspects of
that end-product will need to be planned and designed. QA requires agreement on the level of
quality controls to be adopted.
Quality Assurance (QA) is a global term covering the quality policy, quality management and
quality control functions, which together ensure that the product will be consistently
manufactured to the required standard. Its aim is to achieve and assure quality through the
adoption of a cost effective quality control system along with external inspections and audits.
Collected & prepared by: WSSC Page 2
Establish Quality Standards Training, Teaching and
Learning Materials Development Lo-2
Quality planning is an essential part of the planning activity and can be seen in the product
descriptions and in the scheduling of quality related activities. The results of the quality planning
activities are reflected in the resource and technical plans.
Quality control is concerned with ensuring that the required qualities are built into all of the
products throughout their development life cycles. It defines the methods of inspection used to
determine whether the product has met its quality specification. Quality control makes use of
measurable quality criteria and is implemented by means of change control, quality reviews,
project reviews and by the testing of products.
Assist in planning of quality assurance procedures and Implement
quality assurance procedures
Quality of the Deliverables
The planning process must address the quality issues raised by a proposed project. Quality
planning should have a major impact on the overall size and scope of the project plans. It is an
essential component of general planning and can be seen in the product descriptions, particularly
in their quality criteria. Quality-related activities should be explicitly integrated into the resource
and technical plans.
Product descriptions should be created during the planning process, as the products that are
required by the project are identified. They should describe the purpose, form and components of
a product and list the quality criteria applicable to that product.
Quality criteria define the characteristics of a product in quantifiable terms to allow it to be
measured at various points in its development life cycle. The quality criteria are used as a
Collected & prepared by: WSSC Page 3
Establish Quality Standards Training, Teaching and
Learning Materials Development Lo-2
benchmark against which to measure the finished product and should be specified in the related
product description.
Quality criteria should be determined by considering important characteristics of a product in
ensuring that it is 'fit for purpose'. They should always be stated objectively. Terms such as
'quick response' or 'easily maintained' should be avoided as they do not permit meaningful
measurement.
Quality of the Process
It is important to distinguish between the quality of the deliverables and the quality of the
project. The project manager must decide how much emphasis to on the quality of the project,
and how much on the quality of the deliverables. Checking project quality involves examining
completely different things than checking the quality of the deliverables.
Deliverable quality refers to the 'fit for purpose' aspect. It covers things like how well
the deliverables meet the user's needs, and the total cost of ownership.
Project quality covers things like applying proper project management practices to cost,
time, resources, communication etc. It also covers managing changes within the project.
In theory a high quality project could result in low quality deliverables and vice versa, but it is
much more likely however that a high quality project will produce high quality deliverables.
Creating a Strategy for Quality
Every project plan should address quality management issues in order to provide the highest
quality products and services. Project quality applies to both deliverables and process quality.
A quality management strategy defines the required quality level for the project and the
approach to be used to ensure that this level is achieved. A more detailed quality management
plan is developed in the planning stage.
A Quality Management Strategy should include:
Quality Objectives
Collected & prepared by: WSSC Page 4
Establish Quality Standards Training, Teaching and
Learning Materials Development Lo-2
Deliverables subject to quality strategy
Processes subject to the quality strategy
Quality standards and methods to be applied
The Project Manager, project sponsors and project stakeholders should all be involved in the
creation of the strategy. The final outcome should be the Quality Management Strategy
component of the Project Plan.
Implementing Quality Assurance
The Quality Assurance Strategy defines the quality standards for the project and determines how
they are satisfied. Implementation involves carrying out systematic quality activities and uses
quality audits to determine which processes should be used to achieve the project requirements
and to assure they are performed efficiently and effectively.
Project team members, the project manager and the stakeholders are all responsible for the
quality assurance of the project, but the Project Manager will have the greatest impact on the
quality of the project.
The inputs to the quality assurance process are likely to include the following:
Quality management plan
Quality metrics
Process improvement plan
Work performance information
Approved change requests
Quality control measurements
Two of the main tools of quality assurance are quality audits and process analysis
Quality Audits
Collected & prepared by: WSSC Page 5
Establish Quality Standards Training, Teaching and
Learning Materials Development Lo-2
Quality audits are independent reviews carried out by trained auditors to identify ineffective or
inefficient processes and procedures used on the project. They may take place randomly or on a
regular schedule, depending on organizational policies.
Correctly performed quality audits will ensure that:
The deliverables are fit for use and meet safety standards.
Applicable laws and standards are adhered to.
Corrective action is recommended and implemented where necessary.
The quality plan is adhered to.
Quality improvements are identified.
The implementation of approved change requests is confirmed.
Quality improvements can come about as a result of the quality audits as auditors may discover
ways of improving the efficiency or effectiveness of the project. These are implemented by
submitting change requests or taking corrective action.
Quality audits are usually carried out by experienced specialists whose task is to produce an
independent evaluation of the quality process. Some organizations are large enough to have their
own quality assurance teams but smaller organizations may have to hire external quality
assurance teams.
Process Analysis
Process analysis looks at process improvement from an organizational and technical perspective
by examining:
Problems experienced while conducting the project
Constraints of the project
Inefficient and ineffective processes identified during process operation
Collected & prepared by: WSSC Page 6
Establish Quality Standards Training, Teaching and
Learning Materials Development Lo-2
One of the techniques of process analysis includes performing root cause analysis. While
examining problems and constraints, for example, the Project Manager should look at what's
causing the problem. The result of this exercise will allow preventive actions to be developed for
similar problems or problems that have similar root causes.
Quality Assurance Outputs
The outputs of the Quality Assurance process include:
Requested changes
Recommended corrective actions
Project management plan updates
Any recommended corrective actions, whether they are a result of a quality audit or process
analysis, should be acted upon immediately. For example, if parts being manufactured for one of
the deliverables of a project are found to be defective then the process should be corrected,
perhaps by recalibrating equipment or changing raw materials.
The Project Triangle
Projects need to be performed and delivered under certain constraints. These are normally listed
as time, cost and scope, where scope includes quality. This is often referred to as the Project
Management Triangle, where each side represents a constraint. One side of the triangle cannot
be changed without impacting the others.
The time constraint refers to the amount of time available to complete a project.
The cost constraint refers to the budgeted amount available for the project.
The scope constraint refers to what must be done to produce the project's end result.
These three constraints are often competing constraints: increased scope typically means
increased time and increased cost, a tight time constraint could mean increased costs and reduced
scope, and a tight budget could mean increased time and reduced scope.
Collected & prepared by: WSSC Page 7
Establish Quality Standards Training, Teaching and
Learning Materials Development Lo-2
The discipline of project management is about providing the tools and techniques that enable the
project team (not just the project manager) to organise their work to meet these constraints.
Another approach to project management is to consider the three constraints as finance, time and
human resources. If you need to finish a job in a shorter time, you can throw more people at the
problem, which in turn will raise the cost of the project, unless by doing this task quicker we will
reduce costs elsewhere in the project by an equal amount.
Self-Check 1 Written Test
Name: _________________________________ Date: _________________
Instruction: Answer all the questions listed below, if you have some difficulty doing this self-check, feels
free to ask your teacher for clarifications.
Part I Match from column ‘A’ to column ‘B’
‘A’ ‘B’
______1. Project quality A. The products that are required by the project are
______ 2. Product descriptions identified
______ 3. Deliverable quality B. Is define the characteristics of a product in
______ 4. Quality criteria quantifiable terms to allow it to be measured at
______ 5. Quality of the Process various points in its development life cycle
C. Is important to distinguish between the quality of the
deliverables and the quality of the project.
D. Refers to the 'fit for purpose' aspect. It covers things
like how well the deliverables meet the user's needs,
and the total cost of ownership.
E. Covers things like applying proper project
management practices to cost, time, resources,
communication etc. It also covers managing changes
within the project.
F. Defines the required quality level for the project and
the approach to be used to ensure that this level is
achieved
G. Are independent reviews carried out by trained
Collected & prepared by: WSSC Page 8
Establish Quality Standards Training, Teaching and
Learning Materials Development Lo-2
auditors to identify ineffective or inefficient processes
and procedures used on the project
You must able to get 8points to be competent otherwise you’ll take another test
Formative exam lo2
Name_________________________________________ Id No.________ Date ____________
Part I match from column ‘A’ to column ‘B’
‘A’ ‘B’
______1. Project quality A. The products that are required by the project are
______ 2. Product descriptions identified
______ 3. Deliverable quality B. Is define the characteristics of a product in
______ 4. Quality criteria quantifiable terms to allow it to be measured at
______ 5. Quality of the Process various points in its development life cycle
C. Is important to distinguish between the quality of the
______ 6. Quality management deliverables and the quality of the project.
strategy D. Refers to the 'fit for purpose' aspect. It covers things
______ 7. Quality audits like how well the deliverables meet the user's needs,
and the total cost of ownership.
E. Covers things like applying proper project
management practices to cost, time, resources,
communication etc. It also covers managing changes
within the project.
F. Defines the required quality level for the project and
the approach to be used to ensure that this level is
achieved
G. Are independent reviews carried out by trained
auditors to identify ineffective or inefficient processes
and procedures used on the project
Collected & prepared by: WSSC Page 9
You might also like
- EHQMS Process MatrixDocument2 pagesEHQMS Process MatrixAbdullahKhan100% (6)
- Audit Program Accounts PayableDocument20 pagesAudit Program Accounts PayableSarang SinghNo ratings yet
- OP 1106 Audit Report Processing To Be Used On or After 31-Oct-2021Document11 pagesOP 1106 Audit Report Processing To Be Used On or After 31-Oct-2021Vijay YadavNo ratings yet
- Financial Accountability at Schools Challenges and ImplicationsDocument22 pagesFinancial Accountability at Schools Challenges and Implicationsmurti51No ratings yet
- Quality Management PlanDocument10 pagesQuality Management PlanAudrey Owens100% (2)
- 4 5832618050993524747Document13 pages4 5832618050993524747Alazer Tesfaye Ersasu TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Yangon Technological University Department of Civil Engineering Construction ManagementDocument18 pagesYangon Technological University Department of Civil Engineering Construction Managementthan zawNo ratings yet
- Software Project: Quality ManagementDocument17 pagesSoftware Project: Quality ManagementImran AhmedNo ratings yet
- DMPM 1104 Project Quality Management Lecture Notes 1Document12 pagesDMPM 1104 Project Quality Management Lecture Notes 1edwinchirchir6130No ratings yet
- Essentials of PM - 10-12Document60 pagesEssentials of PM - 10-12Muhammad Aman Azam100% (1)
- Unit 5 Quality ManagementDocument7 pagesUnit 5 Quality ManagementKezzy KayNo ratings yet
- BSBPMG532 v1.0 Student Workbook and Learning ActivitiesDocument58 pagesBSBPMG532 v1.0 Student Workbook and Learning ActivitiesmiantariqpervazNo ratings yet
- Lecture Qualtiy ManagementDocument103 pagesLecture Qualtiy ManagementAiman ChouhdaryNo ratings yet
- PRINCE2® Theme: QualityDocument3 pagesPRINCE2® Theme: QualitySocrates KontosNo ratings yet
- Online Education Portal Project: Uality Anagement LANDocument10 pagesOnline Education Portal Project: Uality Anagement LANHehe HoNo ratings yet
- Updated Quality Management PlanDocument3 pagesUpdated Quality Management PlanLok SewaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Project ScheduleDocument14 pagesModule 4 - Project ScheduleDenmark WilsonNo ratings yet
- 34 BotaDocument6 pages34 BotaprofbruceNo ratings yet
- Project MGMTDocument32 pagesProject MGMTHussien AliyiNo ratings yet
- 16 Establish Quality StandardsDocument10 pages16 Establish Quality StandardsSamuel AdamuNo ratings yet
- Quality Planning Management - Summary NotesDocument13 pagesQuality Planning Management - Summary NotesGeorge NjolomaNo ratings yet
- P M P Chapter 8Document17 pagesP M P Chapter 8Khaled KhanNo ratings yet
- A PQP Mandarory or NotDocument3 pagesA PQP Mandarory or NotkhaledhaddadNo ratings yet
- TbsmqualitymanagementplanDocument22 pagesTbsmqualitymanagementplanapi-338883409No ratings yet
- Project Management3Document12 pagesProject Management3Veronica Cretu-IonascuNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument63 pagesProject Quality ManagementEljay VinsonNo ratings yet
- Quality Management ProcessDocument13 pagesQuality Management ProcessSukumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Plan Guide: Document NameDocument3 pagesQuality Management Plan Guide: Document NameisolongNo ratings yet
- .Quality - ManagamentDocument31 pages.Quality - Managamentp comNo ratings yet
- Project Quality Management ClaireDocument34 pagesProject Quality Management ClaireDerrick KazoobaNo ratings yet
- CDC UP Quality Management Practices GuideDocument5 pagesCDC UP Quality Management Practices GuideRavi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Management 05Document28 pagesSoftware Quality Management 05tesfanesh 65tgNo ratings yet
- Project Work: Prepare A Quality Plan Document (25%)Document90 pagesProject Work: Prepare A Quality Plan Document (25%)eyerusalem tesfayeNo ratings yet
- PQMT SyllabusDocument44 pagesPQMT Syllabusnjeri njorogeNo ratings yet
- WEEK 6 PresentationDocument43 pagesWEEK 6 Presentationyuvrajsinhgohel15No ratings yet
- Cover Page and Declaration: Master of Business Administration (M.B.A.)Document48 pagesCover Page and Declaration: Master of Business Administration (M.B.A.)Hind ImadNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1Document4 pagesAssignment No. 1saddam walandkarNo ratings yet
- Qlty MGMT in ProjectsDocument5 pagesQlty MGMT in Projectssweet16barbiesNo ratings yet
- Quality PlanDocument3 pagesQuality PlanblackcoutureconsultationsNo ratings yet
- PM 333 Lecture 13 Project Quality ManagementDocument16 pagesPM 333 Lecture 13 Project Quality ManagementJesse TungarazaNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance Statement of Work (Version 2.0)Document21 pagesQuality Assurance Statement of Work (Version 2.0)KomalNo ratings yet
- PM - Lecture 7 Project Quality ManagementDocument43 pagesPM - Lecture 7 Project Quality ManagementMariam MansourNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument32 pagesProject Quality ManagementLemark R.0% (1)
- What Is A Quality Management Process?: 1.1 InstructionsDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Quality Management Process?: 1.1 Instructionsksamanta23No ratings yet
- Project Quality PlanDocument15 pagesProject Quality PlankumaraguruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Project Quality ManagementDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Project Quality ManagementHussen MossaNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal 2Document5 pagesReflective Journal 2suhasana0305No ratings yet
- Construction Quality, Safety and Human ValuesDocument56 pagesConstruction Quality, Safety and Human ValuesGireesh Gowda GiriNo ratings yet
- Sample Project ManagementDocument25 pagesSample Project ManagementVishwa VichuNo ratings yet
- Bsbpmg411 Task 1Document11 pagesBsbpmg411 Task 1Tanmay JhulkaNo ratings yet
- SQA ImportantDocument8 pagesSQA ImportantMuhammad UsamaNo ratings yet
- Project Quality ManagementDocument8 pagesProject Quality ManagementJoereane LlarenaNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Process Checklists 3.2. Benchmarking 3.3. Quality (Project) Audit 3.4. The PCDA (Plan, Do, Check, and Act) CycleDocument32 pages3.1. Process Checklists 3.2. Benchmarking 3.3. Quality (Project) Audit 3.4. The PCDA (Plan, Do, Check, and Act) CycleAnonymous Jo79oINo ratings yet
- DPPM Qly Note3Document21 pagesDPPM Qly Note3OJOK APOLLONo ratings yet
- Group Project Project Quality Management 24-06-2021Document59 pagesGroup Project Project Quality Management 24-06-2021Ubaid ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Quality: Prince 2 Approach To QualityDocument3 pagesQuality: Prince 2 Approach To Qualityquree25No ratings yet
- Quality Management PlanDocument9 pagesQuality Management PlanDhetzz Alvin Sevenfoldism100% (1)
- GSLC IspmDocument2 pagesGSLC IspmaniieendyazhrNo ratings yet
- PQPDocument1 pagePQPislam0207No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Project Quality ManagementDocument7 pagesLesson 6 - Project Quality Managementsandaru malindaNo ratings yet
- Project Quality Management Derrick NewDocument35 pagesProject Quality Management Derrick NewDerrick KazoobaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Project Management Knowledge AreasDocument38 pagesChapter Two: Project Management Knowledge AreasRobel HabtamuNo ratings yet
- IT Audit Domain 1 - v3Document81 pagesIT Audit Domain 1 - v3rewNo ratings yet
- Manpower Audit BackgroundDocument6 pagesManpower Audit Backgroundmagayaprincess169No ratings yet
- The Impact of Information Technology On The Audit Process Session 1Document35 pagesThe Impact of Information Technology On The Audit Process Session 1Nathalia TriandiniNo ratings yet
- Cbo Credit Manual Jul 21Document295 pagesCbo Credit Manual Jul 21prashanth100% (1)
- Guidelines For The Implementation of A Quality Management System in Industrial CompaniesDocument8 pagesGuidelines For The Implementation of A Quality Management System in Industrial CompaniesMilagros MontesinosNo ratings yet
- Auditing For Managers - The Ultimate Risk Management ToolDocument369 pagesAuditing For Managers - The Ultimate Risk Management Toolthenneberry61No ratings yet
- The Effect of Competence, Objectivity, Independence On The Effectiveness of Internal Audit With Management Support As Moderating VariableDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Competence, Objectivity, Independence On The Effectiveness of Internal Audit With Management Support As Moderating VariableInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ethical Matters PDFDocument13 pagesEthical Matters PDFCathyNo ratings yet
- Aau ModelDocument34 pagesAau ModelTayech TayuNo ratings yet
- Psa 530: Audit Sampling and Other Selective TestingDocument49 pagesPsa 530: Audit Sampling and Other Selective TestingJeric IsraelNo ratings yet
- MBA I - 428 Business Ethics Unit - Iv: Corporate Governance MeaningDocument6 pagesMBA I - 428 Business Ethics Unit - Iv: Corporate Governance MeaningJebin JamesNo ratings yet
- BW ResourcesDocument8 pagesBW ResourcesHazel Canoy100% (3)
- Office Performance Commitment and Review Form: Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDocument13 pagesOffice Performance Commitment and Review Form: Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDENNIS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Afm Exam Essentials-2023Document3 pagesAfm Exam Essentials-2023sakhiahmadyarNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditing (Online) - Syllabus - ConcourseDocument15 pagesInternal Auditing (Online) - Syllabus - Concoursebislig water districtNo ratings yet
- Computerized AuditingDocument29 pagesComputerized AuditingpalpitopitooNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Mr. Gaurav RanaDocument36 pagesProject Report: Mr. Gaurav RanaBIKASH BHASKARNo ratings yet
- AIS Complete Testbank QuizDocument74 pagesAIS Complete Testbank QuizRomiline Umayam100% (5)
- Dictionar Conta FinanteDocument27 pagesDictionar Conta FinanteEmilia VasileNo ratings yet
- Client AcceptanceDocument26 pagesClient AcceptanceSaiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Boundries of Management ControlDocument14 pagesBoundries of Management ControlRamesh Rasik PaudelNo ratings yet
- Attachment - FSMS Process Interaction (Rev 0) - 210901Document1 pageAttachment - FSMS Process Interaction (Rev 0) - 210901QA HBTNo ratings yet
- Senthil Kumar Sundaresan: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesSenthil Kumar Sundaresan: ObjectiveAnanthan VijayanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Financial Accounting An Integrated Approach 5th Edition by TrotmanDocument21 pagesSolution Manual For Financial Accounting An Integrated Approach 5th Edition by Trotmana540142314No ratings yet
- ZTE SOC Solutions To Usability and Scalability Guidelines For The DesignDocument4 pagesZTE SOC Solutions To Usability and Scalability Guidelines For The Designinformationsecret0% (1)
- Chapter 2Document30 pagesChapter 2Justin ForondaNo ratings yet