Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsCASH
CASH
Uploaded by
Neeluap WillowNotes from video lesson of sir Win
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Audit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument15 pagesAudit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFSiena Farne100% (1)
- Accounting NotesDocument20 pagesAccounting NotesAnonymous PersonNo ratings yet
- FAR Lecture NotesDocument80 pagesFAR Lecture NotesJuan Miguel Suerte Felipe100% (2)
- Cash and Cash Equivalents ReviewerDocument4 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents ReviewerEileithyia Kijima100% (1)
- Financial Accounting - User Guide: Release R15.000Document66 pagesFinancial Accounting - User Guide: Release R15.000Yousra Hafid100% (1)
- Intermediate Accounting 1: Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument17 pagesIntermediate Accounting 1: Cash and Cash EquivalentClar AgramonNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1 Notes Part 1Document13 pagesIntacc 1 Notes Part 1Crizelda BauyonNo ratings yet
- IA 1 - 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument7 pagesIA 1 - 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsVJ MacaspacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsNicka NavarroNo ratings yet
- Cash Equivalents NotesDocument2 pagesCash Equivalents NotesNeeluap WillowNo ratings yet
- FAR 1 REVIEWER (Unfinished)Document3 pagesFAR 1 REVIEWER (Unfinished)Ruth MuldongNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation NotesDocument2 pagesBank Reconciliation NotesNeeluap WillowNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument7 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents PDFFritzey Faye RomeronaNo ratings yet
- Cash NotesDocument2 pagesCash NotesJeric Lagyaban AstrologioNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument1 pageCash and Cash EquivalentsAshianna KimNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument6 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsPamela Mae PlatonNo ratings yet
- CCE and Bank ReconDocument10 pagesCCE and Bank ReconGellie GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsseunjeincraftNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument7 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentAlex VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For CashDocument3 pagesAccounting For CashmalvardylanNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalent: If The Problem Is Silent, Daily, They Are Part of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument30 pagesCash & Cash Equivalent: If The Problem Is Silent, Daily, They Are Part of Cash and Cash EquivalentsKim Audrey JalalainNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting Volume IDocument1 pageIntermediate Accounting Volume IMary Claudette UnabiaNo ratings yet
- Far Cash & Cash Equi, Bank ReconDocument3 pagesFar Cash & Cash Equi, Bank ReconacctgnotesforreviewNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1Document3 pagesIntacc 1Prescilla Dela SernaNo ratings yet
- Midterm - RFBTDocument12 pagesMidterm - RFBTARON QUINONESNo ratings yet
- 01 Intermediate Accounting 1 PrelimDocument7 pages01 Intermediate Accounting 1 PrelimRoyu BreakerNo ratings yet
- Aud 1&2 - CceDocument6 pagesAud 1&2 - Ccecherish melwinNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash EquivalentsDocument8 pagesCash & Cash Equivalentsbona jirahNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMariene PagsibiganNo ratings yet
- Uf1 1Document12 pagesUf1 1Josemi CastellóNo ratings yet
- Ia1 NotesDocument23 pagesIa1 NotesAssej C AustriaNo ratings yet
- CashDocument3 pagesCashKimNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lessons - Far 1Document23 pagesCompiled Lessons - Far 1Gwyn OliverNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Acc NotesDocument7 pagesIntermediate Acc NotesNathasha Mearch BingatNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsRheea de los SantosNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1Document2 pagesIntermediate Accounting 1kathlenejane.garciaNo ratings yet
- Ia1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesIa1 ReviewerVeronica SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Acccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Document7 pagesAcccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Rey HandumonNo ratings yet
- Intacc ReviewerDocument20 pagesIntacc ReviewerAvos NnNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinals ReviewerMaliha KansiNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesAccounting For Cash and Cash EquivalentsMaybelle BernalNo ratings yet
- Statement of Financial Position and Comprehensive IncomeDocument2 pagesStatement of Financial Position and Comprehensive Incomebuenaflorgladys11No ratings yet
- Int. Acc 1 Chap 1Document6 pagesInt. Acc 1 Chap 1Nicole Anne Santiago SibuloNo ratings yet
- John Bo FAR Lecture NotesDocument80 pagesJohn Bo FAR Lecture NotesAlvaro JheyNo ratings yet
- Far.03 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument8 pagesFar.03 Cash and Cash EquivalentsRhea Royce CabuhatNo ratings yet
- EngelsDocument4 pagesEngelsqyaravandepitteNo ratings yet
- Notes (Audit Prob)Document6 pagesNotes (Audit Prob)kodzuken.teyNo ratings yet
- Sta Clara - Summary Part 1Document49 pagesSta Clara - Summary Part 1Carms St ClaireNo ratings yet
- INTACC - Chapter 1Document4 pagesINTACC - Chapter 1MeriiiNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EShaira BugayongNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management (FABM2) Notes ReviewerDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management (FABM2) Notes ReviewerAngelNo ratings yet
- Audit of Cash Chapter 1Document8 pagesAudit of Cash Chapter 1SAN FELIPE Maria Czarina MontereseNo ratings yet
- Intermediate AccountingDocument2 pagesIntermediate AccountingKylie CortezNo ratings yet
- Session 18Document32 pagesSession 18Sayantan 'Ace' DasNo ratings yet
- Module 2A - ACCCOB2 Lecture 2 - Cash and Cash Equivalents - FHV T1AY2021Document6 pagesModule 2A - ACCCOB2 Lecture 2 - Cash and Cash Equivalents - FHV T1AY2021Cale Robert RascoNo ratings yet
- NU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument14 pagesNU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDawn QuimatNo ratings yet
- Accounting For CashDocument2 pagesAccounting For CashAlexis Jeremie100% (1)
- Accounting For CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS PDFDocument2 pagesAccounting For CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS PDFCj BarrettoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Substantive Test of CashDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Substantive Test of CashJesievelle Villafuerte NapaoNo ratings yet
- Assighnemt Economic Factors in Pak 2022Document6 pagesAssighnemt Economic Factors in Pak 2022Muzamil AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Brightwell CashPickup 40674696Document2 pagesBrightwell CashPickup 40674696Edz carl AberiaNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Currency Risk ManagementDocument7 pagesThesis On Currency Risk Managementlisakennedyfargo100% (2)
- Japanese ArigatoDocument43 pagesJapanese ArigatoHungryhen69No ratings yet
- Money: Money Is Any Item or Verifiable Record That Is Generally AcceptedDocument2 pagesMoney: Money Is Any Item or Verifiable Record That Is Generally AcceptedMokshi shahNo ratings yet
- Money, Its Functions and Characteristics: Origin of The Word "MONEY"Document4 pagesMoney, Its Functions and Characteristics: Origin of The Word "MONEY"rosalyn mauricioNo ratings yet
- Capsule 40 Eco XiiDocument23 pagesCapsule 40 Eco XiiPankaj MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tutorial Questions TVMDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Tutorial Questions TVMSeyyara HasanovaNo ratings yet
- THE FREE ProjectDocument14 pagesTHE FREE ProjectMillstone illuminatorNo ratings yet
- MF0015Document8 pagesMF0015Hetal Mandalia0% (1)
- Rupayan City UttaraDocument52 pagesRupayan City Uttaraabu naymNo ratings yet
- Travel To Israel: Conversation Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesTravel To Israel: Conversation Cheat SheetPedro MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Name of Assignment: International Trade How OurDocument9 pagesAssignment: Name of Assignment: International Trade How OurAmeen IslamNo ratings yet
- Cldxej6uq01z7j4qn1ivmbkdh Global Crypto Onramp Report 2023Document21 pagesCldxej6uq01z7j4qn1ivmbkdh Global Crypto Onramp Report 2023nekekidNo ratings yet
- Financial InstrumentsDocument8 pagesFinancial Instrumentscretuiulia1984No ratings yet
- Pro-Forma - So86661Document1 pagePro-Forma - So86661Trisna SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Account Statement 2022Document71 pagesAccount Statement 2022Rajat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Currency Futures and Options Markets: Dr. Chen, Jo-HuiDocument18 pagesCurrency Futures and Options Markets: Dr. Chen, Jo-HuiPushkaraj SaveNo ratings yet
- CMT8Document20 pagesCMT8Nam HaNo ratings yet
- Autosweep SummaryDocument11 pagesAutosweep SummaryGenevieve-LhangLatorenoNo ratings yet
- DPP Class 5Document42 pagesDPP Class 5docphyicssvenkatk737No ratings yet
- Monetary Policy and Central Banking - Finance 7 SyllabusDocument9 pagesMonetary Policy and Central Banking - Finance 7 SyllabusMarjon DimafilisNo ratings yet
- Alpaslan Exchange Rate Pass-Through Effect On Prices and inDocument18 pagesAlpaslan Exchange Rate Pass-Through Effect On Prices and inJuan CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Rab Fob MV Nar 4600 Zhuhai - 2021Document1 pageRab Fob MV Nar 4600 Zhuhai - 2021Tamara Nursyifa ANo ratings yet
- ICER CourseDocument20 pagesICER CourseOussama ChaoukiNo ratings yet
- Tibongelelo TemakhosiDocument3 pagesTibongelelo TemakhosiBlessing TshumaNo ratings yet
- Inverse and Quanto Inverse Options in A Black-Scholes WorldDocument36 pagesInverse and Quanto Inverse Options in A Black-Scholes WorldJulien KuntzNo ratings yet
- New Central Bank ActDocument34 pagesNew Central Bank ActKLNo ratings yet
- Translation QuestionsDocument6 pagesTranslation QuestionsVeenal BansalNo ratings yet
CASH
CASH
Uploaded by
Neeluap Willow0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesNotes from video lesson of sir Win
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNotes from video lesson of sir Win
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesCASH
CASH
Uploaded by
Neeluap WillowNotes from video lesson of sir Win
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
History of Cash - Non-current Asset = cash is restricted for at
least 12 months at the end of the reporting
Barter System
period.
- exchange of products/goods.
Measurement
- problem: the other party can’t be compelled to
accept the product/good offered in exchange. - Face value
- paglalagay ng value
Development of Discovering Cash
Measurement Period
- not imposed, it is natural
How do we measure Initially
Gold
- unang makita (ngayon)
- informal cash
- cash = face value
- gusto ng lahat
- face value = kung magkano yung nakalagay or
- mineral or natural resources
nakikita mo sa mismong document (bill)
- Gold Standard – measure ng wealth ng isang tao
ay nakadepende sa kung gaano karaming ginto Subsequently
ang meron siya
- paglipas ng panahon
- problem: bigat ng ginto (weight to carry when
- measurement changes
transacting)
- Example: depreciation
Gold Smith - cash = face value
- intervention or initiation of the government Estimated Realizable Value Amount
- kung kanino idedeposit or kung sino ang
- incase na may problema yung cash
magtatago ng ginto
- example: na bankcrupt yung bank kung saan ka
- will give proof of deposit and the one that will
nag-deposit, kahit na 100k and dineposit mong
be used in the transaction
amount, hindi pwedeng 100k parin lalo na kung
Gold is the beginning of cash hanggang 50k lang ang pwedeng ibalik
(Recoverable Amount)
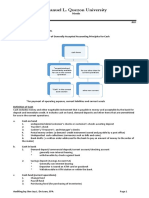
Cash
Foreign Currency
- money
- standard medium of exchange - Convert = Valuation = current exchange rate
- representation of value - Kung magkano yung value nung time na magco-
- nagiging daan or tulay para matuloy yung convert ka, yun ang irerecord mong value.
exchange.
Cash Items
- currency and coins that are circulating and are
in legal tender Cash on Hand
- includes money and other negotiable
instruments that are payable in money and - Undeposited collections = bills and coins
accepted by the bank for deposit and - Customer’s check = ipinambayad ng customer
immediate credit (payable ng bank sa’yo). na hindi pa na-deposit sa bank
- negotiable instrument = tinatanggap ng mga tao - Manager’s check = automatic na may pondo na
- unrestricted = hindi pwedeng pagbawalan kung = approved na ng manager ng bank, kumbaga
saan mo gustong gamitin yung cash confirmed na na may enough siyang pera na
nasa bank para makipagtransact = automatically
Presentation deducted sa kaniyang deposited amount na
nasa bank
- Current Asset
- Cashier’s check = just like managers check iba
lang ang nag-approve = cashier ang nag-aprove
instead na manager
- Traveler’s check = check na dala ng mga sobra sa deposited amount = overdraft
travellers = approved na rin (inabonohan ng bank) – current liability
- Problem in check = hindi ka sure na may - Offsetting = loss in one division can be
sufficient value yung check = may value lamang eliminated by an equal profit in another division
kung magkano yung naka-deposit = NOT ALLOWED IN OVERDRAFT EXCEPT KUNG
- Bank draft = draft na sinulat ni bank = similar sa SAME BANK and IF THE AMOUNT IS
manager’s check = pero mas mabigat and IMMATERIAL (maliit lang yung amount)
guarantee or back-up compared sa manager’s - The overdraft will not be presented as cash, but
check = bank na mismo ang kausap mo na it will be presented as a current liability – bank
nagsasabi sayong may pondo yan = check ni overdraft
bank = tatalbog (magbabounce) lang ang check
*Kapag gumawa ka na ng check, automatic credited na
kapag nagsara na yung bank
sa cash*
- Money order = pwedeng galing sa other
financial institution = magbibigay ng pera kapalit * Kung naiwala ang check or naging stale, pwedeng
ng money order document = GCASH = hindi dala hindi bigyan ng replacement check yung nakawala*
yung physical na pera though electronic yung sa
gcash *Ang check ay isang negotiable instrument, therefore, it
is good as cash*
Cash in Bank
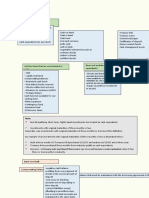
Restriction
- Checking account = gustong gamitin sa
transaction = anytime pwedeng kunin = CHECK - No restriction = cash
- Undelivered checks = ipambabayad mo dapat - Current operation = cash fund (may
siya pero hindi mo nabigay doon sa dapat na pinaglalaanan) = cash parin pero may PURPOSE
makakatanggap = checks that are already siya
prepared but not yet delivered that’s why di - Long term investment = plant expansion fund =
mababawasan yung cash = do reverse entry to long term restriction = Non current asset
correct entry - Sinking fund = nag iipon ng pambayad sa mga
- Post dated checks = the date of the check is matatagal na na utang
higher or later than today (kung kailan mo Cash Fund
ibinigay ang check) = you have to reverse
hangga’t di pa dumarating yung payment dahil - Change fund = panukli
technically cash parin siya. - Tax fund = di pwedeng galawin dahil nakalaan
- Stale Check = check na nasira or napanis na = na as pambayad ng tax
walang ginawa sa check na natanggap niya kaya - Payroll fund = pambayad ng salary
naging stale na yung check = kailangang mapa - Dividend fund =
encash within reasonable amount of time = Compensating Balance
walang definite period para masabi kung kailan
magiging stale ang isang check, it’s a matter of - Restriction
practice = usually 6 months - Papautangin ka ng 1M basta may naka deposit
- Debit: Cash in Bank – Credit: Miscellaneous ka na 200k (200k – compensating balance)
Income = If hindi na papalitan yung nawala or - Formal = long term investment
stale check - Informal = part as cash = pwedeng iwithdraw
- Reverse Entry = kung papalitan mo later on anytime = parang panakot lang at hindi serious
- Savings deposit = ipon - Parang maintaining balance sa bank account =
- Bank overdraft = hindi legal sa Pilipinas = check INFORMAL = dahil pwede mo paring iwithdraw
drawn more than the deposited amount = yung maintaining balance = therefore, cash
pwedeng mangyari kung sakaling may relasyon parin siya
na rin ang bank at yung nag-issue ng check na - SILENT = INFORMAL = TREAT AS CASH
You might also like
- Audit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument15 pagesAudit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFSiena Farne100% (1)
- Accounting NotesDocument20 pagesAccounting NotesAnonymous PersonNo ratings yet
- FAR Lecture NotesDocument80 pagesFAR Lecture NotesJuan Miguel Suerte Felipe100% (2)
- Cash and Cash Equivalents ReviewerDocument4 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents ReviewerEileithyia Kijima100% (1)
- Financial Accounting - User Guide: Release R15.000Document66 pagesFinancial Accounting - User Guide: Release R15.000Yousra Hafid100% (1)
- Intermediate Accounting 1: Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument17 pagesIntermediate Accounting 1: Cash and Cash EquivalentClar AgramonNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1 Notes Part 1Document13 pagesIntacc 1 Notes Part 1Crizelda BauyonNo ratings yet
- IA 1 - 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument7 pagesIA 1 - 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsVJ MacaspacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsNicka NavarroNo ratings yet
- Cash Equivalents NotesDocument2 pagesCash Equivalents NotesNeeluap WillowNo ratings yet
- FAR 1 REVIEWER (Unfinished)Document3 pagesFAR 1 REVIEWER (Unfinished)Ruth MuldongNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation NotesDocument2 pagesBank Reconciliation NotesNeeluap WillowNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument7 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents PDFFritzey Faye RomeronaNo ratings yet
- Cash NotesDocument2 pagesCash NotesJeric Lagyaban AstrologioNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument1 pageCash and Cash EquivalentsAshianna KimNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument6 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsPamela Mae PlatonNo ratings yet
- CCE and Bank ReconDocument10 pagesCCE and Bank ReconGellie GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsseunjeincraftNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument7 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentAlex VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For CashDocument3 pagesAccounting For CashmalvardylanNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalent: If The Problem Is Silent, Daily, They Are Part of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument30 pagesCash & Cash Equivalent: If The Problem Is Silent, Daily, They Are Part of Cash and Cash EquivalentsKim Audrey JalalainNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting Volume IDocument1 pageIntermediate Accounting Volume IMary Claudette UnabiaNo ratings yet
- Far Cash & Cash Equi, Bank ReconDocument3 pagesFar Cash & Cash Equi, Bank ReconacctgnotesforreviewNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1Document3 pagesIntacc 1Prescilla Dela SernaNo ratings yet
- Midterm - RFBTDocument12 pagesMidterm - RFBTARON QUINONESNo ratings yet
- 01 Intermediate Accounting 1 PrelimDocument7 pages01 Intermediate Accounting 1 PrelimRoyu BreakerNo ratings yet
- Aud 1&2 - CceDocument6 pagesAud 1&2 - Ccecherish melwinNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash EquivalentsDocument8 pagesCash & Cash Equivalentsbona jirahNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMariene PagsibiganNo ratings yet
- Uf1 1Document12 pagesUf1 1Josemi CastellóNo ratings yet
- Ia1 NotesDocument23 pagesIa1 NotesAssej C AustriaNo ratings yet
- CashDocument3 pagesCashKimNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lessons - Far 1Document23 pagesCompiled Lessons - Far 1Gwyn OliverNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Acc NotesDocument7 pagesIntermediate Acc NotesNathasha Mearch BingatNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsRheea de los SantosNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1Document2 pagesIntermediate Accounting 1kathlenejane.garciaNo ratings yet
- Ia1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesIa1 ReviewerVeronica SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Acccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Document7 pagesAcccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Rey HandumonNo ratings yet
- Intacc ReviewerDocument20 pagesIntacc ReviewerAvos NnNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinals ReviewerMaliha KansiNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesAccounting For Cash and Cash EquivalentsMaybelle BernalNo ratings yet
- Statement of Financial Position and Comprehensive IncomeDocument2 pagesStatement of Financial Position and Comprehensive Incomebuenaflorgladys11No ratings yet
- Int. Acc 1 Chap 1Document6 pagesInt. Acc 1 Chap 1Nicole Anne Santiago SibuloNo ratings yet
- John Bo FAR Lecture NotesDocument80 pagesJohn Bo FAR Lecture NotesAlvaro JheyNo ratings yet
- Far.03 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument8 pagesFar.03 Cash and Cash EquivalentsRhea Royce CabuhatNo ratings yet
- EngelsDocument4 pagesEngelsqyaravandepitteNo ratings yet
- Notes (Audit Prob)Document6 pagesNotes (Audit Prob)kodzuken.teyNo ratings yet
- Sta Clara - Summary Part 1Document49 pagesSta Clara - Summary Part 1Carms St ClaireNo ratings yet
- INTACC - Chapter 1Document4 pagesINTACC - Chapter 1MeriiiNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCFAS Chapter 4 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsAngelaMariePeñarandaNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EShaira BugayongNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management (FABM2) Notes ReviewerDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management (FABM2) Notes ReviewerAngelNo ratings yet
- Audit of Cash Chapter 1Document8 pagesAudit of Cash Chapter 1SAN FELIPE Maria Czarina MontereseNo ratings yet
- Intermediate AccountingDocument2 pagesIntermediate AccountingKylie CortezNo ratings yet
- Session 18Document32 pagesSession 18Sayantan 'Ace' DasNo ratings yet
- Module 2A - ACCCOB2 Lecture 2 - Cash and Cash Equivalents - FHV T1AY2021Document6 pagesModule 2A - ACCCOB2 Lecture 2 - Cash and Cash Equivalents - FHV T1AY2021Cale Robert RascoNo ratings yet
- NU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument14 pagesNU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDawn QuimatNo ratings yet
- Accounting For CashDocument2 pagesAccounting For CashAlexis Jeremie100% (1)
- Accounting For CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS PDFDocument2 pagesAccounting For CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS PDFCj BarrettoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Substantive Test of CashDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Substantive Test of CashJesievelle Villafuerte NapaoNo ratings yet
- Assighnemt Economic Factors in Pak 2022Document6 pagesAssighnemt Economic Factors in Pak 2022Muzamil AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Brightwell CashPickup 40674696Document2 pagesBrightwell CashPickup 40674696Edz carl AberiaNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Currency Risk ManagementDocument7 pagesThesis On Currency Risk Managementlisakennedyfargo100% (2)
- Japanese ArigatoDocument43 pagesJapanese ArigatoHungryhen69No ratings yet
- Money: Money Is Any Item or Verifiable Record That Is Generally AcceptedDocument2 pagesMoney: Money Is Any Item or Verifiable Record That Is Generally AcceptedMokshi shahNo ratings yet
- Money, Its Functions and Characteristics: Origin of The Word "MONEY"Document4 pagesMoney, Its Functions and Characteristics: Origin of The Word "MONEY"rosalyn mauricioNo ratings yet
- Capsule 40 Eco XiiDocument23 pagesCapsule 40 Eco XiiPankaj MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tutorial Questions TVMDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Tutorial Questions TVMSeyyara HasanovaNo ratings yet
- THE FREE ProjectDocument14 pagesTHE FREE ProjectMillstone illuminatorNo ratings yet
- MF0015Document8 pagesMF0015Hetal Mandalia0% (1)
- Rupayan City UttaraDocument52 pagesRupayan City Uttaraabu naymNo ratings yet
- Travel To Israel: Conversation Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesTravel To Israel: Conversation Cheat SheetPedro MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Name of Assignment: International Trade How OurDocument9 pagesAssignment: Name of Assignment: International Trade How OurAmeen IslamNo ratings yet
- Cldxej6uq01z7j4qn1ivmbkdh Global Crypto Onramp Report 2023Document21 pagesCldxej6uq01z7j4qn1ivmbkdh Global Crypto Onramp Report 2023nekekidNo ratings yet
- Financial InstrumentsDocument8 pagesFinancial Instrumentscretuiulia1984No ratings yet
- Pro-Forma - So86661Document1 pagePro-Forma - So86661Trisna SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Account Statement 2022Document71 pagesAccount Statement 2022Rajat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Currency Futures and Options Markets: Dr. Chen, Jo-HuiDocument18 pagesCurrency Futures and Options Markets: Dr. Chen, Jo-HuiPushkaraj SaveNo ratings yet
- CMT8Document20 pagesCMT8Nam HaNo ratings yet
- Autosweep SummaryDocument11 pagesAutosweep SummaryGenevieve-LhangLatorenoNo ratings yet
- DPP Class 5Document42 pagesDPP Class 5docphyicssvenkatk737No ratings yet
- Monetary Policy and Central Banking - Finance 7 SyllabusDocument9 pagesMonetary Policy and Central Banking - Finance 7 SyllabusMarjon DimafilisNo ratings yet
- Alpaslan Exchange Rate Pass-Through Effect On Prices and inDocument18 pagesAlpaslan Exchange Rate Pass-Through Effect On Prices and inJuan CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Rab Fob MV Nar 4600 Zhuhai - 2021Document1 pageRab Fob MV Nar 4600 Zhuhai - 2021Tamara Nursyifa ANo ratings yet
- ICER CourseDocument20 pagesICER CourseOussama ChaoukiNo ratings yet
- Tibongelelo TemakhosiDocument3 pagesTibongelelo TemakhosiBlessing TshumaNo ratings yet
- Inverse and Quanto Inverse Options in A Black-Scholes WorldDocument36 pagesInverse and Quanto Inverse Options in A Black-Scholes WorldJulien KuntzNo ratings yet
- New Central Bank ActDocument34 pagesNew Central Bank ActKLNo ratings yet
- Translation QuestionsDocument6 pagesTranslation QuestionsVeenal BansalNo ratings yet