Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Boyle's Law Computation
Boyle's Law Computation
Uploaded by
dark iceOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Boyle's Law Computation
Boyle's Law Computation
Uploaded by
dark iceCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: _________________________________________________________ Score: ________________
Grade & Section: _______________________________________________ Date: _________________
BOYLE’S LAW
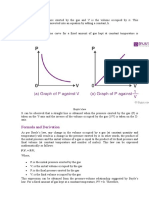
Boyle’s law is a gas law which states that the pressure exerted by a gas (of a given mass, kept
at a constant temperature) is inversely proportional to the volume occupied by it. In other words, the
pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional to each other as long as the temperature and
the quantity of gas are kept constant. Boyle’s law was put forward by the Anglo-Irish chemist Robert
Boyle in the year 1662.
Formula for Boyle’s Law:
P1V1 = P2V2
• P1 is the initial pressure exerted by the gas
• V1 is the initial volume occupied by the gas
• P2 is the final pressure exerted by the gas
• V2 is the final volume occupied by the gas
Example:
The inflated balloon that slipped from the hand of Renn has a volume of 0.50 L at sea level (1.0
atm) and it reached a height of approximately 8 km where the atmospheric pressure is approximately
0.33 atm. Assuming that the temperature is constant, compute for the final volume of the balloon.
In analyzing the problem, it is important that you categorize the initial and final conditions of the
variables:
P1 = 1.0 atm
V1 = 0.50 L
P2 = 0.33 atm
V2 = ?
By applying Boyle’s Law, the final volume will increase. Let’s compute for the numerical value
of the final volume by substituting the given values to this equation.
V1 P1 = V2 P2
V2 = V1 P1
P2
V2 = (0.50 L)(1.0 atm)
0.33 atm
V2 = 1.5 L
ASSESSMENT:
Answer the following problems: (Write the given, formula, your complete solution with cancellation of
units and final answer)
1. Oxygen gas inside a 1.5 L gas tank has a pressure of 0.95 atm. Provided that the temperature remains
constant, how much pressure is needed to reduce its volume by ½?
2. A scuba diver needs a diving tank in order to provide breathing gas while he is underwater. How
much pressure is needed for 6.00 liters of gas at 1.01 atmospheric pressure to be compressed in a 3.00
liter cylinder ?
3. A sample of fluorine gas occupies a volume of 500 mL at 760 torr. Given that the temperature remains
the same, calculate the pressure required to reduce its volume by 1/3.
You might also like
- Water Treatment Plant Capacity CalculationDocument8 pagesWater Treatment Plant Capacity CalculationSantosh Kumar100% (2)
- 4th Periodical Test in Math 5-NewDocument9 pages4th Periodical Test in Math 5-NewMitchz Trinos92% (12)
- Q4 Science10 Week1 LAS2Document1 pageQ4 Science10 Week1 LAS2AvaricioElPecadoNo ratings yet
- Modules On Gas LawsDocument10 pagesModules On Gas LawsJudith Cambri CueNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 Boyles LawDocument40 pagesPresentation1 Boyles LawErnest S. AbiertasNo ratings yet
- NRSL GasLawsDocument48 pagesNRSL GasLawsBrenda Aquino100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet No. 1 Boyles LawDocument1 pageLearning Activity Sheet No. 1 Boyles LawKuya Tiong TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Hand Out m12Document4 pagesHand Out m12mjmabini047No ratings yet
- BOYLE'S LAW Group 1Document13 pagesBOYLE'S LAW Group 1Erich UntalanNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q4 Module-2 Week-2Document5 pagesScience-10 Q4 Module-2 Week-2Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan Boyles LawDocument5 pagesLearning Plan Boyles LawAdan CaacbayNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 1 (Las 8)Document4 pagesSorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 1 (Las 8)Jorgia lianne UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q4 - M1-W1Document6 pagesScience 10 - Q4 - M1-W1Leah Beth CañedoNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws LectureDocument17 pagesGas Laws LectureKim ReyesNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law and Charles' LawDocument27 pagesBoyle's Law and Charles' Lawvezelayjean.jaravataNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Document8 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Differeng Laws of GasesDocument7 pagesChemistry-Differeng Laws of GasesMayette TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Boyle's LawDocument16 pagesLesson 1: Boyle's LawKen ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-Students Chem PDFDocument10 pagesUnit 7-Students Chem PDFHazel AlconNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Gases Properties of Gases: Atmospheric Pressure or Barometric Pressure?Document15 pagesChapter 5 - Gases Properties of Gases: Atmospheric Pressure or Barometric Pressure?Hera EstoseNo ratings yet
- Q4 Behavior of GasesDocument31 pagesQ4 Behavior of Gasesfsean2008No ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument32 pagesGas LawsrenaldNo ratings yet
- 2 Boyle - S LawDocument19 pages2 Boyle - S LawLEIANNE MAE DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Gay-Lussac-6 7 VN Avogadros Law-CombinedDocument48 pagesGay-Lussac-6 7 VN Avogadros Law-Combinednathanielstanaj.mNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument4 pagesGas LawsJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Sci 10 Q4 Week 1Document6 pagesSci 10 Q4 Week 1Jan romar FloresNo ratings yet
- LAS SCI 10 MELC 1 Week 1-2Document11 pagesLAS SCI 10 MELC 1 Week 1-2ALVIN PAJONo ratings yet
- Gases and Gas Laws StudsDocument52 pagesGases and Gas Laws StudssuberexieannNo ratings yet
- Science 10 LAS 4.1.2 The Gas Laws PDFDocument2 pagesScience 10 LAS 4.1.2 The Gas Laws PDFNomio IsraelNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Lesson 1Document36 pagesMODULE 1 Lesson 1Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- States of Matter - GasDocument81 pagesStates of Matter - GasRaymond Godfrey DagwasiNo ratings yet
- GASESDocument26 pagesGASESMaricar SantaceraNo ratings yet
- Boyle's and Charle's LawDocument2 pagesBoyle's and Charle's LawReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- Boyle and Charles LawDocument2 pagesBoyle and Charles LawMher12No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Module 1Document7 pagesUnit 4 Module 1Antonette FrankeNo ratings yet
- Boyles LawDocument47 pagesBoyles Lawcloudyblues69No ratings yet
- Charles LawDocument3 pagesCharles Lawsarausos.zoe08No ratings yet
- Unit 1:: The Behavior and Properties of Gases at The Molecular LevelDocument19 pagesUnit 1:: The Behavior and Properties of Gases at The Molecular LevelRaissa Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Q4 WEEK 1 2 Gas LawDocument56 pagesQ4 WEEK 1 2 Gas LawRon Christian Fernandez LascanoNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument36 pagesGasesMarcus MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Combined Avogadros and Ideal Gas LawsDocument25 pagesCombined Avogadros and Ideal Gas Lawslevi0417No ratings yet
- Boyle's LawDocument25 pagesBoyle's Lawmark gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument2 pagesGas LawspenaroyowensthonNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument102 pagesGasesLya EscoteNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - WEEK 1 - Module 11-Gas LawsDocument16 pagesChemistry - WEEK 1 - Module 11-Gas LawsEZRA THERESE DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Gas Law PT 1Document31 pagesGas Law PT 1renaldNo ratings yet
- Boyles LawDocument13 pagesBoyles Lawkylegian342No ratings yet
- Gas Law PT 1Document31 pagesGas Law PT 1Berlin Wendy ReginaldeNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 GasesDocument6 pagesUnit 4 GasesLhenie DaquizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13, GasesDocument24 pagesChapter 13, GasesTeza Nur FirlyansyahNo ratings yet
- Gas Law PT 1Document31 pagesGas Law PT 1darkrealms98No ratings yet
- Q4-WEEK 1-Boyle's LawDocument34 pagesQ4-WEEK 1-Boyle's LawAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Boyle S LawDocument22 pagesBoyle S LawNanami MumuzunoNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document51 pagesScience 10Jimin ParkNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Mchs Science 10 SY 2017-2018Document15 pagesBoyle's Law: Mchs Science 10 SY 2017-2018AndiNo ratings yet
- Intro To Behavior of GasesDocument44 pagesIntro To Behavior of GasesJerome CameroNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Gases Module 1Document25 pagesBehavior of Gases Module 1Jericho GojocruzNo ratings yet
- Boyles LawDocument4 pagesBoyles LawhuesosNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Document47 pagesTopic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Joshua LaBordeNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Physics IiDocument33 pagesGas Laws: Physics IiEsmeralda Tapiz100% (1)
- Boyles LawDocument18 pagesBoyles LawKARIZA JEAN MALOTANo ratings yet
- Pipe and CisternDocument4 pagesPipe and CisternKailasNo ratings yet
- Sda Ng01006306b Odipl La 0510 00001 c04 Stability AnalysisDocument20 pagesSda Ng01006306b Odipl La 0510 00001 c04 Stability AnalysisDaniel Dambo100% (2)
- (ALBN) FizziologyDocument4 pages(ALBN) FizziologyClaudemir HackerNo ratings yet
- GESMO 2019 Junior Maths 1 - 7Document10 pagesGESMO 2019 Junior Maths 1 - 7Yeni SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Physics For EveryoneDocument307 pagesPhysics For EveryonekaaariinaNo ratings yet
- Rubik 4 X 4 X 4Document17 pagesRubik 4 X 4 X 4Mitch MateychukNo ratings yet
- Qus 207 Principles of EconomicsDocument15 pagesQus 207 Principles of Economicsjudexnams1on1No ratings yet
- IM Unit OverviewDocument1 pageIM Unit OverviewAheedam MohammedNo ratings yet
- Parcc Maths Grade 5 AnswerDocument9 pagesParcc Maths Grade 5 Answerhnd26404No ratings yet
- Angelo Lorenzo S. Tamayo Instructor: Engr. Shiela Marie F. Gatchalian Bsaben - Iii Assignment in Fluid Mechanics (ENSC 107) Properties of FluidsDocument2 pagesAngelo Lorenzo S. Tamayo Instructor: Engr. Shiela Marie F. Gatchalian Bsaben - Iii Assignment in Fluid Mechanics (ENSC 107) Properties of FluidsAngeloLorenzoSalvadorTamayoNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 - Volume of Rectangular PrismsDocument26 pagesLec 9 - Volume of Rectangular PrismsKiumi FabregasNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Setapak IndahDocument21 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Setapak IndahAiman Ahmad NazmiNo ratings yet
- Basic Math For Utility Operators PDFDocument240 pagesBasic Math For Utility Operators PDFGarry PonferradaNo ratings yet
- Screw GaugeDocument4 pagesScrew Gaugenopeyeah88No ratings yet
- Calculating Physical Properties of Slurries - Cheresources PDFDocument3 pagesCalculating Physical Properties of Slurries - Cheresources PDFTamaNo ratings yet
- Maths 4 - TutorialDocument2 pagesMaths 4 - TutorialJakeBondNo ratings yet
- Watertank Sap2000 SampleDocument58 pagesWatertank Sap2000 SampleRoman MiahNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document3 pagesWeek 8api-294626581No ratings yet
- 0580 June 2011 Question Paper 32Document16 pages0580 June 2011 Question Paper 32Sky DriveNo ratings yet
- Product Value-Density: Managing Diversity Through Supply Chain SegmentationDocument17 pagesProduct Value-Density: Managing Diversity Through Supply Chain SegmentationSourabh JainNo ratings yet
- 6th Science and Social in English MediumDocument232 pages6th Science and Social in English MediumGCVishnuKumarNo ratings yet
- California Energy Commission - Fuel Delivery Temperature Study (January 2009)Document157 pagesCalifornia Energy Commission - Fuel Delivery Temperature Study (January 2009)ClaseVirtualNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Field Testing of Reciprocating Compressor PerformanceDocument173 pagesGuideline For Field Testing of Reciprocating Compressor PerformanceSean Clark100% (2)
- Eiga 26-04Document14 pagesEiga 26-04Jose Castro100% (1)
- Chemistry GuidelineDocument59 pagesChemistry GuidelineelishamahubiNo ratings yet
- Tank CalibrationDocument21 pagesTank Calibrationhoxx82No ratings yet
- QS1Document154 pagesQS1Bhagyaraj KoppishettyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Surface Area and VolumeDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 10 Surface Area and VolumesanjaykashiNo ratings yet