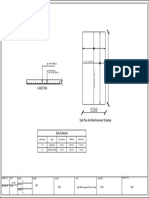
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
mhamzayasin20024Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cultural Landscapes and Food Production in Ghana Guidance NotesDocument107 pagesCultural Landscapes and Food Production in Ghana Guidance NotesAdu Charles Osei100% (2)
- RibeDocument2 pagesRibefabijancic.claudiaNo ratings yet
- IchthologyDocument30 pagesIchthologypujankhanal28No ratings yet
- Seafood IntroductionDocument3 pagesSeafood IntroductionJomar FornisNo ratings yet
- IcthyologyDocument317 pagesIcthyologyRajan KhaniyaNo ratings yet
- Fascinating Fishes Exploration.Document3 pagesFascinating Fishes Exploration.diogopianoNo ratings yet
- IthyologyDocument16 pagesIthyologypujankhanal28No ratings yet
- EEEEEEDocument1 pageEEEEEEIstiak MahmudNo ratings yet
- Universitatea de Stiinte Agronomice Si Medicina Veterinara BucurestiDocument7 pagesUniversitatea de Stiinte Agronomice Si Medicina Veterinara BucurestiMihaiCocorNo ratings yet
- FormFunction BackgroundDocument3 pagesFormFunction BackgroundSamuelNo ratings yet
- Fascinating Facts About FishDocument2 pagesFascinating Facts About FishIrene OriarewoNo ratings yet
- Preparing and Cooking SeafoodDocument3 pagesPreparing and Cooking SeafoodPatricia Kate PachecoNo ratings yet
- Freshwater Aquariums in Your LifeFrom EverandFreshwater Aquariums in Your LifeAmanda PisaniNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Diversity and Adaptations of Fish An OverviewDocument2 pagesExploring The Diversity and Adaptations of Fish An OverviewbantcmNo ratings yet
- Growth in FishesDocument353 pagesGrowth in FishesLizviel BragaNo ratings yet
- Feeding GroupsDocument7 pagesFeeding GroupsSyed AhsanNo ratings yet
- Fish AdaptationsDocument6 pagesFish AdaptationsmoniqueNo ratings yet
- Fisheries Biology and Management: External Fish AnatomyDocument7 pagesFisheries Biology and Management: External Fish AnatomyEezem Rachid AushoNo ratings yet
- Fish and Amphibians: Aiah Clare Filipinas Kurt Al TuburanDocument22 pagesFish and Amphibians: Aiah Clare Filipinas Kurt Al TuburanmagnificatNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Fish: by SpeciesDocument9 pagesDiversity of Fish: by SpeciessamiNo ratings yet
- Learning about Fish and Mammal Species | Children's Fish & Marine LifeFrom EverandLearning about Fish and Mammal Species | Children's Fish & Marine LifeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document26 pagesChapter 6Almira, Maria amorNo ratings yet
- The Internal and External Anatomy of FishDocument5 pagesThe Internal and External Anatomy of FishGienelle BermidoNo ratings yet
- Fish 1Document30 pagesFish 1Adnan mohamedNo ratings yet
- Tec10 - Module 5 (Fishery)Document84 pagesTec10 - Module 5 (Fishery)Noli S. VillacruzNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To:, For Other Uses, SeeDocument5 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To:, For Other Uses, SeefrndgurlNo ratings yet
- Afa Majorship (Fishery)Document81 pagesAfa Majorship (Fishery)Laila UbandoNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Pendidikan Biru Tua Geografi Dan BudayaDocument6 pagesPresentasi Pendidikan Biru Tua Geografi Dan BudayaM.khairul SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Fisheries (Fish) : Types of Fish Consist of Two Types, Namely Consumption Fish and OrnamentalDocument2 pagesFisheries (Fish) : Types of Fish Consist of Two Types, Namely Consumption Fish and OrnamentalSyarina PNo ratings yet
- SamtaDocument15 pagesSamtashubhra_gupta2909No ratings yet
- Fish (Plural: Fish or Fishes) AreDocument4 pagesFish (Plural: Fish or Fishes) AreEric DavisNo ratings yet
- FishDocument2 pagesFishIS SunnyNo ratings yet
- Text 5Document2 pagesText 5enci1018lanczNo ratings yet
- Bony FishesDocument53 pagesBony FishesellenialrafeneNo ratings yet
- Diversity of FishDocument3 pagesDiversity of FishAsif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- SZL102 Topic Five Class Osteichthyes-1Document5 pagesSZL102 Topic Five Class Osteichthyes-1jenkionyangoNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 SheetDocument9 pagesPractical 2 SheetNur IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Fish50 Write UpDocument3 pagesFish50 Write UpSophia ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Cletus Main WorkDocument33 pagesCletus Main Workiernajohn8No ratings yet
- FishDocument1 pageFishhannaslominska.2008No ratings yet
- 12 - Chapter 4 PDFDocument55 pages12 - Chapter 4 PDFVikram DhabaleNo ratings yet
- 3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Document66 pages3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Hailey McLeanNo ratings yet
- External Fish AnatomyDocument4 pagesExternal Fish AnatomyKissha Jane100% (1)
- A Feasibility Study of Establishing A Milk Fish Farmin1Document9 pagesA Feasibility Study of Establishing A Milk Fish Farmin1nathan carreonNo ratings yet
- Fish Culture: External & Internal Parts of Fish - Types of Fish Scales - Parts of GillsDocument55 pagesFish Culture: External & Internal Parts of Fish - Types of Fish Scales - Parts of Gillsbongsky1No ratings yet
- Fish Are: TypologicalDocument1 pageFish Are: TypologicalCynea ArquisolaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sambalpur: Science Project SESSION 2016-17 Topic-Fishes Pujarani Behera Ix - C 16 S.S.Bhoi SirDocument8 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sambalpur: Science Project SESSION 2016-17 Topic-Fishes Pujarani Behera Ix - C 16 S.S.Bhoi SirNiranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Biology ResearchDocument3 pagesBiology ResearchShaddy ShaddyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Skin of FishDocument11 pagesStructure and Function of Skin of FishBijendra PradhanNo ratings yet
- Freshwater Fish - 6.1 Amazonian Round Fish - 01. What To Know Before StartingDocument22 pagesFreshwater Fish - 6.1 Amazonian Round Fish - 01. What To Know Before Startingjoao pedro FonsecaNo ratings yet
- TLE15 Fishery Part 1Document21 pagesTLE15 Fishery Part 1Joanna April100% (5)
- Fish As MeatDocument14 pagesFish As MeatJatinChadhaNo ratings yet
- Upload 5Document30 pagesUpload 5Jurydel RamaNo ratings yet
- Science 2nd Summative TestDocument20 pagesScience 2nd Summative Testmary alyssa dayaoNo ratings yet
- Turtle ConservationDocument50 pagesTurtle ConservationGillian DizonNo ratings yet
- Study Guide:: Date Activity RemindersDocument22 pagesStudy Guide:: Date Activity RemindersMichael Christian TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Research Handout Fish Prod.Document10 pagesResearch Handout Fish Prod.Juwan De CastroNo ratings yet
- TurtlesDocument2 pagesTurtlesnic jNo ratings yet
- World Best PizzaDocument2 pagesWorld Best Pizzamhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled Documentmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Barrage DesignDocument63 pagesBarrage Designmhamzayasin20024100% (1)
- Water Logging and SalinityDocument25 pagesWater Logging and Salinitymhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Valence Bond TheoryDocument2 pagesValence Bond Theorymhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volume II The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volume II The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volu (PDFDrive)Document977 pagesThe Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volume II The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volume II The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volu (PDFDrive)mhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Margalla Ppaers Volume XXVIIssue I2022Document151 pagesMargalla Ppaers Volume XXVIIssue I2022mhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- 19.top Beam SectionDocument1 page19.top Beam Sectionmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Relationship Between Drug Use and Criminal Behavior.Document2 pagesRelationship Between Drug Use and Criminal Behavior.mhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- 14.slab Reinforcement Plan and SectionDocument1 page14.slab Reinforcement Plan and Sectionmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument2 pagesArticlesDragana RankovićNo ratings yet
- Food and Drink Conversation DialogDocument4 pagesFood and Drink Conversation DialogD'iffetDemirci100% (1)
- Reading and Writing: Unit 2 TestDocument3 pagesReading and Writing: Unit 2 TestBeatriz Palomar Burgos100% (1)
- ALS India Food CapabilitiesDocument8 pagesALS India Food CapabilitiesP SENTHIL MURUGANNo ratings yet
- Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition SeminarDocument20 pagesEnteral and Parenteral Nutrition SeminarAmin AksherNo ratings yet
- Menhaden Fish Oil Typical AnalysisDocument1 pageMenhaden Fish Oil Typical Analysismelimaulani-1No ratings yet
- Materi 39 Adverbs of FrequencyDocument31 pagesMateri 39 Adverbs of FrequencyChandra ErickNo ratings yet
- Viticulture in Roman DaciaDocument14 pagesViticulture in Roman Daciagheorghe2No ratings yet
- Spelling List Year 4 2020Document3 pagesSpelling List Year 4 2020Mardhiyatun Nisa0% (1)
- Starter UnitTest 3Document2 pagesStarter UnitTest 3id.70439174No ratings yet
- Meatcuts 1Document23 pagesMeatcuts 1annaliza barondaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesBahasa InggrisRizkirahman rahmanNo ratings yet
- Lago de Oro Proposal 11252022Document1 pageLago de Oro Proposal 11252022Kent Fred LatorreNo ratings yet
- Food Hygiene and SafetyDocument4 pagesFood Hygiene and SafetyMaria ElizabethNo ratings yet
- TestDocument20 pagesTestNguyen Le Minh PhuongNo ratings yet
- Growing Yeast - Sugar FermentationDocument2 pagesGrowing Yeast - Sugar FermentationHiba Ammar100% (1)
- Revision For The Second TermDocument5 pagesRevision For The Second TermchoeNo ratings yet
- Food Waste - Clean Up AustraliaDocument4 pagesFood Waste - Clean Up AustraliaAngus DelaneyNo ratings yet
- By: Elvis Dimwin Cruz RiquelmeDocument2 pagesBy: Elvis Dimwin Cruz RiquelmeELVIS DIMWINNo ratings yet
- MSTK 12e - Example Key Informant Interview - FSLDocument7 pagesMSTK 12e - Example Key Informant Interview - FSLNaveed UllahNo ratings yet
- Pioneers BS 7 COVID Donner PartyDocument2 pagesPioneers BS 7 COVID Donner PartyRuth Eller100% (1)
- Thums Up: Cola Thumbs Up The Coca-Cola Company PepsiDocument1 pageThums Up: Cola Thumbs Up The Coca-Cola Company PepsiAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Ang Mahiwagang PapelDocument26 pagesAng Mahiwagang PapelNicole DijamcoNo ratings yet
- Ilmu Yang Bermanfaat - Rangkuman Materi Bahasa Inggris Kelas 9 Kurikulum 2013Document12 pagesIlmu Yang Bermanfaat - Rangkuman Materi Bahasa Inggris Kelas 9 Kurikulum 2013Rani Indah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Food ServiceDocument78 pagesFood ServiceAnbarasiNo ratings yet
- The Miracle of Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)Document6 pagesThe Miracle of Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)claudiavantrigtNo ratings yet
- Food (Fish) Processing: Washing and Sterilizing of Packaging MaterialsDocument20 pagesFood (Fish) Processing: Washing and Sterilizing of Packaging MaterialsMaria Rose Tariga AquinoNo ratings yet
- De 8Document5 pagesDe 8Nhã Trần ĐứcNo ratings yet
- FixativesDocument6 pagesFixativesmazen jamalNo ratings yet
Untitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
mhamzayasin20024Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled Document
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
mhamzayasin20024Copyright:
Available Formats
Fish are aquatic vertebrates characterized by their streamlined body shape, gills for breathing
underwater, and fins for swimming. They belong to the class Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) or
the class Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish), depending on their skeletal structure. Fish inhabit
various aquatic environments, including freshwater, saltwater, and brackish water.
Here are some key features and characteristics of fish:
1. **Body Structure**: Fish have a streamlined body with a head, trunk, and tail. Their body is
usually covered in scales, which provide protection and reduce friction in water. They also have
fins, which help them to maneuver and propel themselves through the water.
2. **Respiration**: Fish breathe through gills, which are respiratory organs located on the sides
of their head. Gills extract oxygen from water and release carbon dioxide. Some species of fish
can also breathe air through a specialized organ called a labyrinth organ, which is found in
some freshwater fish like bettas and gouramis.
3. **Reproduction**: Fish reproduce in various ways, including external fertilization, where eggs
and sperm are released into the water and fertilization occurs externally, and internal
fertilization, where eggs are fertilized inside the female's body before being laid. Some species
exhibit parental care, where one or both parents protect and care for the eggs and/or young fish.
4. **Diversity**: Fish encompass a vast array of species, ranging from tiny gobies to massive
whale sharks. They come in many shapes, sizes, and colors, adapted to their specific habitats
and lifestyles. Some common types of fish include salmon, trout, tuna, cod, catfish, carp, and
angelfish.
5. **Nutrition**: Fish are a valuable food source for humans and other animals. They provide
high-quality protein, essential omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. Many cultures
around the world rely heavily on fish as a staple food in their diets.
6. **Economic and Ecological Importance**: Fish play crucial roles in aquatic ecosystems as
both predators and prey. They contribute to nutrient cycling and help maintain the balance of
aquatic food webs. Additionally, fish are economically significant, supporting industries such as
commercial fishing, aquaculture, and recreational fishing.
Fish are an integral part of the global biodiversity, with countless species inhabiting diverse
aquatic environments worldwide. They play vital roles in ecosystems and provide valuable
resources for human consumption and enjoyment.
You might also like
- Cultural Landscapes and Food Production in Ghana Guidance NotesDocument107 pagesCultural Landscapes and Food Production in Ghana Guidance NotesAdu Charles Osei100% (2)
- RibeDocument2 pagesRibefabijancic.claudiaNo ratings yet
- IchthologyDocument30 pagesIchthologypujankhanal28No ratings yet
- Seafood IntroductionDocument3 pagesSeafood IntroductionJomar FornisNo ratings yet
- IcthyologyDocument317 pagesIcthyologyRajan KhaniyaNo ratings yet
- Fascinating Fishes Exploration.Document3 pagesFascinating Fishes Exploration.diogopianoNo ratings yet
- IthyologyDocument16 pagesIthyologypujankhanal28No ratings yet
- EEEEEEDocument1 pageEEEEEEIstiak MahmudNo ratings yet
- Universitatea de Stiinte Agronomice Si Medicina Veterinara BucurestiDocument7 pagesUniversitatea de Stiinte Agronomice Si Medicina Veterinara BucurestiMihaiCocorNo ratings yet
- FormFunction BackgroundDocument3 pagesFormFunction BackgroundSamuelNo ratings yet
- Fascinating Facts About FishDocument2 pagesFascinating Facts About FishIrene OriarewoNo ratings yet
- Preparing and Cooking SeafoodDocument3 pagesPreparing and Cooking SeafoodPatricia Kate PachecoNo ratings yet
- Freshwater Aquariums in Your LifeFrom EverandFreshwater Aquariums in Your LifeAmanda PisaniNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Diversity and Adaptations of Fish An OverviewDocument2 pagesExploring The Diversity and Adaptations of Fish An OverviewbantcmNo ratings yet
- Growth in FishesDocument353 pagesGrowth in FishesLizviel BragaNo ratings yet
- Feeding GroupsDocument7 pagesFeeding GroupsSyed AhsanNo ratings yet
- Fish AdaptationsDocument6 pagesFish AdaptationsmoniqueNo ratings yet
- Fisheries Biology and Management: External Fish AnatomyDocument7 pagesFisheries Biology and Management: External Fish AnatomyEezem Rachid AushoNo ratings yet
- Fish and Amphibians: Aiah Clare Filipinas Kurt Al TuburanDocument22 pagesFish and Amphibians: Aiah Clare Filipinas Kurt Al TuburanmagnificatNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Fish: by SpeciesDocument9 pagesDiversity of Fish: by SpeciessamiNo ratings yet
- Learning about Fish and Mammal Species | Children's Fish & Marine LifeFrom EverandLearning about Fish and Mammal Species | Children's Fish & Marine LifeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document26 pagesChapter 6Almira, Maria amorNo ratings yet
- The Internal and External Anatomy of FishDocument5 pagesThe Internal and External Anatomy of FishGienelle BermidoNo ratings yet
- Fish 1Document30 pagesFish 1Adnan mohamedNo ratings yet
- Tec10 - Module 5 (Fishery)Document84 pagesTec10 - Module 5 (Fishery)Noli S. VillacruzNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To:, For Other Uses, SeeDocument5 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump To:, For Other Uses, SeefrndgurlNo ratings yet
- Afa Majorship (Fishery)Document81 pagesAfa Majorship (Fishery)Laila UbandoNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Pendidikan Biru Tua Geografi Dan BudayaDocument6 pagesPresentasi Pendidikan Biru Tua Geografi Dan BudayaM.khairul SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Fisheries (Fish) : Types of Fish Consist of Two Types, Namely Consumption Fish and OrnamentalDocument2 pagesFisheries (Fish) : Types of Fish Consist of Two Types, Namely Consumption Fish and OrnamentalSyarina PNo ratings yet
- SamtaDocument15 pagesSamtashubhra_gupta2909No ratings yet
- Fish (Plural: Fish or Fishes) AreDocument4 pagesFish (Plural: Fish or Fishes) AreEric DavisNo ratings yet
- FishDocument2 pagesFishIS SunnyNo ratings yet
- Text 5Document2 pagesText 5enci1018lanczNo ratings yet
- Bony FishesDocument53 pagesBony FishesellenialrafeneNo ratings yet
- Diversity of FishDocument3 pagesDiversity of FishAsif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- SZL102 Topic Five Class Osteichthyes-1Document5 pagesSZL102 Topic Five Class Osteichthyes-1jenkionyangoNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 SheetDocument9 pagesPractical 2 SheetNur IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Fish50 Write UpDocument3 pagesFish50 Write UpSophia ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Cletus Main WorkDocument33 pagesCletus Main Workiernajohn8No ratings yet
- FishDocument1 pageFishhannaslominska.2008No ratings yet
- 12 - Chapter 4 PDFDocument55 pages12 - Chapter 4 PDFVikram DhabaleNo ratings yet
- 3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Document66 pages3a - Module 3 Biodiversity Animalia Part 3b 2020Hailey McLeanNo ratings yet
- External Fish AnatomyDocument4 pagesExternal Fish AnatomyKissha Jane100% (1)
- A Feasibility Study of Establishing A Milk Fish Farmin1Document9 pagesA Feasibility Study of Establishing A Milk Fish Farmin1nathan carreonNo ratings yet
- Fish Culture: External & Internal Parts of Fish - Types of Fish Scales - Parts of GillsDocument55 pagesFish Culture: External & Internal Parts of Fish - Types of Fish Scales - Parts of Gillsbongsky1No ratings yet
- Fish Are: TypologicalDocument1 pageFish Are: TypologicalCynea ArquisolaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sambalpur: Science Project SESSION 2016-17 Topic-Fishes Pujarani Behera Ix - C 16 S.S.Bhoi SirDocument8 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sambalpur: Science Project SESSION 2016-17 Topic-Fishes Pujarani Behera Ix - C 16 S.S.Bhoi SirNiranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Biology ResearchDocument3 pagesBiology ResearchShaddy ShaddyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Skin of FishDocument11 pagesStructure and Function of Skin of FishBijendra PradhanNo ratings yet
- Freshwater Fish - 6.1 Amazonian Round Fish - 01. What To Know Before StartingDocument22 pagesFreshwater Fish - 6.1 Amazonian Round Fish - 01. What To Know Before Startingjoao pedro FonsecaNo ratings yet
- TLE15 Fishery Part 1Document21 pagesTLE15 Fishery Part 1Joanna April100% (5)
- Fish As MeatDocument14 pagesFish As MeatJatinChadhaNo ratings yet
- Upload 5Document30 pagesUpload 5Jurydel RamaNo ratings yet
- Science 2nd Summative TestDocument20 pagesScience 2nd Summative Testmary alyssa dayaoNo ratings yet
- Turtle ConservationDocument50 pagesTurtle ConservationGillian DizonNo ratings yet
- Study Guide:: Date Activity RemindersDocument22 pagesStudy Guide:: Date Activity RemindersMichael Christian TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Research Handout Fish Prod.Document10 pagesResearch Handout Fish Prod.Juwan De CastroNo ratings yet
- TurtlesDocument2 pagesTurtlesnic jNo ratings yet
- World Best PizzaDocument2 pagesWorld Best Pizzamhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled Documentmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Barrage DesignDocument63 pagesBarrage Designmhamzayasin20024100% (1)
- Water Logging and SalinityDocument25 pagesWater Logging and Salinitymhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Valence Bond TheoryDocument2 pagesValence Bond Theorymhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volume II The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volume II The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volu (PDFDrive)Document977 pagesThe Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volume II The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volume II The Decline and Fall of The Roman Empire, Volu (PDFDrive)mhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Margalla Ppaers Volume XXVIIssue I2022Document151 pagesMargalla Ppaers Volume XXVIIssue I2022mhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- 19.top Beam SectionDocument1 page19.top Beam Sectionmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- Relationship Between Drug Use and Criminal Behavior.Document2 pagesRelationship Between Drug Use and Criminal Behavior.mhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- 14.slab Reinforcement Plan and SectionDocument1 page14.slab Reinforcement Plan and Sectionmhamzayasin20024No ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument2 pagesArticlesDragana RankovićNo ratings yet
- Food and Drink Conversation DialogDocument4 pagesFood and Drink Conversation DialogD'iffetDemirci100% (1)
- Reading and Writing: Unit 2 TestDocument3 pagesReading and Writing: Unit 2 TestBeatriz Palomar Burgos100% (1)
- ALS India Food CapabilitiesDocument8 pagesALS India Food CapabilitiesP SENTHIL MURUGANNo ratings yet
- Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition SeminarDocument20 pagesEnteral and Parenteral Nutrition SeminarAmin AksherNo ratings yet
- Menhaden Fish Oil Typical AnalysisDocument1 pageMenhaden Fish Oil Typical Analysismelimaulani-1No ratings yet
- Materi 39 Adverbs of FrequencyDocument31 pagesMateri 39 Adverbs of FrequencyChandra ErickNo ratings yet
- Viticulture in Roman DaciaDocument14 pagesViticulture in Roman Daciagheorghe2No ratings yet
- Spelling List Year 4 2020Document3 pagesSpelling List Year 4 2020Mardhiyatun Nisa0% (1)
- Starter UnitTest 3Document2 pagesStarter UnitTest 3id.70439174No ratings yet
- Meatcuts 1Document23 pagesMeatcuts 1annaliza barondaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesBahasa InggrisRizkirahman rahmanNo ratings yet
- Lago de Oro Proposal 11252022Document1 pageLago de Oro Proposal 11252022Kent Fred LatorreNo ratings yet
- Food Hygiene and SafetyDocument4 pagesFood Hygiene and SafetyMaria ElizabethNo ratings yet
- TestDocument20 pagesTestNguyen Le Minh PhuongNo ratings yet
- Growing Yeast - Sugar FermentationDocument2 pagesGrowing Yeast - Sugar FermentationHiba Ammar100% (1)
- Revision For The Second TermDocument5 pagesRevision For The Second TermchoeNo ratings yet
- Food Waste - Clean Up AustraliaDocument4 pagesFood Waste - Clean Up AustraliaAngus DelaneyNo ratings yet
- By: Elvis Dimwin Cruz RiquelmeDocument2 pagesBy: Elvis Dimwin Cruz RiquelmeELVIS DIMWINNo ratings yet
- MSTK 12e - Example Key Informant Interview - FSLDocument7 pagesMSTK 12e - Example Key Informant Interview - FSLNaveed UllahNo ratings yet
- Pioneers BS 7 COVID Donner PartyDocument2 pagesPioneers BS 7 COVID Donner PartyRuth Eller100% (1)
- Thums Up: Cola Thumbs Up The Coca-Cola Company PepsiDocument1 pageThums Up: Cola Thumbs Up The Coca-Cola Company PepsiAsad AliNo ratings yet
- Ang Mahiwagang PapelDocument26 pagesAng Mahiwagang PapelNicole DijamcoNo ratings yet
- Ilmu Yang Bermanfaat - Rangkuman Materi Bahasa Inggris Kelas 9 Kurikulum 2013Document12 pagesIlmu Yang Bermanfaat - Rangkuman Materi Bahasa Inggris Kelas 9 Kurikulum 2013Rani Indah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Food ServiceDocument78 pagesFood ServiceAnbarasiNo ratings yet
- The Miracle of Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)Document6 pagesThe Miracle of Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)claudiavantrigtNo ratings yet
- Food (Fish) Processing: Washing and Sterilizing of Packaging MaterialsDocument20 pagesFood (Fish) Processing: Washing and Sterilizing of Packaging MaterialsMaria Rose Tariga AquinoNo ratings yet
- De 8Document5 pagesDe 8Nhã Trần ĐứcNo ratings yet
- FixativesDocument6 pagesFixativesmazen jamalNo ratings yet