Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atom Element Compound
Atom Element Compound
Uploaded by
agentdog175Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atom Element Compound
Atom Element Compound
Uploaded by
agentdog175Copyright:
Available Formats
Elements
Element
Elements are the building blocks of all substances.
They cannot be broken down into simpler substances
by chemical means
+ + +
Na Na Na
+
Na
+
Na Na
+ An Element contains only one type of atom
+ + +
Na Na Na
Each atom has negatively charged electrons orbiting a
Atom positively charged nucleus
Electron
(negative)
Nucleus
(positive)
Shell
Proton
Protons are positive, neutrons
are neutral (no charge). This is
Neutron why the nucleus has an overall
positive charge
The Periodic Table - Basics
Group There are eight groups
across Period
down
Describing Position
Sodium is in Group 1, Period 3
Helium is in Group 0, Period 1
Beryllium is in Group 2, Period 2
2 GCSE Science: Chemistry 1 www.bangor.ac.uk
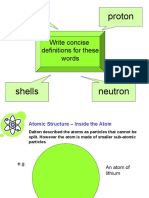
Atomic Structure
Atoms contain a nucleus and electrons
The small central nucleus is made from protons and neutrons.
Around these are shells of electrons.
Here is a diagram showing an atom of Lithium
electron
nucleus
Electron
shell
Nucleus
proton Shell
Proton
neutron
Neutron
This diagram shows that a piece of Potassium is made up of millions of the
same atom.
A piece of
potassium Formed from
metal atoms
Potassium atom
A nucleus of shell of
protons and electrons
neutrons
Atoms of different elements are different.
The number of protons is always different with different elements.
Element Lithium Potassium
Protons 3 19
Neutrons 4 20
Electrons 3 19
Neutron number for some elements are the same.
Electron number is the same as proton number in a neutral atom.
2 GCSE Science: Chemistry 2 www.bangor.ac.uk
Atomic Structure
Atoms have no charge.
The number of protons (in the nucleus) is always the same as the number of
electrons (in shells)
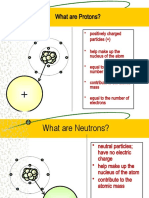
Protons are positively charged. (+)
Electrons are negatively charged (-)
Neutrons do not have a charge (0)
Every electron has a charge of -1
Every proton has a charge of +1
Neutrons have no charge
Therefore an atom of lithium has no charge :- +3p + -3e = 0 no charge
Ion has uneven number of protons and electrons
This happens when an electron is lost
Or when an electron is gained
The proton number does not change.
Mass and Charge of atoms
Here are the relative mass of each particle and their electric charge.
mass charge
proton 1 +1
electron 0
1/1836 -1
neutron 1 0
Protons and neutrons have similar mass.
Electrons have a very small mass.
www.bangor.ac.uk GCSE Science: Chemistry 2 3
Atomic Structure
Atomic Number 7
3 Li
Number on the bottom which means the number of protons or electrons
The number increases across the periodic table
Mass Number 7
3 Li
Number on the top which means the number of protons and neutrons in
the nucleus.
Neutron Number
The number of neutrons in an atom is worked out by subtracting the
number of protons (Atomic number) from the Mass number.
Neutrons = mass number – atomic
number
7-3 = 4 neutrons
Mass number
Protons + Neutrons
Atomic number
Protons or Electrons
Isotopes The same element (as it has the same number of protons) but with different
number of neutrons (making the mass number different). Hydrogen
1H 2H 3H
1 1 1
Proton =
Electron =
Neutron =
Proton number = 1 Proton number = 1 Proton number = 1
Neutron number = 0 Neutron number = 1 Neutron number = 2
4 GCSE Science: Chemistry 2 www.bangor.ac.uk
Compounds Substance that contains two or more elements joined together chemically
Number of elements = 2
Formula Hydrogen
H2O
H2O Elements
Atoms
Oxygen
H H
2 Hydrogen
O
1 Oxygen
Number of atoms = 3
Compound Formula No. of No. of atoms
elements
Sodium Chloride NaCl 2 2 (1 Na, 1 Cl)
Sodium Hydroxide NaOH 3 3 (1 Na, 1 O, 1 H)
Sodium Oxide Na2O 2 3 (2 Na, 1 O)
Sodium Sulfate Na2SO4 3 7 (2 Na, 1 S, 4 O)
Calcium Carbonate CaCO3 3 5 (1 Ca, 1 C, 3 O)
Chemical Reactions Atoms are rearranged but none are created or destroyed
e.g.
Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
Same number of atoms in reactants and products, atoms are differently
arranged.
www.bangor.ac.uk GCSE Science: Chemistry 1 5
You might also like
- Unit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthDocument218 pagesUnit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthBlop100% (1)
- Inorganic Lab ReportDocument11 pagesInorganic Lab Reportmiabil100% (10)
- Price List For FTTH-Jan 2019Document1 pagePrice List For FTTH-Jan 2019ScalperNo ratings yet
- Lecture Powerpoint: Physics: Principles With Applications, 6 EditionDocument46 pagesLecture Powerpoint: Physics: Principles With Applications, 6 EditionJames JimenezNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Refraction Through LensDocument9 pagesPhysics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Refraction Through LensNamdeo JadhavNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Chemistry: (Made Using Pages Taken From Old Bangor Revision Guides)Document32 pagesYear 10 Chemistry: (Made Using Pages Taken From Old Bangor Revision Guides)jaeNo ratings yet
- GCSE Science ChemistryDocument48 pagesGCSE Science ChemistryRobsonNo ratings yet
- Subatomic ParticleDocument48 pagesSubatomic Particlexiandiheraldo020No ratings yet
- 3.1 Physical Chemistry Y12 LolDocument29 pages3.1 Physical Chemistry Y12 LolcallumNo ratings yet
- Good AfternoonDocument69 pagesGood AfternoonHazen HazelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Structure of AtomsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Structure of AtomsAdil Yaqub - 74665/TCHR/CNTBNo ratings yet
- Structure of An Atom (Form 4 Chemistry)Document7 pagesStructure of An Atom (Form 4 Chemistry)Adam NaqibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Lecture 1 F22Document16 pagesChapter 2 - Lecture 1 F22Ali AtwiNo ratings yet
- Atoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1Document38 pagesAtoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1joseph dave pregonerNo ratings yet
- Basic Nuclear Physics: Day 1-Lecture 1Document35 pagesBasic Nuclear Physics: Day 1-Lecture 1jody9090No ratings yet
- Science 8 Module 1 3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesScience 8 Module 1 3rd QuarterSittie Ainah B. Macaumbao100% (1)
- A. Atoms and Atomic StructureDocument40 pagesA. Atoms and Atomic StructurewasimsabriNo ratings yet
- O The Smallest Unit Of: An ElementDocument61 pagesO The Smallest Unit Of: An ElementBrian Laurence BarroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document48 pagesChapter 2lelouchali1234No ratings yet
- Atoms Ions & Isotopes Study Guide AnswersDocument2 pagesAtoms Ions & Isotopes Study Guide AnswersNevaeh DouglasNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Inside The AtomDocument16 pages2.1 Inside The AtomVienna LaoNo ratings yet
- Atoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number 1Document48 pagesAtoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number 1Marielle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 2.Document21 pagesStoichiometry 2.Dalitso SimonNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument225 pagesAtomic StructuresitajanNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument20 pagesAtoms, Elements and CompoundsMenaga Ilangkovan100% (1)
- Topic 2.2 Atomic StructureDocument1 pageTopic 2.2 Atomic StructureRainaf AkifNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 PDFDocument20 pagesTopic 2 PDFNANTHINI DEWI F2005No ratings yet
- Atoms, Ions, IsotopesDocument9 pagesAtoms, Ions, IsotopesHaizel MahendruNo ratings yet
- 1.8 IsotopesDocument6 pages1.8 IsotopesAmelia BellardNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC STRUCTUReeDocument20 pagesATOMIC STRUCTUReeCahayaniFanihuNo ratings yet
- File 2657Document6 pagesFile 2657Alexandra LupuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Atomic Structure and History of Atom)Document15 pagesChapter 3 (Atomic Structure and History of Atom)Tunku Hilman Al-nordinNo ratings yet
- My Revision Notes AQA GCSE (9 1) ChemistryDocument9 pagesMy Revision Notes AQA GCSE (9 1) ChemistrySaad Javeed AuliaNo ratings yet
- Atom, Molecule and Stoichiometry 2023 OnlineDocument10 pagesAtom, Molecule and Stoichiometry 2023 OnlineGan Ee HengNo ratings yet
- Class 9Th: Bir Sikhan Wala FaridkotDocument22 pagesClass 9Th: Bir Sikhan Wala Faridkotapi-19979730No ratings yet
- Science-9 Q2 M3 Wk3Document13 pagesScience-9 Q2 M3 Wk3RILEY JASH GARCIANo ratings yet
- Basic Electrostatics (2019)Document21 pagesBasic Electrostatics (2019)Andile MinenhleNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Notes KP LHDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure Notes KP LHanas.asif2008No ratings yet
- Structure of Atom - Bir Sikhan Wala - FaridkotDocument22 pagesStructure of Atom - Bir Sikhan Wala - Faridkotapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Chapt2-Atomic StructureDocument33 pagesChapt2-Atomic StructureParina JainNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument20 pagesElectricityJürgen GeermanNo ratings yet
- Atoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1Document40 pagesAtoms Elements Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number-1Khalid HdadNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 ReviewDocument14 pagesGrade 11 ReviewAiza Casinillo CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Atomic and PeriodicDocument6 pagesAtomic and PeriodicmeshoeldakroryNo ratings yet
- Elements and AtomsDocument28 pagesElements and AtomsJulien Kristi HernandezNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Md. Abu Nayeem Zakaria Senior Chemistry Teacher Class 9 International Turkish Hope SchoolDocument18 pagesAtomic Structure: Md. Abu Nayeem Zakaria Senior Chemistry Teacher Class 9 International Turkish Hope SchoolAkhlak HossainNo ratings yet
- 929-Mass Numbers Inc Isotopes PresentationDocument18 pages929-Mass Numbers Inc Isotopes PresentationB.Ed. Wing SundargarhNo ratings yet
- AtomosDocument12 pagesAtomosjacqueline suarezNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure StartDocument120 pagesAtomic Structure StartCedrick AltaresNo ratings yet
- Presetation On Atomic StructureDocument11 pagesPresetation On Atomic StructurebashirNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure1stDocument34 pagesAtomic Structure1stDickdick MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesChapter 5 - Atomic StructureMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Atomic StructureDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Atomic StructureRavi SamikNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure & The Periodic TableDocument25 pagesAtomic Structure & The Periodic Tablestan AB6IXNo ratings yet
- What Are Protons?Document48 pagesWhat Are Protons?Dr-naser MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Atom Structureescare Gen Chem 1Document14 pagesAtom Structureescare Gen Chem 1ofeliasebio21No ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics Nuclear Model of Atom: Rutherford Experiment Scattering Experiment Geiger and Marsdens's ExperimentDocument19 pagesNuclear Physics Nuclear Model of Atom: Rutherford Experiment Scattering Experiment Geiger and Marsdens's ExperimentHamza OmranNo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 Atomic Number and Mass Number - v2Document13 pages1 - 1 Atomic Number and Mass Number - v25796fpdfmrNo ratings yet
- Topic:: STPM Term 1 ChemistryDocument47 pagesTopic:: STPM Term 1 ChemistryMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- 2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Document12 pages2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Keshia KatarinaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument30 pagesNuclear PhysicsAreeshaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - 1Document5 pagesAtomic Structure - 1Rosery BlevinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 11 Unit 07 Atoms and The Periodic Table NotesDocument72 pagesChemistry 11 Unit 07 Atoms and The Periodic Table NotesMarina XuNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Factorisation Simultanuous EquationsDocument14 pagesIGCSE Factorisation Simultanuous Equationsagentdog175No ratings yet
- IGCSE Standard Form Ratio ProportionDocument25 pagesIGCSE Standard Form Ratio Proportionagentdog175No ratings yet
- IGCSE Sine Cosine RulesDocument15 pagesIGCSE Sine Cosine Rulesagentdog175No ratings yet
- Gases in The AtmosphereDocument4 pagesGases in The Atmosphereagentdog175No ratings yet
- Separation Techniques Revision CardDocument1 pageSeparation Techniques Revision Cardagentdog175No ratings yet
- Organic DADocument8 pagesOrganic DAagentdog175No ratings yet
- Seismic Reflection Data Interpretation IDocument3 pagesSeismic Reflection Data Interpretation IMonay Indica Caesalpinea PulcerimaNo ratings yet
- Kuantum Gabung Pakalex PDFDocument215 pagesKuantum Gabung Pakalex PDFpaulinaNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics ExercisesDocument16 pagesWave Optics ExercisesRitesh BNo ratings yet
- LaO Habeeb MPhil DefenseDocument21 pagesLaO Habeeb MPhil DefenseHabeeb IjazNo ratings yet
- Observing Microorganisms Through A Micrioscope: Units of MeasurementDocument8 pagesObserving Microorganisms Through A Micrioscope: Units of MeasurementApryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- (Nano-Optics and Nanophotonics) Peter Michler (Eds.) - Quantum Dots For Quantum Information Technologies-Springer International Publishing (2017)Document457 pages(Nano-Optics and Nanophotonics) Peter Michler (Eds.) - Quantum Dots For Quantum Information Technologies-Springer International Publishing (2017)puceiroale100% (2)
- Bruice Organic Chemistry 6eDocument26 pagesBruice Organic Chemistry 6eKim Châu TrầnNo ratings yet
- Anna Series For Luxeon Rebel/Es Leds T: Ledil F'Form OpticsDocument7 pagesAnna Series For Luxeon Rebel/Es Leds T: Ledil F'Form OpticsAle NqnNo ratings yet
- Zenith 12 XPDocument14 pagesZenith 12 XPGIlmanPunkNo ratings yet
- Haptic TechnologyDocument6 pagesHaptic TechnologyNeeluCuteStarNo ratings yet
- Ch11 1 Transition Metals Absorption SpectraDocument29 pagesCh11 1 Transition Metals Absorption SpectraTapas GhatakNo ratings yet
- Characterization and Application of Cerium Fluoride Film in InfraredDocument4 pagesCharacterization and Application of Cerium Fluoride Film in InfrarednguyenthanhhopNo ratings yet
- Drude-Lorentz Model of Semiconductor Optical PlasmonsDocument10 pagesDrude-Lorentz Model of Semiconductor Optical PlasmonsMumba Patrick Jnr MpjNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - II: Join Our Telegram Channel: @airjeeDocument43 pagesChemical Bonding - II: Join Our Telegram Channel: @airjeeVallabhNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document70 pagesPart 1Mehnaz SafdarNo ratings yet
- FHDK 10P5101/S35A Diffuse Sensors With Background SuppressionDocument1 pageFHDK 10P5101/S35A Diffuse Sensors With Background SuppressionBreixo HarguindeyNo ratings yet
- Role of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles For Photodynamic Therapy of CancerDocument9 pagesRole of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles For Photodynamic Therapy of Cancerbelqis ratuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetically Induced Transparency in Mechanical Effects of LightDocument4 pagesElectromagnetically Induced Transparency in Mechanical Effects of LightMottu SinghNo ratings yet
- Emission and Absorption - Principles of Structural ChemistryDocument2 pagesEmission and Absorption - Principles of Structural ChemistryLeon MpalsNo ratings yet
- Fourier Optics - 2f ArrangementDocument5 pagesFourier Optics - 2f ArrangementJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect - WikipediaDocument17 pagesPhotoelectric Effect - WikipediaPriyal SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Worksheet CheDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Worksheet CheSripriyan DandayuthapaniNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Summative Test-MDL Science VII S.Y. 2021-2022Document4 pagesSecond Quarter Summative Test-MDL Science VII S.Y. 2021-2022ShengNo ratings yet
- Principles of SpectrosDocument23 pagesPrinciples of SpectroschebetjudynNo ratings yet
- TurbidimetryDocument22 pagesTurbidimetryjaanabhenchod50% (2)
- Worksheet-1 (Ray Optics)Document4 pagesWorksheet-1 (Ray Optics)Ritika SunilNo ratings yet