Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7 Forces and Motion II
Chapter 7 Forces and Motion II
Uploaded by
eujoekiongCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Test Bank For College Physics 10th Edition Hugh D Young Philip W Adams Raymond Joseph ChastainDocument20 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 10th Edition Hugh D Young Philip W Adams Raymond Joseph Chastainnatasharichardsonfkztbncwqp100% (42)
- Physics Matters For GCEDocument4 pagesPhysics Matters For GCEno one46% (13)
- 5 Worksheet (AS) Work Power and EnergyDocument3 pages5 Worksheet (AS) Work Power and EnergyMahad Asim100% (2)
- 期中复习答案Document14 pages期中复习答案IDKNo ratings yet
- Force and Friction Work Energy Power o Level 1Document25 pagesForce and Friction Work Energy Power o Level 1kasumbaashraf3No ratings yet
- Particle Dynamics (11th JK) WADocument48 pagesParticle Dynamics (11th JK) WAParijat SutradharNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- A3 IB-StyleDocument9 pagesA3 IB-StylezmedendoNo ratings yet
- Phy F5 C1 NotesDocument20 pagesPhy F5 C1 NotesTan Yan Yan, NicoleNo ratings yet
- 5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Almas TalibNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyDocument24 pagesWork, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyChirag SinghNo ratings yet
- UINT-5: Aboker Preparatory School, Harar Physics For Grade 11Document11 pagesUINT-5: Aboker Preparatory School, Harar Physics For Grade 11abdiabu701No ratings yet
- 0.13 PhysicsDocument4 pages0.13 PhysicsKaung Khant ZawNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Dynamics: Newton's Laws of MotionDocument22 pagesUnit 4: Dynamics: Newton's Laws of MotionDandy H HerkoNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Resolution of Forces + 1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021Document13 pages1.2 Resolution of Forces + 1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021pravin manikamNo ratings yet
- 2.9 Force Part 2Document15 pages2.9 Force Part 2sadyehNo ratings yet
- Work, Enegry and Power - Final Exams Revision: Ngwenya PT 1Document23 pagesWork, Enegry and Power - Final Exams Revision: Ngwenya PT 1Thabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - DateDocument4 pagesName: - Class: - DateFrancis Ho HoNo ratings yet
- Exams 2014 - Basic MechanicsDocument6 pagesExams 2014 - Basic Mechanicsdaniel dentehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 BookletDocument28 pagesChapter 10 BookletMIhaela CorcheNo ratings yet
- 08 Plug and Chug - Use of KE PE and Work - eDocument6 pages08 Plug and Chug - Use of KE PE and Work - eMatthew ChingNo ratings yet
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Document12 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Document19 pagesNewtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Swarnlata MishraNo ratings yet
- Maria Rubatto Catholic School Physics Department Grade 9Document4 pagesMaria Rubatto Catholic School Physics Department Grade 9eyobNo ratings yet
- Test-Force & Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesTest-Force & Laws of MotionindividualsumitNo ratings yet
- Physics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1Document8 pagesPhysics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1abdiasfaw7152No ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective QuestionDocument17 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questionphuahhuixin0530No ratings yet
- Work Power and Energy - Solved Examples - Solved ExampleDocument6 pagesWork Power and Energy - Solved Examples - Solved ExampleVasuki SubbarayaswamyNo ratings yet
- Forces - and Newtons Laws 49 Multi Choice QuestionsDocument28 pagesForces - and Newtons Laws 49 Multi Choice QuestionsVenkatesh SundararajanNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Document15 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Farain RashdiNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A/S Level PHYSICS UNIT 01 (Physics On The Go) Tutorial 03 Neranja WeerasingheDocument4 pagesEdexcel A/S Level PHYSICS UNIT 01 (Physics On The Go) Tutorial 03 Neranja WeerasinghePevin De silvaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Motion, A3, 13.09.2009Document4 pagesNewton's Law of Motion, A3, 13.09.2009shiva ram prasad pulagamNo ratings yet
- 110724-61348.work Energy and Power WS4 (AK) (2023-24) .PDF Work Energy and Power WS4 (AK) (2023-24)Document3 pages110724-61348.work Energy and Power WS4 (AK) (2023-24) .PDF Work Energy and Power WS4 (AK) (2023-24)lakshvarma20No ratings yet
- Gardener Forcc Paid: With PaiseDocument4 pagesGardener Forcc Paid: With PaiseKhelan MehtaNo ratings yet
- A Level PhysicsDocument7 pagesA Level PhysicsshmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dynamic RevisionDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Dynamic Revision陈伟明No ratings yet
- Dej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Work, Energy and Power (2003-2011)Document4 pagesDej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Work, Energy and Power (2003-2011)Eyuel Enito0% (1)
- Lom HCVDocument6 pagesLom HCVChallengers ClassesNo ratings yet
- Forces MC Test - EasyDocument9 pagesForces MC Test - EasyWiki KarunaratneNo ratings yet
- 9th Science Work and Energy Test Paper-1Document1 page9th Science Work and Energy Test Paper-1Alok Kumar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Impo. WpeDocument24 pagesImpo. WpeChirayu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PH110Document12 pagesChapter 6 PH110paulmaloba21No ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkDocument26 pagesChapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkRetno IstighfariniNo ratings yet
- Физика 11- 2021-2022Document14 pagesФизика 11- 2021-2022Nameless RFGNo ratings yet
- Physics Equilibrium QueDocument3 pagesPhysics Equilibrium QueLemi NegesoNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: Work, Energy and Power Home Assignment-PhysicsDocument2 pagesAssignment # 3: Work, Energy and Power Home Assignment-PhysicsAtulNo ratings yet
- Work Power and Energy (Practice Questions)Document3 pagesWork Power and Energy (Practice Questions)Burhanuddin SlatewalaNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsDocument6 pagesWork Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsAnusha HussainNo ratings yet
- Tut Test 4 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 4 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- Candidate's Name: Gender Class: Section A (10 Marks)Document6 pagesCandidate's Name: Gender Class: Section A (10 Marks)Simon SimuntalaNo ratings yet
- DP2 HL QPDocument26 pagesDP2 HL QPChinmay BhaveNo ratings yet
- 11 Holiday HomeworkDocument199 pages11 Holiday Homeworksupriyarama413No ratings yet
- AJC TutorialDocument4 pagesAJC TutorialYong Ming HengNo ratings yet
- CH-5 Laws of MotionDocument23 pagesCH-5 Laws of MotionAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Level - 0: CPP - WpeDocument15 pagesLevel - 0: CPP - Wpechaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- Superb Academy: Test # 7.1 PhysicsDocument4 pagesSuperb Academy: Test # 7.1 PhysicsKamran Ali100% (2)
- PM TB Solutions C03Document5 pagesPM TB Solutions C03Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (5)
- Electrolysis Experiment & ActivityDocument30 pagesElectrolysis Experiment & ActivityeujoekiongNo ratings yet
- Su Mo Tu We TH: 5 Sains 2Document1 pageSu Mo Tu We TH: 5 Sains 2eujoekiongNo ratings yet
- 5.16 Sound WavesDocument4 pages5.16 Sound WaveseujoekiongNo ratings yet
- MATEMATIK TG5 - BAB 3Document1 pageMATEMATIK TG5 - BAB 3eujoekiongNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Models of The AtomDocument7 pagesElectrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Models of The AtomHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Tut Unit 4Document4 pagesTut Unit 4Sunny BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Composites With Hybrid FillersDocument155 pagesPolymer Composites With Hybrid FillersAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Juan Pablo Physics Paper 1Document27 pagesJuan Pablo Physics Paper 1juanfogedaNo ratings yet
- Allen Jee Mains Phy April-2024Document79 pagesAllen Jee Mains Phy April-2024Ashok GuptaNo ratings yet
- Faulhaber 2342l012crDocument1 pageFaulhaber 2342l012crHugito ConnorNo ratings yet
- Phy Sample Paper Xi-2023-24 S 04Document17 pagesPhy Sample Paper Xi-2023-24 S 04ANSUMAN SUVANKARNo ratings yet
- Cable Sheeth EarthingDocument15 pagesCable Sheeth EarthingVaibhav Gholase100% (1)
- Advanced Pattern Cumulative Test-1 (Act-1) : Course: AbhimanyuDocument20 pagesAdvanced Pattern Cumulative Test-1 (Act-1) : Course: AbhimanyuYatharth DangiNo ratings yet
- Astm G 170 2006 PDFDocument16 pagesAstm G 170 2006 PDFJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTANo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 - Fatigue From Variable Amplitude LoadingDocument73 pagesChapter - 9 - Fatigue From Variable Amplitude Loadingodjakm100% (1)
- Ama Computer College: Assignment Electricity and MagnetismDocument4 pagesAma Computer College: Assignment Electricity and MagnetismMary Jane Evardone EspinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Properties of FluidsDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Properties of FluidsAhmad IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Challenges in Modern Astronomy: 1. The Glorious History of Astronomy and StatisticsDocument7 pagesStatistical Challenges in Modern Astronomy: 1. The Glorious History of Astronomy and StatisticsGabriel MarinelloNo ratings yet
- 17a. Newtons Firts Law of MotionDocument18 pages17a. Newtons Firts Law of MotionVicky Fortuna OliverosNo ratings yet
- Phys2 Midterm Exam F2019 20 With NotesDocument12 pagesPhys2 Midterm Exam F2019 20 With NotesaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- St. Peter's College Sabayle ST., Poblacion, Iligan City: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesSt. Peter's College Sabayle ST., Poblacion, Iligan City: ObjectiveDonnald YambaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Time and SpaceDocument384 pagesTheory of Time and SpaceV.I.A.R Technology100% (1)
- ELJODocument3 pagesELJOElvira CuestaNo ratings yet
- Metal Film Resistors MRS16S/25: Philips Components Product SpecificationDocument12 pagesMetal Film Resistors MRS16S/25: Philips Components Product SpecificationnrsaranNo ratings yet
- 3rd ChapterDocument10 pages3rd ChapterDeepak BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrical GeneratorDocument714 pagesAircraft Electrical GeneratorPIYUSH100% (1)
- Clebsch Gordon KatsayılarıDocument1 pageClebsch Gordon KatsayılarıBurhan EnginNo ratings yet
- Refresher 1-Answer KeyDocument4 pagesRefresher 1-Answer KeyDzyl Karee F. AllenNo ratings yet
- InorganicDocument18 pagesInorganicArchit GatadeNo ratings yet
- Rr322105-High Speed AerodynamicsDocument8 pagesRr322105-High Speed AerodynamicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet Engineering PhysicsDocument13 pagesTutorial Sheet Engineering PhysicsTusharSharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Homework 61 Rotational KinematicsDocument4 pagesPhysics Homework 61 Rotational Kinematicsnsxzktilf100% (1)
- Final Exam Equation Sheet: Id DQ DQ K K R Id S R IdDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Equation Sheet: Id DQ DQ K K R Id S R IdbesillysillyNo ratings yet
Chapter 7 Forces and Motion II
Chapter 7 Forces and Motion II
Uploaded by
eujoekiongOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 Forces and Motion II
Chapter 7 Forces and Motion II
Uploaded by
eujoekiongCopyright:
Available Formats
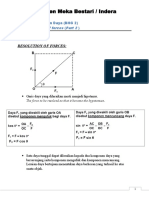
Chapter 7: Forces and motion II
7.1 Resolve forces
Fy = Fsinθ
2. A truck is pulling a wooden log on the surface of the road. If the tension in the chain
attached to the log is 4000 N, determine the force which causes the log to move
Fx = Fcosθ
forward
1. A force can be resolved into two components which are perpendicular to each other.
Exercise 2.14
1. Resolve the following force into its vertical and horizontal components.
a)
b)
3. A gardener pushes a lawn mower of mass 30 kg with a force of 150 N at an angle of
400 to the surface of the field. Calculate the force pushing the lawn mower forward
c)
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 1
4. Based on the diagram above, what is the resultant horizontal force that acts on the log? 5. The figure above shows a box is being pulled by a man.
Given that the tension of the rope is 4000 N and the direction is 300 to the surface a) What is the magnitude of the resultant force that causes the box move
[ 1997 Q16] horizontally?
b) Determine the acceleration for the system
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 2
6. The diagram shows a box being pulled by a boy. What is the acceleration of the box? 7. Diagram 4 shows a woman pushing a trolley. The total downward force is [2012 Q8]
[2003 Q8] A. Fy + mg B. Fy + F C. F - Fx D. F + mg
8. Diagram shows a boy pulling a block on a rough surface with force F. Which diagram
shows the action of forces on the block? [ 2011 Q6]
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 3
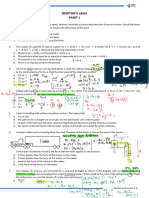
7.2 Forces in equilibrium 3. Which diagram show forces in equilibrium? [ 2009 Q9]
1. When an airplane achieves a state of equilibrium
4. When an object is in equilibrium of forces, the object [2007 Q11]
• Weight = Lift (height is constant)
A. Must be stationary
• Thrust = Drag (velocity is constant / acceleration is zero)
B. Must move with a uniform velocity
• The resultant force / net force acting on the airplane is zero.
C. Is either stationary or moving with a uniform velocity
D. Is moving with a uniform acceleration
Exercise 7.2
1. Which situation shows forces are in equilibrium? [2013 Q10]
A. A car speeding up on a highway.
B. A boat moving with uniform velocity.
C. An aeroplane take – off on a runway. 5. The diagram shows an airplane accelerating at a constant height. Which relationship
D. A cyclist slowing down his bicycle. between the forces is true? [2003 Q10]
A. F = G B. F < G C. U = W D. U > W
6. Which of the following statements is true for an airplane which is moving horizontally
2. Diagram 1 shows a stationary object when forces F1, F2, F3 and F4 are applied. Which with constant velocity? [2001 Q7]
statement is correct? [2012 Q4] A. The lifting force is greater than the weight
A. F 1 > F2 B. F1 < F2 C. F3 = F4 D. F4 > F3 B. The thrust is greater than the drag (frictional force)
C. The gravitational force increased
D. The kinetic energy remains constant
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 4
7. A hot air balloon of mass 400 kg with three passengers of total mass 200 kg is floated
at a constant height. What is the lift force for the balloon? [1999 Q4]
A. 0 N B. 4 000 N C. 6 000 N D. 12 000 N
8. The forces are in equilibrium in all the phenomena below except [2008 Q8]
A. A car descending a hill at constant velocity
B. A lamp hanging at rest in a hall
C. A mango falling from a tree
D. A ship floating at rest in the sea
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 5
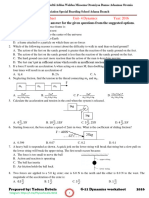
7.3 Work and Power Exercise 7.3
W=Fxs
The work done (W) is defined as the product of the force (F) and the distance (s) in the
direction of force.
1. A boy pushing his bicycle with a force of 25N through a distance of 3m. What is the
work done by the boy?
1. Work is done when
• Force is applied on the object and the object is moving
• Object move in the direction of the force
• The SI unit for work is Joule (J)
• Work is scalar quantity
2. A farmer is lifting up a sack of rice of mass 20kg to a height of 0.8m. What is the work
2. Area under a force – distance graph is equal to the work done
done by the farmer?
Work (W)
Power (P) =
Time (t)
3. Power (P) is defined as the rate of work is done
• The SI unit for power is Js-1 or Watt
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 6
5. Foo Yuan pushes a concrete wall by applying a force of 300N. How much work is done
3. Diagram shows a weightlifter successfully lifted a load of 60 kg. Calculate the work by him?
done in lifting the load [2006 Q4]
6. A student walks a distance of 6m holding a book of mass 1 kg. What is the work done
by the student?
4. Choose the diagram which shows the student doing the maximum work [2003 Q6]
7. Which situation shows no work being done? [ 2008 Q9]
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 7
8. Which of the followings show work is done? [ 1997 Q34]
I) Lifting up a weight
II) Pushing the concrete wall
III) Pushing an object on a rough surface
IV) Turning an object in a circle
A. I and III B. II and IV C. II, III and IV D. I, II, III and IV
11. Base on the force – distance graph above, what is the work done?
9. Diagram shows a worker pulled a weight up a smooth incline plane. P is the tension
force in the rope while x is the distance traveled by the weight. Based on the diagram,
what is the work done? [ 1999 Q29]
A. w x h B. P x C. wx D. P (x + h)
12. A nurse is pushing a patient in a wheelchair with a force of 100N over a distance of 5m
within 20 second. What is the power of the nurse?
10. Base on the force – distance graph above, what is the work done after the object has
move over a distance if 4m?
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 8
13. Figure above shows a workman pulling up a load of mass 50 kg over a distance of 2m
15. Diagram show a student with mass 70kg climbing stairs at a height of 4m in 40s. How
in 10s by using a smooth pulley system. What is the power of the workman?
much power is generated by the student? [2011 Q7]
14. Student of mass 60 kg walks up a flight of stairs 3 m high and 4 m long in 5 minutes.
What it the power of student?
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 9
16. Diagram 6.1 and diagram 6.2 show a student throwing an iron ball in a shout put event III) If the force which acts on the iron ball is 20 N and the distance of hand
movement is 0.5m, calculate the work done by the student [2]
using different throwing techniques [2006 Q6]
b) I) Base on the Anser in a) i), state the relationship between the energy gained by
the iron ball and the distance of projection [1]
II) State the principle involved [1]
a) Observe diagram 6.1 and diagram 6.2
I) Compare the distance of the hand movement to throw the iron ball [1]
b) I) Using diagram 6.1, what happens to the falling time if an iron ball of a bigger
mass is used? [1]
II) Based on the Anser in a) i), compare the work done by the student between II) Give one reason for your answer
the two-throwing technique [1]
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 10
7.4 Energy • Area under a force – extension graph is equal to the elastic potential energy store
1. Energy is the capacity of a system to do work. inside the spring
• The SI unit of energy is Joule (J)
6. Kinetic energy
• Energy is a sclar quantity
• Is the energy possessed by a moving object
2. Energy can exist in various forms such as • Only moving objects possess kinetic energy
• The kinetic energy of a stationary object = 0 J
• Potential energy
• Kinetic energy = ½ mv2
• Kinetic energy
• Heat energy
• Electric energy
• Waves energy
• Nuclear energy Exercise 7.4
1. A boy of mass 40 kg stands on a 3m high tree, what is the gravitational potential energy
3. There are two types of potential energy
for the boy?
• Gravitational potential energy
• Elastic potential energy
4. The gravitational potential energy
• Is the energy stored in the object because of its height above the earth surface.
• Gravitational potential energy = mgh
2. A student of mass 40 kg is climbing a ladder 5m in length as shown in the figure above.
Determine the gravitational potential energy for this student.
5. The elastic potential energy of an object
• Is the energy stored in the object as a result of stretching or compressing
• Elastic potential energy = ½ Fx
• x is compressing or stretching and is expressed in m
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 11
5. What is the kinetic energy of a man of mass 50 kg jogging at a velocity of 3 ms -1?
3. What is the potential energy stored in the spring as shown in the figure
4. Determine the energy stored in the spring when the extension of the spring is 8 cm.
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 12
7.5 The principle of conservation of energy
1. The principle of conservation of energy states that
• The energy in a system is constant
• Energy cannot be created or destroyed
• Energy can be converted from one form to another. 3. Diagram 6 shows a ball bearing P being released on a smooth plane. What is its
velocity at Q? [2011 Q8]
Exercise 7.5
1. A stone was dropped from a height of 8m above the ground, what is the velocity of the
stone when it strikes the ground?
4. A student of mass 20 kg is sitting down on the top of a sliding plane with the height of
2.5 m. Given that the work done against frictional force along the plane is 140 J. What
2. In a softball games, a ball was miss hit and flew vertically upwards with an initial
is the velocity of the boy in ms-1 before he reaches the ground? [ 1996 Q12]
velocity of 15 ms-1. What is the maximum height attained by the ball?
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 13
5. A stone of mass 0.3 kg is thrown vertically with initial velocity 4 ms-1. What is its
maximum gravitational energy? [1993 Q13]
7. Diagram 6 shows a wooden block and a weight connected by an inelastic string through
a frictionless pulley. When the weight is released, the energy change that happens in
the system is [2010 Q9]
A. Potential energy of the wooden block → kinetic energy of the weight
B. Potential energy of the weight → kinetics energy of the wooden block
C. Potential energy of the weight → kinetic energy of 'the wooden block and weight
D. Potential energy of the weight and wooden block → kinetic energy of the wooden
block
6. A stone is released from 5.0 m. What is the velocity of the stone before it hits the
ground? [2000 Q1]
8. Diagram shows a metal sphere oscillating on a frictionless track. Which of the
following statements is true? [2006 Q6]
A. The kinetic energy of the metal sphere is minimum at R
B. The potential energy of the metal sphere is maximum at P
C. The principle of conservation of energy is not obeyed
D. The total energy of the metal sphere at S is higher than that at R
9. The diagram shows a student running up a staircase at a constant speed. Which physical
quantity increases while the student is running up the staircase? [2005 Q5]
A. Inertia of the student C. Kinetic energy of the student
B. Momentum of the student D. Potential energy of the student
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 14
10. Diagram shows a student with the weight mg running up a staircase with the height of h
and a distance of l over t second. What is the power of the student? [ 2002 Q15]
A. mgh/t B. mgl/t C. mgh D. mgl
11. The diagram shows the path of a ball rolling down a smooth slope. The ball has the
greatest change in gravitational energy between the positions [ 2004 Q9]
A. P and Q B. Q and R C. P and S D. R and T
12. Diagram shows the oscillation of a simple pendulum. The pendulum is released at P.
Which if the following energy bar chart is true? [ 2002 Q14]
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 15
7.6 Elasticity
1. Elasticity is the ability to return to its original length after the external force is
removed.
F = kx 5. The higher the spring constant (k), the harder / stiffer the spring
k = F/x = gradient of the graph
k = spring constant (Nm-1)
2. Hooke’s Law state that
• The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied on it,
provided that the elastic limit is not exceeded
3. The elastic limit of a spring is the
6. Usage of elastic property of spring
• Maximum stretching force which can be applied to the spring before it ceases to
• Weighing machine
be elastic
• A spring cradles
• Suspension system of vehicle (to absorbed impacts and vibration)
• Bow (to propel arrow)
• Automatic door
• Toys (to make it move)
4. Factors that affect the elasticity of a spring are
• Length of the spring (shorter springs are more elastic)
• Diameter of the wire which form the spring (thicker wires are more elastic)
• Diameter of the spring (bigger diameter are more elastic)
• Type of material (steel spring is more elastic than copper spring)
• Arrangement of the spring (springs in parallel arrangement is more elastic than
series arrangement)
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 16
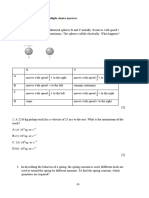
Exercise 7.6 4. When a weight of mass 0.5 kg is hung at the end of a spring, the extension is 4cm.
Determine the total extension for each of the following system
1. A spring with an original length of 10 cm is extended to a length of 15 cm when
subjected to a load of mass 2 kg. What is the length of the spring when its load is 6kg
a)
b)
2. A spring with an original length of 10 cm is extended to a length of 12 cm when
subjected to a load of mass 5 kg. What is the load required to extent the spring to 6 cm?
c)
3. A spring with original length of 10cm is extended to a length of 12 cm when subjected
to a load of mass 100g. Determine the total length in figure Q and R
d)
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 17
7. Diagram shows one spring with original length 10 cm. When 20 N is placed on the
5. The original length of a spring is 20cm. The compression is 5 cm when a load of mass spring, the spring compressed for 2 cm. When 80 N is placed on two springs as shown
10 g is placed atop the spring. What is the mass of object X? in the figure, what is the value of L? [2002 Q10]
8. Which graph shows that F is inversely proportional to X [2013 Q7]
6. Diagram 6 shows three identical springs with the original length of 16cm. What is the
length of Y? [2013 Q12]
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 18
9. Diagram 11.1shows the apparatus set- up to study the elasticity of springs X and Y. The
relationship between length of springs X and Y when stretched by different force is
shown in diagram 11.2. Which comparison about springs X and Y is correct? [2011
Q15]
A. X is harder than Y
B. The original length of X is longer than Y
C. To stretch 1 cm, work done on X is smaller than on Y
10. Which graph shows the correct relationship between the force, F, and the extension, x,
of a spring? [2010 Q6]
11. Which graph represents Hooke’s Law? [2009 Q10]
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 19
II) Thickness of the wire
Reason
12. Diagram 7 shows a load hung on a spring [2013 Q7]
c) The mass of the load can be determined by using the formula F = kx, where F is
force, k is spring constant and x is extension of spring
I) Name the physics law related to the above formula
III) Type of material
II) The mass of the load is 1 kg. Calculate the spring constant of spring P when
the extension of the spring is 2 cm
Reason
e) Another identical spring Q is used to hang the heavy load. Suggest the
d) Spring P breaks when it is used to hang a heavy load. Suggest a modification that
arrangement of these springs to hang the heavy load without breaking the springs
can made to hang heavy load through these aspects
I) Stiffness of the spring
Reason:
郑老师 STPM Physics & Chemistry 网上专科补习班 012 962 3130 20
You might also like
- Test Bank For College Physics 10th Edition Hugh D Young Philip W Adams Raymond Joseph ChastainDocument20 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 10th Edition Hugh D Young Philip W Adams Raymond Joseph Chastainnatasharichardsonfkztbncwqp100% (42)
- Physics Matters For GCEDocument4 pagesPhysics Matters For GCEno one46% (13)
- 5 Worksheet (AS) Work Power and EnergyDocument3 pages5 Worksheet (AS) Work Power and EnergyMahad Asim100% (2)
- 期中复习答案Document14 pages期中复习答案IDKNo ratings yet
- Force and Friction Work Energy Power o Level 1Document25 pagesForce and Friction Work Energy Power o Level 1kasumbaashraf3No ratings yet
- Particle Dynamics (11th JK) WADocument48 pagesParticle Dynamics (11th JK) WAParijat SutradharNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- A3 IB-StyleDocument9 pagesA3 IB-StylezmedendoNo ratings yet
- Phy F5 C1 NotesDocument20 pagesPhy F5 C1 NotesTan Yan Yan, NicoleNo ratings yet
- 5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Almas TalibNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyDocument24 pagesWork, Energy and Power Advanced Practice Problems From Mechanics by DC PandeyChirag SinghNo ratings yet
- UINT-5: Aboker Preparatory School, Harar Physics For Grade 11Document11 pagesUINT-5: Aboker Preparatory School, Harar Physics For Grade 11abdiabu701No ratings yet
- 0.13 PhysicsDocument4 pages0.13 PhysicsKaung Khant ZawNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Dynamics: Newton's Laws of MotionDocument22 pagesUnit 4: Dynamics: Newton's Laws of MotionDandy H HerkoNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Resolution of Forces + 1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021Document13 pages1.2 Resolution of Forces + 1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021pravin manikamNo ratings yet
- 2.9 Force Part 2Document15 pages2.9 Force Part 2sadyehNo ratings yet
- Work, Enegry and Power - Final Exams Revision: Ngwenya PT 1Document23 pagesWork, Enegry and Power - Final Exams Revision: Ngwenya PT 1Thabelo NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Class: - DateDocument4 pagesName: - Class: - DateFrancis Ho HoNo ratings yet
- Exams 2014 - Basic MechanicsDocument6 pagesExams 2014 - Basic Mechanicsdaniel dentehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 BookletDocument28 pagesChapter 10 BookletMIhaela CorcheNo ratings yet
- 08 Plug and Chug - Use of KE PE and Work - eDocument6 pages08 Plug and Chug - Use of KE PE and Work - eMatthew ChingNo ratings yet
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Document12 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Document19 pagesNewtons Law Force & Friction WA (English)Swarnlata MishraNo ratings yet
- Maria Rubatto Catholic School Physics Department Grade 9Document4 pagesMaria Rubatto Catholic School Physics Department Grade 9eyobNo ratings yet
- Test-Force & Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesTest-Force & Laws of MotionindividualsumitNo ratings yet
- Physics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1Document8 pagesPhysics G - 11 Dynamics Worksheet 1abdiasfaw7152No ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective QuestionDocument17 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questionphuahhuixin0530No ratings yet
- Work Power and Energy - Solved Examples - Solved ExampleDocument6 pagesWork Power and Energy - Solved Examples - Solved ExampleVasuki SubbarayaswamyNo ratings yet
- Forces - and Newtons Laws 49 Multi Choice QuestionsDocument28 pagesForces - and Newtons Laws 49 Multi Choice QuestionsVenkatesh SundararajanNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Document15 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Farain RashdiNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A/S Level PHYSICS UNIT 01 (Physics On The Go) Tutorial 03 Neranja WeerasingheDocument4 pagesEdexcel A/S Level PHYSICS UNIT 01 (Physics On The Go) Tutorial 03 Neranja WeerasinghePevin De silvaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of Motion, A3, 13.09.2009Document4 pagesNewton's Law of Motion, A3, 13.09.2009shiva ram prasad pulagamNo ratings yet
- 110724-61348.work Energy and Power WS4 (AK) (2023-24) .PDF Work Energy and Power WS4 (AK) (2023-24)Document3 pages110724-61348.work Energy and Power WS4 (AK) (2023-24) .PDF Work Energy and Power WS4 (AK) (2023-24)lakshvarma20No ratings yet
- Gardener Forcc Paid: With PaiseDocument4 pagesGardener Forcc Paid: With PaiseKhelan MehtaNo ratings yet
- A Level PhysicsDocument7 pagesA Level PhysicsshmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Dynamic RevisionDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Dynamic Revision陈伟明No ratings yet
- Dej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Work, Energy and Power (2003-2011)Document4 pagesDej/Wondirad Preparatory School: Physics UEE Compiled On Work, Energy and Power (2003-2011)Eyuel Enito0% (1)
- Lom HCVDocument6 pagesLom HCVChallengers ClassesNo ratings yet
- Forces MC Test - EasyDocument9 pagesForces MC Test - EasyWiki KarunaratneNo ratings yet
- 9th Science Work and Energy Test Paper-1Document1 page9th Science Work and Energy Test Paper-1Alok Kumar TiwariNo ratings yet
- Impo. WpeDocument24 pagesImpo. WpeChirayu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PH110Document12 pagesChapter 6 PH110paulmaloba21No ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkDocument26 pagesChapter 7. Kinetic Energy and WorkRetno IstighfariniNo ratings yet
- Физика 11- 2021-2022Document14 pagesФизика 11- 2021-2022Nameless RFGNo ratings yet
- Physics Equilibrium QueDocument3 pagesPhysics Equilibrium QueLemi NegesoNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: Work, Energy and Power Home Assignment-PhysicsDocument2 pagesAssignment # 3: Work, Energy and Power Home Assignment-PhysicsAtulNo ratings yet
- Work Power and Energy (Practice Questions)Document3 pagesWork Power and Energy (Practice Questions)Burhanuddin SlatewalaNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsDocument6 pagesWork Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsAnusha HussainNo ratings yet
- Tut Test 4 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 4 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- Candidate's Name: Gender Class: Section A (10 Marks)Document6 pagesCandidate's Name: Gender Class: Section A (10 Marks)Simon SimuntalaNo ratings yet
- DP2 HL QPDocument26 pagesDP2 HL QPChinmay BhaveNo ratings yet
- 11 Holiday HomeworkDocument199 pages11 Holiday Homeworksupriyarama413No ratings yet
- AJC TutorialDocument4 pagesAJC TutorialYong Ming HengNo ratings yet
- CH-5 Laws of MotionDocument23 pagesCH-5 Laws of MotionAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Level - 0: CPP - WpeDocument15 pagesLevel - 0: CPP - Wpechaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- Superb Academy: Test # 7.1 PhysicsDocument4 pagesSuperb Academy: Test # 7.1 PhysicsKamran Ali100% (2)
- PM TB Solutions C03Document5 pagesPM TB Solutions C03Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (5)
- Electrolysis Experiment & ActivityDocument30 pagesElectrolysis Experiment & ActivityeujoekiongNo ratings yet
- Su Mo Tu We TH: 5 Sains 2Document1 pageSu Mo Tu We TH: 5 Sains 2eujoekiongNo ratings yet
- 5.16 Sound WavesDocument4 pages5.16 Sound WaveseujoekiongNo ratings yet
- MATEMATIK TG5 - BAB 3Document1 pageMATEMATIK TG5 - BAB 3eujoekiongNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Models of The AtomDocument7 pagesElectrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Models of The AtomHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Tut Unit 4Document4 pagesTut Unit 4Sunny BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Composites With Hybrid FillersDocument155 pagesPolymer Composites With Hybrid FillersAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Juan Pablo Physics Paper 1Document27 pagesJuan Pablo Physics Paper 1juanfogedaNo ratings yet
- Allen Jee Mains Phy April-2024Document79 pagesAllen Jee Mains Phy April-2024Ashok GuptaNo ratings yet
- Faulhaber 2342l012crDocument1 pageFaulhaber 2342l012crHugito ConnorNo ratings yet
- Phy Sample Paper Xi-2023-24 S 04Document17 pagesPhy Sample Paper Xi-2023-24 S 04ANSUMAN SUVANKARNo ratings yet
- Cable Sheeth EarthingDocument15 pagesCable Sheeth EarthingVaibhav Gholase100% (1)
- Advanced Pattern Cumulative Test-1 (Act-1) : Course: AbhimanyuDocument20 pagesAdvanced Pattern Cumulative Test-1 (Act-1) : Course: AbhimanyuYatharth DangiNo ratings yet
- Astm G 170 2006 PDFDocument16 pagesAstm G 170 2006 PDFJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTANo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 - Fatigue From Variable Amplitude LoadingDocument73 pagesChapter - 9 - Fatigue From Variable Amplitude Loadingodjakm100% (1)
- Ama Computer College: Assignment Electricity and MagnetismDocument4 pagesAma Computer College: Assignment Electricity and MagnetismMary Jane Evardone EspinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Properties of FluidsDocument22 pagesChapter 1 Properties of FluidsAhmad IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Challenges in Modern Astronomy: 1. The Glorious History of Astronomy and StatisticsDocument7 pagesStatistical Challenges in Modern Astronomy: 1. The Glorious History of Astronomy and StatisticsGabriel MarinelloNo ratings yet
- 17a. Newtons Firts Law of MotionDocument18 pages17a. Newtons Firts Law of MotionVicky Fortuna OliverosNo ratings yet
- Phys2 Midterm Exam F2019 20 With NotesDocument12 pagesPhys2 Midterm Exam F2019 20 With NotesaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- St. Peter's College Sabayle ST., Poblacion, Iligan City: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesSt. Peter's College Sabayle ST., Poblacion, Iligan City: ObjectiveDonnald YambaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Time and SpaceDocument384 pagesTheory of Time and SpaceV.I.A.R Technology100% (1)
- ELJODocument3 pagesELJOElvira CuestaNo ratings yet
- Metal Film Resistors MRS16S/25: Philips Components Product SpecificationDocument12 pagesMetal Film Resistors MRS16S/25: Philips Components Product SpecificationnrsaranNo ratings yet
- 3rd ChapterDocument10 pages3rd ChapterDeepak BhaskaranNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrical GeneratorDocument714 pagesAircraft Electrical GeneratorPIYUSH100% (1)
- Clebsch Gordon KatsayılarıDocument1 pageClebsch Gordon KatsayılarıBurhan EnginNo ratings yet
- Refresher 1-Answer KeyDocument4 pagesRefresher 1-Answer KeyDzyl Karee F. AllenNo ratings yet
- InorganicDocument18 pagesInorganicArchit GatadeNo ratings yet
- Rr322105-High Speed AerodynamicsDocument8 pagesRr322105-High Speed AerodynamicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet Engineering PhysicsDocument13 pagesTutorial Sheet Engineering PhysicsTusharSharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Homework 61 Rotational KinematicsDocument4 pagesPhysics Homework 61 Rotational Kinematicsnsxzktilf100% (1)
- Final Exam Equation Sheet: Id DQ DQ K K R Id S R IdDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Equation Sheet: Id DQ DQ K K R Id S R IdbesillysillyNo ratings yet