Professional Documents
Culture Documents
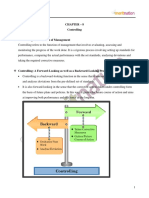
Controlling Functions of Management
Controlling Functions of Management
Uploaded by
JennyMacabulos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
CONTROLLING FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageControlling Functions of Management
Controlling Functions of Management
Uploaded by
JennyMacabulosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
CONTROLLING FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT
The controlling function of management is crucial for ensuring that organizational activities
are on track and aligned with established goals. It involves monitoring performance,
comparing it against predetermined standards, and taking corrective actions when
necessary. Here are the key elements of the controlling function:
1. Establishing Performance Standards: Controlling begins with establishing clear
and specific performance standards against which actual performance can be
measured. These standards may include targets for productivity, quality, efficiency,
profitability, or other relevant metrics. Performance standards provide a benchmark
for evaluating performance and identifying areas needing improvement.
2. Measuring Performance: Once performance standards are established, managers
need to measure actual performance to assess how well organizational activities are
meeting these standards. This may involve collecting data, analyzing reports,
conducting evaluations, and using performance indicators to track progress over
time.
3. Comparing Performance with Standards: After measuring performance, managers
compare it against the established standards to identify any deviations or variances.
This comparison helps managers determine whether performance is meeting
expectations, exceeding targets, or falling short of goals. Variances can highlight
areas of concern that require further investigation and action.
4. Analyzing Deviations: When variances are identified, managers analyze the
underlying causes to understand why performance deviates from the established
standards. This analysis may involve identifying factors such as inadequate
resources, inefficient processes, external factors, or human error contributing to the
deviations.
5. Taking Corrective Action: Based on the analysis of deviations, managers take
corrective action to address any issues and bring performance back in line with the
established standards. Corrective actions may involve making changes to processes,
reallocating resources, providing additional training or support to employees, or
implementing new strategies to improve performance.
6. Feedback and Learning: Controlling provides an opportunity for feedback and
learning within the organization. Managers communicate performance results to
employees, provide feedback on their performance, and encourage continuous
improvement. Lessons learned from the controlling process are used to refine future
plans, strategies, and performance standards.
7. Ensuring Compliance: Controlling also involves ensuring that organizational
activities comply with relevant laws, regulations, policies, and procedures. Managers
monitor compliance with legal and ethical standards, as well as internal policies and
guidelines, to minimize risks and ensure ethical behavior.
8. Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Controlling is an ongoing process that
requires continuous monitoring of performance and adaptation to changing
circumstances. Managers regularly review performance metrics, adjust performance
standards as needed, and remain vigilant to emerging issues or opportunities that
may affect organizational performance.
By effectively implementing the controlling function, managers can ensure that
organizational activities are efficient, effective, and aligned with strategic objectives.
Controlling helps organizations stay on course, identify areas for improvement, and achieve
optimal performance in pursuit of their goals.
You might also like
- PEI Escala de Empowerment PDFDocument15 pagesPEI Escala de Empowerment PDFAntonella María De Jesús Napán CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Online Gaming Addiction Among BSIT Students of Leyte Normal University Philippines Its Implications Towards Academic PerformanceDocument11 pagesOnline Gaming Addiction Among BSIT Students of Leyte Normal University Philippines Its Implications Towards Academic PerformanceAnonymous PcPkRpAKD5100% (1)
- Mpa FinalDocument9 pagesMpa FinalShashwat GoyalNo ratings yet
- Controlling and Decision MakingDocument10 pagesControlling and Decision MakingChristine FernandezNo ratings yet
- oRGANicayion ManabgetmentDocument4 pagesoRGANicayion ManabgetmentIrish LudoviceNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument6 pagesControllingShaik SuhaibNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument6 pagesControllingsuhaib shaikhNo ratings yet
- Controlling As A Management FunctionDocument7 pagesControlling As A Management FunctionZaidielNo ratings yet
- Performance Management: Semester-5Document8 pagesPerformance Management: Semester-5Ruhani AroraNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 ControllingDocument4 pagesTopic 2 ControllingPINEDA CRISTIAN PAUL C.No ratings yet
- L1-Definition and Nature of Management ControlDocument16 pagesL1-Definition and Nature of Management ControlMichael BautistaNo ratings yet
- 6 ControllingDocument8 pages6 Controllingtanjimalomturjo1No ratings yet
- Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Revision NotesDocument9 pagesClass 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Revision NotesSuchi SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesClass 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Revision NotesYash FattepuriaNo ratings yet
- Controlling NotesDocument3 pagesControlling Noteszahran0zannu01No ratings yet
- Controlling Class 12 Cbse NotesDocument24 pagesControlling Class 12 Cbse Notesviraj100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Controlling Notes PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 8 - Controlling Notes PDFabhishekNo ratings yet
- Definition of ControllingDocument6 pagesDefinition of ControllingAi Åi100% (1)
- PMASDocument14 pagesPMASSaima NishatNo ratings yet
- Best HR PracticesDocument15 pagesBest HR Practicesdhruvprep16015No ratings yet
- Performance MONITORINGDocument15 pagesPerformance MONITORINGVasuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Ajlal Haider MalikNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument4 pagesControllingSeema ModiNo ratings yet
- SM VTH Unit NotesDocument17 pagesSM VTH Unit NotesShubh BanshalNo ratings yet
- My Love My Wife My EverythingDocument3 pagesMy Love My Wife My EverythingKatherine Key BullagayNo ratings yet
- ControlDocument7 pagesControlGaurav KhemkaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDocument16 pagesAssignment: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCNisha RanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight Introduction To ManagementDocument6 pagesChapter Eight Introduction To ManagementbikilahussenNo ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument25 pagesControl SystemaasmaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7Document6 pagesTopic 71907060091No ratings yet
- 5th Handout Controlling Function ES24 Ip2770Document12 pages5th Handout Controlling Function ES24 Ip2770Catherine Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter SevenDocument4 pagesChapter SevenAd FikNo ratings yet
- LS 12 ControllingDocument24 pagesLS 12 ControllingAnish Sidharth ChekuriNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument5 pagesControllingHimkar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Controlling Management FunctionDocument31 pagesControlling Management FunctionNaokhaiz AfaquiNo ratings yet
- Principle of Management Control. 2Document38 pagesPrinciple of Management Control. 2durugofavour64No ratings yet
- CONTROLDocument5 pagesCONTROLkiborNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV Performance Management: Training & Development Definition of Performance ManagementDocument27 pagesUnit - IV Performance Management: Training & Development Definition of Performance ManagementPrachiNo ratings yet
- Controlling TechniquesDocument40 pagesControlling TechniquesArun PrasadNo ratings yet
- 6 Chapter 6 ControllingDocument11 pages6 Chapter 6 ControllingRomar DurianNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: Course Code: 8616Document33 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: Course Code: 8616Waleed KhanNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument3 pagesControllingLyrine SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Chapter 8. Controlling-1599071834870Document3 pagesChapter 8 Chapter 8. Controlling-1599071834870Harsh SahukarNo ratings yet
- Chapter EightDocument7 pagesChapter EightAbreham KassaNo ratings yet
- HRMG Unit 5Document10 pagesHRMG Unit 5Hemanth ParakhNo ratings yet
- 8 ControllingDocument4 pages8 Controllingadhishreesinghal24No ratings yet
- Module 13 ControllingDocument4 pagesModule 13 ControllingMarla Brigitte GalvanNo ratings yet
- Controlling FunctionDocument7 pagesControlling FunctionyosefNo ratings yet
- Performance MonitoringDocument19 pagesPerformance Monitoringkafi70156No ratings yet
- Unit VDocument14 pagesUnit VMohithNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 8 ControllingDocument6 pagesChapter - 8 ControllingyusraNo ratings yet
- What Is Controlling?Document28 pagesWhat Is Controlling?carol valenciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 ControllingDocument3 pagesChapter-8 ControllingPaavane ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Management ReportDocument8 pagesManagement ReportMhel Piamonte NitroNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Human Resource ManagementDocument2 pagesUnit 4 Human Resource Managementshreyamk17No ratings yet
- Functions of Management in NursingDocument19 pagesFunctions of Management in NursingJessie James LlanesNo ratings yet
- Controlling Organization: Predetermined Standards, Attempts To Take Corrective MeasuresDocument11 pagesControlling Organization: Predetermined Standards, Attempts To Take Corrective MeasuresJaninaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management AssignmentDocument4 pagesIndustrial Management AssignmentRashid KanetsaNo ratings yet
- PCM Unit - IIDocument51 pagesPCM Unit - IInmhrk1118No ratings yet
- Business Management Principles for Today's Leaders: A Practical Guide for ProfessionalsFrom EverandBusiness Management Principles for Today's Leaders: A Practical Guide for ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Marketing Research by SmithDocument448 pagesAn Introduction To Marketing Research by SmithKali Das100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Survey Research MethodologyDocument28 pagesFundamentals of Survey Research MethodologyAstley Henry100% (3)
- Sample Literature Book ReviewDocument9 pagesSample Literature Book Reviewgw2xyzw9100% (1)
- Lecture 1-Intro To EIADocument8 pagesLecture 1-Intro To EIANazirah MamatNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal: AN ANALYSIS OF THE PROVINCIAL GOVERNMENT'S SUPPORT FOR CHILDREN IN NEED OF SPECIAL PROTECTION IN SORSOGONDocument17 pagesResearch Proposal: AN ANALYSIS OF THE PROVINCIAL GOVERNMENT'S SUPPORT FOR CHILDREN IN NEED OF SPECIAL PROTECTION IN SORSOGONNazrene AspraNo ratings yet
- Geography Coursework Analysis ExampleDocument8 pagesGeography Coursework Analysis Examplebatesybataj3100% (2)
- Apa Sociology Research Paper ExampleDocument4 pagesApa Sociology Research Paper Exampleozbvtcvkg100% (1)
- Lesson 10 - Practical Research 2Document20 pagesLesson 10 - Practical Research 2Jimmy Bong ArabitNo ratings yet
- Auditor/Lead Auditor Training Course: Based On OHSAS 18001:2007Document69 pagesAuditor/Lead Auditor Training Course: Based On OHSAS 18001:2007Eslam IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Effects of Large Class Size On The Academic Performance As Percieved by Pupils and Teachers in Sibulan Central Elementary SchoolDocument28 pagesEffects of Large Class Size On The Academic Performance As Percieved by Pupils and Teachers in Sibulan Central Elementary SchoolHanna Darlyn Colong TomaroyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Online Impulsive Buying Behaviour of Students-RefferenceDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Online Impulsive Buying Behaviour of Students-RefferenceRose AnneNo ratings yet
- Effects of Traffic Violation and Demographic Characteristics On Traffic Safety in Sulaymaniyah CityDocument9 pagesEffects of Traffic Violation and Demographic Characteristics On Traffic Safety in Sulaymaniyah CityBurhan MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics: Code: OMT-602 M.Sc. (OPT) - I SemDocument15 pagesProbability and Statistics: Code: OMT-602 M.Sc. (OPT) - I SemSandeep MoghaNo ratings yet
- Repairing Jobs That Fail To SatisfyDocument8 pagesRepairing Jobs That Fail To SatisfyNicoloNo ratings yet
- A Qualitative Study of User Perceptions of Mobile Health AppsDocument11 pagesA Qualitative Study of User Perceptions of Mobile Health AppsCaptionNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Planning ProcessDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Planning Processc5p6e5z1100% (1)
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness Measurement of TPM Manager Model Machines in Flexible Manufacturing EnvironobileDocument13 pagesOverall Equipment Effectiveness Measurement of TPM Manager Model Machines in Flexible Manufacturing EnvironobileDIEGO FERNANDO HUAMANI TORRESNo ratings yet
- Nancy Kumari SynopsisDocument14 pagesNancy Kumari SynopsisAbc 13 XyzNo ratings yet
- Murry, Heide - Managing Promotion Program Participation Within Manufacturer-Retailer-RelationshipsDocument12 pagesMurry, Heide - Managing Promotion Program Participation Within Manufacturer-Retailer-RelationshipsAhmad QuNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic FunctionsDocument20 pagesLogarithmic FunctionsThomas WashNo ratings yet
- 9702 w15 QP 53 PDFDocument8 pages9702 w15 QP 53 PDFDaanial KhanNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Lutero, Cherrylyn RDocument17 pagesPrepared By: Lutero, Cherrylyn R민은 아No ratings yet
- Research Paper Topics For Library ScienceDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Topics For Library Sciencec9snjtdx100% (1)
- Research On Dry Skin Care in BangladeshDocument89 pagesResearch On Dry Skin Care in Bangladeshnazua1No ratings yet
- Batiancila-Group 4 2Document30 pagesBatiancila-Group 4 2MARITES M. CUYOSNo ratings yet
- Systematic Literature ReviewDocument16 pagesSystematic Literature ReviewSheetal MaviNo ratings yet
- Figurative Language in AdvertisementsDocument33 pagesFigurative Language in AdvertisementsSorin CiutacuNo ratings yet
- A Sustainable Lean Production Framework With A Case Implementation - Practice-Based View TheoryDocument14 pagesA Sustainable Lean Production Framework With A Case Implementation - Practice-Based View TheoryNuriaNo ratings yet