Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A6 - Spectrocscopic Identification
A6 - Spectrocscopic Identification
Uploaded by
Alyasin FrougaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A6 - Spectrocscopic Identification
A6 - Spectrocscopic Identification
Uploaded by
Alyasin FrougaCopyright:
Available Formats
SL & HL Answers to Spectroscopic identification of organic
compounds: Question 6
(a) From the elemental analysis
Element Amount / mol Simplest ratio
Carbon 48.63/12.01 = 4.05 3
Hydrogen 8.18 / 1.01 = 8.10 6
Oxygen 43.19 / 16.00 = 2.70 2
The empirical formula of Compound F is C3H6O2
(b) The M+ peak at m/z = 74 leads to the conclusion that the molar mass of Compound F is the same as
the empirical mass so the molecular formula is C3H6O2. The fragment at m/z 57 is due to C3H5O+ due to
the loss of –OH and the fragment at 45 is due to COOH+ following the loss of -C2H5.
(c) The very broad absorption at approximately 3000 cm-1 shows the presence of –OH and the shoulder
at about 2950 cm-1 is due to C–H. The absorption at 1715 cm-1 shows the presence of a carbonyl group,
C=O. This supports the mass spectral data that a carboxylic acid is present in Compound F.
(d) The 1H NMR spectrum shows that the hydrogen atoms are in three different chemical environments.
These equate to one –CH3 group (integration trace 3) one –CH2- group (integration trace 2) and a further
single hydrogen atom very far upfield at 11.5 ppm which equates to the carboxylic acid hydrogen atom. .
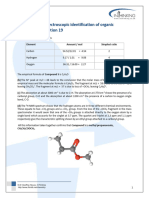
All this information taken together confirms that Compound F is propanoic acid, CH3CH2COOH.
© Dr Geoffrey Neuss, InThinking
http://www.thinkib.net/chemistry 1
You might also like
- (Organo) Part BDocument9 pages(Organo) Part BAmirul Amin Bin ShukriNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - RecoverDocument13 pagesExperiment 1 - RecoverChristina ApriliaNo ratings yet
- SL & HL Answers To: Spectroscopic Identification of Organic Compounds: Question 1Document1 pageSL & HL Answers To: Spectroscopic Identification of Organic Compounds: Question 1Priya Vijay kumaarNo ratings yet
- Ws10 AnswersDocument4 pagesWs10 AnswersKassimNo ratings yet
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIFrom EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A19 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA19 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A5 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA5 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A17 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA17 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A13 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA13 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A14 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA14 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A15 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA15 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A11 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA11 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A12 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA12 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A16 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationDocument2 pagesA16 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A2 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA2 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A18 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA18 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A20 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA20 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 - Measurement - Data Processing q1 MsDocument9 pagesTopic 11 - Measurement - Data Processing q1 MsClaudia JaukinNo ratings yet
- Topic 15 Organic Chemistry: Carbonyls, Carboxylic Acids and ChiralityDocument9 pagesTopic 15 Organic Chemistry: Carbonyls, Carboxylic Acids and ChiralitysalmaNo ratings yet
- SCH 121 Lecture Notes (2024)Document224 pagesSCH 121 Lecture Notes (2024)Mwalimu Rashid RashooNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Structural AnalysisDocument27 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Structural AnalysisRAIEL ALVARONo ratings yet
- Che 111 Lecture Notes (2023)Document224 pagesChe 111 Lecture Notes (2023)alvaeuv66No ratings yet
- CHM 102 Past Test QuestionsDocument15 pagesCHM 102 Past Test Questionsalexapierre08No ratings yet
- Synthesis of Indolo (3,2-b) Carbazole-Based New Colorimetric Receptor For Anions: A Unique Color Change For Fluoride IonsDocument8 pagesSynthesis of Indolo (3,2-b) Carbazole-Based New Colorimetric Receptor For Anions: A Unique Color Change For Fluoride IonskamalnandreNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of (M+H) + Formation in AtmosphericDocument6 pagesMechanism of (M+H) + Formation in AtmosphericFábio Teixeira da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper3Document6 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper3Sharon ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemo Selectivity FinishedDocument9 pagesChemo Selectivity FinishedTom FlemingNo ratings yet
- Answer: (A) and (B)Document18 pagesAnswer: (A) and (B)Germaine Manangan100% (1)
- Synthesis and Characterization of Coordi PDFDocument1 pageSynthesis and Characterization of Coordi PDFMuhammad Naeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Maskill Exercisesolutions ch06Document5 pagesMaskill Exercisesolutions ch06yosefkebeba7No ratings yet
- Org Part 1 With AnsDocument7 pagesOrg Part 1 With AnsDeepak PradhanNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectroscopy InterpretationDocument44 pagesMass Spectroscopy InterpretationRenjitha J RNo ratings yet
- Aieee 2009 PaperDocument20 pagesAieee 2009 PaperBhanu Pratap RathoreNo ratings yet
- pH-Controlled Oxidation of An Aromatic Ketone: Structural Elucidation of The Products of Two Green Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagespH-Controlled Oxidation of An Aromatic Ketone: Structural Elucidation of The Products of Two Green Chemical ReactionsbabiquimNo ratings yet
- Molecules 12 01796Document9 pagesMolecules 12 01796Kalpesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Chiroptical Studies On Brevianamide B: Vibrational and Electronic Circular Dichroism ConfrontedDocument23 pagesChiroptical Studies On Brevianamide B: Vibrational and Electronic Circular Dichroism ConfrontedTIAGO DA SILVA AROUCHENo ratings yet
- Topics 1.1 - 1.3Document9 pagesTopics 1.1 - 1.3casperinrocNo ratings yet
- Contest 3Document3 pagesContest 3bakosua141No ratings yet
- CHM112 CBT Ca (Merit)Document4 pagesCHM112 CBT Ca (Merit)teamtruth50No ratings yet
- Chlorophyll - WikipediaDocument53 pagesChlorophyll - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Strong Donor-Acceptor Couplings in A Special Pair-Antenna ModelwDocument3 pagesStrong Donor-Acceptor Couplings in A Special Pair-Antenna ModelwtygkrishnaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry I: Incomplete Combustion (Where There Is Not Enough Oxygen Present) Can LeadDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry I: Incomplete Combustion (Where There Is Not Enough Oxygen Present) Can LeadEian InganNo ratings yet
- Limonoids From Cedrela SinensisDocument7 pagesLimonoids From Cedrela Sinensisnishi@sainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document5 pagesChapter 9Stephen BrownNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document27 pagesChapter 15anastark100% (6)
- Basics of MicrobiologyDocument19 pagesBasics of Microbiologymoo0% (1)
- 1455877785CHE P12 M35 EtextDocument8 pages1455877785CHE P12 M35 EtextSaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- NMR Solving StrategyDocument2 pagesNMR Solving Strategysorrow Lemon100% (1)
- Arsenic 3 SensingDocument3 pagesArsenic 3 SensingAamir AhmedNo ratings yet
- ANALYSISDocument32 pagesANALYSISTendaiNo ratings yet
- Tetrahedron Letters: Olugbeminiyi O. Fadeyi, R. Nathan Daniels, Sean M. Deguire, Craig W. LindsleyDocument4 pagesTetrahedron Letters: Olugbeminiyi O. Fadeyi, R. Nathan Daniels, Sean M. Deguire, Craig W. LindsleyNopasantiNo ratings yet
- Structural and Luminescence Studies of Trivalent Europium Complexes With Pentaethylene Glycol and 18-Crown-6 Ligands in The Presence of Picrate AnionDocument10 pagesStructural and Luminescence Studies of Trivalent Europium Complexes With Pentaethylene Glycol and 18-Crown-6 Ligands in The Presence of Picrate Anionsaudagar_minang72No ratings yet
- Ukraine Chemistry Olympiad - 2009Document29 pagesUkraine Chemistry Olympiad - 2009AryanNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy and ChromatographyDocument7 pagesSpectroscopy and ChromatographyPa GesNo ratings yet
- Answers To Topic 9 Test Yourself Questions: 9 Spectroscopy and ChromatographyDocument5 pagesAnswers To Topic 9 Test Yourself Questions: 9 Spectroscopy and ChromatographyAunik BaruaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionFrom EverandQuantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Theoretical Approaches to Actinide ChemistryFrom EverandExperimental and Theoretical Approaches to Actinide ChemistryJohn K. GibsonNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Protein Post-Translational Modifications by Mass SpectrometryFrom EverandAnalysis of Protein Post-Translational Modifications by Mass SpectrometryNo ratings yet
- Physico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentFrom EverandPhysico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 1 WO3 Round Any Number 2019Document2 pagesY6 Autumn Block 1 WO3 Round Any Number 2019Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 2 WO7 Long Division 3 2020 AnswersDocument1 pageY6 Autumn Block 2 WO7 Long Division 3 2020 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 1 WO3 Round Any Number 2019 AnswersDocument1 pageY6 Autumn Block 1 WO3 Round Any Number 2019 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 2 WO11 Primes To 100 2020 AnswersDocument2 pagesY6 Autumn Block 2 WO11 Primes To 100 2020 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 2 WO5 Long Division 1 2020Document2 pagesY6 Autumn Block 2 WO5 Long Division 1 2020Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 2 WO3 Short Division 2020 AnswersDocument2 pagesY6 Autumn Block 2 WO3 Short Division 2020 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6AutEoB2 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division B v2 AnswersDocument4 pagesY6AutEoB2 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division B v2 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 1 WO2 Compare and Order Any Numbers 2019 AnswersDocument1 pageY6 Autumn Block 1 WO2 Compare and Order Any Numbers 2019 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6AutEoB1 Place Value BDocument2 pagesY6AutEoB1 Place Value BAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 1 WO6 Compare and Order Any Integers 2022 AnswersDocument1 pageY6 Autumn Block 1 WO6 Compare and Order Any Integers 2022 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Common MultiplesDocument2 pagesCommon MultiplesAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6AutEoB2 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division ANSWERSDocument4 pagesY6AutEoB2 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division ANSWERSAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A - Ahl Electrochemical CellsDocument1 pageA - Ahl Electrochemical CellsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Interactive PDF The Circulatory System - Ver - 1Document2 pagesInteractive PDF The Circulatory System - Ver - 1Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A - Lewis Acids and BasesDocument1 pageA - Lewis Acids and BasesAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A AlkenesDocument1 pageA AlkenesAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PYP 5 - Brian Murray - Oxford 2019Document168 pagesMathematics PYP 5 - Brian Murray - Oxford 2019Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- The Eye WorksheetDocument6 pagesThe Eye WorksheetAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A12 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA12 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A AlcoholsDocument1 pageA AlcoholsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A11 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA11 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A - Coloured Complexes QuestionsDocument1 pageA - Coloured Complexes QuestionsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A - Energy Cycles QuestionsDocument2 pagesA - Energy Cycles QuestionsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A Data ResponseDocument2 pagesA Data ResponseAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet