Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A - Bond Enthalpies
A - Bond Enthalpies
Uploaded by
Alyasin FrougaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A - Bond Enthalpies
A - Bond Enthalpies
Uploaded by
Alyasin FrougaCopyright:
Available Formats
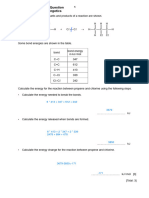
SL & HL Answers to Bond enthalpies questions
1. The sum of the strong O―H and C=O bonds being formed is always greater than the sum of the
weaker C―H, O=O (and C=C or CΞC where relevant) bonds being broken.
2. Energy in to break NΞN and 3H―H = 945 + (3 x 436) = 2253 kJ
Energy out to form 6N-H = 6 x 391 = 2346 kJ
∆H for reaction (which involves formation of two mol of NH3) = 2253 – 2346 = – 93 kJ
Enthalpy of formation of ammonia = ½ x - 93 = – 46.5 kJ mol–1
3. Energy in to break C―H and Cl―Cl = 414 + 242 = 656 kJ
Energy out to form C―Cl and H―Cl = 324 + 431 = 755 kJ
∆H = 656 – 755 = – 99 kJ mol–1
4. (a) Energy in to break C=C and H―H = 614 + 436 = 1050 kJ
Energy out to form C―C and 2C―H = 346 + (2 x 414) = 1174 kJ
∆H = 1050 – 1174 = – 124 kJ mol–1
(b) Extra energy in to vaporize cyclohexene to gaseous state = 33.5 kJ mol–1
Extra energy out to condense cyclohexane gas to liquid state = 32.0 kJ mol-–1
Enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene = –124 + (33.5 – 32.0) = – 122.5 kJ mol–1
Difference with literature value = [(122.5 – 121.9) / 121.9] x 100 = 0.49%.
This difference is because average bond enthalpies were used for the C-C, C-H and C=C bonds
which are not the exact values for the bonds in cyclohexene and cyclohexane.
(c) Energy in to vaporise C6H6 and to break 3C=C and 3H―H = 33.9 + (3 x 614) + (3 x 436) = 3184 kJ
Energy out to form 3C―C and 6C―H and condense C6H12 = (3 x 346) + (6 x 414) + 32.0 = 3554 kJ
Enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene = 3184 – 3554) = – 370 kJ mol–1
(d) Benzene is expected to give out either 370 kJ mol–1 (calculated from average bond enthalpies)
or 366 kJ mol–1 ( calculated from 3 x literature value) when hydrogenated. In fact it only gives
out 210 kJ mol–1 as the difference in energy has been used to overcome the delocalization
energy. Hence the delocalization energy of benzene is approximately 160 kJ mol–1.
© Dr Geoffrey Neuss, InThinking
http://www.thinkib.net/chemistry 1
You might also like
- 2014 Enthalpy Tutorial With Solution UpdatedDocument17 pages2014 Enthalpy Tutorial With Solution Updatedmenglay100% (4)
- Tutorial Chemical Energetics Part I SolutionsDocument20 pagesTutorial Chemical Energetics Part I SolutionsDarren LimNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry 4 (Born-Haber Cycle and Bond Energy) - 2022Document13 pagesThermochemistry 4 (Born-Haber Cycle and Bond Energy) - 2022Glory100% (1)
- Answers To End of Chapter Questions: A Q M × C × B Number of Moles Ethanol Used 0.02Document4 pagesAnswers To End of Chapter Questions: A Q M × C × B Number of Moles Ethanol Used 0.02Fernando PalokaNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2 Model AnswerDocument3 pagesAssignment # 2 Model AnswerTarek MadkourNo ratings yet
- Bond Energies NotesDocument3 pagesBond Energies NotesKarthi100% (1)
- Calculations On Bond EnergyDocument4 pagesCalculations On Bond EnergyThecla DadaNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsReviewQuestions 2020 SOLUTIONS UpdatedDocument7 pagesEnergeticsReviewQuestions 2020 SOLUTIONS UpdatedHakkyu KimNo ratings yet
- Estimating Enthalpy Using Bond EnergyDocument3 pagesEstimating Enthalpy Using Bond EnergyEmille IlmansyahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ks4 Lesson CHM Y10 U5 l6Document10 pagesChemistry ks4 Lesson CHM Y10 U5 l6LuisNo ratings yet
- Gcesoln 3Document4 pagesGcesoln 3api-3734333No ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics - Year - 10 - QPDocument20 pagesChemical Energetics - Year - 10 - QPtoilet.rouletteNo ratings yet
- Final Initial: Products ReactantsDocument14 pagesFinal Initial: Products ReactantsAlisa DowningNo ratings yet
- Example #2: The Complete Combustion of Propane Can Be Represented by The Following EquationDocument5 pagesExample #2: The Complete Combustion of Propane Can Be Represented by The Following EquationIka Khusnul KhNo ratings yet
- Energetics and Enthalpy ChangesDocument5 pagesEnergetics and Enthalpy ChangesNaury N OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Ch1 PDFDocument31 pagesCh1 PDFrashidNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets AS 1205 QC Energetics C ANSDocument1 pageChemsheets AS 1205 QC Energetics C ANSchinkey lolNo ratings yet
- Energetics - CN - STDT5Document2 pagesEnergetics - CN - STDT5NkemziNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HSSC-I Solution (3) - 220510 - 150450Document20 pagesChemistry HSSC-I Solution (3) - 220510 - 150450Alina Syedd32No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ThermodynamicsDocument12 pagesChapter 6 ThermodynamicsYash PlayNo ratings yet
- CLASS 11 CHEMISTRY NCERT SOLUTION Chapter - 6 - ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesCLASS 11 CHEMISTRY NCERT SOLUTION Chapter - 6 - ThermodynamicsAnantNo ratings yet
- Calculations For Enthalpy ChangesDocument20 pagesCalculations For Enthalpy Changesclementmondo80No ratings yet
- 2.1 Energetics Assessed Homework Ms 1. (1) : (Allow - 2300 To - 2323)Document3 pages2.1 Energetics Assessed Homework Ms 1. (1) : (Allow - 2300 To - 2323)123456No ratings yet
- 08-Bond Energies and Enthalpy ChangesDocument3 pages08-Bond Energies and Enthalpy ChangesNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Paper 2Document8 pagesTopic 5 Paper 2Random GuyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MCQSDocument27 pagesUnit 5 MCQSFiras Ahmad100% (2)
- PDFDocument16 pagesPDFMary Rose AllinegNo ratings yet
- Bond Enthalpies Chemistry H-W 2024-02-07 08 - 02 - 41Document1 pageBond Enthalpies Chemistry H-W 2024-02-07 08 - 02 - 41Olta LuliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1kapilNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Hess - S LawDocument8 pagesThermochemistry Hess - S LawsumathiNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry JM21Document2 pagesThermochemistry JM21himanshipant2007No ratings yet
- Exercises: Norganic HermodynamicsDocument8 pagesExercises: Norganic HermodynamicskjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 (Bonding)Document22 pagesChapter 8 (Bonding)Yossef AmrNo ratings yet
- M1-6F - Enthalpy Calculations-Bond EnergiesDocument13 pagesM1-6F - Enthalpy Calculations-Bond EnergiesestherNo ratings yet
- HW7 SolnDocument5 pagesHW7 SolnCrizaldo MempinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-1-With AnswerDocument4 pagesTutorial-1-With AnswerHayicNo ratings yet
- CH108 Workshop + Revision Questions PDFDocument5 pagesCH108 Workshop + Revision Questions PDFwhooooostherrrrrrrrNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Calculations NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry Calculations Notesyoonmimikyaw2008No ratings yet
- Practise Questions-2Document1 pagePractise Questions-2PARVATHY ANILNo ratings yet
- A Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Document8 pagesA Energetics Notes Chem Unit 1 - (New)Khaila SimmondNo ratings yet
- CHE201 Ch8b Skeletal Notes SP23Document12 pagesCHE201 Ch8b Skeletal Notes SP23Reade YTNo ratings yet
- Key For Qs 33-37Document1 pageKey For Qs 33-37MRMFARAHNo ratings yet
- Born Haber CycleDocument6 pagesBorn Haber Cycle观龙No ratings yet
- Molecular Orbitals-Convalent BondingDocument10 pagesMolecular Orbitals-Convalent Bondingestellasr00No ratings yet
- 5.3 Bond Enthalpy: IB SL Chemistry Mrs. Page 2015-2016Document26 pages5.3 Bond Enthalpy: IB SL Chemistry Mrs. Page 2015-2016Patrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- 11HThermoPracticeQsDocument5 pages11HThermoPracticeQsJust BetoNo ratings yet
- 11th Chem ch6Document12 pages11th Chem ch6Shri Radhe KripaNo ratings yet
- A - Entropy - SpontaneityDocument2 pagesA - Entropy - SpontaneityAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Jee FTDocument5 pagesJee FTDeena chemistNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Bond Energy Calculations WorksheetDocument4 pagesYear 10 Bond Energy Calculations WorksheetVICKNESWARY MUNIYANNo ratings yet
- Δ H C H = -103.9 kJ mol Δ H CO = -393.5 kJ mol Δ H H O = -285.8 kJ molDocument1 pageΔ H C H = -103.9 kJ mol Δ H CO = -393.5 kJ mol Δ H H O = -285.8 kJ mollakadia taylorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 Exam 3 Fall 2017 Form ADocument5 pagesChemistry 1 Exam 3 Fall 2017 Form AKyle LoughranNo ratings yet
- HW02 - Thermo 2-SolutionsDocument9 pagesHW02 - Thermo 2-SolutionsKeerthana KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsDocument17 pagesPhysics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument15 pagesThermo ChemistrySachin Kumar50% (2)
- Thermodynamics Worksheet MSDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Worksheet MSMalcolmJustMalcolmNo ratings yet
- Hess Cycle QuestionsDocument3 pagesHess Cycle QuestionsNujod HolaNo ratings yet
- (Pearson) IB Chemistry HL AnswerDocument3 pages(Pearson) IB Chemistry HL AnswerAn Ho XuanNo ratings yet
- Bond EnthalpyDocument10 pagesBond EnthalpyPartha SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 1 WO3 Round Any Number 2019Document2 pagesY6 Autumn Block 1 WO3 Round Any Number 2019Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 1 WO3 Round Any Number 2019 AnswersDocument1 pageY6 Autumn Block 1 WO3 Round Any Number 2019 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 2 WO11 Primes To 100 2020 AnswersDocument2 pagesY6 Autumn Block 2 WO11 Primes To 100 2020 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 2 WO3 Short Division 2020 AnswersDocument2 pagesY6 Autumn Block 2 WO3 Short Division 2020 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 2 WO5 Long Division 1 2020Document2 pagesY6 Autumn Block 2 WO5 Long Division 1 2020Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 1 WO2 Compare and Order Any Numbers 2019 AnswersDocument1 pageY6 Autumn Block 1 WO2 Compare and Order Any Numbers 2019 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 1 WO6 Compare and Order Any Integers 2022 AnswersDocument1 pageY6 Autumn Block 1 WO6 Compare and Order Any Integers 2022 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A AlkenesDocument1 pageA AlkenesAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6 Autumn Block 2 WO7 Long Division 3 2020 AnswersDocument1 pageY6 Autumn Block 2 WO7 Long Division 3 2020 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Common MultiplesDocument2 pagesCommon MultiplesAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics PYP 5 - Brian Murray - Oxford 2019Document168 pagesMathematics PYP 5 - Brian Murray - Oxford 2019Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6AutEoB1 Place Value BDocument2 pagesY6AutEoB1 Place Value BAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6AutEoB2 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division B v2 AnswersDocument4 pagesY6AutEoB2 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division B v2 AnswersAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- The Eye WorksheetDocument6 pagesThe Eye WorksheetAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Y6AutEoB2 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division ANSWERSDocument4 pagesY6AutEoB2 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division ANSWERSAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Interactive PDF The Circulatory System - Ver - 1Document2 pagesInteractive PDF The Circulatory System - Ver - 1Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A AlcoholsDocument1 pageA AlcoholsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A - Lewis Acids and BasesDocument1 pageA - Lewis Acids and BasesAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A - Ahl Electrochemical CellsDocument1 pageA - Ahl Electrochemical CellsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A11 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA11 - Spectrocscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A - Coloured Complexes QuestionsDocument1 pageA - Coloured Complexes QuestionsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A12 - Spectroscopic IdentificationDocument1 pageA12 - Spectroscopic IdentificationAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A - Energy Cycles QuestionsDocument2 pagesA - Energy Cycles QuestionsAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- A Data ResponseDocument2 pagesA Data ResponseAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet