Professional Documents
Culture Documents
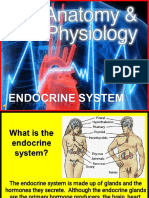
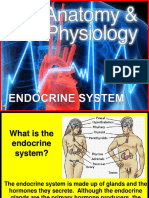
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Maryna KryvenkoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Maryna KryvenkoCopyright:
Available Formats
Glands Hormones Function
Hypothalamus liberins and plays an important role in controlling body temperature, thirst and hunger, water balance, sexual function,
statins emotional activity, and sleep. The hypothalamus sends hormones through the blood vessels which cause
the pituitary either to release or to inhibit the production of specific hormones.
adrenocorticotropic stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol which is important for regular carbohydrate
hormone metabolism and normal response to any stress;
somatotropin encourages the growth of bones and skeletal muscles and converts proteins into glucose;
prolactin stimulates the secretion of breast milk after childbirth ;
follitropin triggers the development of gametes in the respective sex;
Pituitary їЇ
(hypophysis) thyrotropin activates the thyroid to release hormones;
luteinizing stimulates ovulation in the female and the secretion female and
hormone the secretion of sex hormones (progesterone and testosterone)
in both the female and the male.
E melanocyte- increases the production of melanin in melanocytes causing the darkening of the skin.
stimulating hormone
§
oxytocin stimulates the muscles of the uterus during the delivery and the muscles surrounding the mammary ducts to
release milk.
"÷"
: antidiuretic stimulates water reabsorption by the kidneys and increases blood pressure. When more
hormone antidiuretic hormone is secreted, less urine is produced.
Pineal gland melatonin that influences the sleep-wake cycle. The production of melatonin increases during darkness.
(epiphysis)
thyroxine (T4) and increase cell metabolism.
Thyroid gland + triiodothyronine (T3)
parathyroids
+ calcitonin regulate the calcium levels in the blood and tissues.
Thymus thymosin responsible for stimulating the maturation of lymphocytes into T cells of the immune system.
epinephrine
(adrenaline) both of them are capable of increasing the heart rate, the force of the heart contrac-tion, blood pressure,
Adrenal
medulla vasoconstriction in the skin and viscera, relaxing airway smooth muscles, and assisting in glucose
norepinephrine
metabolism.
(noradrenaline)
cortisol helps to control the body's use of fats, proteins and carbohydrates, responds to stress, suppresses
inflammation, and regulates blood pressure.
Adrenal
aldosterone regulates blood volume, blood pressure, and electrolytes;
cortex
estrogen and may contribute to rapid body growth during early puberty.
androgen
Pancreas glucagon response to raise blood sugar levels
insulin response to low blood sugar levels.
Gonads estrogen is important in the development and maintenance of the female secondary sex characteristics (eg. body hair
growth, breast development) and the regulation of the menstrual cycle.
progesterone complete the pregnancy prepa-rations. If pregnancy happens, the placenta takes over the production of
pro-gesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, secretion of the hormone stops, and the
menstrual period is followed.
testosterone stimulates the development of the male secondary sex characteristics (e.g. development of the
reproductive organs, growth of facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and
growth of the skeletal muscles), promotes the maturation of sperm.
You might also like
- An Introduction To Behavioral Endocrinol PDFDocument887 pagesAn Introduction To Behavioral Endocrinol PDFPaula100% (23)
- Onion Root Tip MitosisDocument5 pagesOnion Root Tip MitosisNor Ashikin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Document61 pagesEndocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Almira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesEndocrine Systemmarygracenezel13No ratings yet
- Role of Hormones Endocrine 1Document37 pagesRole of Hormones Endocrine 1zyrle (zayrieeo)No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemUzma Khan100% (1)
- 10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument34 pages10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- No Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesNo Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandKush KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Week5 Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesWeek5 Endocrine SystemHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Q3 1 EndocrineDocument42 pagesQ3 1 Endocrineerlamay.valeNo ratings yet
- 3 +endocrine+systemDocument41 pages3 +endocrine+systemDew JirawatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKirsten GomezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System RevDocument3 pagesEndocrine System RevWena Grace NonanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Functions & GlandsDocument11 pagesEndocrine System Functions & Glandssaeed qurashiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument60 pagesEndocrine SystemseibdNo ratings yet
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDocument39 pagesCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 5 Endocrine SystemJiro MarianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Hormone PairingDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Hormone PairingDóra ImreNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System LessonDocument47 pagesEndocrine System LessonMA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- Different Glands of The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesDifferent Glands of The Endocrine SystemNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesThe Endocrine SystemPhea VillarealNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Animal HormonesDocument16 pagesAnimal HormonesMaria Theresa HerreroNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 2nd Check Edited 5Document13 pagesDiabetes 2nd Check Edited 5Catiereign VerdeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine-System Science LessonDocument38 pagesEndocrine-System Science LessonKea BlankyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and Intregation 11 BioDocument5 pagesChemical Coordination and Intregation 11 BioAkanksha AvasthiNo ratings yet
- Task 3Document15 pagesTask 3maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- Async Ina2 Medicalsurgicalnsg Midterm Usls Bsn4 Feb2023 v2 With Vids AsynchDocument156 pagesAsync Ina2 Medicalsurgicalnsg Midterm Usls Bsn4 Feb2023 v2 With Vids AsynchMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Assignment MetabolismDocument10 pagesAssignment MetabolismCherrylyn RaytosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument17 pagesHuman PhysiologySharanya BasakNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of HormonesDocument26 pagesBiochemistry of HormonesZayan Haider0% (1)
- Endocrine System HandoutDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Handoutker KerNo ratings yet
- AnP Endocrine System 2Document21 pagesAnP Endocrine System 2Nicole JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDocument38 pagesHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid GlandsDocument3 pagesParathyroid GlandsRosita RamosNo ratings yet
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Lesson 4-The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesLesson 4-The Endocrine SystemkreativekerelleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Lecture - Chapter 37 - Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesLecture - Chapter 37 - Endocrine SystemAnonymous SrGzihNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine SystemReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyJoanna EdenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UNIT IIDocument10 pagesChapter 2 UNIT IIAyen LatosaNo ratings yet
- An Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesAn Endocrine SystemEvbogame Iyare IbhadeNo ratings yet
- ABT Endocrine PPDocument39 pagesABT Endocrine PPABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NoteDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NoteFumzy AdelakunNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System A & P MODDocument14 pagesEndocrine System A & P MODDollyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System A & PDocument14 pagesEndocrine System A & PDollyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemJason MacatuggalNo ratings yet
- Science 10 The Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesScience 10 The Endocrine SystemTO NT ONNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 pagesEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiNo ratings yet
- Anfis EndokrinDocument14 pagesAnfis Endokrinyolanda merinskyNo ratings yet
- Control of Our Bodies HomeostasisDocument20 pagesControl of Our Bodies HomeostasisJohn Philip VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReportDocument5 pagesNervous System ReportsharkNo ratings yet
- Muscular-Endocrine 1Document7 pagesMuscular-Endocrine 1JD BunielNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Week 1 Module 1Document34 pagesQuarter 3 Week 1 Module 1Juliana Sophia BungalsoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Neurotransmitter and HormonesDocument17 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Neurotransmitter and HormonesRachel Ann FranchescaNo ratings yet
- Balancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthFrom EverandBalancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Табл Англ DigestiveDocument3 pagesТабл Англ DigestiveMaryna KryvenkoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System + Cardiovascular System (1 Part)Document16 pagesRespiratory System + Cardiovascular System (1 Part)Maryna KryvenkoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesDigestive SystemMaryna KryvenkoNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument17 pagesUrinary SystemMaryna KryvenkoNo ratings yet
- 10 Simple Home Remedies For Flawless Smooth Glowing SkinDocument2 pages10 Simple Home Remedies For Flawless Smooth Glowing SkinFirdous BhatNo ratings yet
- Teeth SettingDocument53 pagesTeeth Settingdoctor0002No ratings yet
- tmpD6E8 TMPDocument38 pagestmpD6E8 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Genetic RecombinationDocument55 pagesGenetic RecombinationRiyaniMartyasariNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure MeasurementDocument5 pagesBlood Pressure Measurementksjanarthanan_sriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Leaves - The Food Factory of PlantsDocument4 pagesLesson 2 Leaves - The Food Factory of PlantsRama Nathan0% (2)
- N5 Biology All 2018Document48 pagesN5 Biology All 2018Sajida CheemaNo ratings yet
- Sorenson Atlas of Human Histology Chapter 14Document42 pagesSorenson Atlas of Human Histology Chapter 14NUEVO SUSANNA N.No ratings yet
- 5851 978-1-5386-4658-8/18/$31.00 ©2019 Ieee Icassp 2019Document5 pages5851 978-1-5386-4658-8/18/$31.00 ©2019 Ieee Icassp 2019Swarnadip SahaNo ratings yet
- Pyschology CAT MKUDocument3 pagesPyschology CAT MKUPeter KNo ratings yet
- PeroxisomesDocument8 pagesPeroxisomesDayana PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Exam Earth and Life SciencesDocument4 pagesSecond Quarter Exam Earth and Life SciencespudoydoyNo ratings yet
- Sub Division 1. Enterocoelous Coelomata: Coelom Is Enterocoel Which OriginatesDocument2 pagesSub Division 1. Enterocoelous Coelomata: Coelom Is Enterocoel Which OriginatesyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology May 2009 D. BambicDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Psychology May 2009 D. Bambicangeljin1207No ratings yet
- Revised SNCU Mentoring ChecklistDocument6 pagesRevised SNCU Mentoring Checklistrani26octNo ratings yet
- Bio Essay CardioDocument3 pagesBio Essay CardiopadmaszNo ratings yet
- Lab1ESR 08Document11 pagesLab1ESR 08Muhamad AfidinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills ChecklistDocument8 pagesNursing Skills Checklistapi-353656227No ratings yet
- Fish Anatomy For Fish BreedingDocument2 pagesFish Anatomy For Fish BreedinghumanupgradeNo ratings yet
- Brain ExercisesDocument2 pagesBrain Exercisespaulxe100% (1)
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument31 pagesFundamentals of NursingCherrie Dianne SeriñaNo ratings yet
- 4 Merged 1516624856 PDFDocument50 pages4 Merged 1516624856 PDFVya PrabandariNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Mind MapDocument1 pageHypertension Mind MapBrett DaleNo ratings yet
- Activity 6-Module 1Document1 pageActivity 6-Module 1Kristine Ibarreta-JazulNo ratings yet
- Murthy Et Al 2011 Starch Hydrolysis Modeling Application To Fuel Ethanol ProductionDocument13 pagesMurthy Et Al 2011 Starch Hydrolysis Modeling Application To Fuel Ethanol ProductionMatache GabrielaNo ratings yet
- BCH301Document19 pagesBCH301yabdallahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format Ready To PrintDocument2 pagesDrug Study Format Ready To Printmay_hisolerNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids in Animal NutritionDocument515 pagesAmino Acids in Animal NutritionLuciana EmanuelleNo ratings yet