Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Sheet 5 Questions
Tutorial Sheet 5 Questions
Uploaded by
Gautam ChauhanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Sheet 5 Questions
Tutorial Sheet 5 Questions
Uploaded by
Gautam ChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial sheet - 5
Q1. Consider two-dimensional square lattice of side 3.0 Å. At what electron momentum values
do the sides of first Brillouin zone appear? What is the energy of free electrons with the
momentum ?
Q2. Find the position of Fermi level EF (w.r.t. EC) at room temperature (= 27°C) for
germanium crystal having 5 × 1022 atoms/m3.
Q3. Consider the Fermi level, 0.3 eV below the conduction band at room temperature (27°C)
in an n-type semiconductor. If the temperature is raised to 57°C, what would be the new
position of Fermi level?
Q4. For an intrinsic semiconductor having band gap Eg = 0.7eV, calculate the density of
holes and electrons at room temperature (= 27°C).
Q5. Calculate the Hall coefficient of sodium on the basis of free electron model, given that
Sodium has a bcc (body centered cubic) structure of cell of side 4.28A.
Q6. Assuming that there are 5 × 1028 atoms/m3 in copper, find the Hall coefficient.
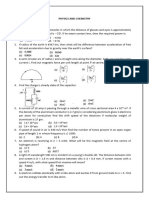
Q7. The figure below shows a portion of a silver ribbon with z1 = 11.8 mm and y1 = 0.23 mm
carrying a current of 120 A in the + x-direction. The ribbon lies in a uniform magnetic field, in
the y-direction, with magnitude 0.95 T. If there are 5.85 × 1028 electrons per cubic meter, find
(a) the magnitude of the drift velocity of the electrons in the x-direction; (b) the magnitude and
direction of the electric field in the z-direction due to the Hall effect; (c) the Hall emf.
Q8. Hall coefficient of a specimen of silicon found to be 3.66 × 10–4 m3C–1. The resistivity of
the specimen is 8.93 × 10–3 m. Find the mobility and density of the charge carriers.
You might also like
- Problem Sheet - 1: Figure 1. Conduction Band Figure 2. Valance BandDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet - 1: Figure 1. Conduction Band Figure 2. Valance BandM DNo ratings yet
- LMS Solutions QuantumDocument260 pagesLMS Solutions QuantumMartin SeungWhan Kim86% (7)
- Engn 0410 HW #9Document5 pagesEngn 0410 HW #9Red BrokerNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Vishal VermaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 4Document2 pagesAssignment 3 4Anuza PaneruNo ratings yet
- Updated Unit 1 - Semiconductors Question Bank AY-2022-2023Document3 pagesUpdated Unit 1 - Semiconductors Question Bank AY-2022-2023Lavanya JadhavNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi: I 15 3/2 E /2KT 3 G o oDocument2 pagesDepartment of Physics and Astrophysics University of Delhi: I 15 3/2 E /2KT 3 G o oAmalendu PramanickNo ratings yet
- Physical Electronics PRACTICE QUESTIONS SheetDocument3 pagesPhysical Electronics PRACTICE QUESTIONS SheetHosea MuchiriNo ratings yet
- Department of Applied Sciences (Physics)Document2 pagesDepartment of Applied Sciences (Physics)gshreyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Electronics Devices and Circuit - Module 2Document3 pagesAssignment - Electronics Devices and Circuit - Module 2ankit sauravNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument30 pagesProblemsjustinl1375535100% (1)
- VL2023240107488 DaDocument5 pagesVL2023240107488 Dapranavdeshpande2499No ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 (Semiconductor Basics)Document2 pagesAssignment - 1 (Semiconductor Basics)Utkarsh AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Bohr and Rydberg - Atomic Spectra ProblemsDocument13 pagesBohr and Rydberg - Atomic Spectra ProblemssubstitutescribdNo ratings yet
- MM406: Semiconductor Devices and Processing Tutorial 1Document4 pagesMM406: Semiconductor Devices and Processing Tutorial 1Vasit AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 Chapter - Quantum Mechanics (Applications of Schrodinger's Equation)Document6 pagesAssignment 5 Chapter - Quantum Mechanics (Applications of Schrodinger's Equation)Aditya TararNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document2 pagesHW 2AlaaeeeNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 98Document2 pagesQuiz1 98Rajveer FandanNo ratings yet
- INPhO 2001Document6 pagesINPhO 2001gudapudi ramaniNo ratings yet
- Physics of MetalDocument3 pagesPhysics of MetalChayon MondalNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentf20211509No ratings yet
- Slides PHY 112Document221 pagesSlides PHY 112salman104alviNo ratings yet
- Physics of VLSI Devices (ECE-5018) Digital Assignment - IDocument5 pagesPhysics of VLSI Devices (ECE-5018) Digital Assignment - IShreyas RaoNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Important Topic List 2024Document2 pagesXII Physics Important Topic List 2024khaanianasNo ratings yet
- Tut SheetDocument9 pagesTut SheetramparkNo ratings yet
- 2003 Qualifying ExamDocument5 pages2003 Qualifying ExamrujintoNo ratings yet
- CommentaryDocument31 pagesCommentaryasdasdNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems Proposed 2013-2014 INGDocument17 pagesPhysics I Problems Proposed 2013-2014 INGVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- Msci406 Sols05 PDFDocument3 pagesMsci406 Sols05 PDFEryWiyadi100% (1)
- Problem Set SemiconductorDocument1 pageProblem Set SemiconductorTushaarKumarNo ratings yet
- PYL558: Statistical MechanicsDocument2 pagesPYL558: Statistical MechanicsAkriti SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 PHY121Document2 pagesAssignment2 PHY121ወልደ መስቀል ፍቅሩNo ratings yet
- Tugas Fisika IntiDocument35 pagesTugas Fisika IntiSharasanty PNo ratings yet
- Sample Assignments SDMDocument10 pagesSample Assignments SDMSankar SaroNo ratings yet
- Physics Assignment 5Document2 pagesPhysics Assignment 5Anuza PaneruNo ratings yet
- 1 3 Class 12 Cbse Physics - Test - Ncert Problems: 1.06 Å Separation?Document3 pages1 3 Class 12 Cbse Physics - Test - Ncert Problems: 1.06 Å Separation?Harshnna GururajanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet Statistical PhysicsDocument2 pagesTutorial Sheet Statistical PhysicsDIVYANSH BAJPAINo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-1. Semiconductor Models: E H H Planck's Constant (H 6.63Document6 pagesChapter 2-1. Semiconductor Models: E H H Planck's Constant (H 6.63Anish BansalNo ratings yet
- Practice Set - 1Document1 pagePractice Set - 1rishavkmNo ratings yet
- (Assignments 4) : I I I I IDocument3 pages(Assignments 4) : I I I I IAhmed JamalNo ratings yet
- SMD 3apowerDocument104 pagesSMD 3apowerGregory LevantNo ratings yet
- DielectricsDocument61 pagesDielectricsKanda VelanNo ratings yet
- University Exam QBDocument3 pagesUniversity Exam QBthaakurraahilNo ratings yet
- Past Papers PDFDocument34 pagesPast Papers PDFAllan AzamboNo ratings yet
- Energy Levels in One DimensionDocument13 pagesEnergy Levels in One DimensionSaiia GusttiNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics: Ij Ij M Ij N IjDocument4 pagesSolid State Physics: Ij Ij M Ij N Ijc1ee5686f5No ratings yet
- Physics XII: Important Questions 2020 NumericalDocument3 pagesPhysics XII: Important Questions 2020 NumericalShaheer JafriNo ratings yet
- Physics of VLSI Devices (ECE5018) - CAT-1 Solutions: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDocument14 pagesPhysics of VLSI Devices (ECE5018) - CAT-1 Solutions: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEVibha M VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 Homework Solution On University Physics IIDocument8 pagesChapter 27 Homework Solution On University Physics IIFrancisco JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics SolutionDocument28 pagesModern Physics Solutionskadogg2250% (2)
- Pdf&rendition 1 1Document13 pagesPdf&rendition 1 1vijay balajiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet: Origin of Quantum TheoryDocument5 pagesTutorial Sheet: Origin of Quantum TheorySukhwinder Singh Gill100% (1)
- Question Bank For Physics - Ii Regulation 2013Document10 pagesQuestion Bank For Physics - Ii Regulation 2013PRIYA RAJINo ratings yet
- Physics Mar 2009 EngDocument8 pagesPhysics Mar 2009 EngPrasad C M50% (2)
- Lecture Notes For: Solid State Electronic Devices: With Modifications by M. Nadeem Akram and Per OhlckersDocument45 pagesLecture Notes For: Solid State Electronic Devices: With Modifications by M. Nadeem Akram and Per OhlckersSaleha QuadsiaNo ratings yet
- Important ProblemsDocument2 pagesImportant ProblemsGanesh MogaveeraNo ratings yet
- III The Sommerfeld Free Electron Theory of Metals 2000 Solid State PhysicsDocument25 pagesIII The Sommerfeld Free Electron Theory of Metals 2000 Solid State PhysicsChristian Julian ForeroNo ratings yet
- MM5017 Assignment1Document2 pagesMM5017 Assignment1Arg SreekarNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Real Kabaddi Fixtures.Document2 pagesReal Kabaddi Fixtures.Gautam ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Hall EffectDocument10 pagesHall EffectGautam ChauhanNo ratings yet
- IH CurveDocument8 pagesIH CurveGautam ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Newton's RingsDocument8 pagesNewton's RingsGautam ChauhanNo ratings yet