Professional Documents
Culture Documents
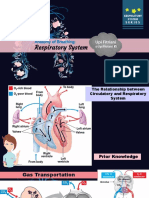
Double Circulation
Double Circulation
Uploaded by
Aarushi PhilemCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Respiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)Document4 pagesRespiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)PkernNo ratings yet
- Transporte de GasesDocument9 pagesTransporte de GasesSebastián Jurado PintoNo ratings yet
- Pulmo Physio-Transport 2Document35 pagesPulmo Physio-Transport 2Mich Therese AbejeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41, Pages 527-537: Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in Blood and Tissue FluidsDocument46 pagesChapter 41, Pages 527-537: Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in Blood and Tissue FluidsAlia HaiderNo ratings yet
- ANPS 020 Cornbrooks 04-11-14Document41 pagesANPS 020 Cornbrooks 04-11-14Sandeep ManuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Breath - HemoglobinDocument21 pagesAnatomy of Breath - HemoglobinAfifah NadiaNo ratings yet
- Respiration 3 SlidesDocument28 pagesRespiration 3 SlidesSaajid AmraNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Gaseous ExchangeDocument46 pages6.3 Gaseous ExchangeSurvin KandhariNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument12 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessneh882016No ratings yet
- Physio Paramed Complete 2009 NewDocument69 pagesPhysio Paramed Complete 2009 NewJose Luis BlancoNo ratings yet
- Cap No GraphyDocument41 pagesCap No GraphyCheryls RajuNo ratings yet
- 10a. HipoksiaDocument21 pages10a. HipoksiaputrianitaNo ratings yet
- Bers Resp No Anim 03Document65 pagesBers Resp No Anim 03Alexandra NadinneNo ratings yet
- Respiration at High Altitudes AtfDocument5 pagesRespiration at High Altitudes Atfpnsscsny29No ratings yet
- Transport of Co2 in The BloodDocument8 pagesTransport of Co2 in The BloodTaimoor Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Cardiovascular SystemDocument119 pagesChapter 13 - Cardiovascular SystemmalakajameahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41Document81 pagesChapter 41Dane SucbotNo ratings yet
- Benevision Benevision: Vco2 & Metabolic MonitoringDocument28 pagesBenevision Benevision: Vco2 & Metabolic MonitoringItalmarNo ratings yet
- Central Venous Blood Gas Analysis PDFDocument11 pagesCentral Venous Blood Gas Analysis PDFZamzam DomaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ProcedureDocument5 pagesDiagnostic ProcedureCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- (Materi) Jurus Jitu Paham Ventilator Tanpa Tapi - Dr. Arie Zainul Fatoni, SP - An, KICâDocument62 pages(Materi) Jurus Jitu Paham Ventilator Tanpa Tapi - Dr. Arie Zainul Fatoni, SP - An, KICâGladys JuaneNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document9 pagesNull 1sscvijay98No ratings yet
- Respiration - Behavior of GasesDocument25 pagesRespiration - Behavior of GasesSodeinde SimeonNo ratings yet
- RespiDocument11 pagesRespiMonique BorresNo ratings yet
- Gas Transport in Blood PPT 1Document34 pagesGas Transport in Blood PPT 1CLEMENTNo ratings yet
- CapnografiaDocument19 pagesCapnografiaJunior BarbozaNo ratings yet
- Calibration Gas DatasheetDocument5 pagesCalibration Gas DatasheetSiti MustanirohNo ratings yet
- Ans MachineDocument105 pagesAns MachineDebreworkNo ratings yet
- Sample S Lides: CapnographyDocument19 pagesSample S Lides: Capnographykadek andika dwi putra100% (1)
- Respiratory Lecture 2 (1 Slide Per Page)Document33 pagesRespiratory Lecture 2 (1 Slide Per Page)AnshikaNo ratings yet
- 09 Principios en Ventilacion MecanicaDocument35 pages09 Principios en Ventilacion Mecanicadalialm1944No ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Human (Exercise)Document4 pagesGaseous Exchange in Human (Exercise)Daniel LohNo ratings yet
- Transport of Carbon DioxideDocument9 pagesTransport of Carbon DioxideBarkat ShazliNo ratings yet
- Respiration SystemDocument2 pagesRespiration SystemCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange, Transport of O2 and Co2 in The BloodDocument81 pagesGas Exchange, Transport of O2 and Co2 in The Bloodspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Presentation Colmac Iiar 2017 GDL EnglishDocument29 pagesPresentation Colmac Iiar 2017 GDL EnglishgamunozdNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood GasDocument255 pagesArterial Blood GasMark Joshua S CruzNo ratings yet
- Hudson 2012Document10 pagesHudson 2012Rin4lNo ratings yet
- 15, 16, and 17 - Respiratorio 2011Document86 pages15, 16, and 17 - Respiratorio 2011Redes HostNo ratings yet
- Pendekatan Awal Penderita EmergencyDocument16 pagesPendekatan Awal Penderita EmergencyFeni DianiNo ratings yet
- TERAPI OKSIGEN (Basic: Binasal Dan Facemask) PDFDocument43 pagesTERAPI OKSIGEN (Basic: Binasal Dan Facemask) PDFchristintinneNo ratings yet
- Respirasi Internalnya BuyungDocument7 pagesRespirasi Internalnya BuyungBuyung RamadhanNo ratings yet
- DIFFISIONDocument51 pagesDIFFISIONkhamisiabdulNo ratings yet
- Ventricule UniqueDocument31 pagesVentricule UniquesurasuarezlopezNo ratings yet
- Rs4-Gas Exchange and TransportDocument5 pagesRs4-Gas Exchange and TransportGabriella ChafrinaNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System/4: Ventilation Perfusion RateDocument28 pagesRespiratory System/4: Ventilation Perfusion RateMohammad AlomariNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Transport2Document49 pagesOxygen Transport2Michelle SalimNo ratings yet
- HOBSON - Nylon Bolts and NutsDocument2 pagesHOBSON - Nylon Bolts and NutsJJ FloresNo ratings yet
- PSG 503 Respiratory LectureDocument54 pagesPSG 503 Respiratory LectureOdunfa OlufeyikemiNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange 2-1Document21 pagesGas Exchange 2-1asmaaalmesaifriNo ratings yet
- Capnography 48Document18 pagesCapnography 48kota vamshiNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure 2010Document87 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure 2010bassist5217100% (1)
- Respiratory and Blood VesselsDocument14 pagesRespiratory and Blood VesselsAngelika VargasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure: Lack of Respiratory SuccessDocument41 pagesRespiratory Failure: Lack of Respiratory SuccessYS NateNo ratings yet
- Transfer FaktorDocument19 pagesTransfer FaktorJelenaJankovNo ratings yet
- BSF Brochure 2022Document88 pagesBSF Brochure 2022Wagner LimaNo ratings yet
- First Step To ModDocument41 pagesFirst Step To Modcarlos ali issaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Document29 pagesGas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Fatiha TamadNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsFrom EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy of Heart, Circulation Aortic Arches EtcDocument36 pagesComparative Anatomy of Heart, Circulation Aortic Arches EtcNarasimha Murthy100% (4)
- AS Biology F211 Animal Transport Workbooklet Answers p1-10Document11 pagesAS Biology F211 Animal Transport Workbooklet Answers p1-10T-Jay Ellis-DaleNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemrobhel740% (2)
- ME Sci 9 Q1 0103 PSDocument18 pagesME Sci 9 Q1 0103 PScassiopeia bianca sartigaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Veterinary Pharmacology and Clinical ToxicologyDocument155 pagesSystemic Veterinary Pharmacology and Clinical ToxicologySunil100% (1)
- Circulatory System-ELSDocument44 pagesCirculatory System-ELSJomer CasimNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Grade 9 - Blood CirculationDocument7 pagesPpt-Grade 9 - Blood CirculationEdralyn Panes VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1Document24 pagesLife Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1raghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Worksheet 12 Heart Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesLaboratory Worksheet 12 Heart Structure and FunctionAndrea SaldivarNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Periodic TestDocument2 pagesFirst Quarter Periodic TestNur ShaNo ratings yet
- HUman Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesHUman Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Strategi A - Sains Tingkatan 3Document159 pagesJawapan Strategi A - Sains Tingkatan 3helenafrancis245No ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 8 The Circulatory System - Edexcel Biology GCSEDocument63 pagesFlashcards - Topic 8 The Circulatory System - Edexcel Biology GCSEPraise Kinkin Princess GanaNo ratings yet
- Nota Dan Amali Anatomi Dan Fisiologi - 3 - Nota Jantung & Sis. KardiovaskularDocument32 pagesNota Dan Amali Anatomi Dan Fisiologi - 3 - Nota Jantung & Sis. KardiovaskularFadilla LayangNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument13 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyDwi Junita SariNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemMr. Christian ParabuacNo ratings yet
- Modules23 01to23 Animal03Document11 pagesModules23 01to23 Animal03Robitha Rahmi ArindiniNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ch 11-Ans SheetDocument6 pagesAssignment-Ch 11-Ans Sheetrachna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High School: Department of Education Schools Division Office-Quezon CityDocument7 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High School: Department of Education Schools Division Office-Quezon CityEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- acutecaretestinghandbookPDFversion v2Document236 pagesacutecaretestinghandbookPDFversion v2nompanemNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Q2 - Test No 3Document2 pagesScience 6 - Q2 - Test No 3MARY JANE PALISPISNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Comprehensive Exam With Answers and RationaleDocument16 pages100 Item Comprehensive Exam With Answers and RationaleJoeben L. DisuNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp 4Document13 pagesLab Report Exp 4NURUL AIHAN AHMAD HILMINo ratings yet
- Sci 9 Q1 Module 1Document22 pagesSci 9 Q1 Module 1John Merby GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology Ii - Long QuizDocument14 pagesReviewer in General Biology Ii - Long QuizBernardine Angela YanezaNo ratings yet
- Transport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsDocument17 pagesTransport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsTekomiNo ratings yet
- Oberoi International School Teacher's Name : Shobi Nandkeolyar Class : GR 9 Biology Student's Name : Parashie Sidhwani Date : 15/04/20Document44 pagesOberoi International School Teacher's Name : Shobi Nandkeolyar Class : GR 9 Biology Student's Name : Parashie Sidhwani Date : 15/04/20Parashie SidhwaniNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesThe Circulatory SystemAyesha DuaNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceDocument11 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceGodfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.No ratings yet
- First Grading VIDocument82 pagesFirst Grading VIIvy Villanueva Divino100% (1)
Double Circulation
Double Circulation
Uploaded by
Aarushi PhilemOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Double Circulation
Double Circulation
Uploaded by
Aarushi PhilemCopyright:
Available Formats
BREATHING AND EXCHANGE 63 U5
OF GASES
INSPIRED AIR EXPIRED AIR
ALVEOLAR
PO2 104
AIR
PCO2 =
40
mm H9
mm Hg
-
ALVEOLUS OF LUNG
BLOOD ENTERING Co2 O2
ALVEOLAR CAPILLARIES/
Po 40 mm Hg BLOOD LEAVING
Pco 45 mm Hg CO2 OP2 ALVEOLAR CAPILLARIES
Po 95 mm Hg
PULMONARY ARTERIES Pco 40 mm Hg
- PULMONARY VEINs
RIGHT ATRIUM
LEFT ATRIUM
RIGHT VENTRICLE
-LEFT VENTRICLE
SYSTEMIC VEINS.
CARRYING DEOXYGENATED HEART SYSTEMIC ARTERIES
BLOOD) (CARRYING OXYGENATED
BLOOD)
BLOOD LEAVING CO2 O2
TISSUE CAPILLARIES BLOOD ENTERING
TISSUE CAPILLARIES
PO2 40 mm Hg PO2 95 mm Hg
PCO2 = 45 mm Hg
PCO2 40 mm Hg
CO2
oo
BODY TISSUE CELLS
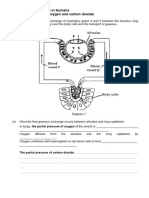
Fig. 17.11. Diagrammatic representation of exchange of gases () between the alveolus
and pulmonary blood capillary and (i) between the blood capillary and body tissue cells.
xchange. of gases between blood and tissue cells (Fig. 17.l
Ihe exchange
lange of gases (i.e., oxygen and carbon
dioxide) between tissue blood capillaries
of oxygen is higher
C s 1s called internal respiration. The partial pressure carbon dioxide
Hg) than mm Hg) and the partial pressure of
a(40n that
cr
that of
of the body cells (40
Therefore, oxygen diffuses
mm ) than that of the body cells (45 mm Hg).
Hg)
he fluid and carbon dioxide
diffuses
apillary blood
a r y blood to to the body cells through tissue
becomes deoxgenated.
dy cells of the capillary blood via tissue fluid. Now the blood
later is
i n e d to the heart and hence to the lungs.
ort of Gases Fig. 17.11
od
transports oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Bood ansport
carmies of Oxygerfrom
in the Blood
the lungs the heart and
to
from the heart
to varnous boy
Dygenis
gen is gen
Is transported in the following manners
You might also like
- Respiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)Document4 pagesRespiratory-Equations (Adam Hollingworth)PkernNo ratings yet
- Transporte de GasesDocument9 pagesTransporte de GasesSebastián Jurado PintoNo ratings yet
- Pulmo Physio-Transport 2Document35 pagesPulmo Physio-Transport 2Mich Therese AbejeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41, Pages 527-537: Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in Blood and Tissue FluidsDocument46 pagesChapter 41, Pages 527-537: Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in Blood and Tissue FluidsAlia HaiderNo ratings yet
- ANPS 020 Cornbrooks 04-11-14Document41 pagesANPS 020 Cornbrooks 04-11-14Sandeep ManuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Breath - HemoglobinDocument21 pagesAnatomy of Breath - HemoglobinAfifah NadiaNo ratings yet
- Respiration 3 SlidesDocument28 pagesRespiration 3 SlidesSaajid AmraNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Gaseous ExchangeDocument46 pages6.3 Gaseous ExchangeSurvin KandhariNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument12 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessneh882016No ratings yet
- Physio Paramed Complete 2009 NewDocument69 pagesPhysio Paramed Complete 2009 NewJose Luis BlancoNo ratings yet
- Cap No GraphyDocument41 pagesCap No GraphyCheryls RajuNo ratings yet
- 10a. HipoksiaDocument21 pages10a. HipoksiaputrianitaNo ratings yet
- Bers Resp No Anim 03Document65 pagesBers Resp No Anim 03Alexandra NadinneNo ratings yet
- Respiration at High Altitudes AtfDocument5 pagesRespiration at High Altitudes Atfpnsscsny29No ratings yet
- Transport of Co2 in The BloodDocument8 pagesTransport of Co2 in The BloodTaimoor Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Cardiovascular SystemDocument119 pagesChapter 13 - Cardiovascular SystemmalakajameahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41Document81 pagesChapter 41Dane SucbotNo ratings yet
- Benevision Benevision: Vco2 & Metabolic MonitoringDocument28 pagesBenevision Benevision: Vco2 & Metabolic MonitoringItalmarNo ratings yet
- Central Venous Blood Gas Analysis PDFDocument11 pagesCentral Venous Blood Gas Analysis PDFZamzam DomaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ProcedureDocument5 pagesDiagnostic ProcedureCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- (Materi) Jurus Jitu Paham Ventilator Tanpa Tapi - Dr. Arie Zainul Fatoni, SP - An, KICâDocument62 pages(Materi) Jurus Jitu Paham Ventilator Tanpa Tapi - Dr. Arie Zainul Fatoni, SP - An, KICâGladys JuaneNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document9 pagesNull 1sscvijay98No ratings yet
- Respiration - Behavior of GasesDocument25 pagesRespiration - Behavior of GasesSodeinde SimeonNo ratings yet
- RespiDocument11 pagesRespiMonique BorresNo ratings yet
- Gas Transport in Blood PPT 1Document34 pagesGas Transport in Blood PPT 1CLEMENTNo ratings yet
- CapnografiaDocument19 pagesCapnografiaJunior BarbozaNo ratings yet
- Calibration Gas DatasheetDocument5 pagesCalibration Gas DatasheetSiti MustanirohNo ratings yet
- Ans MachineDocument105 pagesAns MachineDebreworkNo ratings yet
- Sample S Lides: CapnographyDocument19 pagesSample S Lides: Capnographykadek andika dwi putra100% (1)
- Respiratory Lecture 2 (1 Slide Per Page)Document33 pagesRespiratory Lecture 2 (1 Slide Per Page)AnshikaNo ratings yet
- 09 Principios en Ventilacion MecanicaDocument35 pages09 Principios en Ventilacion Mecanicadalialm1944No ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in Human (Exercise)Document4 pagesGaseous Exchange in Human (Exercise)Daniel LohNo ratings yet
- Transport of Carbon DioxideDocument9 pagesTransport of Carbon DioxideBarkat ShazliNo ratings yet
- Respiration SystemDocument2 pagesRespiration SystemCarina JLNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange, Transport of O2 and Co2 in The BloodDocument81 pagesGas Exchange, Transport of O2 and Co2 in The Bloodspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Presentation Colmac Iiar 2017 GDL EnglishDocument29 pagesPresentation Colmac Iiar 2017 GDL EnglishgamunozdNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood GasDocument255 pagesArterial Blood GasMark Joshua S CruzNo ratings yet
- Hudson 2012Document10 pagesHudson 2012Rin4lNo ratings yet
- 15, 16, and 17 - Respiratorio 2011Document86 pages15, 16, and 17 - Respiratorio 2011Redes HostNo ratings yet
- Pendekatan Awal Penderita EmergencyDocument16 pagesPendekatan Awal Penderita EmergencyFeni DianiNo ratings yet
- TERAPI OKSIGEN (Basic: Binasal Dan Facemask) PDFDocument43 pagesTERAPI OKSIGEN (Basic: Binasal Dan Facemask) PDFchristintinneNo ratings yet
- Respirasi Internalnya BuyungDocument7 pagesRespirasi Internalnya BuyungBuyung RamadhanNo ratings yet
- DIFFISIONDocument51 pagesDIFFISIONkhamisiabdulNo ratings yet
- Ventricule UniqueDocument31 pagesVentricule UniquesurasuarezlopezNo ratings yet
- Rs4-Gas Exchange and TransportDocument5 pagesRs4-Gas Exchange and TransportGabriella ChafrinaNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument5 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessonu kumarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System/4: Ventilation Perfusion RateDocument28 pagesRespiratory System/4: Ventilation Perfusion RateMohammad AlomariNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Transport2Document49 pagesOxygen Transport2Michelle SalimNo ratings yet
- HOBSON - Nylon Bolts and NutsDocument2 pagesHOBSON - Nylon Bolts and NutsJJ FloresNo ratings yet
- PSG 503 Respiratory LectureDocument54 pagesPSG 503 Respiratory LectureOdunfa OlufeyikemiNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange 2-1Document21 pagesGas Exchange 2-1asmaaalmesaifriNo ratings yet
- Capnography 48Document18 pagesCapnography 48kota vamshiNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure 2010Document87 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure 2010bassist5217100% (1)
- Respiratory and Blood VesselsDocument14 pagesRespiratory and Blood VesselsAngelika VargasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Failure: Lack of Respiratory SuccessDocument41 pagesRespiratory Failure: Lack of Respiratory SuccessYS NateNo ratings yet
- Transfer FaktorDocument19 pagesTransfer FaktorJelenaJankovNo ratings yet
- BSF Brochure 2022Document88 pagesBSF Brochure 2022Wagner LimaNo ratings yet
- First Step To ModDocument41 pagesFirst Step To Modcarlos ali issaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Document29 pagesGas Exchange - Respirasi Blok 2.1.maret.15Fatiha TamadNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsFrom EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy of Heart, Circulation Aortic Arches EtcDocument36 pagesComparative Anatomy of Heart, Circulation Aortic Arches EtcNarasimha Murthy100% (4)
- AS Biology F211 Animal Transport Workbooklet Answers p1-10Document11 pagesAS Biology F211 Animal Transport Workbooklet Answers p1-10T-Jay Ellis-DaleNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemrobhel740% (2)
- ME Sci 9 Q1 0103 PSDocument18 pagesME Sci 9 Q1 0103 PScassiopeia bianca sartigaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Veterinary Pharmacology and Clinical ToxicologyDocument155 pagesSystemic Veterinary Pharmacology and Clinical ToxicologySunil100% (1)
- Circulatory System-ELSDocument44 pagesCirculatory System-ELSJomer CasimNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Grade 9 - Blood CirculationDocument7 pagesPpt-Grade 9 - Blood CirculationEdralyn Panes VillacrucisNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1Document24 pagesLife Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1raghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Worksheet 12 Heart Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesLaboratory Worksheet 12 Heart Structure and FunctionAndrea SaldivarNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Periodic TestDocument2 pagesFirst Quarter Periodic TestNur ShaNo ratings yet
- HUman Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesHUman Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Strategi A - Sains Tingkatan 3Document159 pagesJawapan Strategi A - Sains Tingkatan 3helenafrancis245No ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 8 The Circulatory System - Edexcel Biology GCSEDocument63 pagesFlashcards - Topic 8 The Circulatory System - Edexcel Biology GCSEPraise Kinkin Princess GanaNo ratings yet
- Nota Dan Amali Anatomi Dan Fisiologi - 3 - Nota Jantung & Sis. KardiovaskularDocument32 pagesNota Dan Amali Anatomi Dan Fisiologi - 3 - Nota Jantung & Sis. KardiovaskularFadilla LayangNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument13 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyDwi Junita SariNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemMr. Christian ParabuacNo ratings yet
- Modules23 01to23 Animal03Document11 pagesModules23 01to23 Animal03Robitha Rahmi ArindiniNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ch 11-Ans SheetDocument6 pagesAssignment-Ch 11-Ans Sheetrachna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High School: Department of Education Schools Division Office-Quezon CityDocument7 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High School: Department of Education Schools Division Office-Quezon CityEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- acutecaretestinghandbookPDFversion v2Document236 pagesacutecaretestinghandbookPDFversion v2nompanemNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Q2 - Test No 3Document2 pagesScience 6 - Q2 - Test No 3MARY JANE PALISPISNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Comprehensive Exam With Answers and RationaleDocument16 pages100 Item Comprehensive Exam With Answers and RationaleJoeben L. DisuNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp 4Document13 pagesLab Report Exp 4NURUL AIHAN AHMAD HILMINo ratings yet
- Sci 9 Q1 Module 1Document22 pagesSci 9 Q1 Module 1John Merby GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology Ii - Long QuizDocument14 pagesReviewer in General Biology Ii - Long QuizBernardine Angela YanezaNo ratings yet
- Transport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsDocument17 pagesTransport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsTekomiNo ratings yet
- Oberoi International School Teacher's Name : Shobi Nandkeolyar Class : GR 9 Biology Student's Name : Parashie Sidhwani Date : 15/04/20Document44 pagesOberoi International School Teacher's Name : Shobi Nandkeolyar Class : GR 9 Biology Student's Name : Parashie Sidhwani Date : 15/04/20Parashie SidhwaniNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesThe Circulatory SystemAyesha DuaNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceDocument11 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceGodfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.No ratings yet
- First Grading VIDocument82 pagesFirst Grading VIIvy Villanueva Divino100% (1)