Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AP Physics 1 Session1 Worksheet
AP Physics 1 Session1 Worksheet
Uploaded by
jaspienoodleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AP Physics 1 Session1 Worksheet
AP Physics 1 Session1 Worksheet
Uploaded by
jaspienoodleCopyright:
Available Formats
2024 AP DAILY: PRACTICE SESSIONS
AP Physics 1 Session 1 – MCQ
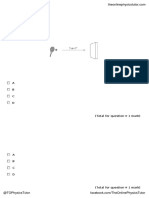
1. A Clay ball of mass 2m is moving horizontally with speed v0 just before colliding with a block of
mass m, as shown above. The block is suspended from a light string with length L. The clay sticks to
the block, and the block swings up to a maximum height h0 above the block’s initial position (where
h0<<L). The block then oscillates about its lowest position with period T0.
Which of the following quantities is the same immediately after the collision and at the instant the
block reaches height h0?
a. Linear momentum of the clay-block system
b. Angular momentum of the clay-block system about the top of the string
c. Total mechanical energy of the clay-block system
d. Total mechanical energy of the clay-block-Earth system
Source: Released AP Exam; Taken from: AP Classroom 1
2. Two people of unequal mass are initially standing still on ice with negligible friction. They then
simultaneously push each other horizontally. Afterward, which of the following is true?
a. The kinetic energies of the two people are equal.
b. The speeds of the two people are equal.
c. The momenta of the two people are of equal magnitude.
d. The less massive person has a smaller initial acceleration than the more massive person
Block 1 of mass m1 and block 2 of mass m2 are sliding along the same line on a horizontal
frictionless surface when they collide at time tc. The graph above shows the velocities of the
blocks as a function of time.
3. How does the kinetic energy of the two-block system after the collision compare with its kinetic
energy before the collision, and why?
a. It is less, because the blocks have the same velocity after the collision, so some of their kinetic
energy was transformed into internal energy.
b. It is less, because the blocks have velocities in opposite directions before the collision, so some of
their kinetic energy cancels.
c. It is the same, because the collision was instantaneous, so the effect of external forces during the
collision is negligible.
d. It is the same, because the blocks have the same velocity after the collision, and there is no friction
acting on them.
4. Which block has the greater mass, and what information indicates this?
a. Block 1, because it had a greater speed before the collision.
b. Block 1, because the velocity after the collision is in the same direction as its velocity before the
collision.
c. Block 2, because it had a smaller speed before the collision.
d. Block 2, because the final velocity is closer to the initial velocity of block 2 than it is to the initial
velocity of block 1.
Source: Released AP Exam; Taken from: AP Classroom 2
You might also like
- Unit 5 ExercisesDocument4 pagesUnit 5 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 ch09 Test BankDocument15 pagesWolfson Eup3 ch09 Test Bank陳禹誌No ratings yet
- Assignment 6 (19, 20) PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 6 (19, 20) PDFRRFNo ratings yet
- Ap Phys1 - Momentum Multiple Choice - 2019 01 09Document10 pagesAp Phys1 - Momentum Multiple Choice - 2019 01 09黃吏維No ratings yet
- General Physics Periodic Exam - 3rd QuarterDocument5 pagesGeneral Physics Periodic Exam - 3rd Quarterrubiejoycoprada.bariasNo ratings yet
- Momentum Learning GuideDocument14 pagesMomentum Learning GuideRana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch09 Test BankDocument15 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch09 Test BankifghelpdeskNo ratings yet
- AP Phys 1 Quiz MomentumDocument10 pagesAP Phys 1 Quiz MomentumWenyang LiNo ratings yet
- HW7.2 ConservationofMomentumWSDocument4 pagesHW7.2 ConservationofMomentumWSmaalmeida85No ratings yet
- Chapter 8-Phy220Document42 pagesChapter 8-Phy220Jordan TuckerNo ratings yet
- 3NAB0 - Problems Chapter 4Document2 pages3NAB0 - Problems Chapter 4seherNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions OscillationsDocument8 pagesChapter Questions OscillationsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- PART 2 - REMEDIAL ACTIVITY - 4th QTRDocument8 pagesPART 2 - REMEDIAL ACTIVITY - 4th QTRXxmarielxXNo ratings yet
- FR MomentumDocument22 pagesFR MomentumJanel Edwards0% (1)
- Chapter 9. Impulse and Momentum: Chapter Goal: To IntroduceDocument32 pagesChapter 9. Impulse and Momentum: Chapter Goal: To IntroduceJanaki KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Friction, Inclines and Multi-Body Problems: Forces and Laws of MotionDocument6 pagesFriction, Inclines and Multi-Body Problems: Forces and Laws of MotionJoyce Anne MonzonNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 2nd LE ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhysics 71 2nd LE ReviewerAnne Glydel Cruzado DalaganNo ratings yet
- Part A - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPart A - Multiple Choice QuestionsBryan SutantoNo ratings yet
- EM11Document17 pagesEM11Jerry LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Mini PhyDocument22 pagesMini PhyMichael LeungNo ratings yet
- Physics C FRQ PracticeDocument12 pagesPhysics C FRQ Practiceamelia_823No ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Linear MomentumDocument6 pagesChapter Questions Linear MomentumJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1-HW1204Document4 pagesAP Physics 1-HW1204張晉嘉No ratings yet
- Class Questions Ia 3Document293 pagesClass Questions Ia 3agil syahrirNo ratings yet
- +1 Model 2011Document4 pages+1 Model 2011Xavier KattukulamNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Shella Eva - TKPDocument28 pagesChapter5 Shella Eva - TKPshellaeva0960No ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument27 pagesLaws of Motionlotus25369No ratings yet
- (Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education) : General InstructionsDocument24 pages(Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education) : General Instructionsdeetchu10No ratings yet
- GenPhysics W7 Post TestDocument3 pagesGenPhysics W7 Post TestqhuenzielNo ratings yet
- 06 Newtons 3rd Law WorksheetDocument4 pages06 Newtons 3rd Law WorksheetyinanddwangNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Momentum QSDocument29 pagesEdexcel Momentum QSBilawalSadiqNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Questions: Unit 1: Mechanics Chapter 9: Linear Momentum and CollisionsDocument22 pagesConceptual Questions: Unit 1: Mechanics Chapter 9: Linear Momentum and CollisionsEsther Kaye Joana PanaliganNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document25 pagesCH 05msy83635No ratings yet
- AP Physics 19 April Test (2 HRS)Document4 pagesAP Physics 19 April Test (2 HRS)Dheeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Week#4 Wednesday Chapter6SETBDocument4 pagesWeek#4 Wednesday Chapter6SETBmanadaNo ratings yet
- ForumDocument10 pagesForumfestus wikannandaNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Topic 2-4 Paper 1 ProblemsDocument20 pagesIB Physics Topic 2-4 Paper 1 Problemswonjunlim0819No ratings yet
- UINT-5: Aboker Preparatory School, Harar Physics For Grade 11Document11 pagesUINT-5: Aboker Preparatory School, Harar Physics For Grade 11abdiabu701No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Impulse and MomentumDocument8 pagesChapter 7 - Impulse and Momentumflame1 virusNo ratings yet
- Ch9-Linear Momentum and CollisionDocument28 pagesCh9-Linear Momentum and CollisionLAVA HASSANNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 and Long Quiz 1Document1 pageExercise 2 and Long Quiz 1casseyshane.bayosNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 and Long Quiz 1Document1 pageExercise 2 and Long Quiz 1AthanNo ratings yet
- End of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CDocument4 pagesEnd of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CChristina ZhangNo ratings yet
- Force MCQ (21-9-21)Document47 pagesForce MCQ (21-9-21)Md Ahsan Habib MizanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Physics 1 2 Semester 2018 2019Document6 pagesPrinciples of Physics 1 2 Semester 2018 2019tvan7426No ratings yet
- University Entrance Examination Sample PDocument15 pagesUniversity Entrance Examination Sample PGabriella GloriaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetDocument9 pagesAP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetEAGLEFORCE06No ratings yet
- Xi Phy-7 Jee 14.08.2023 SolutionsDocument11 pagesXi Phy-7 Jee 14.08.2023 Solutionsadehcm2021tsiNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum and CollisionsDocument16 pagesLinear Momentum and Collisionsyusuf efendiNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011 Final SAMPLEDocument10 pagesPhys 1011 Final SAMPLEJonah the mixerNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 ExercisesDocument4 pagesUnit 8 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Linear Momentum NotesDocument59 pagesLinear Momentum NotesruukiNo ratings yet
- Note Taking Worksheet ForcesDocument15 pagesNote Taking Worksheet Forcesludivino escardaNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Quezon City Civil Engineering Department Ce407Earthquake Engineering Prelim ExaminationDocument7 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines Quezon City Civil Engineering Department Ce407Earthquake Engineering Prelim ExaminationGerardoNo ratings yet
- Conceptest 9.1: Rolling in The RainDocument16 pagesConceptest 9.1: Rolling in The RainAlba ArjunNo ratings yet
- IitDocument47 pagesIitvishal110085100% (1)
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument8 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionRoda Gayle RañadaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 TutorialDocument29 pagesWeek 1 TutorialDevika PNo ratings yet
- Ultramid® A3HG5 en SI - Product DatasheetDocument2 pagesUltramid® A3HG5 en SI - Product Datasheetshahin_723No ratings yet
- U3-One Dimensional Heat Flow EquationsDocument22 pagesU3-One Dimensional Heat Flow Equationsmochan31No ratings yet
- Rhythmic Oscillations and Resonant InforDocument6 pagesRhythmic Oscillations and Resonant Infornikoleta_tmmNo ratings yet
- 180 TOP Concrete Technology & Design of Concrete SDocument49 pages180 TOP Concrete Technology & Design of Concrete SQaria shehzadiNo ratings yet
- Oso 9780198849070 Chapter 11Document47 pagesOso 9780198849070 Chapter 11علي وحيدNo ratings yet
- Managing Track Stiffness in Transition Zones enDocument5 pagesManaging Track Stiffness in Transition Zones enxinfang.tumNo ratings yet
- 8th Class Chemistry TextbookDocument192 pages8th Class Chemistry Textbookmunna777No ratings yet
- LC FY2019 - PETRONAS R8 (00000002a)Document44 pagesLC FY2019 - PETRONAS R8 (00000002a)hasif sheikhNo ratings yet
- HDPE Pipe Thickness CalculationsDocument5 pagesHDPE Pipe Thickness CalculationsSantanu Karar100% (2)
- Fixed-Order H Infty Tension Control in The UnwindiDocument9 pagesFixed-Order H Infty Tension Control in The Unwindisheng-huang WuNo ratings yet
- Phy SyllabusDocument83 pagesPhy SyllabusBiswa Ranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document31 pagesChapter 8Nguyễn Minh HoàngNo ratings yet
- Flange Mawp Reduction PV EliteDocument8 pagesFlange Mawp Reduction PV EliteMudasir MughalNo ratings yet
- BT301 Tutorial 5 SolutionsDocument13 pagesBT301 Tutorial 5 SolutionsShivaani EswaranNo ratings yet
- Cve 201 Module 1Document5 pagesCve 201 Module 1Samuel Silas100% (1)
- Solutions To Jaan Kalda's Problems in Waves and Optics: With Detailed Diagrams and Walkthroughs Edition 1.2.1Document8 pagesSolutions To Jaan Kalda's Problems in Waves and Optics: With Detailed Diagrams and Walkthroughs Edition 1.2.1Alexandre CasteloNo ratings yet
- Unveiling The Mysteries of Particle Physics - A Journey Into The Subatomic WorldDocument3 pagesUnveiling The Mysteries of Particle Physics - A Journey Into The Subatomic WorldLuciferNo ratings yet
- Article 33856Document12 pagesArticle 33856SNEHA DEVARAJUNo ratings yet
- Eg8 Geo Chapter01Document16 pagesEg8 Geo Chapter01Thimalka Rukmal JayasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Motorndash Operated Sand SifterDocument15 pagesMotorndash Operated Sand SifterJohndelon P. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Copper and Copper Alloy Clad Steel Plate: Standard Specification ForDocument7 pagesCopper and Copper Alloy Clad Steel Plate: Standard Specification Forist93993100% (1)
- K X N X K X N X: 1. PeriodicityDocument13 pagesK X N X K X N X: 1. PeriodicitymakNo ratings yet
- GD&T WorkbookDocument96 pagesGD&T WorkbookramasandyaNo ratings yet
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 4 - 5Document15 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 4 - 5Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- Efektivitas Metode Magic Number Untuk Penyelesaian Soal-Soal Energi Kinetik RelativistikDocument9 pagesEfektivitas Metode Magic Number Untuk Penyelesaian Soal-Soal Energi Kinetik RelativistikTri ArianiNo ratings yet
- Project - HCC - Fully ObservationsDocument12 pagesProject - HCC - Fully Observationsswastik hazraNo ratings yet
- Design Fabrication of Universal Driving Wheel With Forklift ApplicationDocument10 pagesDesign Fabrication of Universal Driving Wheel With Forklift Applicationkifle abelNo ratings yet
- Sae14 12 02 0013Document16 pagesSae14 12 02 0013Joanne WNo ratings yet
- Tutorial10 SolutionDocument24 pagesTutorial10 SolutionIdhichote BenNo ratings yet
- Sheet2 - SolutionsDocument17 pagesSheet2 - SolutionsMöstafa MohamedNo ratings yet