Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sci
Sci
Uploaded by
Erica BiancaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sci
Sci
Uploaded by
Erica BiancaCopyright:
Available Formats
What is charles law?
Charles's Law states that, at constant pressure, the volume of a given mass of gas is directly
proportional to its absolute temperature.
In simpler terms, as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume also increases, and as the
temperature decreases, its volume decreases, assuming the pressure remains constant. This law
is one of the fundamental principles of ideal gases and is often applied in various scientific and
engineering contexts.
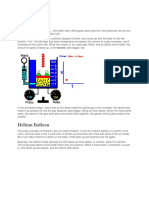
Have you ever noticed what happens to a balloon when it's left out in the hot sun? It gets bigger
and bigger, right? Well, that's because of something called Charles's Law, and it's all about how
gases behave when we change their temperature.
To understand Charles's Law, let's start with the basics. You see, gases are all around us, like the
air we breathe. They're made up of tiny particles that move really fast and bounce off each
other and the walls of their container. Now, imagine these particles as tiny, energetic bouncy
balls.
[balloon experiment]
when we dip the balloon in hot water the volume of gas increases as temperature also increases
What happens to the balloon?
When you dip the balloon in hot water, the air molecules inside the balloon gain energy, causing
them to move faster and spread out. This increase in kinetic energy leads to an increase in
pressure inside the balloon, causing it to expand. So, the balloon gets bigger as the air inside it
expands due to the increase in temperature.
WHY?
This happens because gases consist of molecules that are in constant motion. When you heat
the air inside the balloon, you transfer energy to these molecules, causing them to move faster
and collide more frequently with the walls of the balloon. These collisions exert pressure on the
balloon's walls, leading to an increase in volume as the balloon expands to accommodate the
increased pressure.
now when we dip it in cold water the volume of gas decreases as temperature also decreases
What happens to the balloon ?
When you dip the balloon in cold water, the temperature of the air inside the balloon
decreases. As a result, the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules decreases, causing them
to move slower and exert less pressure on the walls of the balloon. This decrease in pressure
leads to a contraction of the volume of the gas inside the balloon, causing it to shrink. So, the
balloon gets smaller as the air inside it contracts due to the decrease in temperature.
This happens because temperature is directly related to the average kinetic energy of gas
molecules. When the temperature decreases, the molecules move more slowly, resulting in
fewer collisions with the walls of the balloon. Consequently, there is less pressure exerted on
the balloon's walls, causing it to contract and decrease in volume.
Imagine you have a balloon, and inside that balloon are tiny invisible balls bouncing around.
When we make the balloon warm, those little balls start bouncing really fast and need more
space to move around. So, the balloon gets bigger! But when we make it cold, the little balls
slow down and don't need as much space, so the balloon gets smaller. Charles's Law is like a
rule that helps us understand how the balloon changes size when we make it hot or cold.
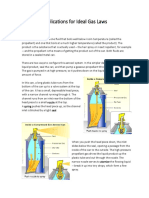
Experiment for jun
Grab a ceramic plate, a few drops of water, and food coloring. Next, place the candle in the
middle of the plate, light the wick, and place a glass cup over it. You'll see that the water around
the candle begins to rise. The candle warms the air and this increases the air volume inside the
glass. When the candle burns out, because all the oxygen is used up, the temperature cools
quickly. 00:21 This temperature decrease also means that the volume decreases, which lets the
water rise up to fill that space. This is called Charles Law. It tells us that the ratio of volume to
temperature must remain the same.
You might also like
- 201: Health & Safety: Sample Questions Answer GuideDocument7 pages201: Health & Safety: Sample Questions Answer GuideGheorghe Ciubotaru78% (9)
- Electronic Principles 8th Edition Malvino Test BankDocument14 pagesElectronic Principles 8th Edition Malvino Test BankDanaGonzalezqietn100% (20)
- Dislocation Mobility and Hydrogen - A Brief ReviewDocument6 pagesDislocation Mobility and Hydrogen - A Brief ReviewIchsan HakimNo ratings yet
- Charles' Law - Real Life Applications: Watch What Happens To A Helium Balloon On A Cold DayDocument2 pagesCharles' Law - Real Life Applications: Watch What Happens To A Helium Balloon On A Cold DayEnriquez JohnNo ratings yet
- Chem Law LawDocument2 pagesChem Law LawFaye Lianne MaderoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 1Document9 pagesChemistry Chapter 1MaticsNo ratings yet
- Document 15Document9 pagesDocument 15haashniNo ratings yet
- Use The Law To Explain The Following ObservationsDocument6 pagesUse The Law To Explain The Following ObservationsCedric Adrian AblogNo ratings yet
- Applications of Gas LawsDocument3 pagesApplications of Gas LawsCharm GorospeNo ratings yet
- Charles LawDocument12 pagesCharles LawLerr Real RelleNo ratings yet
- Science ScriptDocument2 pagesScience ScriptTrixie San DiegoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTERY Chap1Document42 pagesCHEMISTERY Chap1ushaecNo ratings yet
- BehaviorofGases3 3Document7 pagesBehaviorofGases3 3Melanie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- SolidsDocument4 pagesSolidsAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Changes in The States of MatterDocument8 pagesChanges in The States of MatterNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument33 pagesCHEMISTRYemiyaNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument7 pagesStates of MatterShubhra MoreNo ratings yet
- The Can CrusherDocument2 pagesThe Can CrusherMildred FerrerNo ratings yet
- Gas PressureDocument3 pagesGas Pressurestefania kaklamaniNo ratings yet
- Heat Enegy TransferDocument6 pagesHeat Enegy TransferManya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Thermal Energy: Matter Is Made Up of Tiny Particles CalledDocument22 pagesTemperature and Thermal Energy: Matter Is Made Up of Tiny Particles CalledCabalan O. Charles KevinNo ratings yet
- The Nature of HeatDocument101 pagesThe Nature of HeatfaezzuNo ratings yet
- CharlessDocument2 pagesCharlessRevilloNo ratings yet
- Charles SDocument2 pagesCharles SRevilloNo ratings yet
- Melting Boiling and Evaporation PDFDocument2 pagesMelting Boiling and Evaporation PDFTahmeed AzizNo ratings yet
- Handout # 2.4 Particle Model For MatterDocument5 pagesHandout # 2.4 Particle Model For MatterMr. KhanNo ratings yet
- What Is A Practical Application of BoyleDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Practical Application of BoyleArmstrong BosantogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDF MeteoDocument24 pagesChapter 2 PDF MeteosecretzNo ratings yet
- Boyles LawDocument6 pagesBoyles LawMara TillesNo ratings yet
- Applications For Ideal Gas LawsDocument6 pagesApplications For Ideal Gas Lawsdreamxtreme16No ratings yet
- FluidsDocument55 pagesFluidsdanena88No ratings yet
- Fizik Thermal ExpansionDocument19 pagesFizik Thermal ExpansionMirahmad FadzlyNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument55 pagesFluidsOsama Abd ElkawiNo ratings yet
- 2 States of Matter NotesDocument14 pages2 States of Matter Notesafnan.6556No ratings yet
- (2.1) Kinetic Particle Model of MatterDocument9 pages(2.1) Kinetic Particle Model of Matterzahra1No ratings yet
- Lightning Is One of The Most Beautiful Displays in NatureDocument1 pageLightning Is One of The Most Beautiful Displays in NatureAditya1412No ratings yet
- Notes States of Matter & GassesDocument18 pagesNotes States of Matter & GassesKaran KapoorNo ratings yet
- The Nature of MatterDocument26 pagesThe Nature of MatterEsma KurtanovićNo ratings yet
- Hay Op Is AnimalDocument18 pagesHay Op Is AnimalDaryl RasonabeNo ratings yet
- Act 8a. Convection Current ArticleDocument2 pagesAct 8a. Convection Current ArticleGUILLER BELENNo ratings yet
- Charles Law Thermo Lab 3Document5 pagesCharles Law Thermo Lab 3Arif MuziratNo ratings yet
- How Can I Make My NSTP Engagement Meaningful Sec39 DagcutanDocument1 pageHow Can I Make My NSTP Engagement Meaningful Sec39 DagcutanMaxine TaeyeonNo ratings yet
- ConChem Guide 4t QuarterDocument19 pagesConChem Guide 4t QuarterKiller KnightNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Chapter 16 New Book-1Document84 pagesPhysical Science Chapter 16 New Book-1api-248629627No ratings yet
- Final SciDocument6 pagesFinal SciDANAO, Izek Hyden P.No ratings yet
- JYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesDocument16 pagesJYOTI Chemistry IGCSE Revision NotesJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point of LiquidDocument3 pagesBoiling Point of LiquidDebasish BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Candle Experiment UnmaskedDocument13 pagesCandle Experiment UnmaskedVijay TrivediNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 5070Document93 pagesChemistry Notes 5070yawerakNo ratings yet
- Document About Literature and HistoryDocument2 pagesDocument About Literature and HistoryMarieta GonzalesNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument12 pagesExamplesMoldir SerikNo ratings yet
- Si UnitsDocument92 pagesSi UnitsRAVI2296No ratings yet
- Mass Earth's Atmosphere: DensityDocument23 pagesMass Earth's Atmosphere: DensityRahul MoottolikandyNo ratings yet
- Matter: Definition & The Five States of Matter: AtomsDocument10 pagesMatter: Definition & The Five States of Matter: AtomsJeonila Margarette RapadaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Model of MatterDocument25 pagesKinetic Model of MatterHafiza JaweriaNo ratings yet
- 5 CH 2 Sec 2 Changes in State and Energy - UploadDocument74 pages5 CH 2 Sec 2 Changes in State and Energy - Uploadapi-270861823No ratings yet
- Charles Law Cape Yr 1Document4 pagesCharles Law Cape Yr 1ericaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge MsDocument7 pagesCambridge MstaliassalimNo ratings yet
- Why Do Gas Bubbles Get Larger As They Rise?: Why Does The Bubble Grow?Document4 pagesWhy Do Gas Bubbles Get Larger As They Rise?: Why Does The Bubble Grow?Princes Katherine VergaraNo ratings yet
- LawDocument6 pagesLawJaymart BobilesNo ratings yet
- The Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument7 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogKatrina Baldas Kew-isNo ratings yet
- Gem 3.0Document35 pagesGem 3.0balaNo ratings yet
- Seeing Into The Soul: N Fourteenth Century IenaDocument4 pagesSeeing Into The Soul: N Fourteenth Century Ienasalveregina1917No ratings yet
- Masters2 52558Document91 pagesMasters2 52558nermeen ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Education of Albert Einstein: Clayton A. GearhartDocument23 pagesThe Education of Albert Einstein: Clayton A. GearhartJudith Banabatac OreganoNo ratings yet
- Basic Data Kar Part 4Document11 pagesBasic Data Kar Part 4vpmohammedNo ratings yet
- Abb Drives: User'S Manual Flashdrop Mfdt-01Document62 pagesAbb Drives: User'S Manual Flashdrop Mfdt-01Сергей СалтыковNo ratings yet
- Cables: June 2015Document27 pagesCables: June 2015Gaurav NeermulNo ratings yet
- Su 80 GPDocument3 pagesSu 80 GPKurtis SchmidtNo ratings yet
- St. Augustine As EducatorDocument7 pagesSt. Augustine As EducatorMaria Soledad TubayNo ratings yet
- Eposter For Art & Science of Patient PreparationDocument50 pagesEposter For Art & Science of Patient PreparationdrsmritiNo ratings yet
- Drug Monitoring PDFDocument1 pageDrug Monitoring PDFImran ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Gea Varivent Hygienic Special Application Valves 262509Document162 pagesGea Varivent Hygienic Special Application Valves 262509DianaNo ratings yet
- Form 02 QuestionsDocument7 pagesForm 02 QuestionsMagomed KitaevNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet - ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet - ThermodynamicsDivyaprakash PatelNo ratings yet
- The Literary Formofthe QuranDocument10 pagesThe Literary Formofthe QuranTrina CanizoNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry NotesDocument24 pages1st Year Chemistry NotesShasha Jain88% (8)
- Jurnal FormulasiDocument8 pagesJurnal FormulasiAdilah AthtahirahNo ratings yet
- ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018: Lecture 13: Folded Cascode & Two Stage Miller OTADocument25 pagesECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Spring 2018: Lecture 13: Folded Cascode & Two Stage Miller OTAUdai ValluruNo ratings yet
- TvtgurpsnewDocument94 pagesTvtgurpsnewKevin HutchingsNo ratings yet
- Please Quote This Reference Number in All Future CorrespondenceDocument2 pagesPlease Quote This Reference Number in All Future CorrespondenceSaipraveen PerumallaNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter Week 6 MusicDocument3 pages3RD Quarter Week 6 MusicMichaella Liongco AmanteNo ratings yet
- Lauren Del Valle: Education Hofstra University Honors College, Hempstead, NYDocument2 pagesLauren Del Valle: Education Hofstra University Honors College, Hempstead, NYLauren del ValleNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering 1Document19 pagesMaintenance Engineering 1Suienish SultangazinNo ratings yet
- IssuancesDocument347 pagesIssuancesReia RuecoNo ratings yet