Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clauses Infographic
Clauses Infographic
Uploaded by
Jose KeborkCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 32642892-PL WelcomeLetterDocument4 pages32642892-PL WelcomeLetterMohan ChandraNo ratings yet
- Antonia LoLordo Pierre Gassendi and The Birth of Early Modern PhilosophyDocument295 pagesAntonia LoLordo Pierre Gassendi and The Birth of Early Modern PhilosophyAllison Kasandra100% (3)
- Clause and Sentence Grammar 3Document8 pagesClause and Sentence Grammar 3Indah Mala HikmaNo ratings yet
- Independent and Dependent ClausesDocument6 pagesIndependent and Dependent ClausesJune SorianoNo ratings yet
- Sentence PartsDocument1 pageSentence PartsNicole Nabasca GorneNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 06 Mar 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 06 Mar 2024ammar6996shariffNo ratings yet
- The Sentence Week 1 3Document3 pagesThe Sentence Week 1 3abigael fiderNo ratings yet
- Compound SentencesDocument6 pagesCompound SentencesChristopher SamuelNo ratings yet
- Grammar Groups 56 Lecture OneDocument6 pagesGrammar Groups 56 Lecture Oneبوزيد OuleddahmaneNo ratings yet
- On Time, The Movie Had Already Started, The SecondDocument11 pagesOn Time, The Movie Had Already Started, The Secondmamdemesa23No ratings yet
- Escrita II ResumenDocument13 pagesEscrita II ResumenBárbara AvilaNo ratings yet
- Phrases Vs ClausesDocument29 pagesPhrases Vs ClauseshasbiNo ratings yet
- Academic English: Yonatan Tri Oktavianus 0113u026 Kelas BDocument16 pagesAcademic English: Yonatan Tri Oktavianus 0113u026 Kelas BYonatan TriNo ratings yet
- Last MaterialDocument38 pagesLast MaterialNaufal Al AsadyNo ratings yet
- Topic Sentence by Group 4Document10 pagesTopic Sentence by Group 4Nurul Aini SavitriNo ratings yet
- Type of Phrase and Clauses by Group 6Document9 pagesType of Phrase and Clauses by Group 6Alvonzo VlImoteNo ratings yet
- Correcting Sentence FragmentsDocument3 pagesCorrecting Sentence FragmentsbetelgueseNo ratings yet
- SENTENCEDocument16 pagesSENTENCEMarie Joy BrionesNo ratings yet
- Effective Communicative English-Class NotesDocument61 pagesEffective Communicative English-Class Notesraj pandiNo ratings yet
- What Is ClauseDocument8 pagesWhat Is ClauseNoshadTechNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Clauses 1. Independent Clause: What Is A Clause?Document1 pageKinds of Clauses 1. Independent Clause: What Is A Clause?Nica IlanoNo ratings yet
- Clauses and PhrasesDocument4 pagesClauses and PhrasesFitriaNo ratings yet
- Sentence StructureDocument155 pagesSentence Structureapi-3808291100% (4)
- Subordinate Clause (Also Called Dependent Clauses)Document4 pagesSubordinate Clause (Also Called Dependent Clauses)Rosana Villordon SoliteNo ratings yet
- Introduction-to-Phrases-and-SentencesDocument9 pagesIntroduction-to-Phrases-and-SentencesSubono HutagalungNo ratings yet
- Glossary Grammar TermsDocument2 pagesGlossary Grammar TermsMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Phrases Sentence and Clauses 1Document28 pagesPhrases Sentence and Clauses 1Randy Basa MantaringNo ratings yet
- Missing-Subject Fragment: How To Correct Sentence FragmentsDocument3 pagesMissing-Subject Fragment: How To Correct Sentence FragmentsKonstantinNo ratings yet
- Training ModuleDocument259 pagesTraining Modulepeter ryanNo ratings yet
- Ept Preparation Chapter - 2Document21 pagesEpt Preparation Chapter - 2TiwoqPoenyaNo ratings yet
- CLAUSESDocument17 pagesCLAUSESsamiNo ratings yet
- Understanding English GlossaryDocument3 pagesUnderstanding English GlossaryChidinma UwadiaeNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of PurposeDocument34 pagesAdverbs of PurposeChandra Erick100% (1)
- Writing GrammarDocument21 pagesWriting GrammarSana BenyaminaNo ratings yet
- Writing Explanation - 1681147573630Document72 pagesWriting Explanation - 1681147573630Hossam SabryNo ratings yet
- 8 EnglishDocument9 pages8 EnglishAbhishikta DasNo ratings yet
- Clauses Simple Sentences Compound Sentences Complex Sentences Subjects ObjectsDocument8 pagesClauses Simple Sentences Compound Sentences Complex Sentences Subjects ObjectsdianaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Paper Adv Grammar Kelompok 3Document7 pagesTugas Paper Adv Grammar Kelompok 3fauzn muhammadNo ratings yet
- Meeting 4 Strategic On Multiple Clause NOUN CLAUSEDocument14 pagesMeeting 4 Strategic On Multiple Clause NOUN CLAUSENabilla ChristantiNo ratings yet
- Guide To English GrammarDocument16 pagesGuide To English GrammarLearn English OnlineNo ratings yet
- English Grammar I, Summary.Document7 pagesEnglish Grammar I, Summary.Celeste HervasNo ratings yet
- Clause Packet 2015-2016Document13 pagesClause Packet 2015-2016Praveen UrwaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A SentenceDocument25 pagesHow To Write A SentenceOscar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Types of SentencesDocument13 pagesTypes of SentencesFathimah Al-Ma'shumah100% (1)
- Chapter ReportDocument5 pagesChapter ReportRia NirwanaNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Units: They Are Meaningful and Combine With Each Other in Systematic WaysDocument8 pagesGrammatical Units: They Are Meaningful and Combine With Each Other in Systematic WaysNoe GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument13 pagesPart of SpeechtiffiNo ratings yet
- Sentence ClauseDocument4 pagesSentence ClauseDilip JaniNo ratings yet
- 7 - M17 - S3, Grammar3, The Remaining Lectures, Weeks 7+8+9+10, Pr. ElmouhtarimDocument18 pages7 - M17 - S3, Grammar3, The Remaining Lectures, Weeks 7+8+9+10, Pr. ElmouhtarimSimo SimoNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument9 pagesGrammaraleNo ratings yet
- English Material 1 Parts of SpeachDocument17 pagesEnglish Material 1 Parts of SpeachFerdika Dwi CandraNo ratings yet
- Merged DocumentDocument28 pagesMerged DocumentJamirah Maha ShahinurNo ratings yet
- What Is A Clause?: Independent ClausesDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Clause?: Independent ClausesRahul DubeyNo ratings yet
- PresentaciónDocument8 pagesPresentaciónFrancheska PérezNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument5 pagesClausesMohamed GUERSNo ratings yet
- Cajuelan, Lee Andrew A. BSE-English 1-1 Worksheet #8 (Final)Document48 pagesCajuelan, Lee Andrew A. BSE-English 1-1 Worksheet #8 (Final)Lee Andrew Añonuevo CajuelanNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument5 pagesClausesBreeze BoukhrissNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Clauses and Sentence StructureDocument13 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Clauses and Sentence StructureAmy100% (18)
- New Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetFrom EverandNew Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Instruction of Installation The Operating Manual For The 220kv TransformerDocument12 pagesInstruction of Installation The Operating Manual For The 220kv TransformerArman PracoyoNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Design - Overview: Slew Create or Modify Track Horizontal Track Design Slew AnalysisDocument16 pagesHorizontal Design - Overview: Slew Create or Modify Track Horizontal Track Design Slew AnalysisReepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Simulation-Based Optimization Methodology For FaDocument11 pagesA Simulation-Based Optimization Methodology For FahenokzewduNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument28 pagesFuels and CombustionDrupad PatelNo ratings yet
- DivergentDocument3 pagesDivergentsasingNo ratings yet
- Citra Log - Txt.oldDocument57 pagesCitra Log - Txt.oldEmmanuel PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide 2 1 4Document58 pagesTeaching Guide 2 1 4Anu KhanNo ratings yet
- Speech System For Dumb PeopleDocument32 pagesSpeech System For Dumb PeopleJaspreet Singh WaliaNo ratings yet
- Dogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.Document16 pagesDogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.ciprilisticusNo ratings yet
- Name: License No License No: 2862 License Issue Date Issue Date:11/7/2007 License Expiry Date Expiry Date:10/7/2019Document139 pagesName: License No License No: 2862 License Issue Date Issue Date:11/7/2007 License Expiry Date Expiry Date:10/7/2019ArabyAbdel Hamed SadekNo ratings yet
- Chapter One The Problem and Its Setting 1.1 Background of The StudyDocument10 pagesChapter One The Problem and Its Setting 1.1 Background of The StudyJholo BuctonNo ratings yet
- Role of MNC in IndiaDocument41 pagesRole of MNC in IndiaKhundongbam SureshNo ratings yet
- ECE Lab Solutions OnlineDocument4 pagesECE Lab Solutions OnlineBharath PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document39 pagesLesson 4Anne FloresNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument207 pages09 - Chapter 2 PDFAarthi PriyaNo ratings yet
- QCD For RMD 2021Document9 pagesQCD For RMD 2021Rod BushmanNo ratings yet
- Tales From The Evil Empire - Building A Favicon Module For OrchardDocument7 pagesTales From The Evil Empire - Building A Favicon Module For OrchardActive8No ratings yet
- Ebook 7 Tutorials - Cake Craft SchoolDocument45 pagesEbook 7 Tutorials - Cake Craft SchoolmariaNo ratings yet
- Grammar ManualDocument130 pagesGrammar ManualJahnaviNo ratings yet
- Patrol GR: GI MA EM LC EC FE CL MT Automatic Transmission AT TF PD FA RA BR ST RS BT HA EL IDXDocument2 pagesPatrol GR: GI MA EM LC EC FE CL MT Automatic Transmission AT TF PD FA RA BR ST RS BT HA EL IDXAttila SomorjaiNo ratings yet
- Bab 5 Unit - Gear (Nota Politeknik)Document13 pagesBab 5 Unit - Gear (Nota Politeknik)Syfull musicNo ratings yet
- Siemens 3af 01Document24 pagesSiemens 3af 01Nhat Nguyen VanNo ratings yet
- Angel CVDocument2 pagesAngel CValexandraNo ratings yet
- SWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsDocument6 pagesSWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsmaneeshmogallpuNo ratings yet
- Crystal Ball Installation GuideDocument40 pagesCrystal Ball Installation Guidebogdann_damianNo ratings yet
- Election Law CasesDocument155 pagesElection Law CasesJa VillaromanNo ratings yet
- (1996) JOSA 13 Space-Bandwidth Product of Optical Signals and SyDocument4 pages(1996) JOSA 13 Space-Bandwidth Product of Optical Signals and Sythanhevt92No ratings yet
- Method Statement For Marble Flooring and Marble Wall CladdingDocument10 pagesMethod Statement For Marble Flooring and Marble Wall Claddingumit100% (1)
Clauses Infographic
Clauses Infographic
Uploaded by
Jose KeborkCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Clauses Infographic
Clauses Infographic
Uploaded by
Jose KeborkCopyright:
Available Formats
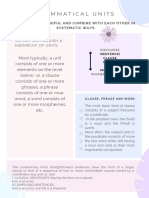
GUIDE TO UNDERSTAND
CLAUSES
Clause Types of Clauses:
A clause is a word group
Independent (or
that contains a verb and
Main)
its subject and that is
Dependent (or
used as a sentence or
Subordinate)
as part of a sentence.
Independent Dependent
A subordinate (or dependent)
Main (or independent) clause does not express a
clause is a clause that complete thought and cannot
expresses a complete stand alone as a sentence.
thought and can stand as a Also, it can be used as
sentence. Ex: Subject/ adjectives, adverbs, or nouns.
Verb Example:
The outfielders missed whom we spoke to yesterday
easy fly balls.
Noun Clauses
Adjective Clauses
It is a subordinate clause that A noun clause is a dependent clause that
functions grammatically like a noun in a
modifies a noun or a pronoun. sentence. In other words, it takes the place
Also, tells what kind or which one. of a noun but has its own subject and verb.
Ex: I am now reading this book, Ex. The rumor that the bakery was closing
spread quickly.
which is a historical novel about the
In this sentence, the noun clause is "that
Irish revolt of 1798. (Modifies the the bakery was closing." It acts as the
noun book, telling what kind of direct object of the verb "spread." While it
book conveys information like a noun ("rumor"), it
has its own subject ("bakery") and verb
("was closing").
Adverb Clauses
Verb Clauses
An adverb clause is a dependent clause
that functions like an adverb within a
sentence. In other words, it provides more A verb clause is a group of words containing
information about: a subject and a verb that expresses a
When something happened (time) complete thought. The key thing here is that
Where something happened (place) it has the potential to stand alone as a
How something happened (manner) sentence, even though it might not always
Why something happened (reason) be used that way in a full sentence.
To what extent something happened Ex. The dog chased the frisbee.
(degree) This group of words functions as a complete
Unlike verb clauses, adverb clauses cannot sentence because it has:
stand alone as a sentence because they Subject: "The dog"
lack the independence of a subject and Verb: "chased"
verb expressing a complete thought. Expresses a complete thought: We
ex. understand what action is happening
She arrived after the movie started.
(chasing) and who is performing the
action (the dog).
Common Subordinating
Conjunctions Common Conjuctive
Adverbs
after
even
also
though
however
unless
nevertheless
although
if
anyway
until instead
otherwise
You might also like
- 32642892-PL WelcomeLetterDocument4 pages32642892-PL WelcomeLetterMohan ChandraNo ratings yet
- Antonia LoLordo Pierre Gassendi and The Birth of Early Modern PhilosophyDocument295 pagesAntonia LoLordo Pierre Gassendi and The Birth of Early Modern PhilosophyAllison Kasandra100% (3)
- Clause and Sentence Grammar 3Document8 pagesClause and Sentence Grammar 3Indah Mala HikmaNo ratings yet
- Independent and Dependent ClausesDocument6 pagesIndependent and Dependent ClausesJune SorianoNo ratings yet
- Sentence PartsDocument1 pageSentence PartsNicole Nabasca GorneNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 06 Mar 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 06 Mar 2024ammar6996shariffNo ratings yet
- The Sentence Week 1 3Document3 pagesThe Sentence Week 1 3abigael fiderNo ratings yet
- Compound SentencesDocument6 pagesCompound SentencesChristopher SamuelNo ratings yet
- Grammar Groups 56 Lecture OneDocument6 pagesGrammar Groups 56 Lecture Oneبوزيد OuleddahmaneNo ratings yet
- On Time, The Movie Had Already Started, The SecondDocument11 pagesOn Time, The Movie Had Already Started, The Secondmamdemesa23No ratings yet
- Escrita II ResumenDocument13 pagesEscrita II ResumenBárbara AvilaNo ratings yet
- Phrases Vs ClausesDocument29 pagesPhrases Vs ClauseshasbiNo ratings yet
- Academic English: Yonatan Tri Oktavianus 0113u026 Kelas BDocument16 pagesAcademic English: Yonatan Tri Oktavianus 0113u026 Kelas BYonatan TriNo ratings yet
- Last MaterialDocument38 pagesLast MaterialNaufal Al AsadyNo ratings yet
- Topic Sentence by Group 4Document10 pagesTopic Sentence by Group 4Nurul Aini SavitriNo ratings yet
- Type of Phrase and Clauses by Group 6Document9 pagesType of Phrase and Clauses by Group 6Alvonzo VlImoteNo ratings yet
- Correcting Sentence FragmentsDocument3 pagesCorrecting Sentence FragmentsbetelgueseNo ratings yet
- SENTENCEDocument16 pagesSENTENCEMarie Joy BrionesNo ratings yet
- Effective Communicative English-Class NotesDocument61 pagesEffective Communicative English-Class Notesraj pandiNo ratings yet
- What Is ClauseDocument8 pagesWhat Is ClauseNoshadTechNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Clauses 1. Independent Clause: What Is A Clause?Document1 pageKinds of Clauses 1. Independent Clause: What Is A Clause?Nica IlanoNo ratings yet
- Clauses and PhrasesDocument4 pagesClauses and PhrasesFitriaNo ratings yet
- Sentence StructureDocument155 pagesSentence Structureapi-3808291100% (4)
- Subordinate Clause (Also Called Dependent Clauses)Document4 pagesSubordinate Clause (Also Called Dependent Clauses)Rosana Villordon SoliteNo ratings yet
- Introduction-to-Phrases-and-SentencesDocument9 pagesIntroduction-to-Phrases-and-SentencesSubono HutagalungNo ratings yet
- Glossary Grammar TermsDocument2 pagesGlossary Grammar TermsMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Phrases Sentence and Clauses 1Document28 pagesPhrases Sentence and Clauses 1Randy Basa MantaringNo ratings yet
- Missing-Subject Fragment: How To Correct Sentence FragmentsDocument3 pagesMissing-Subject Fragment: How To Correct Sentence FragmentsKonstantinNo ratings yet
- Training ModuleDocument259 pagesTraining Modulepeter ryanNo ratings yet
- Ept Preparation Chapter - 2Document21 pagesEpt Preparation Chapter - 2TiwoqPoenyaNo ratings yet
- CLAUSESDocument17 pagesCLAUSESsamiNo ratings yet
- Understanding English GlossaryDocument3 pagesUnderstanding English GlossaryChidinma UwadiaeNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of PurposeDocument34 pagesAdverbs of PurposeChandra Erick100% (1)
- Writing GrammarDocument21 pagesWriting GrammarSana BenyaminaNo ratings yet
- Writing Explanation - 1681147573630Document72 pagesWriting Explanation - 1681147573630Hossam SabryNo ratings yet
- 8 EnglishDocument9 pages8 EnglishAbhishikta DasNo ratings yet
- Clauses Simple Sentences Compound Sentences Complex Sentences Subjects ObjectsDocument8 pagesClauses Simple Sentences Compound Sentences Complex Sentences Subjects ObjectsdianaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Paper Adv Grammar Kelompok 3Document7 pagesTugas Paper Adv Grammar Kelompok 3fauzn muhammadNo ratings yet
- Meeting 4 Strategic On Multiple Clause NOUN CLAUSEDocument14 pagesMeeting 4 Strategic On Multiple Clause NOUN CLAUSENabilla ChristantiNo ratings yet
- Guide To English GrammarDocument16 pagesGuide To English GrammarLearn English OnlineNo ratings yet
- English Grammar I, Summary.Document7 pagesEnglish Grammar I, Summary.Celeste HervasNo ratings yet
- Clause Packet 2015-2016Document13 pagesClause Packet 2015-2016Praveen UrwaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A SentenceDocument25 pagesHow To Write A SentenceOscar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Types of SentencesDocument13 pagesTypes of SentencesFathimah Al-Ma'shumah100% (1)
- Chapter ReportDocument5 pagesChapter ReportRia NirwanaNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Units: They Are Meaningful and Combine With Each Other in Systematic WaysDocument8 pagesGrammatical Units: They Are Meaningful and Combine With Each Other in Systematic WaysNoe GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument13 pagesPart of SpeechtiffiNo ratings yet
- Sentence ClauseDocument4 pagesSentence ClauseDilip JaniNo ratings yet
- 7 - M17 - S3, Grammar3, The Remaining Lectures, Weeks 7+8+9+10, Pr. ElmouhtarimDocument18 pages7 - M17 - S3, Grammar3, The Remaining Lectures, Weeks 7+8+9+10, Pr. ElmouhtarimSimo SimoNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument9 pagesGrammaraleNo ratings yet
- English Material 1 Parts of SpeachDocument17 pagesEnglish Material 1 Parts of SpeachFerdika Dwi CandraNo ratings yet
- Merged DocumentDocument28 pagesMerged DocumentJamirah Maha ShahinurNo ratings yet
- What Is A Clause?: Independent ClausesDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Clause?: Independent ClausesRahul DubeyNo ratings yet
- PresentaciónDocument8 pagesPresentaciónFrancheska PérezNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument5 pagesClausesMohamed GUERSNo ratings yet
- Cajuelan, Lee Andrew A. BSE-English 1-1 Worksheet #8 (Final)Document48 pagesCajuelan, Lee Andrew A. BSE-English 1-1 Worksheet #8 (Final)Lee Andrew Añonuevo CajuelanNo ratings yet
- ClausesDocument5 pagesClausesBreeze BoukhrissNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Clauses and Sentence StructureDocument13 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Clauses and Sentence StructureAmy100% (18)
- New Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetFrom EverandNew Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Instruction of Installation The Operating Manual For The 220kv TransformerDocument12 pagesInstruction of Installation The Operating Manual For The 220kv TransformerArman PracoyoNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Design - Overview: Slew Create or Modify Track Horizontal Track Design Slew AnalysisDocument16 pagesHorizontal Design - Overview: Slew Create or Modify Track Horizontal Track Design Slew AnalysisReepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Simulation-Based Optimization Methodology For FaDocument11 pagesA Simulation-Based Optimization Methodology For FahenokzewduNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument28 pagesFuels and CombustionDrupad PatelNo ratings yet
- DivergentDocument3 pagesDivergentsasingNo ratings yet
- Citra Log - Txt.oldDocument57 pagesCitra Log - Txt.oldEmmanuel PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide 2 1 4Document58 pagesTeaching Guide 2 1 4Anu KhanNo ratings yet
- Speech System For Dumb PeopleDocument32 pagesSpeech System For Dumb PeopleJaspreet Singh WaliaNo ratings yet
- Dogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.Document16 pagesDogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.ciprilisticusNo ratings yet
- Name: License No License No: 2862 License Issue Date Issue Date:11/7/2007 License Expiry Date Expiry Date:10/7/2019Document139 pagesName: License No License No: 2862 License Issue Date Issue Date:11/7/2007 License Expiry Date Expiry Date:10/7/2019ArabyAbdel Hamed SadekNo ratings yet
- Chapter One The Problem and Its Setting 1.1 Background of The StudyDocument10 pagesChapter One The Problem and Its Setting 1.1 Background of The StudyJholo BuctonNo ratings yet
- Role of MNC in IndiaDocument41 pagesRole of MNC in IndiaKhundongbam SureshNo ratings yet
- ECE Lab Solutions OnlineDocument4 pagesECE Lab Solutions OnlineBharath PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document39 pagesLesson 4Anne FloresNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument207 pages09 - Chapter 2 PDFAarthi PriyaNo ratings yet
- QCD For RMD 2021Document9 pagesQCD For RMD 2021Rod BushmanNo ratings yet
- Tales From The Evil Empire - Building A Favicon Module For OrchardDocument7 pagesTales From The Evil Empire - Building A Favicon Module For OrchardActive8No ratings yet
- Ebook 7 Tutorials - Cake Craft SchoolDocument45 pagesEbook 7 Tutorials - Cake Craft SchoolmariaNo ratings yet
- Grammar ManualDocument130 pagesGrammar ManualJahnaviNo ratings yet
- Patrol GR: GI MA EM LC EC FE CL MT Automatic Transmission AT TF PD FA RA BR ST RS BT HA EL IDXDocument2 pagesPatrol GR: GI MA EM LC EC FE CL MT Automatic Transmission AT TF PD FA RA BR ST RS BT HA EL IDXAttila SomorjaiNo ratings yet
- Bab 5 Unit - Gear (Nota Politeknik)Document13 pagesBab 5 Unit - Gear (Nota Politeknik)Syfull musicNo ratings yet
- Siemens 3af 01Document24 pagesSiemens 3af 01Nhat Nguyen VanNo ratings yet
- Angel CVDocument2 pagesAngel CValexandraNo ratings yet
- SWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsDocument6 pagesSWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsmaneeshmogallpuNo ratings yet
- Crystal Ball Installation GuideDocument40 pagesCrystal Ball Installation Guidebogdann_damianNo ratings yet
- Election Law CasesDocument155 pagesElection Law CasesJa VillaromanNo ratings yet
- (1996) JOSA 13 Space-Bandwidth Product of Optical Signals and SyDocument4 pages(1996) JOSA 13 Space-Bandwidth Product of Optical Signals and Sythanhevt92No ratings yet
- Method Statement For Marble Flooring and Marble Wall CladdingDocument10 pagesMethod Statement For Marble Flooring and Marble Wall Claddingumit100% (1)