Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shubhangi Sharma Poster On Awareness of Complications of DM
Shubhangi Sharma Poster On Awareness of Complications of DM
Uploaded by
Shubhangi SharmaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shubhangi Sharma Poster On Awareness of Complications of DM
Shubhangi Sharma Poster On Awareness of Complications of DM
Uploaded by
Shubhangi SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
AWARENESS OF COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES AND MYTHS ABOUT
INSULIN IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES MELLITUS
Dr. Shubhangi Sharma
Guided by: Dr. Manoj K. Rai, Dr. Sandhya Chandel & Dr. Vijay K. Shrivas
Abstract Results
The reduction of diabetes-related morbidity and mortality relies The sample included 72% male and 28% female patients. Out of 50
heavily on the awareness of complications. This research aimed to patients 58% of patients had been diagnosed with diabetes over 5
evaluate the level of awareness regarding diabetes complications years ago, of which only 40% were aware of more than 2
and the factors associated with it among patients with type 2 complications of diabetes. Surprisingly, amongst patients with
diabetes. Additionally, it also aimed to explore the prevailing diagnosis within the last 5 years, the awareness of more than 2
myths about insulin among these patients. A cross-sectional study complications was 56%. Only 38% patients were aware about the
was conducted at a tertiary care institution from December 2023 target blood sugar range. Increased urinary frequency was the
to January 2024, utilizing a sample size of 50 patients and most commonly known symptom of hyperglycemia (70%). 60%
predesigned interviewer-administered questionnaires. patients selected Glucometer as the best option to monitor blood
sugar at home, while 28% believed keeping track of dietary intake
to be sufficient, the rest 12% mentioned noticing signs of
Introduction hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia to be the best method. Taking
insulin and oral hypoglycemics on time was chosen as the most
Diabetes Mellitus in Asian Indian population is characterized by effective way to control persistently high blood sugar by 68%
young age of onset and occurrence at low level of BMI. The patients. 54% of the patients had suffered from one or more
perception of diabetes in India has shifted, no longer only complications of diabetes since diagnosis. 18% of patients even
affecting the wealthy. It now affects those in urban slums, middle- mentioned taking insulin (8%) and exercising (10%) as correct
income areas, and rural regions{1}. People from lower methods to manage hypoglycemia at home. 100% Patients were
socioeconomic backgrounds need immediate attention to increase aware that stopping alcohol and smoking could help in preventing
awareness and prevent complications. Research shows the complications. Similarly, 98% patients were aware of dietary and
importance of understanding the disease, glycemic control, and exercise recommendations for diabetes. Interestingly, 44%
self-care practices for better outcomes{2}. patients believed drinking bitter juice could control high blood
Over 70% of diabetes-related cost is attributed to its sugar. There was not a significant difference between awareness in
complications, particularly for macro-vascular diseases that most patients who could read and write(48%) and those who could not
commonly occur in type 2 diabetics{3}. There is evidence available (44%).
that knowledge about DM and its complications has a positive
association with attitude and practices for self-care and glycemic
Diabetic kidney disease was the most commonly known
control among diabetics {4}. This article discusses the results of a
study conducted among people with DM, visiting the outpatient
complication of diabetes (92%), followed by diabetic foot
and inpatient department at Apollo Hospitals, Bilaspur, with an disease(80%).
objective to assess their knowledge about DM and its The commonest myth (78%) about Insulin: If used once, they
complications, practices, and myths about insulin among those
would become dependent on insulin for life.
who are suffering.
Least commonly known complications of diabetes were Stroke,
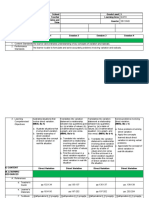
COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES AWARENESS PRESENT UNAWARE
known by just 24% patients, and delayed wound healing by just
32% of the patients.
DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY 46/ 92% 4/ 8%
DIABETIC FOOT 40 / 80% 10/ 20% Discussion
DIABETIC EYE DISEASE 30/ 60% 10/ 40%
The study's sample was predominantly male (72%), with a
DIABETIC NEUROPATHY 32/ 64% 18/ 36% significant proportion of patients (58%) having been diagnosed
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS AND COMA 27/ 54% 23/ 46% with diabetes over five years ago. It was found that long-term
patients had less awareness of more than two complications of
DELAYED WOUND HEALING 16/ 32% 36/ 72% diabetes (40%) compared to those diagnosed within the last five
DIABETIC HEART DISEASE 29/ 58% 21/ 42% years (56%). This suggests that recent diagnostic procedures may
include more comprehensive patient education. However, general
STROKE 12/ 24% 38/ 76%
knowledge about diabetes management, such as the target blood
sugar range, was low (38%), indicating a gap in patient education.
Methods and Materials The majority of patients relied on glucometers to monitor their
blood sugar (60%), highlighting the importance of these devices in
A pretested, predesigned, semi-structured questionnaire in local diabetes management. Interestingly, misconceptions about insulin
language consisting of items on the demographic profile including use were common, with 78% of patients believing that insulin use
age, sex and occupation, was used. Questionnaire consisted of would lead to lifelong dependency. This misconception could be a
items to assess their knowledge (cause, symptoms and barrier to effective diabetes management for some patients {5}.
complications), practices for management and prevention of
complications (exercise, drugs and dietary modifications) and Conclusions
myths about insulin. Questionnaire was pilot tested among adult
DM patients for assessing its feasibility and reliability. Opinion of This study underscores the crucial role of patient education in
experts on each questionnaire item was obtained. Suitable managing diabetes and preventing complications. While patients
modifications were done afterward. Average time duration of each demonstrated some knowledge about diabetes complications and
interview was approximately 15 to 20 minutes. Subjects consisted management strategies, several gaps and misconceptions were
of 50 adult patients from OPD and IPD, of which only 21 (42%) identified. These findings highlight the need to improve patient
patients could read and write, and 29 (58%) were unable to read, education, dispel myths, and promote a comprehensive
hence each component was verbally explained to obtain answers. understanding of diabetes. This could potentially improve disease
All patients were explained the purpose of the study and management, prevent complications, and enhance patients' quality
confidentiality was assured. of life.
Contact: References
1. Singla A, Sharma T, Kaeley N. Awareness of Diabetic Patients towards Diabetes Mellitus: A Survey Based Study. Natl J Community Med
Dr. Shubhangi Sharma [Internet]. 2017 Oct. 31 [cited 2024 Jan. 11];8(10):606-10. Available from: https://njcmindia.com/index.php/file/article/view/1429
2. Study on complications of diabetes mellitus among the diabetic patients Mr. Panari Hazaratali1,*, Mrs. Vegunarani M
3. Belsti, Y., Akalu, Y., Fekadu, H. et al. Awareness of complications of diabetes mellitus and its associated factors among type 2 diabetic patients
Email: shubhangi.medicine @gmail.com at Addis Zemen District Hospital, northwest Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes 12, 602 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-019-4637-x
4. Knowledge of diabetic complications in patients with diabetes mellitus, Vol. 27 No. 2 (2015): Journal of Ayub Medical College, Abbottabad
5. N. Murugesan, C. Snehalatha, R. Shobhana, G. Roglic, A. Ramachandran, Awareness about diabetes and its complications in the general and
Institute: Apollo Hospitals, Bilaspur diabetic population in a city in southern India, Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, Volume 77, Issue 3,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2007.01.004.(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016882270700037X)
You might also like
- 100 Q&A of GCE O'Level Economics 2281Document32 pages100 Q&A of GCE O'Level Economics 2281Hassan Asghar100% (4)
- Assessment of Knowledge of Diabetes Among Diabetic and Non-Diabetic IndividualsDocument5 pagesAssessment of Knowledge of Diabetes Among Diabetic and Non-Diabetic IndividualsCharlosNo ratings yet
- Article 233554Document11 pagesArticle 233554رقية ياسينNo ratings yet
- KAP Towards DMDocument10 pagesKAP Towards DMHabtamu Wondifraw100% (1)
- Ass Knowledge and MaDocument1 pageAss Knowledge and MaB04-BALKIS SOLEHAHNo ratings yet
- Results and DiscussionDocument5 pagesResults and DiscussionDrDeepak PawarNo ratings yet
- Sanofi-Aventis' India SITE Study Shows 62% of Diabetic Population in New Delhi Has Uncontrolled' DiabetesDocument4 pagesSanofi-Aventis' India SITE Study Shows 62% of Diabetic Population in New Delhi Has Uncontrolled' DiabetesMadhu ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Prevalence and Major Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Cross-Sectional Study in EcuadorDocument5 pagesPrevalence and Major Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Cross-Sectional Study in EcuadorJorge Andres Talledo DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Adherence To Oral Hypoglycemic Medication Among Patients With Diabetes in Saudi ArabiaDocument5 pagesAdherence To Oral Hypoglycemic Medication Among Patients With Diabetes in Saudi ArabiamajedNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Awareness of Diabetic Retinopathy Among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Cross Sectional Study From Central IndiaDocument7 pagesAssessment of Awareness of Diabetic Retinopathy Among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Cross Sectional Study From Central IndiaAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Prospective Study On Prescribing Patterns ofDocument11 pagesProspective Study On Prescribing Patterns ofthirunagari praveenNo ratings yet
- Ijcmr 3211 v1 PDFDocument5 pagesIjcmr 3211 v1 PDFAtul DwivediNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Knowledge and Self Care Practices in PDFDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Knowledge and Self Care Practices in PDFpraveena thanavelNo ratings yet
- Review LiteratureDocument23 pagesReview LiteratureDrDeepak Pawar50% (4)
- JDM 2017110814284359Document8 pagesJDM 2017110814284359Mochamad BilalNo ratings yet
- REVIEWDocument20 pagesREVIEWSanjeet DuhanNo ratings yet
- 2699 PDFDocument4 pages2699 PDFSeptya widhiafniNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Knowledge and Self Care Practices in Diabetic Patients and Their Role in Disease ManagementDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Knowledge and Self Care Practices in Diabetic Patients and Their Role in Disease ManagementSharmela BrijmohanNo ratings yet
- Selfcare and Related Factors in Patients With Type 2 DiabetesDocument5 pagesSelfcare and Related Factors in Patients With Type 2 DiabetesCM GabriellaNo ratings yet
- EN-the-correlation-between-level-of-diabetiDocument6 pagesEN-the-correlation-between-level-of-diabetiMutiara Khaerun NisaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Inertia in T2DM ManagementDocument11 pagesClinical Inertia in T2DM ManagementEva GabrielNo ratings yet
- Nusantara Medical Science JournalDocument7 pagesNusantara Medical Science JournalIslamiah DewiNo ratings yet
- Studi Penggunaan Oad Pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2Document13 pagesStudi Penggunaan Oad Pada Pasien Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2Fatwaa AizzahraaNo ratings yet
- dm sankaraDocument7 pagesdm sankarahenokbirukNo ratings yet
- Assessing Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Diabetes Type 2 Patients Attending Keruguya Referral HospitalDocument10 pagesAssessing Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Diabetes Type 2 Patients Attending Keruguya Referral HospitalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & ReviewsDocument5 pagesDiabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & ReviewsPetra Diansari ZegaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & ReviewsDocument5 pagesDiabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & ReviewsDR VENKATARAMANA MurthyNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Assessment of The Common Risk Factors Associated With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in JeddahDocument9 pagesResearch Article: Assessment of The Common Risk Factors Associated With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in JeddahAdytia SuparnaNo ratings yet
- Kolar KarnatakaDocument5 pagesKolar KarnatakaSkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Compliance To Diabetes Self-Management in Rural El-Minia, EgyptDocument7 pagesCompliance To Diabetes Self-Management in Rural El-Minia, Egyptchintya claraNo ratings yet
- ICMR Guidelines for Management of Type 1 DiabetesDocument173 pagesICMR Guidelines for Management of Type 1 DiabetesAlphani MwaniNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patient's Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Regarding HypertensionDocument6 pagesAssessment of Patient's Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Regarding HypertensionScintya NasutionNo ratings yet
- Retensi UrinDocument13 pagesRetensi UrinSulhan SulhanNo ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Fenugreek Water To Reduce Blood Glucose Levels Among Clients With Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Fenugreek Water To Reduce Blood Glucose Levels Among Clients With Diabetes MellitusEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Undiagnosed and Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus Among Adults in South ChennaiDocument5 pagesPrevalence of Undiagnosed and Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus Among Adults in South ChennaiVishakha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- A Descriptive Study To Assess The Level of Knowledge and Attitude of Hypertensive Patients Regarding Lifestyle Modification in Hypertensive Clinic, Opd Kgmu, Lucknow, Uttar PradeshDocument8 pagesA Descriptive Study To Assess The Level of Knowledge and Attitude of Hypertensive Patients Regarding Lifestyle Modification in Hypertensive Clinic, Opd Kgmu, Lucknow, Uttar PradeshEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Practice Regarding Foot Care Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesKnowledge and Practice Regarding Foot Care Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Dmso 13 2317Document9 pagesDmso 13 2317PutriutamiNo ratings yet
- DM Conclusion 222Document2 pagesDM Conclusion 222DrDeepak PawarNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument10 pagesSchizophreniajhuNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of Medical Officers in Primary Health Centres Regarding Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesAssessment of Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of Medical Officers in Primary Health Centres Regarding Type 2 Diabetes MellitusTengiz Verulava100% (1)
- Discussion: Summary & ConclusionDocument29 pagesDiscussion: Summary & ConclusionVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Health Beliefs, Self-Care Behaviors and Quality of Life in Adults With Type 2 DiabetesDocument9 pagesHealth Beliefs, Self-Care Behaviors and Quality of Life in Adults With Type 2 DiabetesgamzeNo ratings yet
- Use of Lipid-, Blood Pressure-, and Glucose-Lowering PharmacotherapyDocument15 pagesUse of Lipid-, Blood Pressure-, and Glucose-Lowering PharmacotherapyTuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- 7052-Article Text-148734-1-10-20110930Document7 pages7052-Article Text-148734-1-10-20110930allenshanique1999No ratings yet
- Management of Diabetes Mellitus in Older People With ComorbiditiesDocument11 pagesManagement of Diabetes Mellitus in Older People With ComorbiditiesEmanuel BaltigNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument8 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- DM in IranDocument5 pagesDM in IranSeptian PutraNo ratings yet
- 853Document7 pages853Villegas OsvaldoNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Diabetes and Its Effects On Stroke Outcomes: A Meta-Analysis and Literature ReviewDocument13 pagesPrevalence of Diabetes and Its Effects On Stroke Outcomes: A Meta-Analysis and Literature ReviewarinyNo ratings yet
- KretchyDocument10 pagesKretchyPoppy ArnitaNo ratings yet
- Screening, Prevention, Counseling, and Treatment For The Complications of Type II Diabetes MellitusDocument14 pagesScreening, Prevention, Counseling, and Treatment For The Complications of Type II Diabetes MellitusElis HartatiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Medical Care For Diabetic and Hypertensive Patients in Primary Care in Mexico: Observational Retrospective StudyDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Medical Care For Diabetic and Hypertensive Patients in Primary Care in Mexico: Observational Retrospective StudyMirna Liliana Carmona GarciaNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Depression Symptoms in Diabetes Mellitus: Salih EkerDocument4 pagesPrevalence of Depression Symptoms in Diabetes Mellitus: Salih EkerNathayaNeilaVarneliaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring On Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Randomized Clinical TrialDocument10 pagesEffect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring On Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes A Randomized Clinical TrialClaudia NgNo ratings yet
- HipoDocument10 pagesHipoDwi atikaNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument11 pagesResearch ArticleWahyuniNo ratings yet
- CaídasDocument5 pagesCaídasRocio ConsueloNo ratings yet
- Drug Utilization Pattern of Anti-Diabetic Drugs Among Diabetic Outpatients in A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument3 pagesDrug Utilization Pattern of Anti-Diabetic Drugs Among Diabetic Outpatients in A Tertiary Care HospitalTazkiyatan IsriaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Diabetes and Its ComplicationsDocument5 pagesJournal of Diabetes and Its ComplicationsQqNo ratings yet
- DLL WK 10 LC 171819Document14 pagesDLL WK 10 LC 171819Regiel Guiang ArnibalNo ratings yet
- Reading PashtoDocument17 pagesReading PashtoUmer Khan0% (1)
- Diagnostic-Test English5 2022-2023Document5 pagesDiagnostic-Test English5 2022-2023Queen Ve NusNo ratings yet
- HP Scanjet Pro 2500 F1 Flatbed Scanner: DatasheetDocument2 pagesHP Scanjet Pro 2500 F1 Flatbed Scanner: DatasheetKarkittykatNo ratings yet
- Town Planning Assistant in A.P Towncountry PlanningDocument3 pagesTown Planning Assistant in A.P Towncountry Planningbhavesh gangurdeNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument15 pagesSample QuestionsAnonymous MtKJkerbpUNo ratings yet
- Examen Blanc Et Corrige 3ASLLE Anglais 2e Sujet 2017Document4 pagesExamen Blanc Et Corrige 3ASLLE Anglais 2e Sujet 2017dila sailNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument32 pagesConstitutionAbhisht HelaNo ratings yet
- Types of Mutual FundDocument5 pagesTypes of Mutual FundGourav BulandiNo ratings yet
- Trades About To Happen - David Weiss - Notes FromDocument3 pagesTrades About To Happen - David Weiss - Notes FromUma Maheshwaran100% (1)
- Adhd Add Individualized Education Program GuideDocument40 pagesAdhd Add Individualized Education Program Guidelogan0% (1)
- Manual For Personnel: ProposedDocument11 pagesManual For Personnel: Proposedjsopena27No ratings yet
- Review Questions IODocument9 pagesReview Questions IOMarionne DagolsapoNo ratings yet
- Kult - The Dark Art PDFDocument7 pagesKult - The Dark Art PDFalnevoNo ratings yet
- Staircase Lift Design For Elderly at HomeDocument19 pagesStaircase Lift Design For Elderly at Homesabareesh91mechNo ratings yet
- Billing Reports Export 1702384478083Document82 pagesBilling Reports Export 1702384478083vinjamuriraviteja123No ratings yet
- LAS - Week 3 FunctionsDocument15 pagesLAS - Week 3 FunctionsLeywila Mae Yo BianesNo ratings yet
- (G.R. No. 136448. November 3, 1999.) Lim Tong Lim, Petitioner, V. Philippine Fishing Gear Industries, Inc, Respondent. DecisionDocument23 pages(G.R. No. 136448. November 3, 1999.) Lim Tong Lim, Petitioner, V. Philippine Fishing Gear Industries, Inc, Respondent. Decisionalay orejudosNo ratings yet
- Account of MR Pybus S Mission To The KinDocument133 pagesAccount of MR Pybus S Mission To The KinHarendraAlwisNo ratings yet
- Of Mice and Men EssayDocument7 pagesOf Mice and Men Essayjon782No ratings yet
- What A Body Can DoDocument26 pagesWhat A Body Can DoMariana Romero Bello100% (1)
- Marketing Rule BookDocument20 pagesMarketing Rule BookAnn Holman75% (4)
- Java Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceDocument16 pagesJava Cheat Sheet & Quick Referencedad dunnoNo ratings yet
- M15 Joining Processes - Welding Part 1Document52 pagesM15 Joining Processes - Welding Part 1Gita SaragihNo ratings yet
- Indonesian - 1 - 1 - Audiobook - KopyaDocument93 pagesIndonesian - 1 - 1 - Audiobook - KopyaBurcu BurcuNo ratings yet
- Economic and Political WeeklyDocument8 pagesEconomic and Political WeeklynaveensarimallaNo ratings yet
- PDF Medical Management of Thyroid Disease 3Rd Ed 3Rd Edition David S Cooper Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Medical Management of Thyroid Disease 3Rd Ed 3Rd Edition David S Cooper Ebook Full Chapterrebecca.baez273100% (5)
- Principles of Growth and DevelopmentDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Growth and DevelopmentMerlin AlfaneNo ratings yet
- Scope: Airport Planning ManualDocument4 pagesScope: Airport Planning ManualclebersjcNo ratings yet