Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure and Functions
Cell Structure and Functions
Uploaded by
Danilo JR. BuaquiñaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure and Functions
Cell Structure and Functions
Uploaded by
Danilo JR. BuaquiñaCopyright:
Available Formats
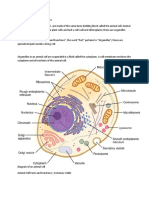
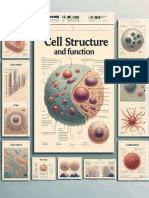
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
All living things have cells that share fundamental structural parts, which include:
Cell membrane/Plasma membrane - regulates the passage of materials
into and out of the cell. It separates the contents of the cell from its
environment and permits communication with other cells.
Cytoplasm - a gel-like substance making up the cell’s internal environment.
Various metabolic reactions like protein synthesis and breakdown of sugar
into ATP take place in the cytoplasm. Organic materials such as glucose,
amino acid, nucleic acids and etc. can be found and dissolved in the
cytoplasm.
Nucleus - a central genetic region containing the genetic material in the
form of DNA that provides instructions to make proteins, regulates,
activities, and enables cells to reproduce. It is the control center of the cell
that regulates and coordinates all activities of the cell.
An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to
perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body. Organelles are found and
perform their functions in the jelly-like substance called cytosol in the cytoplasm.
The following are the basic organelles found in the cytoplasm:
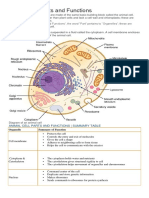
BASIC ORGANELLES FOUND IN THE
DEFINITION
CYTOPLASM
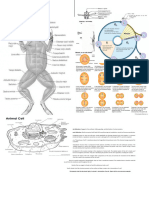
Mitochondria Supply energy to the cell. They
are the sites for the breakdown
of sugar molecules into
adenosine triphosphate or ATP,
which is the main source of
energy in the body.
Ribosomes Are the sites of protein synthesis.
The coded message from DNA as
to what kind of protein is to be
synthesized and carried by the
mRNA from the nucleus to the
ribosome.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Consists of flattened sheets,
sacs, and tubes of membranes
that extend throughout the
cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It
is structurally continuous with the
nuclear membrane, and it
specializes in the transport of
lipids and membrane proteins.
Golgi Apparatus A system of flattened,
membrane-bound sacs that looks
like stack of pancakes. Its
function is to modify, sort, and
pack macromolecules (protein)
for secretion or for transport to
other organelles. Rounded
vesicles are associated to the
Golgi apparatus that pinched off
from its flattened sacs and carry
the materials to other parts of
the cell.
Lysosomes Produced by the Golgi apparatus.
It is a membrane- bound
organelle that comes in various
sizes and shapes. It contain
numerous hydrolytic or digestive
enzymes for the breakdown of
carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
within the cell. Thus, they are
known as “digestive sacs. ”
Destruction or repair of defective
parts of the cell is another
function of lysosomes.
Peroxisomes Contain digestive enzymes for
breaking down toxic materials in
the cell and oxidative enzymes
for metabolic activity.
Peroxisomes are oxidative
organelles. Their enzymes break
down fatty acids and amino
acids.
Vacuoles Are large storage sacs in cells. In
animals, some vacuoles function
for storage of water or food,
while others are for excretion of
waste materials. Plants have a
central vacuole which is a single
large vacuole that takes up most
of the space inside a plant cell.
Cytoskeleton Provides the cell’s structura
support. It is responsible for cell
shape and motility. it also
provides mechanical support that
enables cells to carry out
essential functions like division
and movement.
Plastids Plastids are large membrane-
bound organelle found in plant
cells. Some classification of
plastids are chloroplast, the
green-colored plastid which is
caused by the green pigment
called chlorophyll and is the
site for photosynthesis.
Chromoplasts, pigments such
as red, orange, and yellow.
Leucoplasts, the colorless
plastid that contain stored food.
Cell Wall Another organelle found in plant
cells only is the cell wall. It
protects and supports the cells of
the plants.
You might also like
- Animal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableDocument16 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableAnnie Lyn Villamor100% (1)
- Animal Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and FunctionsKarren Ferrer-Mora Handayan100% (1)
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocument10 pagesAnimal Cell DefinitionAngelique VeteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Cell OrganellesAly FayeNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- JetDocument14 pagesJetAnnie Lyn VillamorNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- Cell Structure2Document6 pagesCell Structure2CRYSTAL A. ARIETANo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (Contrast)Document2 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (Contrast)Joyce DegomaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Organisation of The OrganismDocument6 pages2 - Organisation of The OrganismAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Body PartsDocument1 pageAnimal Cell Body Partsnako simpNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Manifestation of LifeDocument6 pagesStructural and Functional Manifestation of LifeKaila StefanieNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- "Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology IDocument23 pages"Life Begins With Cells": Cell Biology ITeacher Ella MorillaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LectureDocument13 pagesModule 2 LectureJeal NochefrancaNo ratings yet
- Isnain - Biochem Lec - Assignment 1Document4 pagesIsnain - Biochem Lec - Assignment 1Erich IsnainNo ratings yet
- Act 2CDocument3 pagesAct 2CCHARLIENE FAYE ASPRERNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 Cell ReviewDocument5 pagesCh. 3 Cell ReviewDivine GelasiusNo ratings yet
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- FB - Sevilla - Module 4Document5 pagesFB - Sevilla - Module 4Joyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledGlenisse DvyneNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure and FunctionHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaDocument6 pagesPamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaJosett RomanoNo ratings yet
- Document 4Document11 pagesDocument 4pragany.saiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument11 pagesCellNicole ArangurenNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM (Exercise 1)Document4 pagesBIOCHEM (Exercise 1)KATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- Cell Biology BasicsDocument23 pagesCell Biology BasicsAbume DougyNo ratings yet
- Scrapy Group 3Document7 pagesScrapy Group 3Andrea Ericka CanawayNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The CellDocument4 pagesExercise 1 The CellKATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologyKent TediosNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures & Organelles FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Structures & Organelles Functionsnasimzand78100% (1)
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology: The CellDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Celllourd nabNo ratings yet
- Cells and Their StructuresDocument18 pagesCells and Their StructuresJessie CalipusanNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- Bio 221 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBio 221 Lecture NotesMuhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYAngel ManlaviNo ratings yet
- Module For Anaphy CellDocument11 pagesModule For Anaphy CellBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- 11a Revision Pack T1Document36 pages11a Revision Pack T1Najat BteichNo ratings yet
- PRPM110L Module 3 & 4Document10 pagesPRPM110L Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument2 pagesZoologygabrf.pascualNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Endomembrane System (Seminar)Document11 pagesEndomembrane System (Seminar)Prachi TayadeNo ratings yet
- Polio Sabin GDS03.IPI01 PDFDocument5 pagesPolio Sabin GDS03.IPI01 PDFDevalina JunaharNo ratings yet
- 10th Summer Research Program in TsukubaDocument33 pages10th Summer Research Program in TsukubaSarah SafiraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunoassaysDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Immunoassaysvidhi100% (1)
- Exhibitor / Company Name Stall Name AreaDocument56 pagesExhibitor / Company Name Stall Name AreaJyotsna PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Other Emerging TechnologiesDocument100 pagesChapter 7 - Other Emerging TechnologiesAmirNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1 Mod6 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration v3Document45 pagesScience 9 q1 Mod6 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration v3Keith Kevin Dave DandanNo ratings yet
- 6 ADC Piramal1Document37 pages6 ADC Piramal1anitaNo ratings yet
- A. Delonix Regia: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument9 pagesA. Delonix Regia: Answer All Questions in This SectionNorbert LimNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Cycle 8.03Document47 pages1 Cell Cycle 8.03Rawbeena RamtelNo ratings yet
- Genetics Bits gpbr-111Document10 pagesGenetics Bits gpbr-111Adan FatimaNo ratings yet
- IAL - Biology - SB2 - Mark Scheme - 8BDocument3 pagesIAL - Biology - SB2 - Mark Scheme - 8BsalmaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Virology MCQ Paper 2Document8 pagesAnswers To Virology MCQ Paper 2Idrissa ContehNo ratings yet
- Pharmacogenetics and Pharmacogenomics: Kevin Zbuk, MD Medical Oncologist Juravinski Cancer Centre Mcmaster UniversityDocument72 pagesPharmacogenetics and Pharmacogenomics: Kevin Zbuk, MD Medical Oncologist Juravinski Cancer Centre Mcmaster UniversityAnubhuti JhaNo ratings yet
- 4 Mapping in EukaryotesDocument36 pages4 Mapping in EukaryotesSabesan TNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Goods and Medical Equipment - Romanian ImportersDocument5 pagesPharmaceutical Goods and Medical Equipment - Romanian Importersmarketing lakshNo ratings yet
- Combinatorial ChemistryDocument2 pagesCombinatorial Chemistryapi-26277448No ratings yet
- Dna Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument2 pagesDna Replication, Transcription and TranslationJenna PretalNo ratings yet
- 2D Gel Electrophoresis Training: Proteomics and Mass Spectrometry FacilityDocument12 pages2D Gel Electrophoresis Training: Proteomics and Mass Spectrometry FacilityEli HeberNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Unit 2 by Jeeshan AhmadDocument11 pagesBiotechnology Unit 2 by Jeeshan AhmadYug PatelNo ratings yet
- Erica Cai Named ALPCO's Summer 2020 Diabetes Research Travel Grant RecipientDocument3 pagesErica Cai Named ALPCO's Summer 2020 Diabetes Research Travel Grant RecipientPR.comNo ratings yet
- MSC BiotechnologyDocument82 pagesMSC BiotechnologyJanikaa Singaravel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Mitocondria y ParkinsonDocument13 pagesMitocondria y ParkinsonEstebanNo ratings yet
- Reviews: DNA Methylation Profiling in The Clinic: Applications and ChallengesDocument14 pagesReviews: DNA Methylation Profiling in The Clinic: Applications and ChallengesVivi ZhouNo ratings yet
- Updated Vaccination Card KNHSDocument4 pagesUpdated Vaccination Card KNHSlemar aribalNo ratings yet
- Feature: The Global Pipeline of GM Crops Out To 2020Document6 pagesFeature: The Global Pipeline of GM Crops Out To 2020Sergio IglesiasNo ratings yet
- High-Resolution Screening of Metabolite-Like Lead LibrariesDocument114 pagesHigh-Resolution Screening of Metabolite-Like Lead LibrariesBuscador AlfaNo ratings yet
- Cross Matchung Renal TransplantDocument52 pagesCross Matchung Renal Transplantanderson roberto oliveira de sousaNo ratings yet
- Small-Molecule Library Screening by Docking With Pyrx: Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.) January 2015Document12 pagesSmall-Molecule Library Screening by Docking With Pyrx: Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.) January 2015Zoya AmjadNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control of Protein SynthesisDocument27 pagesGenetic Control of Protein SynthesisDICKSONNo ratings yet
- DNA Transcription - Learn Science at ScitableDocument4 pagesDNA Transcription - Learn Science at ScitableSheryl Lin Dayrit DolorNo ratings yet