Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Life Processes (Digestion)
Life Processes (Digestion)
Uploaded by
Farid AhemadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Life Processes (Digestion)
Life Processes (Digestion)
Uploaded by
Farid AhemadCopyright:
Available Formats
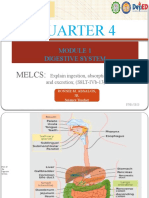
SCIENCE
CLASS-X (Life processes) Digestion Dt-20/04/2024
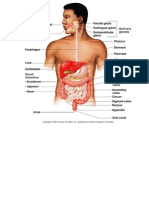
Stomach
The stomach is a thick-walled bag-like structure.
Its receives food from the oesophagus at one end and opens into the small intestine at the other end.
The inner lining of the stomach has gastric glands which secretes mucous, hydrochloric acid and digestive juices.
Food is churned into a semi-solid mass in the stomach and is called chyme.
HCl provides acidic medium for protein digestion.
Hydrochloric acid activates the pepsinogen convert to pepsin which digest partially the proteins and also kills
harmful bacteria.
Mucus secreted by the wall of the stomach resists the action of HCl on itself.
Small Intestine
The small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal, about 20 feet long in humans.
It has regions, duodenum, the region which follows stomach, jejunum is the middle part and ileum is the
later region which continues further into the large intestine.
The internal surface of the small intestine is folded into finger-like projections called villi. Villi increase the
internal surface area of the intestinal walls making available a greater surface area for absorption. Digested
nutrients pass into the semipermeable villi through diffusion.
A common pancreatic duct from pancreas and liver opens into the duodenum.
Most of the chemical digestion and absorption takes place in the small intestine.
Large Intestine
The large intestine in humans is about 5 feet long.
It has two regions, colon ( about 1.5 m) and rectum (10 cm in length in the adult).
The region of large intestine after ileum is called colon while the last part is called the rectum.
Colon has three regions as, ascending colon, transverse colon and descending colon.
At the base of the ascending colon, a small finger-like out-growth is seen and is called an
appendix.
It houses many useful bacteria required for digestion of food.
Rectum opens to outside by anus.
The anus has internal and external anal sphincters.
Digestive Glands
Several glands produce digestive juices that help in digestion of the food.
Salivary glands, Gastric glands, Liver, Pancreas and intestinal gland .
Salivary glands secrete salivary amylase which initiates digestion in the mouth. It digest
starch.
Gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach secrete hydrochloric acid and enzyme
pepsin.
The liver secretes bile which is stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps in emulsification of fats
(larger fat molecule convert into small particles) and make the alkaline medium of the small
intestine.
The pancreas secretes many digestive enzymes and its secretion is called as pancreatic
juice.
Enzymes like trypsin, , lipase are present in the pancreatic juice. Trypsin digest the partial
digested protein and lipase digest the fat.
End products--: Carbohydrate --------> Glucose Protein --------> Amino acid
Fat------> Fatty acids and glycerol
You might also like
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaDocument37 pagesUman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaBishal Khaidem0% (1)
- Shakila Hamed Report PDFDocument9 pagesShakila Hamed Report PDFShakila HamidNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesOverview of The Digestive SystemMehmet SaylıkNo ratings yet
- Inglés II - TP 1 - Respuestas TipoDocument14 pagesInglés II - TP 1 - Respuestas TipoDaniNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Human BeingsDocument8 pagesNutrition in Human Beingsparashakthi PRNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Human Beings Class 6Document5 pagesNutrition in Human Beings Class 6Sarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument5 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionSheehan MathurNo ratings yet
- Essay # 4. DigeDocument9 pagesEssay # 4. DigeAbdul Karim BurkiNo ratings yet
- BIO103 Lec-17.46 ArIm Digestive System 220424Document27 pagesBIO103 Lec-17.46 ArIm Digestive System 220424bilashqipNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument4 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionMin NimNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument18 pagesBiology NotesajairafingerishiNo ratings yet
- Karthik Bharadwaj'S: PresentationDocument32 pagesKarthik Bharadwaj'S: PresentationMahir AfranNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument44 pagesThe Digestive SystemJoy NatividadNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument39 pagesDigestive SystemArjay MartinNo ratings yet
- (Ăm'ə-Lāce ) or Ptyalin (Tī'ə-Lĭn) Is The Digestive Enzyme Found in Saliva. ItDocument5 pages(Ăm'ə-Lāce ) or Ptyalin (Tī'ə-Lĭn) Is The Digestive Enzyme Found in Saliva. ItKyle Keen TaerNo ratings yet
- m6 Digestive SystemDocument23 pagesm6 Digestive Systemapi-464344582No ratings yet
- 35.1 - The Digestive SystemDocument16 pages35.1 - The Digestive SystemMostafa Galal El Din100% (1)
- Digestive System A&p BookletDocument11 pagesDigestive System A&p Bookletnurse1990No ratings yet
- Human Digestion PresentationDocument35 pagesHuman Digestion PresentationYamyang Galay-BañoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AND Physiology: (Gastrointestinal System)Document6 pagesAnatomy AND Physiology: (Gastrointestinal System)Antonette LeiNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesDigestive Systemapi-269652707No ratings yet
- Digestive System Grade 10-11Document7 pagesDigestive System Grade 10-11Nandana Nayana KumaraNo ratings yet
- Digestion Is The Breaking Down of Chemicals in The Body, Into A Form That Can Be Absorbed. It IsDocument10 pagesDigestion Is The Breaking Down of Chemicals in The Body, Into A Form That Can Be Absorbed. It IsSean McleanNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy: RugaeDocument5 pagesGross Anatomy: RugaeKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Alimentary Tract, or Alimentary Canal. The Term Gastrointestinal TractDocument10 pagesAlimentary Tract, or Alimentary Canal. The Term Gastrointestinal TractEugenia Lopez DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Digestion 20240208 125021 0000Document21 pagesDigestion 20240208 125021 0000khandurreshahwar14No ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument11 pagesNUTRITIONRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- 10 BiologyDocument3 pages10 BiologyNaveen NNo ratings yet
- M1 Lesson 2Document6 pagesM1 Lesson 2Catherine Sinen ObinqueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive System: Tongue MusclesDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive System: Tongue Musclesbarbiegirl9497No ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument82 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionCoc FanNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NewDocument49 pagesDigestive System NewPHAMAE JOY MEMBREVENo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Human DigestionDocument38 pagesHuman DigestionSheeba AliNo ratings yet
- Digestive System and Process of DigestionDocument4 pagesDigestive System and Process of DigestionSid QNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PPT 1Document38 pagesDigestive System PPT 1robloxaltacc356No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiolog AMOEBIASISDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiolog AMOEBIASISSamer SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Teeth and Tongue-: I. MouthDocument11 pagesTeeth and Tongue-: I. Moutharisu100% (1)
- Digestion & Absorption NotesDocument15 pagesDigestion & Absorption NotesKankana BiswasNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 Human Digestive System - PPTX 4thDocument47 pagesQ4 Week 3 Human Digestive System - PPTX 4thdenveralbarico143No ratings yet
- Digestive System HandoutDocument7 pagesDigestive System Handouttheodore_estradaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PresentationDocument23 pagesNutrition Presentationanneborja511No ratings yet
- Main Book DigestiveDocument9 pagesMain Book DigestivealinegustriNo ratings yet
- Digestive System, Educational PlatformDocument77 pagesDigestive System, Educational Platformluckytraders0511No ratings yet
- Digestive System ReviewDocument2 pagesDigestive System ReviewSherriena LeangNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive Systemsikandercheema123No ratings yet
- Digestive System ScriptDocument4 pagesDigestive System ScriptNEPERESM TALCEY BORCESNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis FinalDocument13 pagesUlcerative Colitis FinalAngelique100% (1)
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY EditedDocument3 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY EditedBSN 2 - Sasis, Rusmaryte C.No ratings yet
- BIO Lect Powerpoint InfoDocument18 pagesBIO Lect Powerpoint InfoEarl ReyesNo ratings yet
- 3.3 The Digestion and Absorption Process - Medicine LibreTextsDocument1 page3.3 The Digestion and Absorption Process - Medicine LibreTextsManishNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy PhysiologyDocument20 pagesDigestive System Anatomy PhysiologyKids JangNo ratings yet
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandDocument25 pagesUman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Presentati On On BiologyDocument13 pagesWelcome To The Presentati On On BiologySHILPANo ratings yet
- Leaky Gut Syndrome Stop! - A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyFrom EverandLeaky Gut Syndrome Stop! - A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyNo ratings yet
- Presentation (1) - 1Document8 pagesPresentation (1) - 1Farid AhemadNo ratings yet
- Life Processes (Transportation)Document3 pagesLife Processes (Transportation)Farid AhemadNo ratings yet
- Literary DeviceDocument1 pageLiterary DeviceFarid AhemadNo ratings yet
- The Frog and The NightingaleDocument1 pageThe Frog and The NightingaleFarid Ahemad100% (1)
- Class 10 History Chapter 1 NotesDocument16 pagesClass 10 History Chapter 1 NotesFarid AhemadNo ratings yet
- English Results ViiiDocument3 pagesEnglish Results ViiiFarid AhemadNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disorders, 2nd EdDocument2 pagesSurgical Management of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disorders, 2nd EdiweNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing Madurai Medical College Madurai-20Document23 pagesCollege of Nursing Madurai Medical College Madurai-20monishaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Summative Exam Q4Document4 pagesScience 8 Summative Exam Q4Kelvin Jason ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE Biology 0610 GCSE O LevelDocument38 pagesHuman Nutrition Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE Biology 0610 GCSE O LevelIGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology-IiDocument17 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology-IiMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation AppendicitisDocument79 pagesCase Presentation AppendicitisCristina Tagle Garcia100% (5)
- Formulation of Small Molecules: Prof Abdul BasitDocument32 pagesFormulation of Small Molecules: Prof Abdul Basitchegu BusinessNo ratings yet
- Surgical Diseases of PancreasDocument17 pagesSurgical Diseases of PancreasIris BakerNo ratings yet
- LP1Document6 pagesLP1Huo XingNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CholelitiasisDocument8 pagesPathophysiology of CholelitiasisJASMINENICHOLE �GALAPONNo ratings yet
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument37 pagesObstructive JaundiceDronacharya RouthNo ratings yet
- AD285230700512 LO230700610: Patient ReportDocument1 pageAD285230700512 LO230700610: Patient ReportReal Gamer 6No ratings yet
- What Is HirschsprungDocument4 pagesWhat Is HirschsprungMicah SaberNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGEYum CNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 3Document11 pagesDigestive System 3ronnieNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy 4 PrintingDocument19 pagesCholecystectomy 4 PrintingKyle Punzalan100% (2)
- GIT Physiology CHAPTER NO 62 Guyton by Dr. RoomiDocument41 pagesGIT Physiology CHAPTER NO 62 Guyton by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi86% (14)
- What Is Acute Pancreatitis?Document5 pagesWhat Is Acute Pancreatitis?leonard1971No ratings yet
- The Case of Brenda Brown WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Case of Brenda Brown Worksheetshya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Laju Digesti Pada Ikan FiksDocument12 pagesLaju Digesti Pada Ikan FiksfataNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodical Exam Science 8Document4 pages3rd Periodical Exam Science 8Franz JonsonNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Animals NotesDocument6 pagesNutrition in Animals NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7ANo ratings yet
- Digestion Science Form 2Document25 pagesDigestion Science Form 2tengkusuhaidaNo ratings yet
- Class Xi - Digestion and AbsorptionDocument38 pagesClass Xi - Digestion and AbsorptionketakiNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System TQS 4th FormDocument18 pagesThe Digestive System TQS 4th FormrandyhmthsNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Scoring in Histology: Exercise 11: Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesRubrics For Scoring in Histology: Exercise 11: Digestive SystemEdgar DumagpiNo ratings yet
- 4 Walton2018Document6 pages4 Walton2018meeNo ratings yet
- Sitz MarksDocument3 pagesSitz MarksFercee PrimulaNo ratings yet