Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SEC017 Construction Management
SEC017 Construction Management
Uploaded by
diana.mhaydv08010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesOriginal Title
SEC017-Construction-Management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesSEC017 Construction Management
SEC017 Construction Management
Uploaded by
diana.mhaydv0801Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
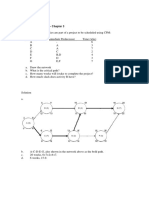
LECTURE CONTENT SITUATION 3 - The table shown below tabulates the
activities for making a network diagram for a
✓ Basic Elements of Project Scheduling project together with duration and cost in normal
✓ Methods in Project Scheduling and accelerated conditions.
✓ Crashing of Project Network
Normal Conditions Accelerated
✓ Presidential Decree 1594 Activity Conditions
✓ Concrete Mix Design Duration Costs Duration Costs
(Pesos) (Pesos)
SITUATION 1 – The table below shows the schedule of 0-1 (A) 5 1000 3 1600
works necessary to carry out a construction 0-2 (B) 5 3000 4 4000
project. Critical Path Method is used for
scheduling. 0-3 (D) 3 12000 2 12000
1-2 (C) 7 3000 5 3500
2-3 (E) 4 1000 3 1500
3-4 (F) 5 1000 3 1800
7. Determine the critical path.
A. A-C-E-F B. B-D-E-F
C. A-B-E-F D. A-D-C-F
8. Determine the cost (in Pesos) if it is
accelerated to the minimum duration.
A. 21,700 B. 24,400
C. 22,500 D. 24,100
9. Determine which activity is the most cost
effective in converting to the accelerated
program.
A. Activity A B. Activity D
C. Activity C D. Activity F
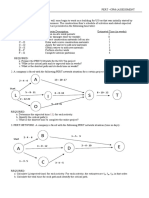
SITUATION 4 – A project has been bid out by the
Department of Public Works and Highways. The
Approved Agency Estimate is P 2,000,000. The result
of responsive bids are as follows:
1. Determine the critical path for the project. Bidder A P 2,320,000
A. A-B-D-G-I-K B. A-C-H-J-K Bidder B P 2,600,000
C. A-B-E-I-K D. A-C-F-I-K Bidder C P 2,040,000
2. Determine the number of days required to carry
Bidder D P 1,780,000
out the entire project
A. 45 CD B. 65 CD Bidder E P 1,290,000
C. 55 CD D. 75 CD Bidder F P 1,650,000
3. Determine the total float of activity H. Bidder G P 2,440,000
A. 15 CD B. 25 CD Bidder H P 2,700,000
C. 20 CD D. 30 CD
4. Determine the free slack of activity F. 10. Determine which of the following are considered
as responsive bidders.
A. 18 CD B. 32 CD
A. A,D,E,F B. C,D,F,G
C. 27 CD D. 41 CD
C. B,G,H D. A,C,D,E,F
SITUATION 2 – The table below shows the schedule of 11. Which of the following most nearly gives the
activities necessary for assembling computer. By value of Allowable Government Estimate?
using Gantt Analysis, determine the following: A. P 1,911.667 B. P 2,051,250
C. P 1,908,000 D. P 1,880,000
12. Which of the following bidders should the
project be awarded?
B. Bidder A B. Bidder D
C. Bidder C D. Bidder F
SITUATION 5 – The quantities and contract prices for
a government project are as follows:
Items Quantity Unit Price (Pesos)
AAE Contract
Item 1 100 900 1,000
Item 2 50 12,000 10,000
Item 3 500 4,000 5,000
Item 4 60 7,500 6,000
Item 5 1,000 2,800 3,000
Item 6 400 2,000 1,500
5. Determine the number of days required to carry Item 7 3,000 2,100 2,000
out the entire project Item 8 20 20,000 25,000
A. A-C-F-G B. A-C-D-F-G
C. A-B-E-F-G D. A-D-F-G 13. Which of the following most nearly gives the
6. Determine the critical path for the projects (in approved agency estimate (AAE)?
weeks). C. P 13.95 M B. P 15.39 M
A. 35 B. 41 C. P 14.34 M D. P 13.44 M
C. 38 D. 44
14. Determine the complete list of the major items.
D. Items 2,5,7 B. Items 2,7
C. Items 5,7 D. Item 8 C. 0.681 B. 0.708
C. 0.693 D. 0.715
15. Which of the following need not be covered 24. Determine the required amount of cement in kN
by a change order? for a 10 m3 concrete.
D. 23.88 B. 36.79
A. Decrease in quantity from 50 to 37 for item
C. 29.04 D. 41.35
2.
25. If the combined solid volume of cement, water,
B. Decrease in quantity from 1000 to 750 for
coarse aggregate, and entrapped air is 0.55 m3,
item
determine the weight of the dry sand (in kN).
C. Increase in quantity from 500 to 625 for
item D. Increase in quantity from 20 to 26 E. 11.65 B. 13.67
for item 8. C. 12.34 D. 14.52
SITUATION 9 – Section 426.12.2 of NSCP 2015 states
SITUATION 6 – The responsive bids for a government the provision for the frequency of testing for
project with 8 bid items are as follows: concrete. It is required to determine the number of
test sample per day for the following items:
Item Qty AAE Bid A Bid B Bid C
1 100 1000 1000 500 800 Description Dimension Qty.
2 100 20000 27000 16000 19000 Column 1m x 1m x 3.50m 12 pcs.
3 500 5000 4000 3000 5000 Beam 1m x 1.7m x 6.0m 17 pcs.
4 60 6000 5000 6000 5000 Slab 6m x 6m x 0.20m 8 pcs.
5 1000 3000 2000 2500 3000 Shear Wall 6m x 3m x 0.30m 4 pcs.
6 400 1600 2000 1500 1200
26. Determine the required number of tests per day
7 3000 3000 3000 3500 2500 according to NSCP 2015.
8 20 25000 24000 12000 33000 F. 1 B. 3
16. Which of the following most nearly gives the C. 2 D. 4
total AAE?
A. 64,600 B. 72,300
C. 71,500 D. 82,200 CONCEPTS
17. Determine the complete list of major items.
B. Items 2,8 B. Items 2,4,8 Construction
C. Item 2,4 D. Items 2,3,4,8 Is the mobilization and utilization of capital and
18. Determine the complete list of unbalanced bids. specialized personnel, materials, and equipment to
A. Bid B B. Bids A,B,C assemble materials and equipment on a specific site
C. Bids A,C D. Bids B,C in accordance with drawings, specifications, and
contract documents prepared to serve the purpose of
the client.
SITUATION 7 – It is required to produce 25 cu. m. of
Class B (1:2.5:5 mix) concrete using the below
material properties. Assume 1 bag of cement has Construction Management
volume of 0.028 cu. m. Use 26 liters of water per Is an arrangement whereby the tasks of planning,
bag of cement. Determine the following: designing, and constructing may be integrated by a
project team comprising the owner, the designer,
consultants and the contractor working together at
the construction stage of the project with the
common objective of best serving the owner’s
interest.
Basic Elements of Project Schedule
Activity on Arrow (AOA)
19. Number of bags of cement required.
A project diagram in which activities are
A. 143 B. 152 represented by arrows and are connected at points
C. 148 D. 160 called nodes to illustrate activity sequencing.
20. The quantity of sand (cu. m.) required.
A. 8.14 B. 10.38
C. 9.06 D. 11.45
21. The quantity of gravel (cu. m.) required.
A. 17.18 B. 19.63
C. 18.44 D. 20.72
22. The quantity of water (liters) required.
B. 3848 B. 3861
C. 3856 D. 3875 Event
It denotes either the start or completion of an
activity. Represents as nodes in network diagram.
SITUATION 8 – The basic date for proportioning trial A. Successor Event – The event or events which
batches for normal weight concrete with an average follow another event.
compressive strength of 25 MPa at 28 days are as B. Predecessor Event – The event or events
follows: which occur before another event.
Slump 75 mm to 100 mm Activity
Water-cement ratio by weight 0.48 It represents the distinct operation to be done as
the project proceeds. An activity (except dummy
S.G. of cement 3.15
activity) consumes time and resources as it
S.G. of coarse aggregate 2.68 happens. It is represented by an arrow between two
S.G. of fine aggregate 2.64 events in network diagram.
Water (net mixing) 180 kg/m3 Dummy Activity
Any activity which does not consume either any
Entrapped air 1%
resource or time (zero duration). It is an
Unit weight of concrete 23.6 kN/m3 artificial activity represented by dotted line,
which indicates that no succeeding activity shall
23. Determine the total solid volume (in m3) of commence until all previous activities are
water, cement, coarse aggregates, and entrapped complete.
air if the dry unit weight of coarse aggregate
is 10.1 kN/m3.
Duration (D) Estimated time it takes an activity Crashing of Project Network
to be finished. It is when you shorten the duration of a project by
reducing the time of one or more tasks.
Early Start (ES)
The earliest possible time an activity can start. Crashing is done by increasing the resources to the
project, which helps make tasks take less time than
Early Finish (EF) what they were planned for.
The earliest possible time an activity can finish.
EF = ES + D Of course, this also adds to the cost of the overall
project. Therefore, the primary objective of project
Late Start (LS) crashing is to shorten the project while also
The latest possible time an activity can start keeping costs at a minimum.
without delaying the project completion date. LS =
LF - D Presidential Decree No.1594
PRESCRIBING POLICIES, GUIDELINES, RULES & REGULATIONS FOR
Late Finish (LF) GOVERNMENT INFRASTRUCTURE CONTRACTS
The latest possible time an activity can be A. Bids
completed without delaying the overall project The implementing rules and regulation of P.D 1594
completion date. states that no award of contract shall be made to a
Bidder whose bid price is higher than the allowable
Backward Pass government estimate (AGE) or the Approved Agency
The technique that determines the LATE START and Estimate (AAE) whichever is higher, or lower than
LATE FINISH dates for each activity. seventy percent (70%) of the AGE.
Forward Pass For the purpose of these implementing rules and
The technique to determine the EARLY START and EARLY regulations, the AGE shall be equal to one-half the
FINISH dates for each activity. sum of the AAE and the average of all responsive
bids.
Free Slack (FS) or Free Float (FF)
The amount of time an activity can be delayed without For purpose of determining the average of all
delaying the early start of any immediately following responsible bids, bids higher than One Hundred
activity. Twenty Percent (120%) of the AAE or lower than
FS or FF = ES NEXT ACTIVITY – EF CURRENT ACITIVITY sixty percent (60%) of the AAE shall not be
considered.
Total Slack (TS) or Total Float (TF)
The amount of time an activity can be delayed from B. Unbalanced Bids
its early start without delaying the planned project The implementing rules of PD 1594 defines an
completion date. unbalanced bid as a bid containing one or more pay
TF = LS – ES = LF – EF items that are 30% higher than the unit allowable
government estimate (AGE) in respect to major items
Methods in Project Scheduling whereas other pay items are priced lower than the
1. Gantt Analysis (GA) unit AGE.
It is created by Henry Gantt during World War I for
scheduling work in factories. Major items are defined as pay items representing
at least 20% of the AAE or the first two items
It is a technique that utilizes bar charts that having the highest percentage of the AAE or those
illustrates a project schedule. It can show indicated or specified in the instruction to
dependencies among activities and current schedule bidders.
of those activities.
C. Change Order
GA lists the tasks in a chart to be performed on the The implementing rules and regulations of PD 1594
vertical axis, and time intervals on the horizontal states that for a unit price contract, quantity
axis. The width of the horizontal bars in the graph overruns or underruns of not more than fifteen
shows the duration of each activity. (15%) percent of the estimates per major pay item
and twenty-five percent (25%) per minor pay item in
It illustrates the start and finish dates of the the Bill of Quantities need not be covered by a
Change Order provided that the same is authorized
terminal elements and summary elements of a project.
by the Approving Authority for the contract.
However, they do not show relationships and
dependencies between tasks as network diagrams do.
Concrete Mix Design
2. Critical Path Method (CPM) For designing concrete mix, ABSOLUTE VOLUME METHOD
It is a deterministic technique that requires is used. It calculates mix proportions by basis of
mapping out every key task that is necessary to volume of components.
complete a project.
𝑊𝑙𝑜𝑜𝑠𝑒
It includes identifying the amount of time necessary 𝑉𝑎𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 =
to finish each activity and the dependencies of each 𝛾𝑏𝑢𝑙𝑘
activity on any others.
𝛾𝑙𝑜𝑜𝑠𝑒 = 𝛾𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑎𝑙 𝛾𝑏𝑢𝑙𝑘
It is used to set a realistic deadline for a project
and to track its progress along the way. = 𝑆. 𝐺.× 𝛾𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟
3. Program Evaluation & Review Technique (PERT)
A network analysis technique used to estimate
project duration when there is a high degree of
uncertainty about the individual duration estimates.
It uses probabilistic time estimates – estimates of
activity duration using optimistic, most likely and
pessimistic estimates of activity duration. Thus, it
attempts to address the risk associated with
duration estimates.
𝑂𝑇 + 4 × 𝑀𝐿𝑇 + 𝑃𝑇 The table above is true, on the assumption that the
𝐸𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑 𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒 = cement paste enters the void of the sand and at the
6 same instance, the composition of these two
materials fill the voids of the gravel and
thereafter, form a solid mass called concrete
equivalent to 1 cubic meter.
Frequency of Testing
426.12.2.1 Compliance Requirements:
a. Samples for preparing strength test specimens of
each concrete mixture placed each day shall be
taken in accordance with (1) through (3):
1. At least once a day;
2. At least once for each 110 m3 of concrete;
3. At least once for each 460 m2 of surface area for
slabs or walls.
b. On a given project, if total volume of
concrete is such that frequency of testing would
provide fewer than five strength tests for a given
concrete mixture, strength test specimens shall be
made from at least five randomly selected batches
or from each batch if fewer than five batches are
used;
c. If the total quantity of a given concrete
mixture is less than 38 m3, strength tests are not
required if evidence of satisfactory strength is
submitted to and approved by the building official.
You might also like
- Exam Revision - INF3708Document5 pagesExam Revision - INF3708noxaNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Assessment Task 1 STELR Depth Study Report PDFDocument5 pagesYear 9 Assessment Task 1 STELR Depth Study Report PDFGremlin ChildNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - PERT and CPM NumericalsDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - PERT and CPM NumericalsKartik Gupta100% (7)
- Case Study - BCD Construction CompanyDocument14 pagesCase Study - BCD Construction CompanyAgatta Arce100% (2)
- CPM HandoutsDocument2 pagesCPM HandoutsPaolo LibradaNo ratings yet
- CPM PertDocument5 pagesCPM PertAdman EdNo ratings yet
- Pow of Proposed Tennis CourtDocument131 pagesPow of Proposed Tennis CourtErnesto LopezNo ratings yet
- Operations Management OPIM 330: Chapter 8-CDocument25 pagesOperations Management OPIM 330: Chapter 8-CAhmed El KhateebNo ratings yet
- Recitation 2 PDFDocument3 pagesRecitation 2 PDFiNo ratings yet
- 3 Power Assignment 6-2-15 V1Document3 pages3 Power Assignment 6-2-15 V1Ayman EsaNo ratings yet
- Construction Set 1Document2 pagesConstruction Set 1Jasmine MonesNo ratings yet
- POW Proposed Tennis Court ImprovementDocument183 pagesPOW Proposed Tennis Court ImprovementErnesto LopezNo ratings yet
- GBEPM 520 Take Home Test - October 2020Document5 pagesGBEPM 520 Take Home Test - October 2020Govat PhiriNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Project Management Body oDocument19 pagesA Guide To The Project Management Body omawandeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Project Management (PERT - CPM) 003Document5 pagesChapter 10 Project Management (PERT - CPM) 003Vickie Goh100% (1)
- 01 Activity 3Document4 pages01 Activity 3Jylian SogocNo ratings yet
- Assignment 9Document3 pagesAssignment 9Jackline KhouryNo ratings yet
- Quesbank 270216063430Document4 pagesQuesbank 270216063430Man C Is a SuksNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Project Planning: Jesper Larsen March 6, 2008Document4 pagesExercises in Project Planning: Jesper Larsen March 6, 2008SSShakeelNo ratings yet
- Reviconstruct 012Document1 pageReviconstruct 012blink blinkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Planning and ControlDocument5 pagesAssignment 4 Planning and ControlRahul sardanaNo ratings yet
- Project Management AssessmentDocument2 pagesProject Management AssessmentChristopher RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document17 pagesAssignment 7Arif AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Assignment IIDocument5 pagesAssignment IIsoham agarwalNo ratings yet
- Primavera ProjectsDocument41 pagesPrimavera ProjectsMUUTHUKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Capacity MGMTDocument5 pagesCapacity MGMTSamarth LahotiNo ratings yet
- Questions On CPMDocument3 pagesQuestions On CPMVasthy Rani VNo ratings yet
- Nodes Activity Time (Weeks)Document2 pagesNodes Activity Time (Weeks)Nico GeotinaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument5 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityTNo ratings yet
- Crashing Worksheet 7: Tmi / DbeDocument4 pagesCrashing Worksheet 7: Tmi / DbeHasiburNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Project Scheduling Lagging, Crashing and Activity NetworksDocument26 pagesChapter 6 Project Scheduling Lagging, Crashing and Activity NetworksMỹ Mộc LinhNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. EXAMINATION, Dec. 2017: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Document3 pagesB. Tech. EXAMINATION, Dec. 2017: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Sukrit JainNo ratings yet
- HHSM ZG519 Ec-3r First Sem 2015-2016Document3 pagesHHSM ZG519 Ec-3r First Sem 2015-2016amarpal07No ratings yet
- # Numericals - Project PlanningDocument11 pages# Numericals - Project Planningyogesh lohotNo ratings yet
- HW 3 SolDocument3 pagesHW 3 Solavni1601No ratings yet
- 06spm l02Document12 pages06spm l02akram1978No ratings yet
- Construction ManagementDocument3 pagesConstruction ManagementNOR-FATMAH SARIPNo ratings yet
- IEDA 2010 Assignment 2 - SolutionDocument5 pagesIEDA 2010 Assignment 2 - SolutionNorris wongNo ratings yet
- Exercises Project ManagementDocument3 pagesExercises Project ManagementNina DlloNo ratings yet
- 12RE0517Document16 pages12RE0517Nakshtra DasNo ratings yet
- MGT PERT ATsDocument2 pagesMGT PERT ATsIan EmbileNo ratings yet
- Examination Spring 12 Online 302 AlmorqiDocument4 pagesExamination Spring 12 Online 302 AlmorqilolaNo ratings yet
- Operations Management - Section ADocument3 pagesOperations Management - Section Ajoyshree royNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Cashing ProjectDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Cashing ProjectHernan Ochoa0% (1)
- OM Week3Document4 pagesOM Week3Adoree RamosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Ahmed Ehab MohamedNo ratings yet
- Case Studies For EMBA 615Document3 pagesCase Studies For EMBA 615mzhouryNo ratings yet
- MODULE EXERCISES CONSTRUCTION 2 Ans KeyDocument1 pageMODULE EXERCISES CONSTRUCTION 2 Ans KeyRein manzanoNo ratings yet
- Walton - PMAN635 Final Exam v1Document6 pagesWalton - PMAN635 Final Exam v1BINIT AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Time or Cost Trade-OffDocument16 pagesTime or Cost Trade-OffAI KoNo ratings yet
- Model QuestionDocument5 pagesModel QuestionWilfharry billyNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Midterm ExamDocument2 pagesOperations Management Midterm ExamCharisa SamsonNo ratings yet
- Project - Managemnt Pratice Problem PDFDocument5 pagesProject - Managemnt Pratice Problem PDFAnushka KanaujiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Test 2 EomDocument1 pageAssignment Test 2 Eompochireddy revathiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document3 pagesAssignment 8bluestacks3874No ratings yet
- Wa0033.Document1 pageWa0033.Abhinay ChallaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Schedule Compression and Cost-Time Trade-OffDocument32 pagesChapter 5-Schedule Compression and Cost-Time Trade-Offmajdsaab1497No ratings yet
- Activity 7.6 - Module Problems: 495346184Document3 pagesActivity 7.6 - Module Problems: 495346184JayramNo ratings yet
- Individual Project AsseignmentDocument2 pagesIndividual Project AsseignmentAbdunasir AbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Estimating Greenhouse Gas Emissions of ADB Projects: Additional Guidance for Clean Energy ProjectsFrom EverandGuidelines for Estimating Greenhouse Gas Emissions of ADB Projects: Additional Guidance for Clean Energy ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Quotation With Specification - Kitchen LatestDocument8 pagesQuotation With Specification - Kitchen LatestNehaa HemnaniNo ratings yet
- DAC AnalysisDocument19 pagesDAC Analysisమురళీధర్ ఆది ఆంధ్రుడుNo ratings yet
- SEL Lesson Plan: Family LoveDocument5 pagesSEL Lesson Plan: Family LoveNur Ain Mohd Amin100% (3)
- Lauren Del Valle: Education Hofstra University Honors College, Hempstead, NYDocument2 pagesLauren Del Valle: Education Hofstra University Honors College, Hempstead, NYLauren del ValleNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain.Document53 pagesChest Pain.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- OverviewDocument346 pagesOverviewarnaldospbrNo ratings yet
- Vo Dai Quang Semantics - Lectures in Broad OutlineDocument89 pagesVo Dai Quang Semantics - Lectures in Broad OutlineThu PhạmNo ratings yet
- The Dualism of Nondualism: Advaita Vedanta and The Irrelevance of NatureDocument28 pagesThe Dualism of Nondualism: Advaita Vedanta and The Irrelevance of NatureTur111No ratings yet
- In Case of Doubts in Answers, Whatsapp 9730768982: Cost & Management Accounting - December 2019Document16 pagesIn Case of Doubts in Answers, Whatsapp 9730768982: Cost & Management Accounting - December 2019Ashutosh shahNo ratings yet
- OSB Error HandlingDocument45 pagesOSB Error Handlingabhishek_acharya_13100% (1)
- Evs - Final Unit 3 - Environment Management & Sustainable DevelopmentDocument105 pagesEvs - Final Unit 3 - Environment Management & Sustainable DevelopmentchhaviNo ratings yet
- S.nelson Physical GeologyDocument252 pagesS.nelson Physical Geologysatyam mehta100% (2)
- 4 Lec AJ Culture Fall2023Document50 pages4 Lec AJ Culture Fall2023muhammad zohaibNo ratings yet
- Amit ResumeDocument5 pagesAmit ResumeASHOK KUMAR LENKANo ratings yet
- Lab 1 PSpice Op - Amp - BasicsDocument13 pagesLab 1 PSpice Op - Amp - BasicsTooba ArshadNo ratings yet
- System Security-Virus and WormsDocument26 pagesSystem Security-Virus and WormsSurangma ParasharNo ratings yet
- Correlational Relationship of Nursing Professional Subjects and Board Exam Performance of Isabela State University-Echague November 2022 Nursing Licensure Examination TakersDocument20 pagesCorrelational Relationship of Nursing Professional Subjects and Board Exam Performance of Isabela State University-Echague November 2022 Nursing Licensure Examination TakersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Fresh VisionDocument2 pagesFresh VisionTerry DehartNo ratings yet
- Fema f2Document2 pagesFema f2santoshkumar86No ratings yet
- Way He Talks, Appearance and His Overall Physical AttributesDocument2 pagesWay He Talks, Appearance and His Overall Physical AttributesShella Mae LineNo ratings yet
- Makerere UniversityDocument40 pagesMakerere UniversityWinnie Janice100% (1)
- 1st Year Chemistry NotesDocument24 pages1st Year Chemistry NotesShasha Jain88% (8)
- Bryant and Smith 2001 - Refining The Architecture of AggressionDocument30 pagesBryant and Smith 2001 - Refining The Architecture of AggressionIstván BeregiNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument59 pagesInheritanceTiju ThomasNo ratings yet
- Key Answer Org DevDocument15 pagesKey Answer Org DevSheennah Lee LimNo ratings yet
- Busn - Final Exam PaperDocument21 pagesBusn - Final Exam Paperapi-582516447No ratings yet
- Nitrogrn - Gate Valve Data SheetDocument2 pagesNitrogrn - Gate Valve Data SheetHabib ur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Oracle Rac Pratice On Virtual BoxDocument94 pagesOracle Rac Pratice On Virtual BoxpandsinNo ratings yet
- Format 8 Synchronizing ReportDocument4 pagesFormat 8 Synchronizing ReportSameerNo ratings yet