Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transistors
Transistors
Uploaded by
naidoori0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageTransistor description
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTransistor description
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageTransistors
Transistors
Uploaded by
naidooriTransistor description
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
A transistor is a fundamental component of modern electronics.
It is a
semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical
power. Essentially, transistors control the flow of electrical current by acting
as a switch or an amplifier.
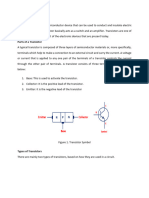
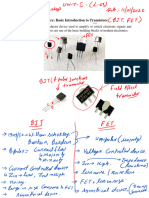
There are two main types of transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and
field-effect transistors (FETs).
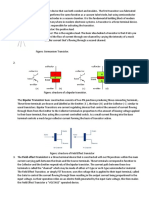
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs): BJTs are made of three semiconductor
layers: the emitter, the base, and the collector. They operate by controlling
the flow of current between the collector and emitter terminals, depending on
the current applied to the base terminal. BJTs can amplify signals and are
commonly used in analog circuits.
Field-Effect Transistors (FETs): FETs are made of three terminals: the source,
the gate, and the drain. They work by controlling the flow of current between
the source and drain terminals through the voltage applied to the gate terminal.
FETs are commonly used in digital circuits and integrated circuits (ICs).
Transistors revolutionized the field of electronics because they are smaller,
more reliable, and more energy-efficient than earlier vacuum tube technology.
They are the building blocks of modern electronic devices such as computers,
smartphones, televisions, and many more.
You might also like
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsJoão CorreiaNo ratings yet
- L4 Basic-ElectronicsDocument16 pagesL4 Basic-Electronicstheo dominic silvosaNo ratings yet
- EEE 202 Lecture Note On TransistorDocument7 pagesEEE 202 Lecture Note On Transistoralexapierre08No ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorXhaNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument1 pageNothingJyothula VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2Document16 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2leon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Difference Between BJT and FETDocument2 pagesDifference Between BJT and FETkanwaljiaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between BJT and FETDocument2 pagesDifferences Between BJT and FETJESSYLLNNo ratings yet
- 3 TransistorDocument7 pages3 TransistorrameshNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorSummer WangNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument2 pagesTransistorSOR SOTYNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXDocument17 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXleon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Transistor: by P.Sai SrivathsaDocument15 pagesTransistor: by P.Sai Srivathsak.saikumarNo ratings yet
- NextechDocument15 pagesNextechNEXTECH ElectroicsNo ratings yet
- FET and BJTDocument7 pagesFET and BJTshaik usmanganiNo ratings yet
- What Is A TransistorDocument5 pagesWhat Is A TransistorSOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor Is Abbreviated As MOSFET. It Is Merely A UnipolarDocument6 pagesMosfet: Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor Is Abbreviated As MOSFET. It Is Merely A UnipolarJade JoseNo ratings yet
- TransDocument8 pagesTransvanshraheja05No ratings yet
- Electronic EngeeniringDocument11 pagesElectronic EngeeniringMuataz ZyadaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Transistors: DiscussionDocument9 pagesTopic 3 Transistors: DiscussionEnitsuj Eam EugarbalNo ratings yet
- (Done) Compare and Contrast The FET With The BJTDocument8 pages(Done) Compare and Contrast The FET With The BJTexe.dave.qNo ratings yet
- Explain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesExplain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsS Dispiser100% (1)
- TransisterDocument10 pagesTransisterart101988No ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument7 pagesTransistorsMuzakki SathorNo ratings yet
- IP 4 TransistorDocument3 pagesIP 4 TransistorRifky OfficialNo ratings yet
- The Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesThe Bipolar TransistorMohammed MushfiqurNo ratings yet
- Jamaica Naz Online Worksheet - Laboratory 6 Part 2Document3 pagesJamaica Naz Online Worksheet - Laboratory 6 Part 2Koji OdoNo ratings yet
- Types of Transistors - Junction Transistors and FETsDocument16 pagesTypes of Transistors - Junction Transistors and FETsKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- Transistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?Document7 pagesTransistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?study buddyNo ratings yet
- Adio's Elect Term PaperDocument13 pagesAdio's Elect Term PaperAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument7 pagesTransistorsericoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 0 - Điện tử tương tự I: 1. BJT and FETDocument6 pagesAssignment 0 - Điện tử tương tự I: 1. BJT and FETQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument1 pageTransistorsAkshay DhandaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument2 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorJason BreguilesNo ratings yet
- English (Transistor) : Jurusan Teknik Elektro Program Studi D-Iv Teknik Elektronika Politeknik Negeri Malang 2019Document5 pagesEnglish (Transistor) : Jurusan Teknik Elektro Program Studi D-Iv Teknik Elektronika Politeknik Negeri Malang 2019Zulfikar Iannur AwwalNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument25 pagesTransistorAdnan Hyder SoomroNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - L-3-4 - Introduction To BJT and FETDocument13 pagesUnit-1 - L-3-4 - Introduction To BJT and FETwebip33713No ratings yet
- Transistor and It's Applications - 20240514 - 134952 - 0000Document12 pagesTransistor and It's Applications - 20240514 - 134952 - 0000Tushar KanojiyaNo ratings yet
- NAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorDocument3 pagesNAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorChoiril AthoNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument44 pagesTransistorsramil.bocaNo ratings yet
- STE Electronics10 Q2 Mod1 Lesson2-TRANSISTOR ANABELLE-BRONOLA v1Document12 pagesSTE Electronics10 Q2 Mod1 Lesson2-TRANSISTOR ANABELLE-BRONOLA v1April EspiñaNo ratings yet
- Transistors and Logic GatesDocument17 pagesTransistors and Logic GatesJef SotisNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicDocument27 pagesBasic Electronicglobal kind resortNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument4 pagesTransistorcomputer tricksNo ratings yet
- Transistor2 TypesDocument5 pagesTransistor2 TypesidanzbhNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesBipolar TransistorAndrei Josef NizaNo ratings yet
- Transistor EnglishDocument5 pagesTransistor EnglishArif KusumaNo ratings yet
- UNIT II (Part 2) PDFDocument7 pagesUNIT II (Part 2) PDFZulkifl KhairoowalaNo ratings yet
- Diff BTWN MOSFET and BJTDocument2 pagesDiff BTWN MOSFET and BJTMadan R HonnalagereNo ratings yet
- Ewp 5Document12 pagesEwp 5Aakansha PaunikarNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument22 pagesTransistorRahul DevNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument11 pagesTransistorEllaine P. De ClaroNo ratings yet
- Phy210 Notes-2Document8 pagesPhy210 Notes-2Praise AribisalaNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument4 pagesTransistorsFuture Technology LKNo ratings yet
- Transistors: Building Blocks of Modern ElectronicsDocument2 pagesTransistors: Building Blocks of Modern ElectronicsTuana Deniz BozanNo ratings yet
- Introduction EE212 Lab 4Document2 pagesIntroduction EE212 Lab 4Naayaab SarfraazNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument15 pagesTransistorAshvini SugaNo ratings yet
- ECE 027 - Module 3 - Introduction of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Document58 pagesECE 027 - Module 3 - Introduction of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Miyuki NakiriNo ratings yet
- History of BoltsDocument1 pageHistory of BoltsnaidooriNo ratings yet
- ResistorsDocument1 pageResistorsnaidooriNo ratings yet
- JjjreaaaDocument1 pageJjjreaaanaidooriNo ratings yet
- HFGFVCNVCCCCGDocument1 pageHFGFVCNVCCCCGnaidooriNo ratings yet
- Ppon BasDocument1 pagePpon BasnaidooriNo ratings yet
- HJGHGH DsDocument1 pageHJGHGH DsnaidooriNo ratings yet
- SsdertDocument1 pageSsdertnaidooriNo ratings yet
- SSDFGFGNHHFNDocument1 pageSSDFGFGNHHFNnaidooriNo ratings yet
- HJHJ PP PDFDocument1 pageHJHJ PP PDFnaidooriNo ratings yet
- XFGGFCDocument1 pageXFGGFCnaidooriNo ratings yet
- AaaswpDocument1 pageAaaswpnaidooriNo ratings yet
- New Text Document - TXT Fiihvvb UjDocument1 pageNew Text Document - TXT Fiihvvb UjnaidooriNo ratings yet
- MMH DDFFDVVDocument1 pageMMH DDFFDVVnaidooriNo ratings yet
- KkaseDocument1 pageKkasenaidooriNo ratings yet
- MMBSGWDocument1 pageMMBSGWnaidooriNo ratings yet
- CVGGKDocument1 pageCVGGKnaidooriNo ratings yet
- DDFGPMDocument1 pageDDFGPMnaidooriNo ratings yet
- DffeaaabDocument1 pageDffeaaabnaidooriNo ratings yet
- BuuupiwDocument1 pageBuuupiwnaidooriNo ratings yet
- XxcvbssaaDocument1 pageXxcvbssaanaidooriNo ratings yet
- JHJJGGPDocument1 pageJHJJGGPnaidooriNo ratings yet
- VVDDWXDocument1 pageVVDDWXnaidooriNo ratings yet
- MmkcaDocument1 pageMmkcanaidooriNo ratings yet
- DdfgqwaDocument1 pageDdfgqwanaidooriNo ratings yet
- MmpouDocument1 pageMmpounaidooriNo ratings yet
- Aawrtza PDFDocument1 pageAawrtza PDFnaidooriNo ratings yet
- MMMNBGDocument1 pageMMMNBGnaidooriNo ratings yet
- AaqcxzDocument1 pageAaqcxznaidooriNo ratings yet
- AawrtzaDocument1 pageAawrtzanaidooriNo ratings yet
- PooiiuDocument1 pagePooiiunaidooriNo ratings yet