Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GCSE Maths Formulae To Learn HandF
GCSE Maths Formulae To Learn HandF
Uploaded by
studybuddy.bhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE Maths Formulae To Learn HandF
GCSE Maths Formulae To Learn HandF
Uploaded by
studybuddy.bhCopyright:
Available Formats
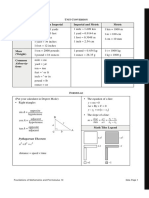
GCSE Maths:
Formulae and rules you need to LEARN (1)
Cylinder vol Cylinder SA Foundation formulae in black
= ℎ =2 +2 ℎ Higher formulae in blue
Volume =
⅓ vol of prism Vol = area of Sector area
cross-section For surface area,
Circle area = = ×
x length sketch the net
PYRAMID PRISM (inc cuboid Arc length
& cylinder) Circumference = ×2
CIRCLES = or 2
3D SHAPES Pythagoras: a2 + b2 = c2
short2 + short2 = hypotenuse2
GEOMETRY TRIANGLES RIGHT-ANGLED
TRIANGLES
AREAS SOHCAHTOA
Shape Area
Square length2 ANY O A O
Rectangle length x width TRIANGLE sinθ H cosθ H tanθ A
Parallelogram length x perp. height Exact trig
Triangle ½ base x perp. height
or ½ a b sin C values:
Kite/rhombus ½ diagonal 1 x diagonal 2
(since it’s 2 triangles)
Cosine rule:
Trapezium ½ (a + b) x h
a = + −2 cos !
h Sine rule: to find side, or
b = = "# "$ "
cos ! =
to find side, or to find angle
1 kg = 1000 g
1 g = 1000 mg = =
1 L of water has a OR:
to find angle 0° 30° 45° 60° 90°
mass of 1 kg MEASURES sin 0 1 2 3 4
cos 4 3 2 1 0
METRIC
2
234
1 cm = 10 mm EQUIVALENTS and tan 1 = 53 234
1 m = 100 cm = 1000 mm COMPOUND
1 km = 1000 m = 1 000 000 mm METRIC/
1 m2 = 10 000 cm2 IMPERIAL MEASURES D
(Useful but not required) S T
1 m3 = 1 000 000 cm3
5 miles ≈ 8km or Consider units!
1 L = 1 000 cm3 M
1 mile ≈ 1.6 km e.g. find speed in m/s
1 inch ≈ 2.5 cm by dividing m (distance) D V
1 kg ≈ 2.2 lb (pounds) by s (time)
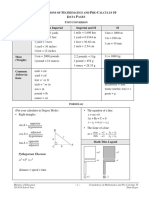
GCSE Maths:
Formulae and rules you need to LEARN (2)
Alternative form: = = 61 +
Foundation formulae in black
= − =? = 6(1 − 1? ) Gradient = m (x1, y1)
(x2, y2) Higher formulae in blue
(optional) y-intercept = c
c
Parallel: same gradient
Mid-point =
Perpendicular: 6? × 6 = −1
(mean 1, mean =)
<; #<" :; #:" 7 8 : $:
= , Gradient 6 = 79
= <"$<;
STRAIGHT " ;
Distance between points LINES Circle
= run + rise (Pythagoras) 1 += =
Square root
= (1 − 1? ) +(= − =? ) ALGEBRA == 1
OTHER
1 posiCve → & GRAPHS
1 negaCve →
SHAPES
To solve, start with Reciprocal
?
1 + 1+ =0 QUADRATICS ==
<
Factorised: Cubic
= = (1 + )(1 + F) Quadratic formula: ==1
" $J
cuts x-axis at − and −F 1=
$ ±
= = (1 − )(1 − )(1 − )
(when y = 0) $
Axis of symmetry at 1 =
Completed square form: −
= = (1 − G) +H 9K 3L MNO98
Mean = 232NO 9KP87 3L MNO98 Median = middle one when
has its vertex at (G, H) arranged in order
For grouped data, use class
Mode = most frequent mid-points position is ½ way up
use ½ (n+1) for small sets,
If A and B are ½ n for bigger sets (~30+)
A B independent then AVERAGE
P(A) x P(B) = P(A ∩ B) & SPREAD Range = biggest – smallest
A∩B (multiplication law) LQ or Q1 = value ¼ way through
STATISTICS & UQ or Q3 = value ¾ way through
P(A) + P(A’) = 1
IQR = UQ – LQ
A and A’ are exhaustive PROBABILITY
(they cover all possible
outcomes) For continuous data,
PROBABILITY HISTOGRAMS no gaps
If A and B are
mutually exclusive Bar area = frequency Bar height
A B AUB
(can’t both happen) = frequency density
then P(A ∩ B) = 0 L78Q98 5R
= 5ON
A B P(A U B) S T2U
= P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
(addition law)
You might also like
- Risk Assessment For Anti Termite TreatmentDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment For Anti Termite TreatmentVictor81% (26)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Education Grade 6Document6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Physical Education Grade 6cia-gail cueto92% (13)
- DW Smith Three Facets of ConsciousnessDocument20 pagesDW Smith Three Facets of ConsciousnessMartin McDermottNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10: Formula Booklet (Web Sample)Document6 pagesMathematics 10: Formula Booklet (Web Sample)ElzerNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10: Formula Booklet (Web Sample)Document6 pagesMathematics 10: Formula Booklet (Web Sample)ElzerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Formula BookDocument16 pagesCambridge Formula BookJaymie AnchumNo ratings yet
- Formula Booklet PDFDocument16 pagesFormula Booklet PDFBasalic GeorgeNo ratings yet
- My FormulasDocument12 pagesMy FormulasThar Lon Lin HtetNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMath 10 Formula SheetSTEPHEN MNo ratings yet
- FORMULAEDocument1 pageFORMULAESNo ratings yet
- 0580 IGCSE Mathematics - Useful FormulaeDocument3 pages0580 IGCSE Mathematics - Useful FormulaeSupermartin767No ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry Hand OutDocument7 pagesPlane Trigonometry Hand OutKRISTINE CHAD NAVALES CANTALEJONo ratings yet
- Math 10 PC Data BookDocument4 pagesMath 10 PC Data Bookyara bNo ratings yet
- Math 10 PC Data BookDocument4 pagesMath 10 PC Data Bookyara bNo ratings yet
- F M P - C 10 D P: U C Common Imperial Imperial and SI SI LengthDocument4 pagesF M P - C 10 D P: U C Common Imperial Imperial and SI SI LengthTaylor MoffittNo ratings yet
- Math Formula SheetDocument8 pagesMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherNo ratings yet
- Year 9 - Formula List: Version 1.4bDocument1 pageYear 9 - Formula List: Version 1.4bSamantha LAUNo ratings yet
- Formula ChartDocument2 pagesFormula Chartdevsharma17795No ratings yet
- Arc Length= θ Arc Length=θ r Sector Area= θ r Sector Area= rDocument8 pagesArc Length= θ Arc Length=θ r Sector Area= θ r Sector Area= rWandaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry BasicsDocument11 pagesTrigonometry BasicsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Gmas Plane and Solid GeometryDocument11 pagesGmas Plane and Solid Geometryjonnel batuigasNo ratings yet
- Gmas Plane and Solid GeometryDocument11 pagesGmas Plane and Solid Geometryjonnel batuigasNo ratings yet
- April 2024 Training - APPLICATION OF CALCULUS TRAINING MANUALDocument10 pagesApril 2024 Training - APPLICATION OF CALCULUS TRAINING MANUALqueenrorisang95No ratings yet
- Chandan Mandal 11Document14 pagesChandan Mandal 11anon_31699417100% (1)
- Triangle Related Formulas Quadrilateral Related FormulasDocument2 pagesTriangle Related Formulas Quadrilateral Related Formulashasibul rojanNo ratings yet
- Area Computation: Baharin AhmadDocument24 pagesArea Computation: Baharin AhmadFadzir AmirNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - MathDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet - MathDevansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chandan Mandal 11.Document14 pagesChandan Mandal 11.jefferson sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Subject: MATHEMATICS (Code No.041) - SET 1 - Answer Key Section ADocument10 pagesSubject: MATHEMATICS (Code No.041) - SET 1 - Answer Key Section ARifatNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry Hand OutDocument6 pagesPlane Trigonometry Hand Outmary christy mantalabaNo ratings yet
- 10th STD - Mathematical Formulae - 2Document4 pages10th STD - Mathematical Formulae - 2ambresh.09No ratings yet
- 12 MensurationDocument66 pages12 Mensurationconor mcgregor100% (1)
- Math SymbolsDocument14 pagesMath SymbolsGoutam AcharjeeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-Basic (241) Marking Scheme SQP-2020-21 Max. Marks: 80 Duration:3HrsDocument16 pagesMathematics-Basic (241) Marking Scheme SQP-2020-21 Max. Marks: 80 Duration:3Hrsmadhav haibateNo ratings yet
- ProblemDocument7 pagesProblemMary Claire NevalgaNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasCarmen FloresNo ratings yet
- GR 11 Trigonometry in Triangles September 2023Document75 pagesGR 11 Trigonometry in Triangles September 2023zmiqbal786No ratings yet
- All The Trig That You Need To KnowDocument16 pagesAll The Trig That You Need To Knowapi-3755447No ratings yet
- GCSE-CheatSheet Foundation2019Document2 pagesGCSE-CheatSheet Foundation2019diya pNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument7 pagesFormulaeVesna NasirNo ratings yet
- Trig1 - Compound Angles - TN - FDocument20 pagesTrig1 - Compound Angles - TN - FSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Circular Functions and Its Graphs Week 5Document42 pagesCircular Functions and Its Graphs Week 5ellamay050921No ratings yet
- Lesson 4-2Document19 pagesLesson 4-2Bela RilloNo ratings yet
- Solid FigureDocument92 pagesSolid Figure246macvillaNo ratings yet
- Math 10C - Unit 1 WorkbookDocument44 pagesMath 10C - Unit 1 WorkbookjimNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocument76 pagesPlane and Spherical TrigonometryAlyssa Marie AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry FormulasDocument3 pagesTrigonometry FormulasZack D. SnutssNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions: 7.1 AnglesDocument11 pagesTrigonometric Functions: 7.1 AnglesGlorilie Perez PazNo ratings yet
- Herons Formula Class 9Document4 pagesHerons Formula Class 9Mohammed ShariqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TrigonometryDocument47 pagesChapter 4 TrigonometrySHAHRUL100% (1)
- Algebra: Conic SectionsDocument32 pagesAlgebra: Conic SectionsRonel FillomenaNo ratings yet
- PrimingDocument3 pagesPrimingLoranel EspirituNo ratings yet
- Mensuration: This Chapter ''Mensuration'' Is Taken From Our BookDocument11 pagesMensuration: This Chapter ''Mensuration'' Is Taken From Our BookSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- List of FormulaeDocument4 pagesList of FormulaeMohamed TahmeedNo ratings yet
- Math Igcse FormulasDocument4 pagesMath Igcse FormulasAbdelrahman MostafaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Plane and Spherical Trigo - Without SolutionDocument54 pages2.1 Plane and Spherical Trigo - Without SolutionNala A.No ratings yet
- 20) Area of A Triangle (Using Sine)Document13 pages20) Area of A Triangle (Using Sine)Dheeraj25No ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical Trigo - With SolutionDocument80 pagesPlane and Spherical Trigo - With SolutionNala A.No ratings yet
- Measure of Angles Domain and Range of A Trigonometrical FunctionDocument4 pagesMeasure of Angles Domain and Range of A Trigonometrical FunctionSHIVARAM KULKARNINo ratings yet
- Prepared by Maricel G. LoDocument19 pagesPrepared by Maricel G. LoAna Rose S. LlameraNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS - Analytic Geometry 1Document2 pagesMATHEMATICS - Analytic Geometry 1ARNOLD MORAN100% (1)
- Year 6 Full Spring TermDocument134 pagesYear 6 Full Spring Termstudybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Science Revision Guide Curriculum ChartDocument10 pagesScience Revision Guide Curriculum Chartstudybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Volume of A Cuboid PDFDocument9 pagesVolume of A Cuboid PDFstudybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Mental CalculationsDocument2 pagesLesson 4 Mental Calculationsstudybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Y6 Lesson 4 White Rose Week 5Document2 pagesY6 Lesson 4 White Rose Week 5studybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Mental Maths TricksDocument10 pagesMental Maths Tricksstudybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Numerical Examples in PhysicsDocument601 pagesNumerical Examples in Physicsstudybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Maths Worksheet Algebraic ExpressionsDocument2 pagesClass 7 Maths Worksheet Algebraic Expressionsstudybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Numeracy Procedural Test Year 7 2018Document12 pagesNumeracy Procedural Test Year 7 2018studybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Cazoom Maths GCSE Higher Revision MatDocument1 pageCazoom Maths GCSE Higher Revision Matstudybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Maths Worksheets Algebraic ExpressionsDocument2 pagesClass 7 Maths Worksheets Algebraic Expressionsstudybuddy.bhNo ratings yet
- Amotions of No Confidence Guidance DocumentDocument2 pagesAmotions of No Confidence Guidance DocumentllybjicNo ratings yet
- Content Analysis-Cory AquinoDocument4 pagesContent Analysis-Cory AquinoDara Rose FilosofoNo ratings yet
- "Wouldn'T It Be Funny If You Didn'T Have A Nose?" by Roger McgoughDocument2 pages"Wouldn'T It Be Funny If You Didn'T Have A Nose?" by Roger McgoughA Puffin LekvárNo ratings yet
- Jan 2019 3h - UnlockedDocument24 pagesJan 2019 3h - UnlockedahmedNo ratings yet
- The Lean WayDocument5 pagesThe Lean Wayrahil_sangNo ratings yet
- Tantongco vs. Kaisahan (106 Phil 199)Document2 pagesTantongco vs. Kaisahan (106 Phil 199)Stephanie ValentineNo ratings yet
- 150 Days in OfficeDocument5 pages150 Days in OfficeMoosa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Anthony D. Smith's Contribution To The Study of NationalismDocument14 pagesAnthony D. Smith's Contribution To The Study of NationalismNejra Hodžić100% (5)
- Soft Skills Teamwork & Leadership Revised 26.10.2020Document25 pagesSoft Skills Teamwork & Leadership Revised 26.10.2020Vachan Abhilekh ThakurNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument45 pagesGravitationthinkiit100% (1)
- Glossary of Literary TermsDocument11 pagesGlossary of Literary Termsmibasura100% (1)
- Assignment On AmniocentesisDocument4 pagesAssignment On Amniocentesissuriya prakash100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENTDocument4 pagesASSIGNMENTMujahidNo ratings yet
- Burisch Don Dep Rain DancerDocument59 pagesBurisch Don Dep Rain DancersisterrosettaNo ratings yet
- Investor S Intrinsic Motives and The Valence of Word of Mouth in Sequential Decision Making Modeling of Triple Serial MediationDocument14 pagesInvestor S Intrinsic Motives and The Valence of Word of Mouth in Sequential Decision Making Modeling of Triple Serial MediationSohail kamranNo ratings yet
- The Effect of A Corrective Functional Exercise Program On Postural Thoracic Kyphosis in Teenagers: A Randomized Controlled TrialDocument9 pagesThe Effect of A Corrective Functional Exercise Program On Postural Thoracic Kyphosis in Teenagers: A Randomized Controlled TrialGaby RojasNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Economics For Examination From 2020Document2 pagesCambridge O Level: Economics For Examination From 2020Walter ShonisaniNo ratings yet
- Managing Occupational Health and Safety in The Mining IndustryDocument12 pagesManaging Occupational Health and Safety in The Mining IndustryalexNo ratings yet
- The Enchanted FishDocument3 pagesThe Enchanted FishImanuel EkaNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument16 pagesBlood VesselsAlen OsmanovicNo ratings yet
- Types of Negotiation in IndiaDocument49 pagesTypes of Negotiation in IndiaBhavana ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Housing Policy in India - The Trend Towards Market MechanismsDocument8 pagesTransformation of Housing Policy in India - The Trend Towards Market MechanismsVaidish SumariaNo ratings yet
- 2018 CAS Path To SuccessDocument1 page2018 CAS Path To SuccesskidNo ratings yet
- Fill in British PoliticsDocument2 pagesFill in British PoliticsMudassiraNo ratings yet
- Theory Questions (1-7)Document2 pagesTheory Questions (1-7)sharmadisha0703No ratings yet
- Moments of Being by Virginia WoolfDocument5 pagesMoments of Being by Virginia WoolfJay-rJohnEstrasSorianoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 What Is CultureDocument12 pagesLecture 1 What Is CulturedivyaNo ratings yet