Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surveying Iv
Surveying Iv
Uploaded by
J16-8110-2021 EDDY TSUMAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surveying Iv
Surveying Iv
Uploaded by
J16-8110-2021 EDDY TSUMACopyright:
Available Formats
MACHAKOS UNIVERSITY
University Examination 2018/2019
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF BUILDING AND CIVIL ENGINEERING
THIRD YEAR SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION FOR
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (CIVIL ENGINEERING)
ECV 311: SURVEYING IV
DATE: 22/5/2019 TIME:2.00-4.00 PM
INSTRUCTIONS: Attempt questions ONE and any other TWO questions.
QUESTION ONE (COMPULSORY) (30 MARKS)
a) Define the following terminologies as used in photogrammetry (5 marks)
i. Base lining
ii. X-parallax
iii. Stereoscopy
iv. Forward compensation mechanism
v. Parallactic angles for points
b) Explain how the optical method is used to connect and orient the underground control
networks into the same coordinate system as the surface networks. (3 marks)
c) Two points A and B situated 10 and 40 m, respectively, above datum, are imaged on a
near-vertical aerial photograph, taken from an altitude of 2000 m with a camera of focal
length 152 mm. The photo coordinates of the points about the fiducial axes are measured
as follows:
x (mm) y (mm)
a +50.00 +100.00
b -100.00 +80.00
Examination Irregularity is punishable by expulsion Page 1 of 4
If the tilt and swing of the photograph are 2◦ and 20◦, respectively, calculate the
horizontal ground distance AB. (5 marks)
d) In a pair of overlapping photographs, (mean photo base length 89.84 mm) the mean
ground level is 70 m above datum. Two nearby points are observed and the following
information obtained:
Point Height above datum (m) Parallax bar reading (mm)
X 55 7.34
Y 9.46
If the flying height was 2200 m above datum and the focal length of the camera was 150
mm find the height of Y above datum. (4 marks)
e) Calculate the approximate number of photographs required for stereographic coverage
(60% forward overlap & 25% side overlap). Consider a photographic scale of 1:30,000,
ground area coverage of 30 km by 45 km & a photographic standard format size of 230
mm × 230 mm (4 marks)
f) Outline the camera constants obtained from the calibration process (3 marks)
g) The image coordinates of three points A, B and C and of the principle points P and Q on
two overlapping photographs were determined as follows:
Left photo Right photo
x (mm) y (mm) x (mm) y (mm)
P 0.0 0.0 -76.2 0.0
Q +76.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
A +10.6 +60.5 -66.0 +59.0
B +11.2 -6.3 -64.5 -6.7
C +14.5 +34.3 -61.5 +33.7
If the ground coordinates of A and B are 79 000 mE, 92 940 mN and 78 910 mE, 92
760mN respectively, estimate those of C. (6 marks)
Examination Irregularity is punishable by expulsion Page 2 of 4
QUESTION TWO (20 MARKS)
a) What is the objective of photogrammetric orientation? (2 marks)
b) Given that the distance between point A and B on a topographic map is 4.75 cm, at a
scale of 1: 50,000, and the distance between the same points on an air photograph is
23.07 cm, calculate the photographic scale (3 marks)
c) Describe the various steps in photogrammetric orientation ( 15 marks)
QUESTION THREE (20 MARKS)
a) Explain how the weisbach triangle method is used to connect and orient the underground
control networks into the same coordinate system as the surface networks. (10 marks)
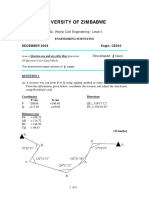
b) From Figure 1 below, the national grid (NG) bearing of an underground base line, CD, is
established by co-planning at the surface onto two wires, W1 and W2, hanging in a
vertical shaft, and then using a Weisbach triangle underground. The measured field data
is as follows:
NG bearing AB: 74 ̊ 28’ 34’’, NG coordinates of A: E 304 625 m, N 511 612 m, the
horizontal angles: BAWs 284 ̊ 32’ 12’’, AWsW2 102 ̊ 16’ 18’’, W2WuW1 0 ̊ 03’ 54’’,
W1WuC 187 ̊ 51’ 50’’, WuCD 291 ̊ 27’ 48’’ and the horizontal distances: W1W2 3.625 m,
WuW2 2.014 m. Compute the bearing of the underground base. (10 marks)
Figure 1
Examination Irregularity is punishable by expulsion Page 3 of 4
QUESTION FOUR (20 MARKS)
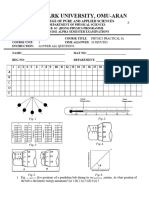
a) In the Figure 2, for a certain photograph, H = 1200m, f = 152, vc is measured as 88.36
mm and vb as 90.78 mm:
Building
Figure 2
i) Derive an equation for the displacement bc
ii) Estimate the height of a building (5 marks)
b) Explain three applications of photogrammetry in Civil Engineering (15 marks)
QUESTION FIVE (20 MARKS)
a) Outline the two basic tasks involved in hydrographic surveys. (1 mark)
b) With the aid of a well labelled diagram, define the most commonly used terms in a near
vertical photograph with the optical axis tilted at θ to the vertical. (9 marks)
c) Describe procedures for mapping water bodies. (10 marks)
Examination Irregularity is punishable by expulsion Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- BS en Iso 08624-2011Document18 pagesBS en Iso 08624-2011Guillermo VegaNo ratings yet
- 2312 Photogrammetry and Remote SensingDocument4 pages2312 Photogrammetry and Remote SensingPeter Mbugua100% (1)
- Ecv 311 Survey Iv Take Away CatDocument6 pagesEcv 311 Survey Iv Take Away CatTimothy MutoroNo ratings yet
- Assignment (3) - Photogrammetry-ParallaxDocument2 pagesAssignment (3) - Photogrammetry-ParallaxAhmed ElsaidNo ratings yet
- NR 220106 Surveying IIDocument8 pagesNR 220106 Surveying IISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- r7210105 SurveyingDocument4 pagesr7210105 SurveyingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- University of Mauritius Faculty of Engineering: Paper No Examination Second Semester 2002 / 2003 DateDocument5 pagesUniversity of Mauritius Faculty of Engineering: Paper No Examination Second Semester 2002 / 2003 DateAkshay BundhooNo ratings yet
- SurveyiingDocument11 pagesSurveyiingELEVATED KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- CE Review01 Module 09Document3 pagesCE Review01 Module 09garcilianvernadethNo ratings yet
- ECV 4316 Paper 2Document9 pagesECV 4316 Paper 2WilliamNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - Diagnostic Exam - CIE 094Document4 pagesQuiz 1 - Diagnostic Exam - CIE 094Wheng JNo ratings yet
- AQS1208200908 Engineering SurveyingDocument6 pagesAQS1208200908 Engineering SurveyingTatenda PaduzeNo ratings yet
- GGE 1205 Surveying 1 2021 Main Exam PrintDocument5 pagesGGE 1205 Surveying 1 2021 Main Exam PrintlucyNo ratings yet
- Sem Q.bankDocument25 pagesSem Q.bankRájãt RøshâñNo ratings yet
- Unit Exam 1Document4 pagesUnit Exam 1Brix Mendoza50% (4)
- Be Winter 2022Document2 pagesBe Winter 2022blastix2104No ratings yet
- Provisional Answer Key-TechnicalDocument47 pagesProvisional Answer Key-Technicalharnishtanna212No ratings yet
- Msteeeeapr 24Document9 pagesMsteeeeapr 24arjiiicryptNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument8 pagesSurveyingSaravanan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Surveying CT 1Document2 pagesSurveying CT 1Gopal SamyNo ratings yet
- TheFinal BFC2103-Answers Script 2010-2011 IDocument11 pagesTheFinal BFC2103-Answers Script 2010-2011 IHussam MurshedNo ratings yet
- Phy 119 - 2020 - 2021 - Exam - ADocument4 pagesPhy 119 - 2020 - 2021 - Exam - AomaNo ratings yet
- 07a30103 SurveyingDocument8 pages07a30103 SurveyingKrishna RaoNo ratings yet
- GEO3101 Cousrework 081019Document3 pagesGEO3101 Cousrework 081019Karungi AroneNo ratings yet
- C1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1Document2 pagesC1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1bhkedarNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionDocument3 pagesRevision QuestionKasyage AbubakaliNo ratings yet
- Chain Survey ProblemDocument4 pagesChain Survey ProblemRathod SRINIVASNo ratings yet
- Phys 11a Problem Set 2Document4 pagesPhys 11a Problem Set 2mfsacedonNo ratings yet
- Question Surveying IIDocument7 pagesQuestion Surveying IIahzamshadabNo ratings yet
- Surveying IIDocument2 pagesSurveying IIsushilNo ratings yet
- Topic:Geometry Time-2 Hrs. Date: 8/02/2024 Set A Marks - 40 STD - XDocument2 pagesTopic:Geometry Time-2 Hrs. Date: 8/02/2024 Set A Marks - 40 STD - XXoxxoNo ratings yet
- Mid Test Exam Geodesy FinalDocument4 pagesMid Test Exam Geodesy FinalAditya Gaur0% (1)
- B.E. 2nd Year, (All Barnchess), IInd Sem, (Supply), Nov - Dec 2013 - 1Document1 pageB.E. 2nd Year, (All Barnchess), IInd Sem, (Supply), Nov - Dec 2013 - 1Gundrathi Narendra GoudNo ratings yet
- Engineering Survey SRMDocument2 pagesEngineering Survey SRMAditya ChopraNo ratings yet
- Model Qpaper GeDocument10 pagesModel Qpaper Geसोनू जगतापNo ratings yet
- Model Qpaper GeDocument10 pagesModel Qpaper GeMr V. Phaninder ReddyNo ratings yet
- PH 110 Assignement One - 2024Document3 pagesPH 110 Assignement One - 2024rogerslossala24No ratings yet
- Surveying 1Document15 pagesSurveying 1stnicogNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering Anna University Question Bank Ce 2254 - Surveying - Ii Two - Mark QuestionsDocument9 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering Anna University Question Bank Ce 2254 - Surveying - Ii Two - Mark Questionsvincent rotichNo ratings yet
- Surveying Model QuestionDocument2 pagesSurveying Model QuestionMahesh Kumar K BNo ratings yet
- Imquestion PaperDocument8 pagesImquestion PaperThulasi Raman KowsiganNo ratings yet
- Surveying & Photogrammetry Exam Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesSurveying & Photogrammetry Exam Practice QuestionsAnietienteabasi100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper Advanced SurveyingDocument5 pagesSample Question Paper Advanced Surveyingchinmoy palNo ratings yet
- 64be085ed52d330019738a06 - ## - City Test - 02: Question PaperDocument9 pages64be085ed52d330019738a06 - ## - City Test - 02: Question PaperAman KumarNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIDocument5 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIMercy SimangoNo ratings yet
- Survey16 PDFDocument2 pagesSurvey16 PDFjhalakduttaNo ratings yet
- Rr220106 Surveying IIDocument8 pagesRr220106 Surveying IISrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Surveying MCQsDocument7 pagesSurveying MCQsDarshak ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Surveying MCQsDocument7 pagesSurveying MCQsDarshak ChauhanNo ratings yet
- rr220106 Surveying IIDocument8 pagesrr220106 Surveying IISRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Final Examination Set2Document7 pagesFinal Examination Set2Divyansh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Surveying TutorialDocument3 pagesSurveying Tutoriallangazelamoyo19No ratings yet
- Insp Lectures Geometrical Optics - Reflection (Mirrors)Document159 pagesInsp Lectures Geometrical Optics - Reflection (Mirrors)arorayash603No ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe: Engineering Surveying December 2009 Engin. CE203Document4 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe: Engineering Surveying December 2009 Engin. CE203Mercy SimangoNo ratings yet
- Drtet2ll5l2012 Oa M': Division: Examiner: Suneying Year Time Four Fo. A Figure, Were HorizontalDocument7 pagesDrtet2ll5l2012 Oa M': Division: Examiner: Suneying Year Time Four Fo. A Figure, Were Horizontalmarwan hazaNo ratings yet
- Building ConstructionDocument2 pagesBuilding ConstructionjadavrimaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological Universitybhartuhari pargiNo ratings yet
- Ece 2202 - Surveying 1 - August 2012Document4 pagesEce 2202 - Surveying 1 - August 2012Joe NjoreNo ratings yet
- Round 5 - Questions PDFDocument12 pagesRound 5 - Questions PDFmarkosNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: The Microscope (10 Points) : Exercise 1.1: Microscope Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesLab 1: The Microscope (10 Points) : Exercise 1.1: Microscope Structure and Functionrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Activity Description Time # ParticipantsDocument1 pageActivity Description Time # ParticipantsNicoNo ratings yet
- Vpod Pro: Smart Vibration MeterDocument2 pagesVpod Pro: Smart Vibration Meterwily fitraNo ratings yet
- MCQs On Refraction of Light Through LensDocument10 pagesMCQs On Refraction of Light Through LensDigant DonthyNo ratings yet
- Bill To Rangs Paramount (23-02-2021)Document2 pagesBill To Rangs Paramount (23-02-2021)মোঃ ফাহিম উর রহমানNo ratings yet
- New Pedagogy Plan For 12th OpticsDocument7 pagesNew Pedagogy Plan For 12th OpticsAshish GambhirNo ratings yet
- Lens Is Present in Human Eye. A. Concave B. Convex C. Plano ConvexDocument2 pagesLens Is Present in Human Eye. A. Concave B. Convex C. Plano ConvexAzan KhokharNo ratings yet
- Soal-To-P1 English Smk-Dki 1718Document7 pagesSoal-To-P1 English Smk-Dki 1718Ayam JagoNo ratings yet
- American Cinematographer - August 2022Document76 pagesAmerican Cinematographer - August 2022basi reddyNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and Functions: Presented By: LORIE MAE N. VIDUYADocument34 pagesMicroscope Parts and Functions: Presented By: LORIE MAE N. VIDUYACamille AndreaNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: DSC-S30/S50Document35 pagesService Manual: DSC-S30/S50Anonymous Lfgk6vygNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument12 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelMohammad Shahidullah ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Police Photography Module 1Document45 pagesPolice Photography Module 1Nichi MartinNo ratings yet
- Owner's Manual 15x50 & 18x50 ISDocument12 pagesOwner's Manual 15x50 & 18x50 ISCraig ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Camera Requirement List - NVMDocument1 pageCamera Requirement List - NVMPrashant MurtyNo ratings yet
- Survey Questionnaire FormatDocument4 pagesSurvey Questionnaire FormatMaarna AminoNo ratings yet
- Praktica Super tl-02Document53 pagesPraktica Super tl-02jmtexla68No ratings yet
- Sony HVR-Z7U and HVR-Z7N Operating GuideDocument143 pagesSony HVR-Z7U and HVR-Z7N Operating GuideMarcio MoraesNo ratings yet
- Continuing Education CourseDocument25 pagesContinuing Education CourseLja CsaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Components For Reflected Light Applications - 2CE-KXQH-7Document17 pagesMicroscope Components For Reflected Light Applications - 2CE-KXQH-7valerioloNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LanguagesDocument17 pagesMedia and Information LanguagesAmzelle Diego LaspiñasNo ratings yet
- Competitive Photography and The Presenta PDFDocument27 pagesCompetitive Photography and The Presenta PDFმირიამმაიმარისიNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - LightDocument35 pagesChapter 10 - LightMadhanNo ratings yet
- Camera Lock Catalog-MinDocument55 pagesCamera Lock Catalog-MinAlex BrasfeltNo ratings yet
- Microhawk Long Range: Specifications and OptionsDocument2 pagesMicrohawk Long Range: Specifications and OptionsAleksandarNo ratings yet
- Bvcls NotesDocument12 pagesBvcls NotesDil Bole DilliNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics - LensDocument10 pagesGeometrical Optics - LensMannyCesNo ratings yet
- Jinta 015 - Pertemuan 8 (Writing)Document3 pagesJinta 015 - Pertemuan 8 (Writing)sepwanti tri assNo ratings yet
- Protocol-XRD XRF SEM OE PDFDocument16 pagesProtocol-XRD XRF SEM OE PDFShyamNo ratings yet