Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan Verbals Draft 2
Lesson Plan Verbals Draft 2
Uploaded by
Josef SamaranayakeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan Verbals Draft 2
Lesson Plan Verbals Draft 2
Uploaded by
Josef SamaranayakeCopyright:
Available Formats
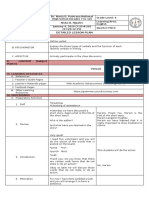
A SEMI-DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN GRADE 9 ENGLISH
DON MARIANO MARCOS MEMORIAL STATE UNIVERSITY
AGOO, LA UNION
LABORATORY HIGH SCHOOL
I. Objectives
By practicing the grammar topic, the students will be able to:
A. recognize the different types of verbals in sentences,
B. understand the concepts of verbals in speaking and writing; and
C. apply the proper uses of verbals in constructing sentences.
II. Subject Matter
A. Topic: Verbals
B. Materials: PowerPoint presentation, Chalk Board, TV
C. References:
The Learning Centre, Marianopolis College. Verbals: Gerunds, Participles,
Infinitives.
http://www.vaniercollege.qc.ca/tlc/files/2016/08/Verbals.pdf
Utah Valley University. Verbals.
https://www.uvu.edu/writingcenter/docs/handouts/grammar-
usage/verbals2018.pdf
III. Procedure
Teacher’s Activity Student’s Activity
Premilinaries
“Good morning sir, good morning
teachers, good morning sir Almonte”
“Good morning class, how are you all today?”
“Is there anyone absent?” “No one is absent today sir, we are
complete.”
A. Motivation
The teacher asks the students the describe
some pictures on the screen using only one word.
These can be either adjectives or nouns.
“Can you describe the pictures on the screen using Expected Answers: “Shiny, Fighting,
only one word?” Intense, Expensive, Tiring.”
B. Lesson Proper
The teacher proceeds with the discussion of
verbals to the class. “Sir, these are words that are verbs
but do not act as verbs”
“Verbals are verbs that do not act as they should in
a sentence.”
The teacher transitions to the different types of
verbals
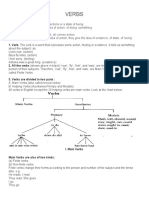
“There are three types of verbals, these are your
gerunds, participles, and infinitives.
Gerunds
- These are verbs that act as nouns or
adjectives in the sentence.
The teacher provides some examples to the
students:
1. My favourite past time is hiking.
- Hiking is the subject complement in
the sentence, and is used to give
more information on what is the
speaker’s favourite past time.
2. He dived into the swimming pool.
- Swimming is an adjective in this
sentence and describes the subject in
the sentence: pool
The teacher proceeds to the next type of verbal,
the participle.
“Our next type of verbal is the participle; can “Sir the different types of participles
anyone give me the different participles?” are the present and past participle.”
“That is correct, participles are generally used to
describe the current ‘state’ of an object.”
“Participles act more as adjectives in a sentence.”
The teacher shows some examples of participles:
1. Practically steaming with frustration,
the commuters wait for their delayed
train to arrive.
- Steaming and delayed are used to
describe the current state of the
objects they are modifying. Steaming
is the adjective for commuters, while
delayed is for ‘train’.
The teacher uses the gerund from the second
example to explain when a participle becomes a
gerund, and when a participle stays as is.
He waved to the swimming children.
- Swimming in this sentence acts more
like a participle rather than a
gerund; this is because it used to
describe the object: ‘children’
The teacher proceeds with the last type of verbal,
the infinitive.
“The last type of verbals are the infinitives”
“Infinitives are verbs that act either as nouns,
adjectives, or adverbs in a sentence.”
“It is usually in its base form followed by the
preposition ‘to’. Can anyone define what a
preposition is?”
The teacher shows examples of some infinitives to
the class:
To fly would be fun.
- ‘To fly’ acts as the subject of the
sentence therefore acting as a noun.
Erika is the woman to visit.
- ‘To visit’ is describing “what kind” of
woman Erika is. So, the infinitive
here is an adjective.
The teacher next discusses the different errors in
using verbals or modifiers.
“We have three common errors in using verbals,
these are your dangling modifiers, misplaced
modifiers, and sentence fragments.”
“Sentence fragments occur when a sentence
contains two different ideas.”
The teacher shows different examples:
Making our party complete. Erin brought
the cake.
- The sentence contains two separate
ideas, one is incomplete and one
gives a complete thought.
Removing his coat. Jack rushed to the
river.
“The next error is the Dangling Modifiers; these are
modifiers that do not modify an object in the
sentence.”
The teacher shows different examples of dangling
modifiers:
Having sent the letter overnight, it will
probably arrive on time.
- The modifying phrase features an
action done; however, the doer of
the action is not present in the
sentence.
Putting on my pajamas, a mouse ran
across the floor.
- The sentence once again features an
action done, however while it does
modify another noun, it isn’t logically
correct. But it isn’t a misplaced
modifier due to the proper noun not
being present.
The teacher proceeds to the last type of error, the
misplaced modifier.
“The last type of error is the misplaced modifier.
These are modifying or verbial phrases put in the
wrong position of the sentence.”
The teacher shows different misplaced modifiers to
the class:
Joe ate the chicken sitting in the chair.
- The modifying phrase is modifying
the noun ‘chicken’ therefore making
it seem that the chicken was sitting
in the chair.
The man walked toward the car carrying
a brief case.
- The modifying phrase is not in its
correct location.
“Has everyone understood what verbals are? Can we “Yes sir, we can now do the
move on with the activity?” activity.”
C. Guided Practice
The class will be shown different sentences
on the screen, then they will need to identify what
kind of verbal has been underlined in the sentence.
Answers:
- Delores noticed her cousin walking -Participle
along the shoreline.
- Being the boss made Jeff feel -Gerund
uneasy.
- The police arrested him for -Gerund
speeding.
- Mom left to buy milk. -Infinitive
- We were exhausted after cleaning -Participle
up the shed.
- The sheep had already jumped -Participle
over the fence.
- I’m happy to be here. -Infinitive
- Finding a needle in a haystack -Gerund
would be easier than what we are
trying to do.
- She bought a new pair of running -Participle
shoes.
- To love someone requires patience -Infinitive
and understanding.
D. Independent Practice
The following sentences have errors that had
been discussed in the lesson. The students will need Answers (Note: some answers may
to identify what type of error is present in the vary due to the existence of 2
sentence, and then write the correct sentence solutions, the teacher will make sure
after. it is grammatically correct to merit a
point):
1. Having fixed the sentence, it
now made more sense. Dangling Modifier, Having fixed the
sentence, he now made more sense.
2. We are really going to have to
hurry. Because we overslept Sentence Fragment, We are really
and missed the bus. going to have to hurry because we
overslept and missed the bus.
3. She saw a kitten and puppy on Misplaced Modifier, On her way to
the way to the store. the store, she saw a kitten and
puppy.
4. Spitting out hot lava, my friend
took photos of the volcano. Misplaced Modifier, My friend took
photos of the volcano spitting out hot
E. Generalization lava.
The teacher summarizes the lesson to the class.
“Verbals are verbs that do not act as verbs in a
sentence. Your different verbals are the gerunds,
participles, and infinitives.”
“The common errors of using verbals are sentence
fragments, dangling modifiers, and misplaced
modifiers.”
“Are there any more questions regarding verbals?”
“None sir, we have understood the
“Then that will be all, Good bye class.” lesson.”
“Good bye and thank you sir Josef.”
Prepared by:
Samaranayake, Rahul Josef R.
Student teacher, English 4A
You might also like
- Lesson Plan in Grade 3 Adverb of Time and MannerDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Grade 3 Adverb of Time and Mannergelie saludaga75% (8)
- DLP-8-Q1mODULE-5-Remefe SolamilloDocument5 pagesDLP-8-Q1mODULE-5-Remefe SolamilloKristell C. Lagarde100% (1)
- Verbals Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesVerbals Lesson PlanMay Ann Bruan100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanMimi33% (3)
- Restalls Logic - Textbook Exercise SolutionsDocument87 pagesRestalls Logic - Textbook Exercise SolutionsJames MaxNo ratings yet
- Preterite Irregular Verbs ClassworkDocument2 pagesPreterite Irregular Verbs ClassworkMY DONo ratings yet
- Vietnamese SyntaxDocument19 pagesVietnamese SyntaxLy Pig100% (1)
- Transitive and Intransitive VerbsDocument14 pagesTransitive and Intransitive VerbsJes Rea EdubalaNo ratings yet
- Sva LP - LoroDocument11 pagesSva LP - LoroKaren Grace LoroNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP in English Grade 4Document7 pagesDetailed LP in English Grade 4Cristine Mae Tumamao100% (1)
- DLP-G-9 VerbalsDocument4 pagesDLP-G-9 VerbalsHaidee IndecioNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lessson Plan in EnglishDocument6 pagesDetailed Lessson Plan in Englishkristen caalimNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan IdiomsDocument7 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan IdiomsIsa Bonni EveNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN ENGLISH 3 LoidaDocument7 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN IN ENGLISH 3 LoidaVergiel Abellano100% (6)
- Detailed Lesson Plan 1Document5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan 1Mary Ann PateñoNo ratings yet
- DLL LP Eng.3Document9 pagesDLL LP Eng.3Marion Piczon100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan For Printing PDFDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan For Printing PDFAnonymous 6O55pR100% (2)
- Ele 202 VerbalsDocument3 pagesEle 202 VerbalsRonaly HiladoNo ratings yet
- Grammar DiagTest Martin Pced02-401aDocument8 pagesGrammar DiagTest Martin Pced02-401aJheris MartinNo ratings yet
- Angels Lesson Plan VerbalsDocument9 pagesAngels Lesson Plan VerbalsCuizon Roydenn A.No ratings yet
- SVA Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesSVA Lesson PlanRhona EstorbaNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Teaching Grade 11Document11 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Teaching Grade 11NORZEN LAGURANo ratings yet
- LP in GerundDocument14 pagesLP in GerundCristine Shayne Bautista100% (1)
- Sultan Kudarat State UniversityDocument6 pagesSultan Kudarat State UniversityMA. CAROL FLORONo ratings yet
- Grammar Review Handout 1Document3 pagesGrammar Review Handout 1Wemart SalandronNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Run-On SentenceDocument10 pagesLesson Plan Run-On SentenceEricah Quider MaestradoNo ratings yet
- Gerund, Its Definition and Its UsesDocument4 pagesGerund, Its Definition and Its UsesSmylene MalaitanNo ratings yet
- ADVERBSDocument4 pagesADVERBSJosiah FlorNo ratings yet
- InfinitivesDocument10 pagesInfinitivesKyleNo ratings yet
- DPL Figurative Language6Document7 pagesDPL Figurative Language6Joana Marie RegondonNo ratings yet
- Detailed LP - Simple Past and Past Perfect TenseDocument3 pagesDetailed LP - Simple Past and Past Perfect TenseNowelynNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Daily Lesson Plan in English 8Document8 pagesA Detailed Daily Lesson Plan in English 8Charmaine Grace Dung-aoNo ratings yet
- Brilliant Footsteps Int'L Academy Teacher Abdulrahim Ibrahim Lesson Plan & NotesDocument5 pagesBrilliant Footsteps Int'L Academy Teacher Abdulrahim Ibrahim Lesson Plan & NotesAbdulRahimNo ratings yet
- DLP. Grade10 Q2.Second PartDocument6 pagesDLP. Grade10 Q2.Second PartRegilyn DayonNo ratings yet
- ImportantDocument7 pagesImportantJamie anne AbreaNo ratings yet
- Detailed-Lesson-Plan-Literalandfigurativespeech-Newest (1) (AutoRecovered)Document5 pagesDetailed-Lesson-Plan-Literalandfigurativespeech-Newest (1) (AutoRecovered)Natanohj BuezaNo ratings yet
- Please Arrange Your Chairs Properly and Pick Up Pieces of Papers. You May Now Take Your SeatDocument7 pagesPlease Arrange Your Chairs Properly and Pick Up Pieces of Papers. You May Now Take Your SeatSUSHI CASPENo ratings yet
- Teaching - Anthony - Traditional DLPDocument11 pagesTeaching - Anthony - Traditional DLPPete Z CampilanNo ratings yet
- Idiomatic Expressions - DetailedDocument5 pagesIdiomatic Expressions - DetailedKristellNo ratings yet
- FeaterDocument7 pagesFeaterNyce Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Transitive and Intransitive VerbsDocument6 pagesTransitive and Intransitive VerbsTivar Victor100% (1)
- WHLP-1ST Quarter-English7-Week 5-6Document6 pagesWHLP-1ST Quarter-English7-Week 5-6Ernest De Mesa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Phrases Clauses and SentenceDocument11 pagesPhrases Clauses and SentenceCamille CruzNo ratings yet
- VOICESDocument9 pagesVOICESMohfry OoiiNo ratings yet
- DLP 7 L9Document7 pagesDLP 7 L9Vanessa R. AbadNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN FOR Past TenseDocument12 pagesLESSON PLAN FOR Past TensehezrinNo ratings yet
- Infinitives Lesson-PlanDocument4 pagesInfinitives Lesson-PlanGwyneth BabaoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 7Document6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade 7Darwin ValdezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan DemoDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan DemoJheris MartinNo ratings yet
- DLP 8 Q1mODULE 5Document4 pagesDLP 8 Q1mODULE 5JOEVANNIE S. PAGAURANo ratings yet
- DemoDocument6 pagesDemoJean VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 7Document12 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 7Eden Grace RamirezNo ratings yet
- InfinitivessemiDocument4 pagesInfinitivessemisheilamariecabarloNo ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan in Speaking ClassDocument5 pagesA Lesson Plan in Speaking ClassAngelene GullebanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 3: Teacher Activity Students Activity A. PreliminariesDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in English 3: Teacher Activity Students Activity A. PreliminariesRocoBabe's PPT100% (1)
- Detailed LP SVA Rule - Docx 1Document21 pagesDetailed LP SVA Rule - Docx 1Reyza Jean Alaya-ay LongcobNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 English 7Document11 pagesCot 2 English 7Winzlet Kate DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Infinitives LP Gr9Document3 pagesInfinitives LP Gr9shaynmirandaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Topic ObjectivesDocument8 pagesLesson Plan Topic Objectivesapi-438880639No ratings yet
- Technical WritingDocument26 pagesTechnical WritingbionaarbenNo ratings yet
- GE EL 118 - Chapter 1 - Sentence FragmentsDocument29 pagesGE EL 118 - Chapter 1 - Sentence FragmentsbionaarbenNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Mother Tongue 1Document6 pagesLesson Plan - Mother Tongue 1Giselle Beserial RosapaNo ratings yet
- My Blue Book of Grammar for Class 6: A Series Based on the Functional ApproachFrom EverandMy Blue Book of Grammar for Class 6: A Series Based on the Functional ApproachNo ratings yet
- Weekly Log Week 4 Grade 10Document2 pagesWeekly Log Week 4 Grade 10Josef SamaranayakeNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Grade 11Document1 pageWeek 6 Grade 11Josef SamaranayakeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Grade 10Document4 pagesReviewer For Grade 10Josef SamaranayakeNo ratings yet
- Week 23-24 Lesson PlansDocument6 pagesWeek 23-24 Lesson PlansJosef SamaranayakeNo ratings yet
- Quiz For Grade 9Document6 pagesQuiz For Grade 9Josef SamaranayakeNo ratings yet
- English 4 Lesson Plan Week 10-11Document16 pagesEnglish 4 Lesson Plan Week 10-11Josef SamaranayakeNo ratings yet
- Compound Noun ListDocument5 pagesCompound Noun ListkamawisNo ratings yet
- Makalah Inggris GerundDocument11 pagesMakalah Inggris GerundNyimas HayatiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Phrases Clauses, and SentencesDocument32 pagesMODULE 6 Phrases Clauses, and SentencesKaren DomondonNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Macam-Macam Kalimat Dalam Bahasa IngrisDocument13 pagesRangkuman Macam-Macam Kalimat Dalam Bahasa IngrisFran Sinatra100% (1)
- Spanish Grammar NotesDocument9 pagesSpanish Grammar NotesDevanshi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Futur ProcheDocument1 pageFutur ProcheStf L'bouclés0% (1)
- Eng Ans NsDocument9 pagesEng Ans NsVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Latin Noun Declension NotesDocument4 pagesLatin Noun Declension NotesMason FullerNo ratings yet
- Materi KlauseDocument13 pagesMateri KlauseMuhammad YusufNo ratings yet
- Sheldon's Advance Language Lessons Answer Key First Half FinalDocument49 pagesSheldon's Advance Language Lessons Answer Key First Half Finala01712045No ratings yet
- The International Journal of LexicographyDocument15 pagesThe International Journal of Lexicographyapi-6708709No ratings yet
- Syntax To ESPDocument19 pagesSyntax To ESPLiezle ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Judgment and Proposition or Logical StatementDocument12 pagesJudgment and Proposition or Logical StatementZoem de LeozNo ratings yet
- Deber InglesDocument28 pagesDeber InglesJairo IdrovoNo ratings yet
- Rules of English Grammar by KundanDocument61 pagesRules of English Grammar by KundanVarun Suresh100% (1)
- Language and LinguisticsDocument22 pagesLanguage and Linguistics0787095494No ratings yet
- Arabic LearningDocument2 pagesArabic LearningImran MohammedNo ratings yet
- Goodenough, W.H. (1956) - Componential Analysis and The Study of MeaningDocument23 pagesGoodenough, W.H. (1956) - Componential Analysis and The Study of MeaningJuan Manuel Ochoa Sambrizzi100% (1)
- Adjectives: of Comparison: Positive, Comparative and Superlative. ExamplesDocument3 pagesAdjectives: of Comparison: Positive, Comparative and Superlative. ExamplespremlatahNo ratings yet
- Review Colinizing EgyptDocument20 pagesReview Colinizing EgyptMichelle MatteiNo ratings yet
- Task Sheet 2 - Psychology of LanguageDocument2 pagesTask Sheet 2 - Psychology of LanguageANA-MARIA SĂLĂVĂSTRUNo ratings yet
- (HTTPS://WWW - Lawlessfrench.c: QuestionsDocument9 pages(HTTPS://WWW - Lawlessfrench.c: Questionsnoel8938lucianoNo ratings yet
- Ingles 2Document14 pagesIngles 2Teacher Anayka MitreNo ratings yet
- VERBSDocument6 pagesVERBSKalai Selvi MohanNo ratings yet
- Formal Letter WritingDocument14 pagesFormal Letter WritingAna-Maria NuţăNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Lesson 1 PronounsDocument47 pagesWeek 4 Lesson 1 Pronounsronaldo messiNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect WordsDocument4 pagesCause and Effect WordsMaría Andrea ReyesNo ratings yet