Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsUnderstanding Market Segmentation and Targeting
Understanding Market Segmentation and Targeting
Uploaded by
Tasebe GetachewCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- First, Break All The Rules - Buckingham.ebsDocument11 pagesFirst, Break All The Rules - Buckingham.ebsPavanPrabhasNo ratings yet
- SocioinformaticaDocument175 pagesSocioinformaticaFabricio NevesNo ratings yet
- Marketing Segmentation 1Document3 pagesMarketing Segmentation 1Adefisayo BoluwatifeNo ratings yet
- Marketing: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10Document16 pagesMarketing: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10Ana García BarbelNo ratings yet
- Notes 5Document2 pagesNotes 5Sabbineni PoojithaNo ratings yet
- Derartu Tulu - AssignmentDocument8 pagesDerartu Tulu - AssignmentibsaashekaNo ratings yet
- The Imc Planning ProcessDocument35 pagesThe Imc Planning ProcessTRIXIA MAE B. ESPIRITUNo ratings yet
- Market SegmentationDocument22 pagesMarket SegmentationTony WariboNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour AssignmentDocument7 pagesConsumer Behaviour AssignmentGeorge AddaiNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentJamilaNo ratings yet
- Unit II MMDocument8 pagesUnit II MMJatinsinghNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing AssignmentDocument12 pagesStrategic Marketing AssignmentDaniel Chege100% (1)
- Marketing Management - CHAPTER 6Document17 pagesMarketing Management - CHAPTER 6Ewan DikoNo ratings yet
- Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Market SegmentationDocument10 pagesCustomer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Market SegmentationNoman KhosaNo ratings yet
- Hinsene's AssignmentDocument8 pagesHinsene's AssignmentibsaashekaNo ratings yet
- Introduction - 1 .Document8 pagesIntroduction - 1 .Greeshma AlwalNo ratings yet
- Marketing NotesDocument25 pagesMarketing NotesEva SherlockNo ratings yet
- TH106 Information Sheet 3.1-1Document5 pagesTH106 Information Sheet 3.1-1Djared James MinasNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategyDocument4 pagesMarketing StrategyPat RiciousNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument19 pagesUnit 2 NotesMayuri ShettiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3Asif IslamNo ratings yet
- CH 6 MarketinghchhhDocument3 pagesCH 6 MarketinghchhhmayankgoylllNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior 11th Edition Schiffman Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesConsumer Behavior 11th Edition Schiffman Solutions ManualAntonio LMNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument11 pagesChapter FourAbdu YaYa AbeshaNo ratings yet
- Kalid's Assignment FinalDocument9 pagesKalid's Assignment FinalibsaashekaNo ratings yet
- AssigmentDocument16 pagesAssigmentEman RajputNo ratings yet
- Marketing Ques 1 To 10Document11 pagesMarketing Ques 1 To 10MukulNo ratings yet
- Haramaya University: Name IdDocument10 pagesHaramaya University: Name IdibsaashekaNo ratings yet
- MARKETINGDocument49 pagesMARKETINGpropraveen1603No ratings yet
- Marketing Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocument5 pagesMarketing Segmentation, Targeting and Positioningnoor.mughal1405No ratings yet
- MarketingDocument8 pagesMarketingpebrianiputri84No ratings yet
- Role of IMC in The Marketing ProcessDocument7 pagesRole of IMC in The Marketing ProcessMuhamad Rizal Ramdani100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENT 7 - CapistranoDocument2 pagesASSIGNMENT 7 - CapistranoAnne Milanes CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5PRECIOUS JOY PATIGDASNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document21 pagesUnit 2Himanshu DarganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Consumer BehaviorDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Consumer BehaviorYUSRA ANSARNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Learning MaterialDocument6 pagesWeek 5 Learning MaterialFatema ZehraNo ratings yet
- Competitive Forces - Collaboration or Differentiation: Instead of Viewing Competitors Solely AsDocument6 pagesCompetitive Forces - Collaboration or Differentiation: Instead of Viewing Competitors Solely Ashabibul basherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 Review Notes MGN 2210Document8 pagesChapter 1-3 Review Notes MGN 2210KaiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Questions - Marketing PrinciplesDocument5 pagesDiscussion Questions - Marketing PrinciplesNguyễnVũHoàngTấnNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument22 pagesConsumer BehaviordishankNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Business OrganisationDocument26 pagesFoundations of Business OrganisationNikolas WidjayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Segmentation-1Document10 pagesChapter Four Segmentation-1Ebisa HailuNo ratings yet
- 131 Marketing Final Exam ReviewDocument35 pages131 Marketing Final Exam ReviewBrendan StevensonNo ratings yet
- Banking TermDocument36 pagesBanking Termarpitpra1994No ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING - Unit 2 STPDocument78 pagesPRINCIPLES OF MARKETING - Unit 2 STPaddityarajNo ratings yet
- MM Short MaterialDocument24 pagesMM Short MaterialThippana GomathiNo ratings yet
- Coke STP Steps-By RobintbgDocument9 pagesCoke STP Steps-By Robintbgintel0000No ratings yet
- SegmentationDocument34 pagesSegmentationDevilNo ratings yet
- Advertizing Mid NoteDocument11 pagesAdvertizing Mid NoteNikNituNo ratings yet
- Marketing ProjectDocument38 pagesMarketing ProjectVidya GNo ratings yet
- Mark 1115 Final Short 1Document9 pagesMark 1115 Final Short 1raymondNo ratings yet
- 2) SegmentationDocument46 pages2) SegmentationSugandhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-2Document5 pagesUnit 3-2Brian MulengaNo ratings yet
- The Below Figure Depicts The STP Process For A Skincare ProductDocument35 pagesThe Below Figure Depicts The STP Process For A Skincare Productshubham kumarNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument7 pagesConsumer BehaviourLiv DNo ratings yet
- Profile The Market NewDocument10 pagesProfile The Market Newdenekedarchu358No ratings yet
- Im Unit 3Document10 pagesIm Unit 3Ankush TyagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Nedzma HrvatNo ratings yet
- Schiffman cb11 Im02Document23 pagesSchiffman cb11 Im02Perihan SalahNo ratings yet
- Bachelor in Business Administration Semester 3: Prepared For: Lecturer's NameDocument11 pagesBachelor in Business Administration Semester 3: Prepared For: Lecturer's NameBrute1989No ratings yet
- Marketing Mastery: Strategies for Building and Sustaining a Strong Customer BaseFrom EverandMarketing Mastery: Strategies for Building and Sustaining a Strong Customer BaseNo ratings yet
- Unit TwoDocument20 pagesUnit TwoTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2Document12 pagesChapter 1 & 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Lnternational Trade - Chapt 3,4,5,6,7Document23 pagesLnternational Trade - Chapt 3,4,5,6,7Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document9 pagesCH 4Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument31 pagesChapter OneTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Entrepreneurship MGMT 3101Document5 pagesAssignment of Entrepreneurship MGMT 3101Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Paragraph On Campus LifeDocument1 pageParagraph On Campus LifeTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- BiogeographyDocument61 pagesBiogeographyTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 1Document80 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 1Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Importance of Forest Development in EthiopiaDocument5 pagesImportance of Forest Development in EthiopiaTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Env Et CH 1-2Document33 pagesEnv Et CH 1-2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Social and Economic Factors Affecting Forest Development in EthiopiaDocument5 pagesSocial and Economic Factors Affecting Forest Development in EthiopiaTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document9 pagesCH 3Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document34 pagesChapter 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document12 pagesChapter 5Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document17 pagesChapter 1Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Forest Development in EthiopiaDocument5 pagesApproaches To Forest Development in EthiopiaTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document47 pagesUnit 1Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Histiry Assignment - C-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesHistiry Assignment - C-WPS OfficeTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Document .1234Document20 pagesDocument .1234Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document44 pagesUnit 3Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document56 pagesUnit 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Assignment of history-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesAssignment of history-WPS OfficeTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Module of Subject Area MethodDocument54 pagesModule of Subject Area MethodTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Enter ch-1 NewDocument19 pagesEnter ch-1 NewTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document50 pagesUnit 4Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document15 pagesUnit 4Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- THESIS Ni An-AnDocument27 pagesTHESIS Ni An-AnAko Intawn C OrlyNo ratings yet
- KWP - Staying Grounded Staying Close To Your On The Go Basics IndonesiaDocument16 pagesKWP - Staying Grounded Staying Close To Your On The Go Basics IndonesiaNerissa AngelinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Personality, Attitudes, and Work BehaviorsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Personality, Attitudes, and Work BehaviorsJUN GERONANo ratings yet
- Kuis SPM - Sebelum UtsDocument30 pagesKuis SPM - Sebelum Utsirina shaykNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence-Case Study PDFDocument20 pagesEmotional Intelligence-Case Study PDFSaddam AwanNo ratings yet
- Chap 9 AnswerDocument4 pagesChap 9 AnswerNancy VõNo ratings yet
- Performence Appraisal For PracticeDocument18 pagesPerformence Appraisal For PracticeAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Influence Processes and LeadershipDocument30 pagesInfluence Processes and LeadershipMohiuddin GaalibNo ratings yet
- VIII. Organizational Structure, Culture and DevelopmentDocument37 pagesVIII. Organizational Structure, Culture and DevelopmentAngelNo ratings yet
- Mod.1 L.1,2,3Document25 pagesMod.1 L.1,2,3Aries SungaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Implications For Marketing Strategy 7th Edition Quester Test BankDocument31 pagesConsumer Behaviour Implications For Marketing Strategy 7th Edition Quester Test Bankselinajacob7nhlfu100% (32)
- Consumer Behavior Towards The New Packaging of FMCG ProductsDocument14 pagesConsumer Behavior Towards The New Packaging of FMCG Products21PBA249 NAVANEEN KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Reflection Report 10 Tutorial 9.2 PM-T123PWB-1 Group 4Document9 pagesReflection Report 10 Tutorial 9.2 PM-T123PWB-1 Group 4Khánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Report Writing and Behavioral ObservationDocument23 pagesReport Writing and Behavioral ObservationFUN FLARE SHADOWNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Final Assignment Jake DowsettDocument7 pagesAssignment 3 Final Assignment Jake Dowsettapi-321376162No ratings yet
- AmanDocument50 pagesAmanGAURAVNo ratings yet
- Complaint ManagementDocument22 pagesComplaint Managementvijendra chanda33% (3)
- What We Know About Effects of Sport and Elite Athletics On Child Development OutcomesDocument82 pagesWhat We Know About Effects of Sport and Elite Athletics On Child Development Outcomesandreea_zgrNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Consumer Buying BehaviorDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Consumer Buying BehaviorFlorbert Caldito Cimatu100% (1)
- Customer Loyalty and Customer Loyalty ProgramsDocument37 pagesCustomer Loyalty and Customer Loyalty ProgramsMeena SivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Antonina N. Agata Mba 2017Document91 pagesAntonina N. Agata Mba 2017Welfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorDocument13 pagesConsumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorBë Ň TőngNo ratings yet
- Handout File - EDU302 Lecture 1-10 (Topics1-35)Document21 pagesHandout File - EDU302 Lecture 1-10 (Topics1-35)Muqaddas ijaz -25No ratings yet
- Consumer Buying BehaviourDocument35 pagesConsumer Buying BehaviourDeeksha SinghNo ratings yet
- OB - CPJ NotesDocument120 pagesOB - CPJ NotesTrisha AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 FinalDocument22 pagesChapter 2 FinalariaNo ratings yet
- The Developmental-Health Framework Within The McGill Model of NursingDocument15 pagesThe Developmental-Health Framework Within The McGill Model of NursingFerdy LainsamputtyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Rebecca Jones 1Document11 pagesCase Study - Rebecca Jones 1api-465726569No ratings yet
Understanding Market Segmentation and Targeting
Understanding Market Segmentation and Targeting
Uploaded by
Tasebe Getachew0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
111111
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesUnderstanding Market Segmentation and Targeting
Understanding Market Segmentation and Targeting
Uploaded by
Tasebe GetachewCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1.
Understanding Market Segmentation and Targeting:
1) Discuss the significance of market segmentation in marketing strategies.
2) How does market segmentation aid in targeting specific consumer groups
effectively?
3) Provide examples of successful market segmentation strategies employed by
companies in diverse industries.
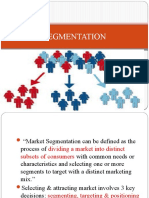
Significance of Market Segmentation in Marketing Strategies:
Market segmentation is a crucial aspect of marketing strategies as it involves dividing a
broad target market into smaller, more manageable segments based on certain
characteristics. This process allows companies to tailor their products, services, and
marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and preferences of each segment. The
significance of market segmentation in marketing strategies can be understood through
the following points:
1. Better Understanding of Customers: By segmenting the market, companies gain
a deeper understanding of their customers’ behaviors, preferences, and buying
patterns. This knowledge enables them to create targeted marketing campaigns
that resonate with specific consumer groups.
2. Increased Customer Satisfaction: When companies target specific segments
with products or services that cater to their unique needs, it leads to higher
customer satisfaction. Customers feel understood and valued when they receive
offerings that align with their preferences.
3. Enhanced Marketing Efficiency: Market segmentation helps companies allocate
their resources more efficiently by focusing on segments that are most likely to
respond positively to their offerings. This targeted approach reduces wastage and
improves the return on investment for marketing activities.
4. Competitive Advantage: Companies that effectively segment their markets gain
a competitive edge by differentiating themselves from competitors. They can
position their products or services as tailored solutions for specific customer
groups, making it harder for competitors to replicate their success.
5. Product Development Opportunities: Market segmentation can also uncover
new product development opportunities by identifying unmet needs within
specific segments. Companies can innovate and create offerings that address these
gaps in the market, driving growth and profitability.
How Market Segmentation Aids in Targeting Specific Consumer Groups
Effectively:
Market segmentation plays a vital role in targeting specific consumer groups effectively
by allowing companies to focus their efforts on those segments that are most likely to
respond positively to their offerings. Here’s how market segmentation aids in targeting
specific consumer groups:
1. Customized Marketing Messages: Through market segmentation, companies
can tailor their marketing messages to resonate with the unique characteristics and
preferences of each segment. This customization increases the relevance of the
message and enhances its impact on the target audience.
2. Optimized Product Offerings: By understanding the distinct needs and
requirements of different consumer groups, companies can develop product
offerings that are optimized for each segment. This targeted approach ensures that
products meet the specific demands of customers within each segment.
3. Improved Customer Engagement: Targeting specific consumer groups allows
companies to engage with customers on a more personal level, building stronger
relationships and loyalty. When customers feel understood and valued, they are
more likely to remain loyal to the brand.
4. Efficient Resource Allocation: Instead of adopting a one-size-fits-all approach,
market segmentation enables companies to allocate resources efficiently by
focusing on segments with the highest potential for conversion. This targeted
strategy maximizes ROI and minimizes wasted resources.
5. Increased Sales and Profitability: By effectively targeting specific consumer
groups through market segmentation, companies can drive higher sales and
profitability. Tailoring products and marketing efforts to meet the unique needs of
each segment results in increased customer acquisition and retention.
Examples of Successful Market Segmentation Strategies:
1. Apple Inc.: Apple has successfully implemented market segmentation by
targeting different consumer groups with its range of products such as iPhones,
iPads, MacBooks, etc. Each product is designed to appeal to a specific segment
based on factors like lifestyle, profession, or tech-savviness.
2. Nike: Nike employs market segmentation by targeting various customer segments
such as athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and fashion-conscious individuals with
specialized product lines like running shoes, basketball sneakers, and athleisure
wear.
3. Starbucks: Starbucks utilizes market segmentation by offering different types of
beverages and food items tailored to diverse customer preferences. They have
created distinct product lines like Frappuccinos for younger consumers and
premium Reserve coffees for connoisseurs.
2. Consumer Behavior and Decision Making:
1) Explain the role of consumer behavior in shaping marketing strategies.
2) How do factors such as cultural, social, and psychological influences impact
consumer decision-making?
3) Analyze the importance of understanding consumer behavior for marketers and
provide real-world examples.
Consumer behavior plays a pivotal role in shaping marketing strategies as it
provides insights into how consumers select, purchase, and use products or services.
Understanding consumer behavior enables marketers to develop effective marketing
mixes that cater to the needs, preferences, and motivations of their target audience.
1. Role of Consumer Behavior in Marketing Strategies: Consumer behavior is the
study of individuals, groups, or organizations and how they select, buy, use, and
dispose of products, services, ideas, or experiences to satisfy their needs and
wants. Marketers use this knowledge to create marketing strategies that resonate
with their target audience. For instance, understanding consumer preferences for
certain product features or brand attributes can guide product development and
positioning decisions. Similarly, recognizing consumer buying patterns can inform
pricing strategies and promotional tactics (Kotler & Keller, 2016).
2. Impact of Cultural, Social, and Psychological Influences on Consumer
Decision-Making: Cultural influences refer to the shared beliefs, values, customs,
behaviors, artifacts, institutions, and practices that characterize a group or society.
These influences shape consumers’ perceptions of products and services by
influencing their attitudes towards them. For example, collectivist cultures may
prioritize group harmony over individual achievement (Hofstede et al., 2010).
Social influences include family members, peers, reference groups (e.g.,
professional organizations), and mass media. These influences can impact
consumer decision-making through social norms and peer pressure. Psychological
influences include personal factors such as motivation (e.g., need for
achievement), perception (e.g., product attributes), learning (e.g., past
experiences), emotion (e.g., joy or fear), personality traits (e.g., extraversion),
beliefs (e.g., religious beliefs), and cognitive processes (e.g., problem-solving
skills) (Ajzen & Fishbein, 1980).
3. Importance of Understanding Consumer Behavior for Marketers:
Understanding consumer behavior is crucial for marketers because it helps them
create effective marketing strategies that meet the needs and preferences of their
target audience. For example:
o Product Development: Understanding consumer preferences can guide
product development decisions by identifying which features are most
desirable to consumers in a given market segment. This can lead to more
successful product launches and higher customer satisfaction levels (Kotler
& Keller, 2016).
o Marketing Mix Decisions: Consumer behavior insights can inform
various aspects of the marketing mix including pricing strategies (based on
price elasticity), promotion tactics (based on communication channels
preferred by target segments), distribution channels (based on convenience
factors for consumers), and product design/positioning decisions based on
consumer preferences (American Marketing Association]. Real-world
examples include Coca-Cola’s successful introduction of Diet Coke in
response to changing consumer preferences towards low-calorie beverages
or Apple’s innovative product design that caters to consumers’ desire for
sleek technology (Coca-Cola](Apple].
3. Product Development and Branding:
1) Describe the process of product development from concept to launch.
2) Discuss the significance of branding in creating differentiation and building
customer loyalty.
3) Evaluate the role of branding strategies in influencing consumer perceptions and
purchasing decisions.
You might also like
- First, Break All The Rules - Buckingham.ebsDocument11 pagesFirst, Break All The Rules - Buckingham.ebsPavanPrabhasNo ratings yet
- SocioinformaticaDocument175 pagesSocioinformaticaFabricio NevesNo ratings yet
- Marketing Segmentation 1Document3 pagesMarketing Segmentation 1Adefisayo BoluwatifeNo ratings yet
- Marketing: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10Document16 pagesMarketing: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10Ana García BarbelNo ratings yet
- Notes 5Document2 pagesNotes 5Sabbineni PoojithaNo ratings yet
- Derartu Tulu - AssignmentDocument8 pagesDerartu Tulu - AssignmentibsaashekaNo ratings yet
- The Imc Planning ProcessDocument35 pagesThe Imc Planning ProcessTRIXIA MAE B. ESPIRITUNo ratings yet
- Market SegmentationDocument22 pagesMarket SegmentationTony WariboNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour AssignmentDocument7 pagesConsumer Behaviour AssignmentGeorge AddaiNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentJamilaNo ratings yet
- Unit II MMDocument8 pagesUnit II MMJatinsinghNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing AssignmentDocument12 pagesStrategic Marketing AssignmentDaniel Chege100% (1)
- Marketing Management - CHAPTER 6Document17 pagesMarketing Management - CHAPTER 6Ewan DikoNo ratings yet
- Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Market SegmentationDocument10 pagesCustomer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Market SegmentationNoman KhosaNo ratings yet
- Hinsene's AssignmentDocument8 pagesHinsene's AssignmentibsaashekaNo ratings yet
- Introduction - 1 .Document8 pagesIntroduction - 1 .Greeshma AlwalNo ratings yet
- Marketing NotesDocument25 pagesMarketing NotesEva SherlockNo ratings yet
- TH106 Information Sheet 3.1-1Document5 pagesTH106 Information Sheet 3.1-1Djared James MinasNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategyDocument4 pagesMarketing StrategyPat RiciousNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument19 pagesUnit 2 NotesMayuri ShettiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3Asif IslamNo ratings yet
- CH 6 MarketinghchhhDocument3 pagesCH 6 MarketinghchhhmayankgoylllNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior 11th Edition Schiffman Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesConsumer Behavior 11th Edition Schiffman Solutions ManualAntonio LMNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument11 pagesChapter FourAbdu YaYa AbeshaNo ratings yet
- Kalid's Assignment FinalDocument9 pagesKalid's Assignment FinalibsaashekaNo ratings yet
- AssigmentDocument16 pagesAssigmentEman RajputNo ratings yet
- Marketing Ques 1 To 10Document11 pagesMarketing Ques 1 To 10MukulNo ratings yet
- Haramaya University: Name IdDocument10 pagesHaramaya University: Name IdibsaashekaNo ratings yet
- MARKETINGDocument49 pagesMARKETINGpropraveen1603No ratings yet
- Marketing Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocument5 pagesMarketing Segmentation, Targeting and Positioningnoor.mughal1405No ratings yet
- MarketingDocument8 pagesMarketingpebrianiputri84No ratings yet
- Role of IMC in The Marketing ProcessDocument7 pagesRole of IMC in The Marketing ProcessMuhamad Rizal Ramdani100% (1)
- ASSIGNMENT 7 - CapistranoDocument2 pagesASSIGNMENT 7 - CapistranoAnne Milanes CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 5PRECIOUS JOY PATIGDASNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document21 pagesUnit 2Himanshu DarganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Consumer BehaviorDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Consumer BehaviorYUSRA ANSARNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Learning MaterialDocument6 pagesWeek 5 Learning MaterialFatema ZehraNo ratings yet
- Competitive Forces - Collaboration or Differentiation: Instead of Viewing Competitors Solely AsDocument6 pagesCompetitive Forces - Collaboration or Differentiation: Instead of Viewing Competitors Solely Ashabibul basherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 Review Notes MGN 2210Document8 pagesChapter 1-3 Review Notes MGN 2210KaiNo ratings yet
- Discussion Questions - Marketing PrinciplesDocument5 pagesDiscussion Questions - Marketing PrinciplesNguyễnVũHoàngTấnNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument22 pagesConsumer BehaviordishankNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Business OrganisationDocument26 pagesFoundations of Business OrganisationNikolas WidjayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Segmentation-1Document10 pagesChapter Four Segmentation-1Ebisa HailuNo ratings yet
- 131 Marketing Final Exam ReviewDocument35 pages131 Marketing Final Exam ReviewBrendan StevensonNo ratings yet
- Banking TermDocument36 pagesBanking Termarpitpra1994No ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING - Unit 2 STPDocument78 pagesPRINCIPLES OF MARKETING - Unit 2 STPaddityarajNo ratings yet
- MM Short MaterialDocument24 pagesMM Short MaterialThippana GomathiNo ratings yet
- Coke STP Steps-By RobintbgDocument9 pagesCoke STP Steps-By Robintbgintel0000No ratings yet
- SegmentationDocument34 pagesSegmentationDevilNo ratings yet
- Advertizing Mid NoteDocument11 pagesAdvertizing Mid NoteNikNituNo ratings yet
- Marketing ProjectDocument38 pagesMarketing ProjectVidya GNo ratings yet
- Mark 1115 Final Short 1Document9 pagesMark 1115 Final Short 1raymondNo ratings yet
- 2) SegmentationDocument46 pages2) SegmentationSugandhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-2Document5 pagesUnit 3-2Brian MulengaNo ratings yet
- The Below Figure Depicts The STP Process For A Skincare ProductDocument35 pagesThe Below Figure Depicts The STP Process For A Skincare Productshubham kumarNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument7 pagesConsumer BehaviourLiv DNo ratings yet
- Profile The Market NewDocument10 pagesProfile The Market Newdenekedarchu358No ratings yet
- Im Unit 3Document10 pagesIm Unit 3Ankush TyagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Nedzma HrvatNo ratings yet
- Schiffman cb11 Im02Document23 pagesSchiffman cb11 Im02Perihan SalahNo ratings yet
- Bachelor in Business Administration Semester 3: Prepared For: Lecturer's NameDocument11 pagesBachelor in Business Administration Semester 3: Prepared For: Lecturer's NameBrute1989No ratings yet
- Marketing Mastery: Strategies for Building and Sustaining a Strong Customer BaseFrom EverandMarketing Mastery: Strategies for Building and Sustaining a Strong Customer BaseNo ratings yet
- Unit TwoDocument20 pagesUnit TwoTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 & 2Document12 pagesChapter 1 & 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Lnternational Trade - Chapt 3,4,5,6,7Document23 pagesLnternational Trade - Chapt 3,4,5,6,7Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document9 pagesCH 4Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument31 pagesChapter OneTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Entrepreneurship MGMT 3101Document5 pagesAssignment of Entrepreneurship MGMT 3101Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Paragraph On Campus LifeDocument1 pageParagraph On Campus LifeTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- BiogeographyDocument61 pagesBiogeographyTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Module 1Document80 pagesEntrepreneurship Module 1Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Importance of Forest Development in EthiopiaDocument5 pagesImportance of Forest Development in EthiopiaTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Env Et CH 1-2Document33 pagesEnv Et CH 1-2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Social and Economic Factors Affecting Forest Development in EthiopiaDocument5 pagesSocial and Economic Factors Affecting Forest Development in EthiopiaTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document9 pagesCH 3Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document34 pagesChapter 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document12 pagesChapter 5Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document17 pagesChapter 1Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Forest Development in EthiopiaDocument5 pagesApproaches To Forest Development in EthiopiaTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document47 pagesUnit 1Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Histiry Assignment - C-WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesHistiry Assignment - C-WPS OfficeTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Document .1234Document20 pagesDocument .1234Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document44 pagesUnit 3Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document56 pagesUnit 2Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Assignment of history-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesAssignment of history-WPS OfficeTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Module of Subject Area MethodDocument54 pagesModule of Subject Area MethodTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Enter ch-1 NewDocument19 pagesEnter ch-1 NewTasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document50 pagesUnit 4Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document15 pagesUnit 4Tasebe GetachewNo ratings yet
- THESIS Ni An-AnDocument27 pagesTHESIS Ni An-AnAko Intawn C OrlyNo ratings yet
- KWP - Staying Grounded Staying Close To Your On The Go Basics IndonesiaDocument16 pagesKWP - Staying Grounded Staying Close To Your On The Go Basics IndonesiaNerissa AngelinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Personality, Attitudes, and Work BehaviorsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Personality, Attitudes, and Work BehaviorsJUN GERONANo ratings yet
- Kuis SPM - Sebelum UtsDocument30 pagesKuis SPM - Sebelum Utsirina shaykNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence-Case Study PDFDocument20 pagesEmotional Intelligence-Case Study PDFSaddam AwanNo ratings yet
- Chap 9 AnswerDocument4 pagesChap 9 AnswerNancy VõNo ratings yet
- Performence Appraisal For PracticeDocument18 pagesPerformence Appraisal For PracticeAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Influence Processes and LeadershipDocument30 pagesInfluence Processes and LeadershipMohiuddin GaalibNo ratings yet
- VIII. Organizational Structure, Culture and DevelopmentDocument37 pagesVIII. Organizational Structure, Culture and DevelopmentAngelNo ratings yet
- Mod.1 L.1,2,3Document25 pagesMod.1 L.1,2,3Aries SungaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Implications For Marketing Strategy 7th Edition Quester Test BankDocument31 pagesConsumer Behaviour Implications For Marketing Strategy 7th Edition Quester Test Bankselinajacob7nhlfu100% (32)
- Consumer Behavior Towards The New Packaging of FMCG ProductsDocument14 pagesConsumer Behavior Towards The New Packaging of FMCG Products21PBA249 NAVANEEN KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Reflection Report 10 Tutorial 9.2 PM-T123PWB-1 Group 4Document9 pagesReflection Report 10 Tutorial 9.2 PM-T123PWB-1 Group 4Khánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Report Writing and Behavioral ObservationDocument23 pagesReport Writing and Behavioral ObservationFUN FLARE SHADOWNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Final Assignment Jake DowsettDocument7 pagesAssignment 3 Final Assignment Jake Dowsettapi-321376162No ratings yet
- AmanDocument50 pagesAmanGAURAVNo ratings yet
- Complaint ManagementDocument22 pagesComplaint Managementvijendra chanda33% (3)
- What We Know About Effects of Sport and Elite Athletics On Child Development OutcomesDocument82 pagesWhat We Know About Effects of Sport and Elite Athletics On Child Development Outcomesandreea_zgrNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Consumer Buying BehaviorDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Consumer Buying BehaviorFlorbert Caldito Cimatu100% (1)
- Customer Loyalty and Customer Loyalty ProgramsDocument37 pagesCustomer Loyalty and Customer Loyalty ProgramsMeena SivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Antonina N. Agata Mba 2017Document91 pagesAntonina N. Agata Mba 2017Welfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorDocument13 pagesConsumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorBë Ň TőngNo ratings yet
- Handout File - EDU302 Lecture 1-10 (Topics1-35)Document21 pagesHandout File - EDU302 Lecture 1-10 (Topics1-35)Muqaddas ijaz -25No ratings yet
- Consumer Buying BehaviourDocument35 pagesConsumer Buying BehaviourDeeksha SinghNo ratings yet
- OB - CPJ NotesDocument120 pagesOB - CPJ NotesTrisha AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 FinalDocument22 pagesChapter 2 FinalariaNo ratings yet
- The Developmental-Health Framework Within The McGill Model of NursingDocument15 pagesThe Developmental-Health Framework Within The McGill Model of NursingFerdy LainsamputtyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Rebecca Jones 1Document11 pagesCase Study - Rebecca Jones 1api-465726569No ratings yet