Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Factoring Checklist
Factoring Checklist
Uploaded by
juanespro444Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Factoring Checklist
Factoring Checklist
Uploaded by
juanespro444Copyright:
Available Formats
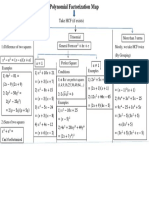
Follow these steps in order to factor any equation or expression.
1. Check for the Greatest Common Factor, Common Binomials or Factor by Grouping.
Examples
a) 5𝑥 2 + 35𝑥 b) 3(𝑥 + 2) − 5𝑥(𝑥 + 2) c) 𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 + 3𝑎𝑥 + 12𝑎
= 5𝑥(𝑥 + 7) = (𝑥 + 2)(3 − 5𝑥) = (𝑥 2 + 4𝑥) + (3𝑎𝑥 + 12𝑎)
= 𝑥(𝑥 + 4) + 3𝑎(𝑥 + 4)
= (𝑥 + 4)(𝑥 + 3𝑎)
2. Check for Perfect Square Trinomials or Difference of Squares Patterns.
Examples
a) 4𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 + 1 b) 𝑥 2 − 10𝑥 + 25 c) 9𝑥 2 − 49
= (2𝑥 + 1)2 = (𝑥 − 5)2 = (3𝑥 − 7)(3𝑥 + 7)
Based on the pattern: Based on the pattern: Based on the pattern:
𝑎2 + 2𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 = (𝑎 + 𝑏)2 2 2
𝑎 − 2𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 = (𝑎 − 𝑏) 2 𝑎2 − 𝑏 2 = (𝑎 − 𝑏)(𝑎 + 𝑏)
3. Use product and sum factoring. There are two options here. It depends if the
coefficient of the squared term is 1 or not. “Cross multiplication” is an alternative here.
If 𝑎 = 1 in 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐, then use product If 𝑎 ≠ 1 in 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐, then use the product
of c and sum of b. of ac and sum of b.
Example Example
𝑥 2 + 7𝑥 + 10 2𝑥 2 − 7𝑥 − 4 (product of -8 and sum of -7)
= (𝑥 + 5)(𝑥 + 2) = 2𝑥 2 − 8𝑥 + 𝑥 − 4
= (2𝑥 2 − 8𝑥) + (𝑥 − 4)
5 and 2 are used since the product of 5 and = 2𝑥(𝑥 − 4) + 1(𝑥 − 4)
2 is 10 and the sum of 5 and 2 is 7. = (𝑥 − 4)(2𝑥 + 1)
-8 and 1 are used to decompose the middle
term and then factor by grouping is used.
You might also like
- Mathematics: Chapter # 5 Factorization Class 9TH (KPK)Document13 pagesMathematics: Chapter # 5 Factorization Class 9TH (KPK)ShEzzZyNo ratings yet
- Multiplication of PolynomialsDocument6 pagesMultiplication of PolynomialsAngel AsisNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Factorization MapDocument1 pagePolynomial Factorization MapWael M. YousefNo ratings yet
- General Differentiation Formula 1. Derivative of A Constant ( ) 0Document10 pagesGeneral Differentiation Formula 1. Derivative of A Constant ( ) 0anon_422073337No ratings yet
- Week 10-11 - CalcDocument5 pagesWeek 10-11 - CalcFlorenceNo ratings yet
- Manipulating Algebraic ExpressionsDocument4 pagesManipulating Algebraic ExpressionsRaajdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths Chap 8 WsDocument3 pages8 Maths Chap 8 Wsheersurti312No ratings yet
- LESSON 8.1:: Rizal National Science High SchoolDocument18 pagesLESSON 8.1:: Rizal National Science High Schooltrisha paclebNo ratings yet
- Review For Prelim in BascalDocument12 pagesReview For Prelim in Bascaljoreza.diazNo ratings yet
- Module 0a. Review On Special ProductsDocument19 pagesModule 0a. Review On Special ProductsKarla YasaNo ratings yet
- ChristianDocument7 pagesChristianJohnny JanulgueNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Solutions - Algebra, Equations and Inequalities - 2020-2Document9 pagesWorksheet Solutions - Algebra, Equations and Inequalities - 2020-2Shinyi GohNo ratings yet
- MethodsDocument3 pagesMethodsbrosreaperNo ratings yet
- Learning Concepts and Activities: Page - 1Document5 pagesLearning Concepts and Activities: Page - 1RexTheKingNo ratings yet
- Operations On Functions GMDocument17 pagesOperations On Functions GMCheryl WooNo ratings yet
- DerivatesDocument2 pagesDerivatesWaseer Ahmed BadshaNo ratings yet
- Indeks Dan Log EditedDocument6 pagesIndeks Dan Log EditedSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Matematik Tambahan: Modul Mas (Minimum Adequate Syllabus) SPM 2019Document37 pagesMatematik Tambahan: Modul Mas (Minimum Adequate Syllabus) SPM 2019Jinny NeutrollNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Solving Equations Module Review SolutionsDocument6 pagesFactoring and Solving Equations Module Review SolutionsElaine zhuNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Math Notes PDF Download Chapther 5Document11 pages9th Class Math Notes PDF Download Chapther 5Owi ShahNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Partial DerivativesDocument12 pages2.2 Partial Derivativesshamarplummer0923No ratings yet
- Unit 14 Binomial Theorem and ProgressionDocument9 pagesUnit 14 Binomial Theorem and ProgressionLouis KapesoNo ratings yet
- 3 Compute The Antiderivative of A Function Using Substitution Rule PolynomialDocument3 pages3 Compute The Antiderivative of A Function Using Substitution Rule PolynomialJenrich MarceloNo ratings yet
- Derivative Handout 2021 GR 11engineeringDocument14 pagesDerivative Handout 2021 GR 11engineeringDevin Jonathan ThedyNo ratings yet
- Zeros of A Polynomial (Part 2)Document1 pageZeros of A Polynomial (Part 2)ayushishruti0209No ratings yet
- Integral 1: Usaha Tidak Pernah Mengkhianati Hasil. Semangat Belajar Di Sekolah Kita!Document1 pageIntegral 1: Usaha Tidak Pernah Mengkhianati Hasil. Semangat Belajar Di Sekolah Kita!HaniNo ratings yet
- 16 - 2 - Special Products. Factoring (M45)Document4 pages16 - 2 - Special Products. Factoring (M45)fady takiNo ratings yet
- Aler Chari:-Exas: Expansion StepsDocument10 pagesAler Chari:-Exas: Expansion StepsAhmed sengabNo ratings yet
- Soal CCM MTK 2017Document7 pagesSoal CCM MTK 2017MarfiNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocument8 pagesAlgebraic ExpressionssethNo ratings yet
- DerivadasDocument4 pagesDerivadasDiogo LimonesNo ratings yet
- ADDMA G12 2020 SOLUTIONS Paper 1Document9 pagesADDMA G12 2020 SOLUTIONS Paper 1siamejachabota41No ratings yet
- Sim Cee 100 Week 1 9 Unit1Document30 pagesSim Cee 100 Week 1 9 Unit1Lance Kristoffer Lamera LewisNo ratings yet
- TL201 - TMS3725 Assignment 03 2022 - PDFDocument14 pagesTL201 - TMS3725 Assignment 03 2022 - PDFMbiselo TshabadiraNo ratings yet
- 2022 TEST 2 SOLUTION INTEGRATION (PURE MATHEMATICS) ShareDocument7 pages2022 TEST 2 SOLUTION INTEGRATION (PURE MATHEMATICS) SharenomoszengNo ratings yet
- Topical Guidance of SPM MathematicsDocument39 pagesTopical Guidance of SPM MathematicsSEOW INN LEENo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 10 Term 1 Week 2 - 2021Document8 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Term 1 Week 2 - 2021martinajoan1No ratings yet
- Simultaneous EquationDocument1 pageSimultaneous EquationErlina DwiNo ratings yet
- Section R.6 FactoringDocument32 pagesSection R.6 Factoringوصايف النهديNo ratings yet
- (Practice) Unit 1 Mod 1 Sba Test 2019-20 (Solutions)Document5 pages(Practice) Unit 1 Mod 1 Sba Test 2019-20 (Solutions)Aaliyah WilsonNo ratings yet
- Cee 100 Week 1-3 UloaDocument29 pagesCee 100 Week 1-3 UloaAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Assignment IPL (Itc)Document2 pagesAssignment IPL (Itc)Anjali SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chennai Public School: Chapter-5 Algebraic Expressions and Special ProductsDocument4 pagesChennai Public School: Chapter-5 Algebraic Expressions and Special ProductsAbishek ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Calculo Diferencial Actividad 3. Derivación de Orden Superior e Implícita Héctor Paniagua Flores ES172011207 LT-LCDI-1902-B1-002Document6 pagesCalculo Diferencial Actividad 3. Derivación de Orden Superior e Implícita Héctor Paniagua Flores ES172011207 LT-LCDI-1902-B1-002hectorNo ratings yet
- DDP - Solutions - JEE ADVANCED - Quadratic & ComplexDocument7 pagesDDP - Solutions - JEE ADVANCED - Quadratic & ComplexArtisticNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (MATH11B)Document19 pagesChapter 3 (MATH11B)Ma. Woodelyn ReyesNo ratings yet
- Special Products and FactoringDocument25 pagesSpecial Products and FactoringjessicaNo ratings yet
- Math8 Quarter1 Week2 Module2Document6 pagesMath8 Quarter1 Week2 Module2HannaNo ratings yet
- G10 FactoringDocument33 pagesG10 FactoringmiwoocyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Differentiation RulesDocument10 pagesBasic Differentiation RulesJunelle Christian ObiceNo ratings yet
- PptsDocument88 pagesPptsXavNo ratings yet
- DerivadasfuncionesDocument12 pagesDerivadasfuncionesjdmontes13No ratings yet
- FACTORISATIONDocument10 pagesFACTORISATIONPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Indices and LogDocument4 pagesIndices and LogLim You ShengNo ratings yet
- Modul GMAT T4 JawapanDocument100 pagesModul GMAT T4 Jawapan卓财天No ratings yet
- Class 21 - Limits and Continuity - 15.03.2021Document16 pagesClass 21 - Limits and Continuity - 15.03.2021johnathanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Derivative of A FunctionDocument3 pagesLesson 3 Derivative of A FunctionJunior LifeNo ratings yet
- Y8 Skills Sheet 4 Algebra Brackets and FormulaeDocument2 pagesY8 Skills Sheet 4 Algebra Brackets and FormulaeJohn LeeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet