Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood and Its Functions
Blood and Its Functions
Uploaded by
divyavdivya680 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesThanks
Original Title
blood and its functions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThanks
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesBlood and Its Functions
Blood and Its Functions
Uploaded by
divyavdivya68Thanks
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 16
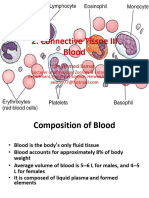
Human Blood
Blood
Main circulatory medium in the human
body
It is a red coloured.
Fluid connective tissue
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited 03/16
Components of Blood
Fluid - plasma Formed elements (blood
cells)
• It is slightly alkaline • Red blood corpuscles
Non-cellular substance (RBC) or Erythrocytes
• 55% of the blood • White blood corpuscles
• Organic substances like (WBC) or Leucocytes
proteins, glucose, urea, • Blood platelets or
enzymes, hormones, Thrombocytes
vitamins and minerals are
present
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited 04/16
Formed Elements of Blood
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited 06/16
Red Blood Corpuscles (Erythrocytes)
Most abundant cells in the human body
Formed in the bone marrow
Red colour due to the presence of
respiratory pigment haemoglobin.
Matured mammalian RBCs do not have cell
organelles and nucleus.
Biconcave and disc-shaped
Life span - 120 days
Transport of oxygen from lungs to tissues
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited 07/16
White Blood Corpuscles (Leucocytes)
Colourless
Absent of haemoglobin
Nucleated cells
Found in the bone marrow, spleen,
thymus and lymph nodes
Amoeboid movement & shape
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited 09/16
WBC’s Two Categories
Granulocytes Agranulocytes
•Neutrophils •Lymphocytes
•Eosinophils •Monocytes
•Basophils
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited 10/16
Neutrophils Eosinophils Basophils Lymphocytes Monocytes
• Large in size • Bilobed nucleus • Lobed nucleus • 20 % - 25% of • Largest of the
• 2-7 lobed • 2%-3% of the • 0.5 % - 1.0% of the total leucocytes
nucleus total leucocytes the total leucocytes • Amoeboid shape
• 60%-65% of the • Allergy and leucocytes • Produce • 5 % - 6 % of the
total leucocytes parasitic • Release antibodies total leucocytes
• Infection and infections chemicals during during bacterial • Phagocytic and
inflammation inflammation and viral can engulf
infections bacteria
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited 12/16
Blood Platelets or Thrombocytes
Small and colourless
Absent of nucleus
2,50,000 - 4,00,000 platelets/cubic mm
of blood
Life span: 8 - 10 days
Blood clotting
Prevent blood loss
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited 15/16
Functions of Blood
Protection of the body and defense against
diseases
It helps in regulation of pH and body
temperature.
It maintains proper water balance in the
body.
Transport of respiratory gases ,digested food
materials to the different body cells,
hormones,nitrogenous excretory products
like ammonia, urea and uric acid.
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited 04/13
QUESTION
1. Blood clot is formed because of
a. lymphocytes
b. erythrocytes
c. chondrocytes
d. platelets
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited
Which part of the body is responsible for the red blood cells?
(a) Lungs
(b) Heart
(c) Brain
(d) Bone Marrow
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited
Who performs the task of capturing oxygen in the blood?
a. Red blood cells
b. Chlorophyll
c. White blood cells
d. Haemoglobin
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited
Which of the following is NOT a type of blood cell made by the bone marrow?
a. Osteoclasts
b. Red blood cells
c. Platelets
d. White blood cells
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited
Which cells in our body are popularly called "soldiers of the human body"?
a. Eosinophils
b. White blood cells
c. Red blood cells
d. Basophils
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited
THANK YOU!
Copyright © Veranda Learning Solutions Private Limited
You might also like
- Germ Cell Final PPT Dev. BioDocument26 pagesGerm Cell Final PPT Dev. BioSales Him IT ServicesNo ratings yet
- For PH NewDocument295 pagesFor PH Newbethlehematnafu38No ratings yet
- Connective Tissue III BloodDocument18 pagesConnective Tissue III Bloodmanoelsha3No ratings yet
- BloodDocument17 pagesBloodfatimamuzammil406No ratings yet
- LEC1Hematology IntroDocument26 pagesLEC1Hematology Introismailmoh4455No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-11 at 3.53.36 PMDocument62 pagesScreenshot 2023-12-11 at 3.53.36 PMahmedmansi055No ratings yet
- 12=Blood STDs TS (1)Document53 pages12=Blood STDs TS (1)myruawanNo ratings yet
- DR Arif Chowdhury Apou, MBBS, DuDocument13 pagesDR Arif Chowdhury Apou, MBBS, DuMuntasirNo ratings yet
- Blood Part 1Document35 pagesBlood Part 1Keziah TampusNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument76 pagesBloodKerby Dela Fuente Alison100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology II: Topic: Anatomy of The Blood Sub Topic: Introduction To Blood and Its CompositionsDocument28 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology II: Topic: Anatomy of The Blood Sub Topic: Introduction To Blood and Its Compositionsngong ngong ametNo ratings yet
- Hematology 2020Document63 pagesHematology 2020odiodi57No ratings yet
- The Blood: Overview of Blood CirculationDocument14 pagesThe Blood: Overview of Blood CirculationHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Clinical Haematology - 4th EdDocument109 pagesClinical Haematology - 4th EdBlitzen BusaingNo ratings yet
- Power Point Week #7Document141 pagesPower Point Week #7Raelene MarceauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Blood Coagulation and Coagulation DisordersDocument27 pagesChapter 4 Blood Coagulation and Coagulation DisordersdaisysintszwaiNo ratings yet
- Blood: Raeesa Sattar Faculty of Allied Health SciencesDocument25 pagesBlood: Raeesa Sattar Faculty of Allied Health SciencesNAMRA RASHEEDNo ratings yet
- Blood LectureDocument76 pagesBlood LecturedoyinsolaolusanyaNo ratings yet
- L15 - Blood - CMDocument32 pagesL15 - Blood - CMAleandra LettNo ratings yet
- 1 BloodDocument77 pages1 BloodVisaNathan100% (1)
- Lecture 2-Blood RBC WBCDocument51 pagesLecture 2-Blood RBC WBCsamayaNo ratings yet
- Blood and Its FunctionsDocument47 pagesBlood and Its FunctionsMatende husseinNo ratings yet
- KRV, PLAZMA, HEMATOPOEZADocument35 pagesKRV, PLAZMA, HEMATOPOEZASinisa RisticNo ratings yet
- Haemopoiesis: Composition of Whole Blood & Its ComponentsDocument8 pagesHaemopoiesis: Composition of Whole Blood & Its ComponentsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Blood Components and Their Function: BIS, Grade 8, BiologyDocument24 pagesBlood Components and Their Function: BIS, Grade 8, BiologyUsername18No ratings yet
- 1 BloodDocument31 pages1 BloodSuchana AcNo ratings yet
- Sgyyzzjct - Chapter 10 - Blood & ImmunityDocument93 pagesSgyyzzjct - Chapter 10 - Blood & Immunitymaikie.ramos29No ratings yet
- Forensic Serology and DNA-1-mergedDocument205 pagesForensic Serology and DNA-1-mergedNandini SinghNo ratings yet
- Blood: Group 1Document25 pagesBlood: Group 1Arian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 CVSDocument118 pagesLecture 9 CVSMuhammad Abbas WaliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24 Physiology-4 6Document11 pagesLecture 24 Physiology-4 6MartinoKhanzaniaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of BLOOD: Preet KaurDocument37 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of BLOOD: Preet KaurPreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Circulatory systemDocument36 pagesCirculatory systemAgriye KambojNo ratings yet
- IntroductionintroductionDocument29 pagesIntroductionintroductionkikaramparmar7408No ratings yet
- Blood 2022Document49 pagesBlood 2022Fady FadyNo ratings yet
- Blood: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument63 pagesBlood: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical Collegedomo domoNo ratings yet
- 2 CVS BloodDocument26 pages2 CVS BloodSepo CaciousNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument28 pagesBloodIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Physio. D. Suroor. L1. BloodDocument24 pagesPhysio. D. Suroor. L1. Bloodزين العابدين محمد عويشNo ratings yet
- 01 Innate Immunity Student File1 2Document80 pages01 Innate Immunity Student File1 2Khadijah AsrarNo ratings yet
- دم عمليDocument35 pagesدم عمليsuad aliNo ratings yet
- HemaDocument20 pagesHemaFlora Angeli PastoresNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument12 pagesBLOODRinalyn BalderramaNo ratings yet
- The BloodDocument24 pagesThe BloodKicki AnderssonNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument46 pagesBloodFarah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- Blood and Body Fluids: PHGY 221 MON 2-5PM Badejogbin O. CarolineDocument23 pagesBlood and Body Fluids: PHGY 221 MON 2-5PM Badejogbin O. CarolineFeranmi AdekunleNo ratings yet
- Blood Physio Formed Tech 2024Document80 pagesBlood Physio Formed Tech 2024Joshua BucioNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Blood PhysiologyDocument91 pagesChapter Five: Blood PhysiologyjarssooNo ratings yet
- TransportationDocument58 pagesTransportatione-SayutiNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument37 pagesBLOODelliot kafumukacheNo ratings yet
- 9 Anatomy 2021 BloodDocument32 pages9 Anatomy 2021 BloodDanica DaniotNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionVikraman ThamotharanNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology 2022Document116 pagesBlood Physiology 2022Gurmessa FekaduNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy Physiology HandoutsDocument6 pagesBlood Anatomy Physiology HandoutsKids JangNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Blood RIT MLT OTTDocument39 pagesPhysiology of Blood RIT MLT OTTmubeenkashif224No ratings yet
- Composition of Blood and Cellular Elements: Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesComposition of Blood and Cellular Elements: Learning Objectivesmarinak_6No ratings yet
- Heamatology Chapter 1Document38 pagesHeamatology Chapter 1Taima'a AlamaratNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Medicine Terminology: Unlocking the Language of Laboratory MedicineFrom EverandLaboratory Medicine Terminology: Unlocking the Language of Laboratory MedicineNo ratings yet
- Shabnam 3Document174 pagesShabnam 3DrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- CBC EsrDocument1 pageCBC EsrIqtiar IslamNo ratings yet
- Blood: 1. Medullary Cavities of Long Bones 2. Spongiosa of Vertebral Bodies, Ribs, Sternum 3. Flat Bones of The PelvisDocument2 pagesBlood: 1. Medullary Cavities of Long Bones 2. Spongiosa of Vertebral Bodies, Ribs, Sternum 3. Flat Bones of The PelvisKrizza Mariz Bautista PolaronNo ratings yet
- 1 - Cells and Tissues of The Immune SystemDocument32 pages1 - Cells and Tissues of The Immune SystemCaitríona BurkeNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells TherapyDocument2 pagesStem Cells TherapyAhmad KHNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument7 pagesStem CellsPrasant NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Cell Differentiation Exercises 10.4Document4 pagesCell Differentiation Exercises 10.4Sanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis, by Definition, Is The Development of Mature Haploid Gametes From Either HaploidDocument5 pagesGametogenesis, by Definition, Is The Development of Mature Haploid Gametes From Either HaploidAlvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasikan Berdasarkan Asalnya Stem CellDocument2 pagesKlasifikasikan Berdasarkan Asalnya Stem CellfathinanisaNo ratings yet
- Netters Essential Histology With Student Consult Access 2nd Edition Ovalle Test BankDocument35 pagesNetters Essential Histology With Student Consult Access 2nd Edition Ovalle Test Bankjacobnigordon100% (17)
- HaemopoiesisDocument35 pagesHaemopoiesisNeshya HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Chapter 33Document16 pagesChapter 33Shfici AdanNo ratings yet
- U804173 Id No: Haematology ReportDocument1 pageU804173 Id No: Haematology ReportTB AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hema Normal ValuesDocument2 pagesHema Normal ValuesKobe Brian Franco PeterosNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow: Andy Mclarnon, University of Birmingham, UkDocument2 pagesBone Marrow: Andy Mclarnon, University of Birmingham, Uknavita guptaNo ratings yet
- HematopoiesisDocument3 pagesHematopoiesisVino OrajayNo ratings yet
- Conflict of Interest List CIRM Directors Quest Awards June 2017Document2 pagesConflict of Interest List CIRM Directors Quest Awards June 2017California Stem Cell ReportNo ratings yet
- Megakaryopoiesis: and ThrombopoiesisDocument2 pagesMegakaryopoiesis: and ThrombopoiesisIberisNo ratings yet
- Hema 1-Module 2 - Topic 2-Answer SheetDocument3 pagesHema 1-Module 2 - Topic 2-Answer SheetKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Periodontal RegenerationDocument8 pagesMesenchymal Stem Cells and Periodontal Regenerationkishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Immunologykaiyeol exoNo ratings yet
- 02 HematopoiesisDocument61 pages02 HematopoiesisDingdongLopezNo ratings yet
- Hematology: PathologyDocument1 pageHematology: PathologyEEC PakistanNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Oligodendrocytes and Schwann CellsDocument5 pagesDifference Between Oligodendrocytes and Schwann CellsSaad HasanNo ratings yet
- CitologieDocument14 pagesCitologieAlexandra CrisanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Penting Mesenchymal Stem Cell 3Document19 pagesJurnal Penting Mesenchymal Stem Cell 3Adniana NareswariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Lesson 0Document17 pagesUnit 2 Lesson 0Apoorva JainNo ratings yet
- GROUP 9 STS Research Term Paper On Stem CellDocument13 pagesGROUP 9 STS Research Term Paper On Stem Cellintroverted bossNo ratings yet