Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Answersheet 4th Quarter Week 1
Physics Answersheet 4th Quarter Week 1
Uploaded by
NymphaNarvasaDecasaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Answersheet 4th Quarter Week 1
Physics Answersheet 4th Quarter Week 1
Uploaded by
NymphaNarvasaDecasaCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Answersheet (4th Quarter 1st week) Guide Questions:
NAME: ______________________________________ 1. The object’s distance (increases, decreases,
remains constant) as it travels downward.
MELC 34: Describe the horizontal and vertical motions of 2. The velocity of the ball is ( 0m/s, 9.8m/s , 19.6
projectile S9FE-IVa-34 m/s) before it is dropped.
3. The stone’s velocity is (9.8m/s , 19.6 m/s , 39.2m/s ,
Speed Velocity Displacement Distance 49.0m/s)
Acceleration Time Force 4.The change in the stone’s velocity every second is (0m/s
9.8m/s, 19.6m/s , 39.2m/s)
Quick Recall (page 1) 5. Objects thrown upward or dropped always fall back to the
1._____________ 2.______________3.________________ ground at a constant (displacement, velocity, acceleration)
4._____________ 5.______________ which has a magnitude of (0m/s2 , 9.8m/s, 9.8m/s2) due to
DIRECTION: (Encircle the correct answer from the choices (force, air resistance, gravity).
inside the parenthesis.) Lesson 2 Projectile Motion
Lesson 1 Uniformly Accelerated Motion Activity 3 Are you a Projectile? (page 3)
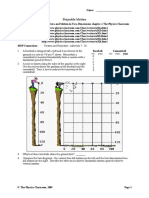
Activity 1: Object in Motion: Horizontal Dimension (page1)
I. Write the letter on the blank space provided. Refer to the
pictures in Activity 3. _____, _____, _____
II.
Projectile Motion Non-projectile Motion
e.g A VOLLEY BALL BEING SERVED CAR RACING
Encircle the correct answer from the choices inside the
parenthesis.
1. The velocity of the ball (increases, decreases, remains
constant) as it rolls down the inclined plane.
2.The change in velocity in every second is (2m/s, 4m/s,
6m/s, 8m/s) Activity 4 Horizontally Launched Cannonball (page 4)
3.The ball (accelerates, does not accelerate) Guide questions:
4. The ball accelerates at (0m/s2 , 2m/s2 , 4m/s2 , 6m/s2) 1. Initial Vertical Velocity (Vy) (0m/s, 9.8m/s, 20m/s)
5. . If a body maintains a constant change in (displacement, Initial Horizontal Velocity (Vx) (0m/s, 9.8m/s, 20m/s)
velocity, acceleration) a given time interval along a straight
2. Horizontal Velocity (Vx) (increases, decreases,
line, then the body is said to have a uniform (displacement,
velocity, acceleration). remains constant)
Vertical Velocity (Vy) (increases, decreases,
Activity 2 Object in Motion:Vertical Dimension (page 2) remains constant)
Encircle the correct answer from the choices inside the 3. The cannon ball accelerates as it moves
parenthesis. (horizontally, vertically, diagonally).
4. The cannon ball follows a (curve, parabolic,
hyperbolic) path.
Activity 5: Vertically Launched Ball (page 5) Answer the questions below.
1. As it moves upward the, 1.Based on the table, what is the initial velocity of the
(Vx) (increases, decreases, remains constant) cannonball launched at different angles? (0m/s, 10m/s,
(Vy) (increases, decreases, remains constant) 20m/s)
2. (Vx) (0m/s, 9.8m/s, 12m/s) at maximum height 2. At what angle the cannonball is launched, covered the
(Vy) (0m/s, 9.8m/s, 12m/s) at maximum height greatest range? (15˚, 45˚, 60˚)
3. From the highest point to the ground the 3.At what angle the cannonball is launched has the highest
(Vx) (increases, decreases, remains constant) maximum height reached? (30˚, 60˚, 75 ˚)
(Vy) (increases, decreases, remains constant) 4.Which pair of angles have equal or the same range?
4. Encircle 2 from the given choices (A&B, B&D, A&E, (15 ˚ &75˚, 30˚ &60˚, 15˚ &60 ˚)
C&E) 5. At what launching angle the cannonball travels the
5. The balls accelerates along its (horizontal motion, fastest? (15 degrees, 45 degrees, 75 degrees)
vertical motion).
6. The ball follows a (curve, parabolic, hyperbolic) Activity 1 Picture Analysis (page7)
path.
EVALUATION: TRUE OR FALSE (page 5)
1._________ 2._________ 3._________ 4._________
5._________ 6._________ 7._________ 8._________
9.__________ 10.________
MELC 35: Investigate the relationship between the angle of
release and the height and the range of projectile S9FE-IVa- 1. The monkey is trying to jump on the branch of
35 another tree with an angle of 38 degrees. If the
angle is changed with the same initial velocity of
Activiy 2 Graphical Analysis: Relationship between height, 10 m/s, at what angle will the monkey have to
angle of inclination, and range (page. 7) jump to land on the same spot? (NOTE:please
disregard the given situation for number 1 on page
7) Answer the given situation.
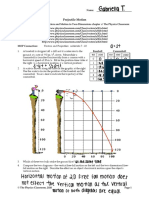
The cannonball is launched at different angles with the same ________________________________________
initial velocity. (Refer to the figure 3 and table 1 on page 7) 2. Give 2 ways on how to increase the horizontal
NOTE: Please disregard the guide questions on page 7 distance or range covered when the ball is kicked.
________________________________________
________________________________________
EVALUATION: Fill in the blanks (page 8)
initial velocity angle of inclination increases
decreases inversely proportional height
1._______________ 2._____________ 3._______________
4._______________ 5._____________ 6._______________
7. ______________
MELC 36 Relate impulse and momentum to collision of Activity 2 Objects in Collision (page 11)
objects (e.g. vehicular collision) S9FE-IVb-36
Situation 1. Car Crash
WORD BOX (page 8) Two cars of the same mass collide. Car A is running faster
F A T I M E R M I than Car B.
O D E M H V G A S a.(Car A, Car B) has greater change in velocity.
R U Z P O E L S T b. (Car A, Car B) has greater change in momentum, (due to
greater velocity, due to mass)
C A L U P T E S X
c. (Car A, Car B) has greater impulse,
E V E L O C I T Y (greater change in momentum, lesser change in momentum)
N O I S I L L O C
d.(lesser, greater) change in momentum
M O M E N T U M N
e. (Car A, Car B) will have greater damage, due to (greater
impulse, lower impulse, lesser change in momentum)
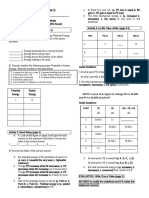
Activity 1 Investigating Momentum (page 9) Situation 2. Pingpong Vs. Basketball
A. a. (pingpong ball, basketball) has lesser momentum
1._____ 2.______ 3.______ b. (pingpong ball, basketball) has greater impulse
4. a. When velocity increases, the momentum (increases,
decreases, remains constant) Situation 3. Two Marbles Colliding
When velocity decreases, the momentum (increases, a. (Marble A , Marble B) has greater momentum
decreases, remains constant)
b. (Marble A , Marble B) has greater impulse
b. When the mass is increased, momentum (increases,
decreases, remains constant) c. (Marble A , Marble B)
When the mass is decreased, momentum (increases,
decreases, remains constant)
EVALUATION (page 11)
c. Object that is not moving/at rest has a momentum that
is (zero, greater than zero, cannot be determined) 1._____ 2.______3.______ 4._______ 5._______
MELC 37 Infer that the total momentum before and after
B. Solve for momentum. Use the equation
(momentum = mass x velocity) collision is equal (e.g. vehicular collision) S9FE-IVb-37
Object Mass Velocity(m/s) Momentum
Activity 1 Car Crash…. (page 13)
(kg) (kg.m/s)
Bird 0.13 18 1.0.13kgX18m/s= 1. (Vehicle A, Vehicle B) is moving fast
e.g. 2.34 (Vehicle A, Vehicle B) is moving slow
Basketball 100 5 2. 2. After collision, the velocity of Vehicle A (increases,
Player decreases) while the velocity of Vehicle B
Buller 0.004 600 3. (increases, decreases)
Use equation (momentum=mass x velocity)
Baseball 0.14 30 4.
3. Before the collision the Momentum of Vehicle A
Frog 0.9 12 5.
(2500kg.m/s, 800 kg.m/s , 3300kg.m/s)
6. (huge truck, small toy cart)
Momentum of Vehicle B
7. (decreased, doubled) (2500 kg.m/s, 800 kg.m/s , 3300 kg.m/s)
8. (greater, lesser)
4. After the collision, the momentum of vehicle A
is (1500kg.m/s , 1800kg.m/s, 3300kg.m/s)
the momentum of Vehicle B is
(1500kg.m/s , 1800kg.m/s, 3300kg.m/s)
5. Total momentum before collision
(1500kg.m/s , 1800kg.m/s, 3300kg.m/s)
6. Total momentum after collision___________kg.m/s
(2500kg.m/s, 800 kg.m/s, 3300kg.m/s)
7. Car A (slows down, speeds up, stops)
Car B (slows down, speeds up, stops)
Total momentum is (reduced, increased, the same)
before the collision
The momentum of the system is (decreased,
increased, conserved)
Activity 2 Colliding differently, conserved similarly
(Momentum) (page 14)
SET A. Elastic Collision
1. In an elastic collision, the momentum before and
after collision is (decreased, increased, conserved)
2. In an elastic collision, the kinetic energy before and
after collision is
(decreased, increased, conserved)
SET B.Inelastic collision
1. In an inelastic collision, the momentum before and
after collision is (decreased, increased, conserved)
3. In an inelastic collision, the kinetic energy in
inelastic collision (the momentum before and after
collision is (decreased, increased, conserved)
EVALUATION: Multiple Choice (page 14)
1.______ 2._____ 3.______ 4.______ 5.______
You might also like
- Student Exploration: Free-Fall LaboratoryDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: Free-Fall LaboratoryVanessa Ramirez56% (16)
- Shoot Monkey FormDocument4 pagesShoot Monkey FormAdam Shuler0% (6)
- Topic Sentences Multiple Choice Questions PDFDocument2 pagesTopic Sentences Multiple Choice Questions PDFLear Zano73% (11)
- IPCRDocument1 pageIPCRTess Legaspi0% (1)
- Projectile Motion: Learning Activity Sheets (LAS)Document6 pagesProjectile Motion: Learning Activity Sheets (LAS)Franz Eugene Almodiente100% (4)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Chess Lesson Plan NewDocument3 pagesChess Lesson Plan NewJhen Mendoza100% (3)
- Module 1 Projectile MotionDocument9 pagesModule 1 Projectile MotionJaen Kieth RociosNo ratings yet
- Science - Grade 9 - Q4 - LP1Document9 pagesScience - Grade 9 - Q4 - LP1Marian GalosoNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesActivity 1 2nd QuarterRicky SerioNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion SEDocument5 pagesUniform Circular Motion SELuka MkrtichyanNo ratings yet
- Generalphysics1 q1 Mod3 Motion-In-Two-Dimensions v1-1Document30 pagesGeneralphysics1 q1 Mod3 Motion-In-Two-Dimensions v1-1Park JiminshiiNo ratings yet
- Physics Projectile Motion NotesDocument6 pagesPhysics Projectile Motion Notessohamdey100% (1)
- PH1011 2018-2019 Semester 2Document35 pagesPH1011 2018-2019 Semester 2Ang YanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE9 Q4 LAS Week1Document8 pagesSCIENCE9 Q4 LAS Week1Jinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Motion II Practice Problems: Regents PhysicsDocument44 pagesUnit 7: Motion II Practice Problems: Regents PhysicsPrincess BarredoNo ratings yet
- CBA Review - KeyDocument7 pagesCBA Review - KeyBredukes2005No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Worksheet For Grade 9-Quarter 4 - Week 2 LessonDocument11 pagesDepartment of Education: Worksheet For Grade 9-Quarter 4 - Week 2 LessonMaribeth Jamero-cusapNo ratings yet
- Bucio - Projectile WS 1Document3 pagesBucio - Projectile WS 1ZhaeNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Grade 11 - Quarter 1 - Week 3 Kinematics: Motion in 1-Dimension and 2 DimensionsDocument12 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Grade 11 - Quarter 1 - Week 3 Kinematics: Motion in 1-Dimension and 2 DimensionsKim CortezNo ratings yet
- 12 Gen. Physics Week 3Document10 pages12 Gen. Physics Week 3Jacqueline Arabis100% (1)
- Las Science 9 Melc 1 q4 Week-1Document4 pagesLas Science 9 Melc 1 q4 Week-1ROVELYN FURATERONo ratings yet
- Teacher Notes and Answers 3 Two-Dimensional Motion and VectorsDocument3 pagesTeacher Notes and Answers 3 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectorsomar ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument8 pagesProjectile Motionapi-336277944No ratings yet
- q1 General Physics Module 4Document13 pagesq1 General Physics Module 4Ciara Adrianne Tiongzon - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - GR 12 Physics - Term 1 2024Document7 pagesAssignment 1 - GR 12 Physics - Term 1 2024jennethpaima0No ratings yet
- q4 g9 Science Las1 Marikina RTPDocument4 pagesq4 g9 Science Las1 Marikina RTPMeyshia Vixen LavalleNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: General Physics 1Document5 pagesDepartment of Education: General Physics 1Kerwin MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Test Turing Jobs Outcome MeasurementDocument6 pagesTest Turing Jobs Outcome MeasurementWassila AlouacheNo ratings yet
- Distance (M) Time of Travel (Sec) Average Time (Sec) Trial - 1 Trial - 2 Trial - 3Document3 pagesDistance (M) Time of Travel (Sec) Average Time (Sec) Trial - 1 Trial - 2 Trial - 3Ricky SerioNo ratings yet
- Physics 3Document6 pagesPhysics 3Iah VergaraNo ratings yet
- PHY107 SP23 Practice Final ExamDocument10 pagesPHY107 SP23 Practice Final Exammaichi5145No ratings yet
- Science THT Paper 2 - Sec2Document7 pagesScience THT Paper 2 - Sec2RathnaNo ratings yet
- ACT. SHEETS SCIENCE 9 4TH QTR W1 3Document5 pagesACT. SHEETS SCIENCE 9 4TH QTR W1 3mareng aryanNo ratings yet
- Momentum and Impulse ReadingDocument7 pagesMomentum and Impulse ReadingParvinder Bhardwaj0% (1)
- General Physics 1: Not For SaleDocument23 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Not For SaleYna ForondaNo ratings yet
- 11.1. Rotational Dynamics QPDocument27 pages11.1. Rotational Dynamics QPxasollaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Sci9 Unit1 Quiz1Document3 pagesQ4 Sci9 Unit1 Quiz1Karen AbidaNo ratings yet
- 300 MCQsDocument10 pages300 MCQsKatherine ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Garrison Cadet Academy Lahore Cantt: Albert EinsteinDocument3 pagesGarrison Cadet Academy Lahore Cantt: Albert EinsteinEngr Anwaar JuttNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument20 pagesExamhecaicedo77No ratings yet
- Target: Learning Guide Module Subject Code Math 3 Module Code 2.0 Lesson Code 2.4.1 Time LimitDocument14 pagesTarget: Learning Guide Module Subject Code Math 3 Module Code 2.0 Lesson Code 2.4.1 Time LimitJoh TayagNo ratings yet
- Projectiles/Projectile Simulator/Projectile Simulator InteractiveDocument4 pagesProjectiles/Projectile Simulator/Projectile Simulator InteractiveEldienGarciaBucol100% (1)
- Student Exploration: Free-Fall LaboratoryDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Free-Fall LaboratorySri Devi Nagarjuna0% (1)
- General Physics 1 q1 Week 3Document24 pagesGeneral Physics 1 q1 Week 3Chool Cydrick B. BascosNo ratings yet
- Vectors and ProjectilesDocument8 pagesVectors and ProjectilesgabytjintjelaarNo ratings yet
- SCI19 Q4 M1 Projectile-MotionDocument14 pagesSCI19 Q4 M1 Projectile-MotionricorodriguezmolinaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 10 PHY1321 - Fall2018 Solutions PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 10 PHY1321 - Fall2018 Solutions PDFBrian LeNo ratings yet
- GENP6 Week 3 (Gonzales, April Joy S.)Document11 pagesGENP6 Week 3 (Gonzales, April Joy S.)April Joy GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesSciTeacher MadzNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument16 pagesUnit 3 NotesOM SHAHNo ratings yet
- Carlson NSCI695 Guided Inquiry Lab On PhET Sim Collision Lab 2.01 Fill inDocument4 pagesCarlson NSCI695 Guided Inquiry Lab On PhET Sim Collision Lab 2.01 Fill inGlenn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Physics Regents Review PacketDocument46 pagesPhysics Regents Review Packethappyy1736No ratings yet
- Lab 1 Assignment TemplateDocument11 pagesLab 1 Assignment Templatenicholaspignone2046No ratings yet
- SLM General Physics 1 3rdWk PDFDocument24 pagesSLM General Physics 1 3rdWk PDFKrestel Faith CabalfinNo ratings yet
- Science 3 Quarter 4 Module 1-2 Projectile MotionDocument20 pagesScience 3 Quarter 4 Module 1-2 Projectile Motionilovebarney100% (2)
- 2009 2nd Exam Physics 211 Summer-SolutionDocument7 pages2009 2nd Exam Physics 211 Summer-Solutionpredrag dNo ratings yet
- Experiment - Image Analysis Using Imagej: Physics 61.1 Physics and Geology Unit, DPSM, Cas, Up ManilaDocument5 pagesExperiment - Image Analysis Using Imagej: Physics 61.1 Physics and Geology Unit, DPSM, Cas, Up ManilaConnieNo ratings yet
- Physics 01-04 Acceleration and GraphsDocument2 pagesPhysics 01-04 Acceleration and GraphsPushpa KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- L - Modeling FaultsDocument3 pagesL - Modeling FaultsDanica DelarosaNo ratings yet
- Merna Baraya - FreeFallSEDocument6 pagesMerna Baraya - FreeFallSEMerna BarayaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Quarter 4 Week 1 STEDocument69 pagesScience 9 Quarter 4 Week 1 STERyan AdranedaNo ratings yet
- School Supplies Giving Oct 15 2023Document1 pageSchool Supplies Giving Oct 15 2023NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- School Supplies Giving August 14, 2021Document1 pageSchool Supplies Giving August 14, 2021NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Score Sheet EditedDocument2 pagesScore Sheet EditedNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Key Answer Summative (4th) 2024Document3 pagesKey Answer Summative (4th) 2024NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Angelsupporteducation Plan Oct 15 2023Document2 pagesAngelsupporteducation Plan Oct 15 2023NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- School Supplies Giving August 27, 2023Document1 pageSchool Supplies Giving August 27, 2023NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- School Supplies Giving August 07, 2022Document1 pageSchool Supplies Giving August 07, 2022NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Angelsupporteducation PlanDocument2 pagesAngelsupporteducation PlanNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Angelsupporteducation Planaug 27 2023Document2 pagesAngelsupporteducation Planaug 27 2023NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- CERT COMM SERVICE by GellicaDocument3 pagesCERT COMM SERVICE by GellicaNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- YEARLY PLAN ACTIVITIES AngelDocument2 pagesYEARLY PLAN ACTIVITIES AngelNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Tejada DraftDocument80 pagesTejada DraftNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Score SheetDocument2 pagesScore SheetNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Activity On VolcanoDocument3 pagesActivity On VolcanoNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Physics Answersheet 4th Quarter Week 2Document4 pagesPhysics Answersheet 4th Quarter Week 2NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- RAW SCORE Automatic Computation 2022Document2 pagesRAW SCORE Automatic Computation 2022NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- 3RD Class AchieversDocument2 pages3RD Class AchieversNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Classroom Officers AttendanceDocument2 pages2023 Classroom Officers AttendanceNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Modular Distance Learning Its Effect in The AcademDocument5 pagesModular Distance Learning Its Effect in The AcademNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Blank Form Item Analysis With ComputationDocument4 pagesBlank Form Item Analysis With ComputationNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Reflection On Quarter 1 Cot 1 2023Document1 pageReflection On Quarter 1 Cot 1 2023NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- 2024 Hrpta Secretary MinutesDocument2 pages2024 Hrpta Secretary MinutesNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- NCAEDocument7 pagesNCAENymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- G10 Nat EnglishDocument6 pagesG10 Nat EnglishNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Main IdeasDocument2 pagesMain IdeasNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- English ACCOMPLISHMENT REPORTS #1Document7 pagesEnglish ACCOMPLISHMENT REPORTS #1NymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- English Journalism ReportDocument3 pagesEnglish Journalism ReportNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- CGP G10 DagohoyDocument2 pagesCGP G10 DagohoyNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- G10 Dagohoy Homeroom Accomplishment ReportDocument2 pagesG10 Dagohoy Homeroom Accomplishment ReportNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Social Responsibility in The Jewelry IndustryDocument6 pagesSocial Responsibility in The Jewelry IndustryMK ULTRANo ratings yet
- Term Paper Rough DraftDocument3 pagesTerm Paper Rough Draftapi-286275721100% (1)
- The Giant and The RockDocument6 pagesThe Giant and The RockVangie SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Escovilla 4qmath3aa2 - Patterns in The World I Live inDocument7 pagesEscovilla 4qmath3aa2 - Patterns in The World I Live inapi-743665882No ratings yet
- Implementing The Weil, Tate and Ate Pairings Using Sage SoftwareDocument19 pagesImplementing The Weil, Tate and Ate Pairings Using Sage SoftwareMuhammad SadnoNo ratings yet
- Sequestrants As A Food Ingredient: GlossaryDocument5 pagesSequestrants As A Food Ingredient: GlossaryFreshia MirandaNo ratings yet
- Kodaks Nos 1A and 3 Series IIIDocument78 pagesKodaks Nos 1A and 3 Series IIIFalcoNo ratings yet
- Gpsmap 8500 Installation Instructions: Registering Your DeviceDocument12 pagesGpsmap 8500 Installation Instructions: Registering Your DeviceGary GouveiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation: War of Independence 1857 - Mubin AliDocument11 pagesPresentation: War of Independence 1857 - Mubin AliMubinNoorNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument4 pagesDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationHendra SshNo ratings yet
- At Professional Responsibilities and Other Topics With AnswersDocument27 pagesAt Professional Responsibilities and Other Topics With AnswersShielle AzonNo ratings yet
- Anuj Nijhon - The Toyota WayDocument35 pagesAnuj Nijhon - The Toyota WayAnuj NijhonNo ratings yet
- Ajit ResumeDocument3 pagesAjit ResumeSreeluNo ratings yet
- Rimba Collective Communications Officer 1Document3 pagesRimba Collective Communications Officer 1Choky SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- SdefdesgaesgaesgDocument3 pagesSdefdesgaesgaesgBeepoNo ratings yet
- Concrete Works Risk AssessmentDocument14 pagesConcrete Works Risk AssessmentUMUT100% (2)
- Accounting Group AssignmentDocument10 pagesAccounting Group AssignmentHailuNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking: Secure Car ParkDocument12 pagesDesign Thinking: Secure Car ParkSiddhesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- Joinery FlowchartDocument1 pageJoinery FlowchartrjNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Child Development A Thematic Approach 6th EditionDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Child Development A Thematic Approach 6th EditionCharles Pando100% (44)
- Importance of Financial Education-1Document11 pagesImportance of Financial Education-1NaiduNo ratings yet
- 195 Santos v. NorthwestDocument4 pages195 Santos v. NorthwestAnn Julienne AristozaNo ratings yet
- English Work - Maria Isabel GrajalesDocument5 pagesEnglish Work - Maria Isabel GrajalesDavid RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Mike Millmore - CHP 7. Strategic Human Resource Planning The Weakest LinkDocument40 pagesMike Millmore - CHP 7. Strategic Human Resource Planning The Weakest LinkAndyHNo ratings yet
- Company Analysis-DELL INC: History and BackgroundDocument4 pagesCompany Analysis-DELL INC: History and BackgroundBivor DhakalNo ratings yet
- Superagent: A Customer Service Chatbot For E-Commerce WebsitesDocument12 pagesSuperagent: A Customer Service Chatbot For E-Commerce WebsitesAisha AnwarNo ratings yet
- Kidshow Childrens Magic CourseDocument22 pagesKidshow Childrens Magic CoursebubblemeNo ratings yet
- PCR Qurbani 2018 TharparkarDocument3 pagesPCR Qurbani 2018 TharparkarKARWAN DEVELOPMENT FOUNDATIONNo ratings yet