Professional Documents
Culture Documents
For Download Inly
For Download Inly
Uploaded by
Noob 3Xx0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pagenot
Original Title
for download inly
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentnot
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageFor Download Inly
For Download Inly
Uploaded by
Noob 3Xxnot
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
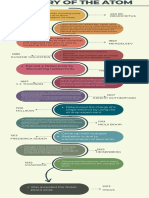
TIMELINE
OF ATOM
John Dalton formulates the
modern atomic theory,
1803
proposing that elements are
made up of atoms and that
atoms of different elements
have different properties.
J.J. Thomson discovers
the electron,
1897 suggesting that atoms
are not indivisible.
Ernest Rutherford proposes
the nuclear model of the
1911
atom, with a small, dense
nucleus surrounded by
orbiting electrons.
Niels Bohr introduces the
Bohr model of the atom,
1913
which suggests that
electrons orbit the nucleus
in specific energy levels.
James Chadwick discovers
the neutron, completing the
1932
picture of the modern atom
with a nucleus composed of
protons and neutrons
surrounded by electrons.
Gell-Mann proposed that
protons, neutrons, and other
hadrons are composed of
1964 smaller particles called
"quarks," which come in
different flavors (such as up,
down, strange, charm, top,
and bottom).
George Zweig, an American
physicist, independently
proposed a similar idea to
Murray Gell-Mann's quark
model. In 1964, Zweig
introduced the concept of
1964
"aces," which are essentially
the same as quarks.
You might also like
- Unveiling The AtomDocument2 pagesUnveiling The AtomRohit SahuNo ratings yet
- Development of Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesDevelopment of Atomic TheoryRohit SahuNo ratings yet
- Chemical ChangesDocument3 pagesChemical ChangesFrankNo ratings yet
- Development of The Atomic Theory 1001Document9 pagesDevelopment of The Atomic Theory 1001Patricio AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument46 pagesChapter 2 Atoms Molecules and IonsASHREN MACABANTOGNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAtomic TheoryTriumfo, DianeNo ratings yet
- Ramil DrugsDocument3 pagesRamil DrugsAileen Labastida BarcenasNo ratings yet
- ATOMS: Development of The Atomic Theory DemocritusDocument3 pagesATOMS: Development of The Atomic Theory DemocritusEros ErosNo ratings yet
- Dem 20231125 081207 0000Document5 pagesDem 20231125 081207 0000d494z6prkcNo ratings yet
- History of The Atomic TheoryDocument1 pageHistory of The Atomic TheoryjosewuNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument3 pagesAtomic Theory TimelineYhan Brotamonte BoneoNo ratings yet
- Empedocles 440 B.C.: J. J. Thomson1897Document3 pagesEmpedocles 440 B.C.: J. J. Thomson1897Eusebio CadagNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesHistorical Development of Atomic TheoryDivyeshNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesHistorical Development of Atomic TheoryDivyeshNo ratings yet
- Atoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryDocument18 pagesAtoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryJamie BaczewskiNo ratings yet
- Atoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryDocument23 pagesAtoms:: Development of The Atomic TheoryAndy SwiftNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Atomic TheoryDocument3 pagesEvolution of Atomic TheoryPaolo Lorenzo LoraNo ratings yet
- 12s080201batomsdevelopment of The Atomic Theory1 171015140731Document21 pages12s080201batomsdevelopment of The Atomic Theory1 171015140731Cristeah AlemaniaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryJoshua GrafiaNo ratings yet
- Prince Harold Silvania 12-Eleazar: Dalton's TheoryDocument4 pagesPrince Harold Silvania 12-Eleazar: Dalton's TheoryAllen AcojidoNo ratings yet
- Athomic Theory TimelineDocument3 pagesAthomic Theory TimelineMariana TrovatelliNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method Quiz Presentation in A Blue Yellow and Orange Hand Drawn StyleDocument8 pagesScientific Method Quiz Presentation in A Blue Yellow and Orange Hand Drawn Stylepaulino012296No ratings yet
- History of The Atom - With TimelineDocument18 pagesHistory of The Atom - With TimelineBrille Anthony BunielNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Lesson 3 12 HUMMS ADocument35 pagesPhysical Science Lesson 3 12 HUMMS AManuel keven MangadaNo ratings yet
- Scientist Timeline CctoDocument3 pagesScientist Timeline CctoEusebio CadagNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument49 pagesAtomic Structure PDFAshishNo ratings yet
- Atomic Nature TimelineDocument2 pagesAtomic Nature TimelinebokanegNo ratings yet
- ChristianDocument21 pagesChristianAdrian John ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Atomos: Not To Be CutDocument34 pagesAtomos: Not To Be Cutemo mHAYNo ratings yet
- Science Atom History ThingyDocument1 pageScience Atom History ThingyConstanza Vitulli RoqueNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAtomic TheoryRodelio ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Discovery Theory of Atoms 400bc-21st CenturyDocument2 pagesDiscovery Theory of Atoms 400bc-21st CenturyMikaella JungcoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory Timeline: Date Discoverer DiscoveryDocument5 pagesAtomic Theory Timeline: Date Discoverer DiscoveryImel Grace FlordelizNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAtomic TheoryAaditya MenonNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelDocument12 pagesAtomic ModelScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Atoms From The Eyes of PhilosophersDocument9 pagesAtoms From The Eyes of Philosophersgina moraNo ratings yet
- History of AtomDocument1 pageHistory of AtomalenanicoleanasNo ratings yet
- The History of The AtomDocument5 pagesThe History of The AtomHussain AliNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 ESL History of Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesActivity 2 ESL History of Atomic StructureAshmi KNo ratings yet
- Atomic Model TheoriesDocument6 pagesAtomic Model Theoriesjustforbuznes1No ratings yet
- Pink Yellow White Organizational Chart 3D Whiteboard PresentationDocument1 pagePink Yellow White Organizational Chart 3D Whiteboard PresentationalenanicoleanasNo ratings yet
- Assignment /quiz 1:: 1 - Dalton Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAssignment /quiz 1:: 1 - Dalton Atomic TheoryRuffa Mae PortugalNo ratings yet
- Baladad Richelle 11 ABM-B Physical ScienceDocument4 pagesBaladad Richelle 11 ABM-B Physical ScienceIvy Jane R AlarconNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- History and Model AtomDocument28 pagesHistory and Model AtomAPRIL EASTER CHUPUICONo ratings yet
- History AtomsDocument12 pagesHistory Atomsmishelle061No ratings yet
- Historical Development of The Atom Precy LicupDocument12 pagesHistorical Development of The Atom Precy LicupAdrian John Manaloto100% (1)
- Atomic Theory Timeline: Models of AtomDocument3 pagesAtomic Theory Timeline: Models of AtomTrisha Denise ReasNo ratings yet
- Students Version 01 - Atomic ModelsDocument26 pagesStudents Version 01 - Atomic ModelsENSANO, RHYNS G.No ratings yet
- ATOMDocument14 pagesATOMMark Anthony EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Different Models of Atom Dalton's Model of The AtomDocument2 pagesDifferent Models of Atom Dalton's Model of The AtomBernardez Grace HannahNo ratings yet
- History in The Developmet of The Structure of Atom: Different Contributions of ScientistDocument4 pagesHistory in The Developmet of The Structure of Atom: Different Contributions of ScientistJin09 GappalNo ratings yet
- Timeline of The Evolution of The Atomic Theory: Activity 4Document6 pagesTimeline of The Evolution of The Atomic Theory: Activity 4acerNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument26 pagesStructure of AtomsyNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Prepared By: Ms. Shaira G. SalardaDocument41 pagesPhysical Science: Prepared By: Ms. Shaira G. SalardaShaira SalardaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument1 pageAtomic Theory TimelineDanilo Macahis100% (1)
- Brief History of An AtomDocument56 pagesBrief History of An AtomJonabelle A. BeroNo ratings yet
- History of The Atom TimelineDocument6 pagesHistory of The Atom Timelineur momNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document9 pagesLesson 2Mary Ann Elacion AballaNo ratings yet