Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistryqdwfwfvevfbfe
Chemistryqdwfwfvevfbfe
Uploaded by
uco4eva0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesdsafeefdqwefwdqfwwd12wq
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdsafeefdqwefwdqfwwd12wq
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesChemistryqdwfwfvevfbfe
Chemistryqdwfwfvevfbfe
Uploaded by
uco4evadsafeefdqwefwdqfwwd12wq
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Chemistry
A. Physical Properties of Metals: Some of the main physical
properties of metals are given below.
● Metals can be hammered into thin sheets. It means they possess
the property of malleability.
● Metals are ductile. They can be drawn into wires.
● Metals are a good conductor of heat and electricity.
● Metals are lustrous which means they have a shiny appearance.
● Metals have high tensile strength. It means they can hold
heavyweights.
● Metals are sonorous. It means when we strike them, they make a
ringing sound.
● Metals are hard. It means they cannot be cut easily.
B. Chemical Properties of Metals: Some of the chemical
properties of metals are given below.
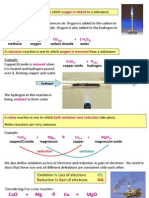
● Reaction with Oxygen – Metals react with oxygen and form
metallic oxides which are basic in nature.
Metal + Oxygen Metal oxide
Metal oxide + water Base
Example –Magnesium is metal and when it reacts with oxygen, it
forms magnesium oxide. When we dissolve magnesium oxide in
water, it gives magnesium hydroxide. The reactions are given
below.
2Mg + O2 2MgO
MgO + H2O Mg(OH)2
● An aqueous solution of metal oxide turns red litmus paper into
blue.
● Reaction with water - Metals react with water. When a metal
reacts with water, metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas are
formed.
Metal + Water Metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Example – Sodium metal reacts with water and forms sodium
hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The reaction is given below –
Na + H2O NaOH + H2
● Reaction With Acid - Metals react with acids and form salt and
hydrogen gas. Some metals vigorously react with acids.
Metal + Acid Metal salt + hydrogen
Example – Magnesium metal reacts with hydrochloric acid and
forms magnesium chloride and hydrogen. The reaction is given
below –
Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
● Reaction With Base - Metals react with bases such as sodium
hydroxide and form salt and hydrogen gas.
Metal + Base Metal salt + hydrogen
Example – Aluminum metal reacts with Sodium hydroxide and
forms sodium aluminate and hydrogen gas. The reaction is given
below –
Al + NaOH NaAlO2 + H2
● Displacement Reaction - A more reactive metal displaces a less
reactive metal from its salt solution. These types of reactions are
called displacement reactions.
Example – Iron is more reactive than copper. So, it displaces
copper from its salt. The reaction is given below –
CuSO4 + Fe FeSO4 + Cu
1. A. Aluminum-Bauxite
B. Tin-Cassiterite, or tinstone
C. Iron-Magnetite, titanomagnetite, hematite
D. Copper-Chalcopyrite
You might also like
- Metals IGCSE NotesDocument27 pagesMetals IGCSE NotesMisbah Kamran100% (1)
- Metals NotesDocument4 pagesMetals NotesDiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Metals and Non MetalsDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Metals and Non Metalskush96122No ratings yet
- Metal and Non Metal Class VIIIDocument9 pagesMetal and Non Metal Class VIIIamrendraNo ratings yet
- Metal and Non Metal Class VIIIDocument9 pagesMetal and Non Metal Class VIIIDr. Amrendra JhaNo ratings yet
- Reading Material by NVS TeacherDocument12 pagesReading Material by NVS Teacher10E Yuvan Sarabeshan Thirumeninathan [3383]No ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals Class 7Document7 pagesMetals and Non Metals Class 7adinathdinesh99No ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument14 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsKunal HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Class 10Document15 pagesChapter 3 Class 10Dishu SinghNo ratings yet
- Metals and NonmetalsDocument7 pagesMetals and Nonmetalstanmaygt07No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Metals and NonmetalsDocument37 pagesChapter 3 Metals and NonmetalsVibi VibesNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument57 pagesMetals and Non MetalsLOLBOINo ratings yet
- Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Uydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4Document6 pagesUydz Uw WV USKa N61 MM JC 4varshatagade126No ratings yet
- 10.1 Properties of MetalsDocument11 pages10.1 Properties of Metalss103038No ratings yet
- Summary Sheet Year 8 Metals and Non-Metals:: The Periodic TableDocument5 pagesSummary Sheet Year 8 Metals and Non-Metals:: The Periodic TableFeman riazNo ratings yet
- 8th Metal and Non MetalDocument8 pages8th Metal and Non MetalsubrotokumarmohantaNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument23 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsAnonymous ufMAGXcskMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3Mohsin ahmedNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chem Metals Chemistry of Gardening EtcDocument25 pagesCSEC Chem Metals Chemistry of Gardening Etcdela2100% (2)
- Silver Hills Public School, Kozhikode: Class NotesDocument12 pagesSilver Hills Public School, Kozhikode: Class NotesMaria Joe.kNo ratings yet
- 03 Metals and Non-MetalsDocument16 pages03 Metals and Non-Metalscbirua1No ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non MetalsKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- X CH 3 Chemistry Notes 1Document9 pagesX CH 3 Chemistry Notes 1vedha.mahendra1No ratings yet
- Properties of Metals G LudhianaDocument7 pagesProperties of Metals G Ludhianaapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Notes - Metals Ad Non-Metals - C-XDocument8 pagesNotes - Metals Ad Non-Metals - C-Xpratishtha MishraNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non-Metalsmonkey.luffy.kenNo ratings yet
- Metal and Non Metal NotesDocument13 pagesMetal and Non Metal NotesShabad SinghNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument11 pagesMetalsZenoxu 7zNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument41 pagesThe Periodic Table of ElementsPawan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Metals and Their Properties - Physical and ChemicalDocument5 pagesMetals and Their Properties - Physical and Chemicalcourtz911No ratings yet
- UNIT-10 Metals: The Reactivity Series of MetalsDocument9 pagesUNIT-10 Metals: The Reactivity Series of MetalsTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument15 pagesInorganic ChemistryKIARA B SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesDocument24 pagesReactivity Series of Metals: Reactions of Metals Effect of Heat On Metal CarbonatesCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Term 2Document3 pagesChemistry Term 2aesthetical.aadya09No ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanDocument17 pagesMetals and Non Metals - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287No ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument13 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesmittalshivamNo ratings yet
- 1 Metals and NonmetalsDocument13 pages1 Metals and Nonmetalsthinkiit100% (1)
- Metals ReviewerDocument8 pagesMetals ReviewerCyber DomingoNo ratings yet
- Metals and Nonmetals - NotesDocument3 pagesMetals and Nonmetals - NotesARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisDocument20 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Redox, Reactivity Series and AnalysisChemistryKlipz93% (14)
- Metals - PropertiesDocument66 pagesMetals - Propertiesrheanna.bartonNo ratings yet
- Materials: Metals and Non-Metals: N. S. RamyaDocument12 pagesMaterials: Metals and Non-Metals: N. S. RamyaRamya100% (1)
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument9 pagesMetals and Non Metalsvishwath donepudiNo ratings yet
- Geography Lesson 2Document5 pagesGeography Lesson 2indaneNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument17 pagesProperties of MetalsDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Shiksha Group Education: Chemical Properties of MetalsDocument18 pagesShiksha Group Education: Chemical Properties of MetalsHarshit RajputNo ratings yet
- Metals, Non Metals, and MetallurgyDocument13 pagesMetals, Non Metals, and MetallurgyM. Amebari NongsiejNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Metal & Non-Metals Lecture SlidesDocument25 pagesPadhle 10th - Metal & Non-Metals Lecture SlidesBitan DasNo ratings yet
- Metals PreliminaryDocument26 pagesMetals PreliminaryIra Katriel NunagNo ratings yet
- METALSDocument12 pagesMETALSjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23Document37 pagesMetals and Non Metals Notes Class 10 2022-23ramkumarsingh12406100% (1)
- Metals & Non MetalsDocument18 pagesMetals & Non MetalsSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Chemical ChangesDocument6 pages4.4 Chemical Changesdynamiccosmic7No ratings yet
- Class X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesDocument14 pagesClass X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesSuraj Luwangcha100% (1)
- D 4-4-Chemical-Changes-TrilogyDocument5 pagesD 4-4-Chemical-Changes-Trilogyishikagajjar123No ratings yet
- 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsDocument6 pages4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsDocument6 pages4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes: Reactivity of MetalsJadyn Mc SweenNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- IGCP BrazilDocument116 pagesIGCP BrazilZildaPenaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Nomenclature Worksheet 345 FormulasDocument7 pagesInorganic Nomenclature Worksheet 345 FormulasKonstantinos KosmidisNo ratings yet
- Layout: 4.1 Steel's GenesisDocument2 pagesLayout: 4.1 Steel's GenesisDroffy GuyNo ratings yet
- Aluminum 5083 H111Document2 pagesAluminum 5083 H111Murat KAYANo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument9 pagesPhysicsGanesh VNo ratings yet
- ASTM A36 Carbon Structural Steel Plate SpecificatDocument1 pageASTM A36 Carbon Structural Steel Plate SpecificatAri sofyanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Metals Use in The Gas Turbine Industry - Challenges and OpportunitiesDocument21 pagesStrategic Metals Use in The Gas Turbine Industry - Challenges and Opportunitiesjohn davidsNo ratings yet
- Iron Ore Sintering: Process: ArticleDocument15 pagesIron Ore Sintering: Process: ArticleS.V.SubrahmanyamNo ratings yet
- Fuel, Furnance and RefactoriesDocument50 pagesFuel, Furnance and RefactoriesKISHORE CHANDRA PATRANo ratings yet
- Types of Overhead Line ConductorDocument7 pagesTypes of Overhead Line ConductorMuhammad MudassarNo ratings yet
- Sulfur Dioxide Capture in Sulfuric Acid and Other Products: 20.1. Nickel Extraction OffgasesDocument11 pagesSulfur Dioxide Capture in Sulfuric Acid and Other Products: 20.1. Nickel Extraction OffgasesJadhira RamirezNo ratings yet
- ME-ICP41 Trace Level Methods Using Conventional ICP-AES AnalysisDocument3 pagesME-ICP41 Trace Level Methods Using Conventional ICP-AES AnalysishNo ratings yet
- KurashikiDocument2 pagesKurashikidiyan tahsenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument8 pagesChemistry: Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelKelvin SerimweNo ratings yet
- Plumbing ToolsDocument241 pagesPlumbing ToolsAngel NuevoNo ratings yet
- Observations On The Bond Standard Grindability Test, and A Proposal For A Standard Grindability Test For Fine MaterialsDocument8 pagesObservations On The Bond Standard Grindability Test, and A Proposal For A Standard Grindability Test For Fine MaterialsFredy PeñaNo ratings yet
- Metal Corrosion and Its Prevention: Material ScienceDocument49 pagesMetal Corrosion and Its Prevention: Material Sciencedr nfNo ratings yet
- Principal Application Fields Ferritic Pearlitic Steel:: Technical CardDocument1 pagePrincipal Application Fields Ferritic Pearlitic Steel:: Technical CardTeodor EzaruNo ratings yet
- Steel, Types of SteelDocument50 pagesSteel, Types of SteelEzhil ThalapathiNo ratings yet
- Gold and Maars at WauDocument18 pagesGold and Maars at WauGeo Geo GeoNo ratings yet
- Material Data Sheet: Ultrachrome® 28% CR, Low C (Heat Treated)Document3 pagesMaterial Data Sheet: Ultrachrome® 28% CR, Low C (Heat Treated)fendix100% (1)
- Manganese, Sulfur and Manganese-Sulfur Ratio Effects in Gray Cast IronDocument30 pagesManganese, Sulfur and Manganese-Sulfur Ratio Effects in Gray Cast IronNetoNo ratings yet
- ASTM A574-98aDocument7 pagesASTM A574-98aNadhiraNo ratings yet
- Gal Rebar SeminarDocument11 pagesGal Rebar SeminarazizNo ratings yet
- Quenched and Tempered Vacuum-Treated Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings For Pressure VesselsDocument9 pagesQuenched and Tempered Vacuum-Treated Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings For Pressure VesselssamehNo ratings yet
- Glycine LeachDocument74 pagesGlycine LeachabrahanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/22Document20 pagesCambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/22Islamabad ALMA SchoolNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Refractory 1: Silica Bricks: TMT619214 Bata Tahan Api Dan Terak 2021Document12 pagesCommonly Used Refractory 1: Silica Bricks: TMT619214 Bata Tahan Api Dan Terak 2021Mugi MaulaNo ratings yet
- Atlas Steels Technical Handbook of Stainless Steels: ForwardDocument58 pagesAtlas Steels Technical Handbook of Stainless Steels: ForwardVANDANA GLOBALNo ratings yet
- The Geology and Mineral Resource of Kasempa Mining LTD - A Management BriefDocument13 pagesThe Geology and Mineral Resource of Kasempa Mining LTD - A Management BriefRamoutar (Ken) Seecharran100% (4)