Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology O Level Summary Notes
Biology O Level Summary Notes
Uploaded by
Adriana MuzfirahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology O Level Summary Notes
Biology O Level Summary Notes
Uploaded by
Adriana MuzfirahCopyright:
Available Formats
*
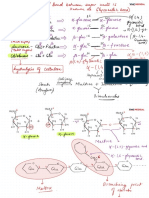
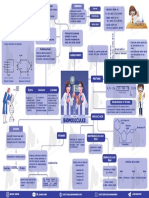
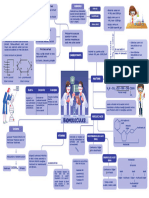
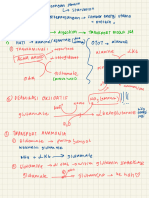
1. d) carbohydrates
① simple carbohydrates
made up of Carbon , Hydrogen & Oxygen
CCHO)
Cn Hzn
On
General formula
:
ce
Glu Frugal s
monosaccharides
<
disaccharides polysaccharides
( ] cellulose
(Eg.) : •
Glucose mono + mono
]
→
f. Condensation
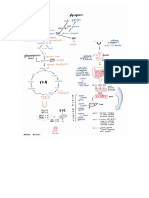
• fructose → starch
☐ maltose ( 2 glu )
Galactose glu Itm)
o
• sucrose C
/ ,
→ glycogen
( most basic unit d-
( 1gal , 1914 )
lactose
]
.
carbohydrate → chitin
☒ simplest form of
sugar
hydrolysis
(-111-20)
• ✓ enzyme
maltose & lactose
Test for reducing sugars ( Benedict 's Test ) Glucose ,
fructose , -
galactose ,
)
( sucrose
✗ reducing
solution ( ]
① Reagent : Benedict 's copper CID sulfate
✗
[ 2cm
3 benedict 's
Blue orange →
I.
Green brick red
☒
change
→
solution :
→
.
fire
☒ Heat the test tube
G- mins )
Non -
reducing sugar
Add HCl → Heat
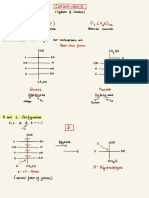
complex carbohydrates
starch
& cellulose
↳ Polysaccharides
: ,
glycogen
☒
glucose
②
① starch : linked tgt in long St .
chains
00
② Glycogen :
glucose =
linked tgt in
highly branched chains
↳ &
storage molecule in animals
fungi
③ cellulose →
glucose molecules linked in
long St chains
①
& Starch → 1) insoluble in Hzo I do not affect Xp in cells
Glycogen
form of glucose]
( storage
→
2) too large to diffuse out of cell
3) ✓ compact shapes
4) easily hydrolysed into glucose for cellular
respiration
Test for starch ( iodine test)
↳ result :
yellow
-
brown to blue black
Fats ciipids ) →
component C. Carbon ,
Hydrogen ✗ oxygen ]
FA
⇐ ratio of e-
hydrogen 2 I
:
oxygen
: =
FA
g
-
② £
& fatty FA
-
made of acids
* up
:
glycerol
@
molecules
storage storing energy
→
*
④ used to make steroids & certain hormones
*
function
⑤
☒ used as insulating material to prevent loss of body heat
@ * Solvent for fat-soluble vitamins
Test for fats ethanol emulsion test
f ethanol
[
H2O
,µ u
mix
- → result :
cloudy white emulsion
, , ,, , , , ,
Proteins made up of C , H . O ,
N
Cmay also contain sulfur)
=
↳ :#
example enzyme antibodies ,
↳ made up of amino acids
}
acid C structure
* Amino general
each amino acid .
diff R -
group
- =
'
Protein is created aa link up in condensation =D
polypeptide chain
=
.
peptide bonds
2
Bonds between aa → →
strong
=
'
chains twisted folded ← coiled
, / more polypeptide .
# 3D structure
" & / changes
Bonds that hold the 3D coiled structure :
weak can be
easily broken by heat in pH
↳ Hydrogen bonds
*
↳ ionic bond
↳ van der Waals (intermolecular bonding]
Denaturation → when the weak bonds are broken & protein loses its 3D shape
↳ caused by heat or unsuitable pH
the structure )
↳ effect : loss of function Cohee
to
✓
the disruption of
: lose solubility 4 percipitate
out
of sold
Test for protein C. Biunet test )
sulfate
NaOH & copper CID
main
reagent
:
NaOH 04504
① [ [ result :
V. b-
.
Turns violet
mixes =
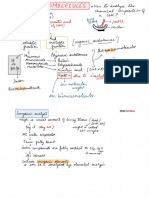
Enzymes
altered
speed of chemical reactions w/out being
.
up rate →
1. Biological catalysts →
2 .
Made of proteins
work ?
How enzymes
of chemical reaction
→
by lowering activation
energy
a
needed reaction to take place
Activation energy for a
:
→
molecules
→ can break down / build up biological
3. shape of active site is specific to substrate ,
unique 3-D structure
keyword : -
ase
? reactants
substrate
'
Eg Amylase
. can
only digest starch
=
lock & Key hypothesis
catalysed
You might also like
- Shred With Keto PDFDocument122 pagesShred With Keto PDFEmma Donoghue100% (2)
- L-Pac ProductionlDocument10 pagesL-Pac ProductionlSonia Patel100% (1)
- SF2 Lecture 04 Biomolecules NotesDocument13 pagesSF2 Lecture 04 Biomolecules Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Carbohydrates 2 (1) - InvertDocument40 pagesBiomolecules Carbohydrates 2 (1) - InvertelluresonyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Mind MapDocument1 pageCarbohydrates Mind MapS3CH-14 Choy Pak MingNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry CarbsDocument78 pagesClinical Chemistry CarbsvnicasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Biochem PDFDocument84 pagesBiochem PDFVeshala PraneethNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument1 pageDigestivenina.kol222No ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument3 pagesGlycolysisAna FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Designed: by PanchalDocument18 pagesDesigned: by PanchalJatinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Menu ACCDocument8 pagesNutrition Menu ACCTom SmithNo ratings yet
- DQ of Biomolecules by Bharat Panchal SirDocument3 pagesDQ of Biomolecules by Bharat Panchal SirsashankkotaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules EDocument7 pagesBiomolecules Efariahanfi13No ratings yet
- Polysaccharides: SugarsDocument7 pagesPolysaccharides: SugarsBikash YadavNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES MHT CET SynopsisDocument4 pagesBIOMOLECULES MHT CET SynopsisAbhishek Mandlik100% (3)
- 營養學筆記 32 45Document14 pages營養學筆記 32 45nicole.liang47No ratings yet
- Class 12 BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesClass 12 BiomoleculesArpit LambaNo ratings yet
- Bnie Ia: Prep MDocument10 pagesBnie Ia: Prep MChota CarryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Biologist 1A Parts 1& 2Document17 pagesChemistry For Biologist 1A Parts 1& 2body fayezNo ratings yet
- (Hydrate Carbon) : SugarDocument3 pages(Hydrate Carbon) : Sugarchemistry tutorialNo ratings yet
- BioMolecules in One ShotDocument46 pagesBioMolecules in One ShotKESHAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Module 2 RevalidaDocument12 pagesModule 2 RevalidaJacosby WorcestershireNo ratings yet
- SF2-Lecture-01 Biomolecules NotesDocument15 pagesSF2-Lecture-01 Biomolecules Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules 1-1Document18 pagesBiomolecules 1-1Madhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument1 pageBiomoleculesAshish GuleriaNo ratings yet
- Process Technology For Natural Gas NGLs and Condensate Applications Lonnie SmithDocument28 pagesProcess Technology For Natural Gas NGLs and Condensate Applications Lonnie SmithReza SalimiNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument1 pageBiomoleculesRaunak JayaswalNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument1 pageBiomoleculessarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- CTTN BiokimiaDocument1 pageCTTN BiokimiaAlicya BriaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument3 pagesBiologys0xynpark18No ratings yet
- Biomolecules: GlucoseDocument1 pageBiomolecules: GlucoseGargi PathakNo ratings yet
- The Metabolic Map Lipids Part Two Illustration AtfDocument1 pageThe Metabolic Map Lipids Part Two Illustration AtfJoax Wayne SanchezNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecules Part 1 Short Notes 1 YbNZvpO1rMiZ3B5YDocument19 pagesBio Molecules Part 1 Short Notes 1 YbNZvpO1rMiZ3B5YBob the clasherNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument1 pageCarbohydrate MetabolismdaefaegagNo ratings yet
- FullSubwayMap221Document1 pageFullSubwayMap221veronicaortega1525No ratings yet
- Ashutosh Sir Biomolcules NotesDocument36 pagesAshutosh Sir Biomolcules Notesalayaacosta16No ratings yet
- A B C D E F G H I J K L M: Pathways of Human MetabolismDocument1 pageA B C D E F G H I J K L M: Pathways of Human MetabolismPranavJamdagneyaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry by DR - AzamDocument98 pagesBiochemistry by DR - AzamArrya DSNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument3 pagesBiological MoleculeshosannaNo ratings yet
- Les Faisal 20 November 2022Document8 pagesLes Faisal 20 November 2022faisal adhiNo ratings yet
- The Metabolic Map Proteins Part Three Illustration AtfDocument1 pageThe Metabolic Map Proteins Part Three Illustration AtfJoax Wayne SanchezNo ratings yet
- Steak N ShakeDocument8 pagesSteak N ShakekatewhatsernameNo ratings yet
- Aladdins Nutritional InfoDocument4 pagesAladdins Nutritional InfogochobatmanNo ratings yet
- Pengolahan: DiketahuiDocument2 pagesPengolahan: DiketahuiUnknown FaqihNo ratings yet
- Apa ItuDocument2 pagesApa Ituhana faqihNo ratings yet
- Tr31 60Document30 pagesTr31 60Minh GiaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Shobhit Nirwan - RemovedDocument9 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Shobhit Nirwan - Removedshoaib1234gkpNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Shobhit NirwanDocument10 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Shobhit NirwanKhushi Roy100% (7)
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Shobhit NirwanDocument9 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Shobhit NirwanMithil MohanrajNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Shobhit NirwanDocument10 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Shobhit NirwanPurab NathNo ratings yet
- Kasus Soca CitraDocument4 pagesKasus Soca CitraPentolNo ratings yet
- Nutrition InformationDocument1 pageNutrition InformationshwiiiNo ratings yet
- Any Theft: Law and Molar VolumeDocument1 pageAny Theft: Law and Molar VolumeAYA SABAH FAREEDNo ratings yet
- FA Synthesis Part One Illustration AtfDocument1 pageFA Synthesis Part One Illustration Atfnofov45585No ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathways of GlucoseDocument11 pagesMetabolic Pathways of GlucosemanikchawlaplusoneNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules (Enzymes)Document16 pagesBiological Molecules (Enzymes)garethongshNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration FlowchartDocument1 pageCellular Respiration FlowchartAndrew100% (5)
- 1.2 CarbohydratesDocument1 page1.2 CarbohydratesBlitzSZNNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules PDFDocument6 pagesBiomolecules PDFPiyali Parui X-A 20No ratings yet
- Sailing - Jo AllehDocument4 pagesSailing - Jo AllehТетяна МешкоNo ratings yet
- Quick Start To Weight Loss: Sophie RobinsonDocument19 pagesQuick Start To Weight Loss: Sophie RobinsonCrazy MomentNo ratings yet
- GM DietDocument4 pagesGM DietPriyanka MalhotraNo ratings yet
- PE Q1W1 Gr12Document13 pagesPE Q1W1 Gr12Tessa Kaye - Rumol AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Food MCB II NotesDocument73 pagesFood MCB II NotesRichard Simon KisituNo ratings yet
- Research On Skipping BreakfastDocument4 pagesResearch On Skipping Breakfastnad100% (2)
- Principles of Biochemistry (Carbohydrates)Document32 pagesPrinciples of Biochemistry (Carbohydrates)Sohaib NazirNo ratings yet
- How The Properties of Matter Relate To Their Chemical StructureDocument99 pagesHow The Properties of Matter Relate To Their Chemical StructureElpi Ferrer80% (5)
- Beast Mentality E-BookDocument40 pagesBeast Mentality E-BookMilton DesignerNo ratings yet
- Herbalife Catalog-Good PDFDocument60 pagesHerbalife Catalog-Good PDFVic Veeraj GoyaramNo ratings yet
- Q4 Long QuizDocument1 pageQ4 Long Quiz2020-100394No ratings yet
- Gen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesGen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Project On Content of Cold DrinksDocument20 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Project On Content of Cold Drinkschitu100% (2)
- Similarities and Differences in Living Things-Edited - KeyDocument100 pagesSimilarities and Differences in Living Things-Edited - KeyJordi Calderon MontesNo ratings yet
- Solutions AIATS Medical-2018 (RM) Test-2 (Code-E & F) (17!12!2017)Document12 pagesSolutions AIATS Medical-2018 (RM) Test-2 (Code-E & F) (17!12!2017)Deeksha pathak100% (2)
- Calorimetry Lab Student Expolartion SheetDocument10 pagesCalorimetry Lab Student Expolartion SheetAli AlzarooniNo ratings yet
- How Are The Terms "Food" and "Nutrition" Different From Each Other?Document11 pagesHow Are The Terms "Food" and "Nutrition" Different From Each Other?Aditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Engineering Internship:: Health Bars For Disaster ReliefDocument19 pagesMetabolism Engineering Internship:: Health Bars For Disaster ReliefRick WuNo ratings yet
- Growth Studies of Potentially Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria in Cereal-Based SubstratesDocument9 pagesGrowth Studies of Potentially Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria in Cereal-Based SubstratesSjjshahaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NutritionDocument472 pagesFundamentals of NutritionDiana MontesNo ratings yet
- Int Esws at Y8 AP SB Answers TTPPDocument105 pagesInt Esws at Y8 AP SB Answers TTPPRocco Nardi100% (1)
- Sugar Consumption in MalaysiaDocument14 pagesSugar Consumption in MalaysiaShi Yen50% (2)
- Human NutritionDocument87 pagesHuman NutritionSamyam DahalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Muskan Singla Class.: Xii-A School:Seth Anandram Jaipuria SchoolDocument22 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Muskan Singla Class.: Xii-A School:Seth Anandram Jaipuria SchoolMuskan singlaNo ratings yet
- 5 6086852463917269055 PDFDocument294 pages5 6086852463917269055 PDFNaveenkumar Neelam100% (1)
- TM - S Q Bank 2nd Edition BiochemistryDocument29 pagesTM - S Q Bank 2nd Edition BiochemistryArthi ReddyNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lecture 3-5Document65 pagesNCM 105 Lecture 3-5Roshin Tejero100% (3)
- NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPHY ModuleDocument11 pagesNUTRITION AND DIET THERAPHY ModuleDon Maur ValeteNo ratings yet