Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8th DLP PROJECTILE MOTION
8th DLP PROJECTILE MOTION
Uploaded by
JOHNERROL CARCELLAROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8th DLP PROJECTILE MOTION
8th DLP PROJECTILE MOTION
Uploaded by
JOHNERROL CARCELLARCopyright:
Available Formats
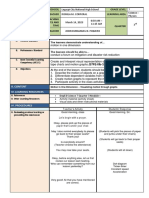
Annex 1B to DepEd Order No. 42, s.
2016
School Calbiga National High School Grade Level GRADE 9
• Topaz
• Garnet
• Emerald
• Pearl
GRADE 1
TO 12 Teacher Monicca S. Abbang Learning Science
DETAILED Area
LESSON Teaching April 11, 2024 Quarter 4th
PLAN Dates and (10:00-11:00)
Time (11:00-12:00)
(2:00-3:00)
(3:00:4:00)
DAY: THURSDAY
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standard Content Standard:
Projectile motion, impulse and momentum, and conservation of
linear momentum.
B. Performance Standards Performance Standard:
Propose ways to enhance sports related to projectile motion.
C. Learning Describe the horizontal and vertical motions of a projectile
Competencies/Objectives S9FE-IVa-34
/
Write the LC Code each
D. Learning Objectives At the end of the lesson, students should be able to
➢ Define projectile motion and projectile
➢ Differentiate the two dimensions of projectile motion
➢ Apply the concept of projectile in real life.
E. CONTENT PROJECTILE MOTION: Motion in Two Dimensions
II. LEARNING
RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide 1-12
Pages
2. Learner’s Material 279-305
Pages
3. Textbook Pages
4. Additional Materials
from (LR) Portal
B. Other Learning PowerPoint, Picture and Laptop
Resources
III. PROCEDURES TEACHER’S ACTIVITY STUDENT’S ACTIVITY
1) Reviewing previous ELICIT
lesson or presenting a • Greetings
new lesson • Attendance
Let’s have first a short review to
check if you have learned something
from last week. We have discussed
about horizontal and vertical motion.
What was again the constant value
of acceleration? -9.8 m/s²
• What does the negative It means that the direction or
means? movement of an object is
downward
• Last question, the uniformly The uniformly accelerated
accelerated motion happens motion happens in both x and
in what axis? y axis, ma’am
2) Establishing a purpose for ENGAGE
the lesson
Now before we proceed to our topic
let’s have first a short activity.
I’ll show pictures. If you know the
picture that being flashed, just stand
up and if you do not know, just sit
down. Do you understand? Yes ma’am
Do you know what are those? Sports ma’am
You will know why these pictures are
related with our topic today
especially the ball used and the
motion of the ball as we go through
our discussion
3) The Presenting EXPLORE
examples/instances of
the new lesson Outr lesson for today is about
PROJICTILE MOTION: MOTION IN
TWO DIMENSIONS
The teacher will show the objectives
and let the students read it aloud.
At the end of the lesson, students
should be able to
➢ Define projectile
➢ Differentiate the two
dimensions of projectile
motion
➢ Apply the concept of projectile
in real life.
• Who among of you have an
idea of what is projectile?
• How about the dimensions
that being mentioned? What
are these dimensions?
First let’s define projectile motion
Projectile motion is a motion in
which an object is thrown near the
earth’s surface, and it moves along
the curved path under the action of
gravity only.
• How can an object have a
When we throw object and it
projectile motion? resulted a curved path
• How curved path formed? Ma’am because of the
gravity?
• Those sports that I’ve shown Yes ma’am
to you earlier, do think there is
projectile motion of the ball?
The teacher will show pictures
• With the image, is there a
Yes ma’am, because it has a
projectile motion? Why and curved path.
why not?
• Is there a projectile motion?
Why and why not?
• What is the factor/s why the
object that is being thrown
eventually come down?
Yes, ma’am because it has
curved path.
• Do you think the only reason
The factor why the object is
why the object that being eventually come down when
thrown up eventually come being thrown is because of
down is because of the the gravity
gravity?
Yes ma’am
4) Discussing new concept EXPLAIN
and practicing new skills
#1
• What is the role of the ball? It is the one that makes a
projectile motion
• The ball called as what? Projectile
• What do you think is the v in Velocity ma’am
this model?
• What is the unit of velocity m/s
again?
• As you can see, there is a The students will try to figure
curve path, right? Do you out what does the curve path
have an idea what is this called
curve path called?
• As you can see, the center Height ma’am
has line, right? What does
this H represent?
• Height in what? In vertical or Vertical ma’am
horizontal?
• How about the R? what is The student will try to guess
that? what is R
Yes, R is range or the distance.
• Distance in what dimension? Horizontal ma’am
• So, what is the important
conclusion about the motion Projectile motion is
of an object in projectile combination of two motions
motion? • Horizontal motion
• Vertical motion
5) Developing mastery ELABORATE
(Leads to formative
Assessment 3) Let’s more elaborate on these two
motions in projectile.
First is horizontal. Earlier it is being
said that the horizontal motion has
constant velocity.
• When we say constant, what
does it mean?
Horizontal motion
If there is no force acting on an
object, then it will continue moving at
a constant speed in the same
direction.
- there will be no change in its
velocity
-distance will increase the same
amount with each second
Free Fall Revisited
An object in free fall is only acted on
by gravity
▪ Acceleration due to gravity is
9.8 m/s2
▪ distance covered increases
with each second
Projectile Motion Combines
Vertical Motion and Horizontal
Motion
The vertical motion of a
projectile is not affected by its
horizontal motion
➢ meaning: The vertical motion
of a projectile is identical to an
object in free fall
The horizontal motion of a
projectile is not affected by its
vertical motion
➢ meaning the projectile will
travel the same horizontal
distance as it would if it were
simply rolling on a flat surface
in the absence of friction
Projectile Calculations
Horizontal Distance
d = v(t)
Horizontal Velocity
vf = vi + at
Vertical Distance
d = vit + ½ gt2
Vertical Velocity
Vf = Vi + gt
6) Making Generalization REVIEW
about
the lesson What is the path of a projectile
called? Trajectory
An object that being thrown
What is projectile motion? and makes the curved path
What is projectile again? Any object that projected in
the air.
Is projectile motion one No, it is 2 dimensional-
dimensional? vertical and horizontal
What force(s) is acting on the Gravity
projectile?
Which direction, horizontal or Vertical
vertical has acceleration?
Which direction, horizontal or Horizontal
vertical has constant speed?
7) Evaluating Learning EVALUATE
Assessment
1. What is the path of a projectile called?
2. What force(s) is acting on the projectile?
3-4. What are the two motions that part in projectile motion?
5-7. Define projectile Motion
8-10. Define projectile
8) Additional activities for EXTEND
the application or ASSIGNMENT:
remediation
Define momentum
IV. REMARKS
V. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation
B. No. of students who
require additional
activities for remediation
who scored below 80%
C. Did the remedial lesson
work? No. of learners who
had caught up with the
lesson.
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation
E. Which of my teaching
strategies work well? Why
did this work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
principal or supervisor
can help me solve
G. What innovation or
localized materials did I
use/discover which I wish
to share with the other
teachers?
Prepared by:
MONICCA S. ABBANG
Practice Teacher
Checked and Reviewed by:
JENNELYN L. RAFALES
Master Teacher II
Cooperating Teacher
Approved by:
LEO A. PENTASON MAEd
Secondary School Head Teacher I
You might also like
- 4L80EDocument156 pages4L80EJames Winsor100% (14)
- I. Objectives: A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument10 pagesI. Objectives: A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceJay Madridano86% (7)
- Strain and Deflection of A Circular Plate - Lab ReportDocument4 pagesStrain and Deflection of A Circular Plate - Lab ReportRoshane NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- 9th DLP ANGLE OF RELEASEDocument13 pages9th DLP ANGLE OF RELEASEJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- 7th DLP Vertical DimensionDocument10 pages7th DLP Vertical DimensionJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q4 Mod8.2Document7 pagesSci9 Q4 Mod8.2JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Differentiated Instruction (Learners With Disabilities)Document4 pagesLesson Plan For Differentiated Instruction (Learners With Disabilities)MICHELLE DIZONNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 9 - Q4Document32 pagesDLL - Science 9 - Q4Nazer M. LacaboNo ratings yet
- DLP - Projectile MotionDocument10 pagesDLP - Projectile Motionchristianlozada000No ratings yet
- DLP - Projectile Motion-2Document11 pagesDLP - Projectile Motion-2christianlozada000No ratings yet
- Le-Apr 2023Document6 pagesLe-Apr 2023Zhaye EscotoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Physics.1.1Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Physics.1.1Adrian TastarNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical EducationDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Physical EducationXyrell Jane Marquez100% (1)
- Projectile Motion Final DemoDocument3 pagesProjectile Motion Final DemoKhenna ToledoNo ratings yet
- FINAL DLP-ENRICOSO-VELOCITY-ST.CATHDocument10 pagesFINAL DLP-ENRICOSO-VELOCITY-ST.CATHjohnrico enricosoNo ratings yet
- DLP AccelerationDocument9 pagesDLP AccelerationJamaika B. ViloriaNo ratings yet
- DistanceDocument4 pagesDistanceleizl MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion LP Grade 9Document6 pagesProjectile Motion LP Grade 9Marlon Antonio100% (3)
- DLP AccelerationDocument8 pagesDLP AccelerationJamaika B. ViloriaNo ratings yet
- 5th LP MapehP.E 9Document8 pages5th LP MapehP.E 9jewel jechelNo ratings yet
- DLP - Light Science 7Document6 pagesDLP - Light Science 7Samara M. SalacayanNo ratings yet
- 6th DLP Horizontal DimentionDocument12 pages6th DLP Horizontal DimentionJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- 7es No. 2 Speed and VelocityDocument23 pages7es No. 2 Speed and VelocityLeanne Krystel CastroNo ratings yet
- DLP Transverse WavesDocument8 pagesDLP Transverse WavesJamaika B. ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 4Document4 pagesLesson Plan in English 4Ana Rose Colarte GlenogoNo ratings yet
- 5Es-Detailed-Lesson-Plan Science 5 - W2Document8 pages5Es-Detailed-Lesson-Plan Science 5 - W2Jackie Rubina OrphianoNo ratings yet
- Phy - W1 D3 - LP - G9 - Sy2023-2024Document4 pagesPhy - W1 D3 - LP - G9 - Sy2023-2024Khenna ToledoNo ratings yet
- FINAL Detailed Lesson Plan Science - Week - 1Document12 pagesFINAL Detailed Lesson Plan Science - Week - 1esterlitaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Motion in GraphsDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Motion in GraphsJohn Emmanuel PiqueroNo ratings yet
- Q4 3 DLLDocument3 pagesQ4 3 DLLLouVeroBaguioNo ratings yet
- Acceleration DLPDocument9 pagesAcceleration DLPlopezchinshin28No ratings yet
- Co1 2023Document8 pagesCo1 2023NIDA DACUTANANNo ratings yet
- Q4 LP5 Projectile Motion WEEK2Document10 pagesQ4 LP5 Projectile Motion WEEK2asmaruhomNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document9 pagesDay 4RENA PRAQUELESNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Differentiated Instruction (For IPs)Document3 pagesLesson Plan For Differentiated Instruction (For IPs)MICHELLE DIZON100% (1)
- Distance Displacement LPDocument6 pagesDistance Displacement LPLexter GuranNo ratings yet
- ProjectileDocument8 pagesProjectileJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- (UAM) Horizontal DimensionDocument5 pages(UAM) Horizontal Dimensionivy rose oconNo ratings yet
- Science 5 RevisedDocument14 pagesScience 5 RevisedJen Perven JaconesNo ratings yet
- Costructing PolygonDAILY LESSON LOG 18Document6 pagesCostructing PolygonDAILY LESSON LOG 18Aji Prato CamposNo ratings yet
- Global Citizenship Education Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesGlobal Citizenship Education Lesson Planapi-499253971No ratings yet
- Final demo-DETAILED LESSON PLAN MATHEMATICS 8 - EditedDocument8 pagesFinal demo-DETAILED LESSON PLAN MATHEMATICS 8 - EditedLESTER LISTANCONo ratings yet
- Free Fall Motion in One Direction Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesFree Fall Motion in One Direction Lesson PlanSHERYL JAVARNo ratings yet
- DLP Science Law of AccelerationDocument4 pagesDLP Science Law of Accelerationezra mark arriesgadoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 3 - Q3 - W3Document3 pagesDLL - Science 3 - Q3 - W3Wesley BrixNo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE W1Day4Document6 pagesDLP SCIENCE W1Day4IMELDA MARFANo ratings yet
- DLL Science 7 First WeekDocument3 pagesDLL Science 7 First WeekIamsuperrichell ReyNo ratings yet
- Living The Dream: Unit Summary Warm-UpDocument14 pagesLiving The Dream: Unit Summary Warm-Upraul gimenoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Force and PressureDocument8 pagesPhysical Science Force and PressureNihar ranjan SunariNo ratings yet
- Pt1 Grade 7 Distance and DisplacementDocument7 pagesPt1 Grade 7 Distance and Displacementmarvin pazNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 7 3rd Quarter EditedDocument23 pagesDLL Grade 7 3rd Quarter EditedJOCELYN HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Speed vs. VelocityDocument5 pagesSpeed vs. Velocitymarjoriebidlan445No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Visualize The Volume of Cube and Rectangular PrismDocument10 pagesLesson Plan in Visualize The Volume of Cube and Rectangular PrismJhon Rey OserinNo ratings yet
- 16.540 Class Format and Structure: 16.540 Notes Spring 2006 E. Greitzer, C. TanDocument20 pages16.540 Class Format and Structure: 16.540 Notes Spring 2006 E. Greitzer, C. TanpfylNo ratings yet
- May 4Document3 pagesMay 4Andrea Jarani LinezoNo ratings yet
- Tinikling (DLP)Document5 pagesTinikling (DLP)Crisalyn ElcanoNo ratings yet
- Class Demonstration ADocument3 pagesClass Demonstration AJames Excommunicado WickNo ratings yet
- Science 4 DLP Day 1Document8 pagesScience 4 DLP Day 1Anagrace Tingcang SanchezNo ratings yet
- Polygon DLPDocument6 pagesPolygon DLPmichelle051921No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Rectilinear Motion: Graphical Representation and InterpretationDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Rectilinear Motion: Graphical Representation and InterpretationeltytanNo ratings yet
- FINAL DLP-ENRICOSO-VELOCITY-ST.CATHDocument10 pagesFINAL DLP-ENRICOSO-VELOCITY-ST.CATHjohnrico enricosoNo ratings yet
- Secondary Student Teachers Internship AssignmentDocument4 pagesSecondary Student Teachers Internship AssignmentJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Star in Group-1Document11 pagesArrangement of Star in Group-1JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q4 Mod8.2Document7 pagesSci9 Q4 Mod8.2JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument13 pagesAssessmentJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- PP John ObjectiveDocument1 pagePP John ObjectiveJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
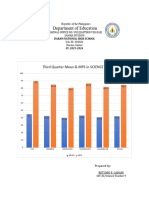
- Third Mean and Mps Word GraphDocument2 pagesThird Mean and Mps Word GraphJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Questions For ExaminationDocument4 pagesQuestions For ExaminationJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Tingog Smart 2024Document156 pagesTingog Smart 2024JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument11 pagesProjectile MotionJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Rationalization of The 1st Pretest in CE1Document51 pagesRationalization of The 1st Pretest in CE1JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument6 pagesQuizJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- In Campus Fs 2 Summary of RatingsDocument2 pagesIn Campus Fs 2 Summary of RatingsJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- LP 4 Sci 6 Inorganic ChemistryDocument11 pagesLP 4 Sci 6 Inorganic ChemistryJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Carcellar PictoDocument15 pagesCarcellar PictoJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- SSU OVPAA FR 018 Course Syllabus Sci6Document11 pagesSSU OVPAA FR 018 Course Syllabus Sci6JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- DLP Carcellar 1Document14 pagesDLP Carcellar 1JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- PROF ED 9 UNIT 4 5 StudentsDocument18 pagesPROF ED 9 UNIT 4 5 StudentsJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Science 7Document2 pagesScience 7JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis North Korea Jessa AngelicaDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis North Korea Jessa AngelicaJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- DLP CarcellarDocument8 pagesDLP CarcellarJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Organizational LeadershipDocument26 pagesOrganizational LeadershipJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Great Books 1001Document7 pagesGreat Books 1001JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- LP2 SCI-12 MICROBIO LABORATORY-fINALDocument21 pagesLP2 SCI-12 MICROBIO LABORATORY-fINALJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 8 LP4 2Document13 pagesProf Ed 8 LP4 2JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- REFLECTIONDocument2 pagesREFLECTIONJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development Models and Designs AutosavedDocument45 pagesCurriculum Development Models and Designs AutosavedJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- PBL InstrumentDocument1 pagePBL InstrumentJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Enzyme MechanismDocument3 pagesEnzyme MechanismJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Learning Packet 1 Unit 1 Prof - Ed.7Document15 pagesLearning Packet 1 Unit 1 Prof - Ed.7JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- LP 4 FINAL Waves and OpticsAutosaved Copy 1Document15 pagesLP 4 FINAL Waves and OpticsAutosaved Copy 1JOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Initial Review: Section A - Basic InformationDocument33 pagesApplication Form For Initial Review: Section A - Basic Informationsaptarshi DasNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Detection Midterm LessonDocument52 pagesCorrosion Detection Midterm LessonVv ZoidNo ratings yet
- Cantilever Slab (Unlocked)Document3 pagesCantilever Slab (Unlocked)WRay TanNo ratings yet
- What I Need To KnowDocument16 pagesWhat I Need To Knowgirlie paraisoNo ratings yet
- Process Flow ChartDocument22 pagesProcess Flow ChartKumar Ashutosh100% (1)
- TPP Steel PlantDocument25 pagesTPP Steel PlantPRASANTHNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator Freezer: Owner's ManualDocument22 pagesRefrigerator Freezer: Owner's ManualthaiNo ratings yet
- Error - Failed To Compute Elastoplastic Strain Variables - 1150 - Knowledge Base PDFDocument3 pagesError - Failed To Compute Elastoplastic Strain Variables - 1150 - Knowledge Base PDFmatinNo ratings yet
- Brac Bank LimitedDocument1 pageBrac Bank LimitedMd Mojibar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming TheoryDocument104 pagesLinear Programming Theorykostas_ntougias5453No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S096098221730708X MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S096098221730708X Mainrotinda bilekNo ratings yet
- On Arushi Murder CaseDocument8 pagesOn Arushi Murder Case0000No ratings yet
- Michigan Strategic Compliance Plan FINALDocument22 pagesMichigan Strategic Compliance Plan FINALbcap-oceanNo ratings yet
- Tacha's ReusmeDocument2 pagesTacha's ReusmeJames HamptonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Discipline of Systems EngineeringDocument31 pagesChapter 1: The Discipline of Systems EngineeringTrixiNo ratings yet
- Shortest Route ProblemDocument7 pagesShortest Route ProblemkaushalmightyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6 Solar ERGY 420Document14 pagesAssignment 6 Solar ERGY 420Mostafa Ahmed ZeinNo ratings yet
- Planificare Calendaristică Anuală Pentru Limba Modernă 1 - Studiu Intensiv. Engleză. Clasa A Vi-ADocument6 pagesPlanificare Calendaristică Anuală Pentru Limba Modernă 1 - Studiu Intensiv. Engleză. Clasa A Vi-Acatalina marinoiuNo ratings yet
- Update Instructions Safety Update - CL092/20/S: Test Definition Version 1.0.EL/EM (System Version 7.1.1.2 and Higher)Document88 pagesUpdate Instructions Safety Update - CL092/20/S: Test Definition Version 1.0.EL/EM (System Version 7.1.1.2 and Higher)esther jaimeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ICT ExcelDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ICT ExcelColleen Vender100% (3)
- Productivity and Leadership SkillsDocument22 pagesProductivity and Leadership SkillsDan Jezreel EsguerraNo ratings yet
- ECE 5325/6325 Fall 2009: Exam 1 SolutionsDocument2 pagesECE 5325/6325 Fall 2009: Exam 1 Solutionswilfred godfreyNo ratings yet
- 3126E Engine: Electrical Circuit DiagramDocument10 pages3126E Engine: Electrical Circuit DiagramPhil B.No ratings yet
- Geostr C: Engineering and Testing ServicesDocument2 pagesGeostr C: Engineering and Testing ServicesTechnical Priyanka GroupNo ratings yet
- Ril Sa71m15017693 R00Document5 pagesRil Sa71m15017693 R00Android100% (1)
- Item Part No Location No - Available No. Used Remaining Min No. Required Reordered No Cost Per Item Total CostDocument1 pageItem Part No Location No - Available No. Used Remaining Min No. Required Reordered No Cost Per Item Total CostRockyNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalogue: AXLE 26.18 - (CM8118) REF: 133821Document8 pagesSpare Parts Catalogue: AXLE 26.18 - (CM8118) REF: 133821Paulinho InformáticaNo ratings yet
- Razones de CambioDocument1 pageRazones de CambioCarlos FloresNo ratings yet