Professional Documents
Culture Documents
05 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 5 Mark Scheme
05 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 5 Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
Supreme KingCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- A Level Further Mechanics 1 MS 2023Document24 pagesA Level Further Mechanics 1 MS 2023lakhtariyavedNo ratings yet
- MYP M21 Mathematics English MSDocument26 pagesMYP M21 Mathematics English MSJohn100% (1)
- A Level Pure Maths Unit Test 4 Mark SchemeDocument9 pagesA Level Pure Maths Unit Test 4 Mark Schemelauren67% (3)
- AS Pure Unit 2 Coordinate Geometry in The (X, Y) Plane MSDocument7 pagesAS Pure Unit 2 Coordinate Geometry in The (X, Y) Plane MSsaNo ratings yet
- 03 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 3 Mark SchemeDocument21 pages03 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 3 Mark SchemeFox HendersonNo ratings yet
- AL Maths Pure Unit 1 MSDocument11 pagesAL Maths Pure Unit 1 MSjim0% (1)
- Topical Revision Notes Additional Mathematics O Level PDFDocument186 pagesTopical Revision Notes Additional Mathematics O Level PDFShamvil Raza100% (6)
- Y2 Pure Proof by Contradiction Exam Questions MsDocument6 pagesY2 Pure Proof by Contradiction Exam Questions Ms陈家乐No ratings yet
- 07 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 7 Mark SchemeDocument18 pages07 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 7 Mark Schemealexander.tarakanovNo ratings yet
- A Level Mathematics Practice Paper F - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeDocument17 pagesA Level Mathematics Practice Paper F - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeZaka AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Practice Questions Mark Scheme: Pearson Edexcel GCE in Mathematics (9MA0)Document34 pagesPure Mathematics Practice Questions Mark Scheme: Pearson Edexcel GCE in Mathematics (9MA0)james rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Algebraic-and-partial-fractions-MS.docx 3Document10 pagesAlgebraic-and-partial-fractions-MS.docx 3spuddylouNo ratings yet
- GCSE 1MA1 - Algebraic Proof Mark SchemeDocument13 pagesGCSE 1MA1 - Algebraic Proof Mark SchemeArchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark SchemeDocument22 pages06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark Schemealexander.tarakanovNo ratings yet
- 11 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 11 Mark SchemeDocument13 pages11 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 11 Mark Schemealexander.tarakanovNo ratings yet
- 04 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 4 Mark SchemeDocument18 pages04 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 4 Mark SchemeSupreme KingNo ratings yet
- 02 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 2 Mark Scheme 1Document19 pages02 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 2 Mark Scheme 1Supreme KingNo ratings yet
- Alevel Ut m1 U8 MarkschemeDocument6 pagesAlevel Ut m1 U8 Markschemeiwan.fothergillNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Baseline Test Mark Scheme - Non-CalculatorDocument3 pagesYear 9 Baseline Test Mark Scheme - Non-CalculatorMasnoon MorshedNo ratings yet
- A Level Mathematics Practice Paper Q - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeDocument13 pagesA Level Mathematics Practice Paper Q - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeShreyNo ratings yet
- MS Binomial Expansion WSDocument4 pagesMS Binomial Expansion WS11178No ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 21Document5 pages9709 w16 Ms 21yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Mathematics 6360Document4 pagesMark Scheme: Mathematics 6360Özgür Oz Yilmaz MehmetNo ratings yet
- Proof by Contradition (A-Level Only)Document6 pagesProof by Contradition (A-Level Only)/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Supplementary Notes On Partial FractionsDocument10 pagesSupplementary Notes On Partial FractionsMmatshepo Molefe Waha MofokengNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper2Document99 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper2Saket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Mathematics 6360Document5 pagesMark Scheme: Mathematics 6360Ayshy ShuruNo ratings yet
- WME Mathematics Advanced Preliminary Solutions 2019Document32 pagesWME Mathematics Advanced Preliminary Solutions 2019Sebastian YoungNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument5 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International ExaminationsHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- G9 Unit 2 Formative Criteria A Questions and Worked AnswersDocument8 pagesG9 Unit 2 Formative Criteria A Questions and Worked Answersengabd345No ratings yet
- 2023 TRIAL SMKJT Math (T) P2 QADocument8 pages2023 TRIAL SMKJT Math (T) P2 QAChin Ling ChiengNo ratings yet
- Sample MSDocument16 pagesSample MShasantheboss9No ratings yet
- Practice Paper C MsDocument17 pagesPractice Paper C MsKostas KostaNo ratings yet
- MAT Paper 1 Mark SchemeDocument31 pagesMAT Paper 1 Mark Schememiatomlin93No ratings yet
- Note 6Document7 pagesNote 6Jiasheng NiNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper1Document124 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper1ishaanNo ratings yet
- CRW 5. Factors and Polynomials MarkSchemeDocument8 pagesCRW 5. Factors and Polynomials MarkSchemeMahdi TasninNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 22Document7 pages9709 w16 Ms 22yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Vectors (H) MSDocument9 pagesVectors (H) MSPujan PatelNo ratings yet
- 01b A Level Mathematics Practice Paper A - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeDocument17 pages01b A Level Mathematics Practice Paper A - Pure Mathematics Mark Schemejotpalak5No ratings yet
- 2306 8FM0-23 AS Further Statistics 1 - June 2023 Mark Scheme PDFDocument11 pages2306 8FM0-23 AS Further Statistics 1 - June 2023 Mark Scheme PDFsol.proctertarabanovNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument12 pagesMark SchemeChanYuYanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Practice Feb 2Document5 pagesMark Scheme Practice Feb 2Owin Nolan GunawanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Forces MSDocument7 pagesApplications of Forces MSjunkthingsandspamandstuffNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument7 pagesMark SchemenazmulNo ratings yet
- PSM1 - Jan 2019 MS PDFDocument14 pagesPSM1 - Jan 2019 MS PDFTae Young ChoiNo ratings yet
- 04b Angles Proof - H - Mark SchemeDocument6 pages04b Angles Proof - H - Mark SchemeAbhinNo ratings yet
- 01.unit-Test 2 MSDocument2 pages01.unit-Test 2 MS185359No ratings yet
- Rev Vectors Paper 1 MSDocument13 pagesRev Vectors Paper 1 MSmac richNo ratings yet
- Y8 End of Year Mark Scheme - Non-CalculatorDocument4 pagesY8 End of Year Mark Scheme - Non-CalculatorKateNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Mid Year 2017 P1Document14 pagesYear 1 Mid Year 2017 P1Viet Quoc HoangNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper 9709Document9 pagesExam Paper 9709MayaNo ratings yet
- A-Levels Mathematics 2004 AnswersDocument20 pagesA-Levels Mathematics 2004 Answersalexiowellington1No ratings yet
- Eecs 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2019 Exam Location: Cory 144MA (DSP)Document46 pagesEecs 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2019 Exam Location: Cory 144MA (DSP)Annabel YauNo ratings yet
- February Mock Decision Exam Mark Scheme 1Document8 pagesFebruary Mock Decision Exam Mark Scheme 1kayef26110No ratings yet
- 4 Maths MsDocument3 pages4 Maths MsAbhay KaushalNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 MATH EASTER Mid Term Worksheet 2023Document2 pagesGRADE 10 MATH EASTER Mid Term Worksheet 2023Elena LoveNo ratings yet
- 8FM0-22 AS Further Pure Mathematics 2 Mark Scheme (Student-Friendly)Document6 pages8FM0-22 AS Further Pure Mathematics 2 Mark Scheme (Student-Friendly)ArjanSSNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Part 2 MSDocument53 pagesTopic 10 Part 2 MSHAN SEUL SHIMNo ratings yet
- 06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark SchemeDocument22 pages06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark Schemealexander.tarakanovNo ratings yet
- BA 501 Chapter 4 Partial FractionsDocument24 pagesBA 501 Chapter 4 Partial FractionsUdin AnuarNo ratings yet
- M 307 Laplace Fact SheetDocument3 pagesM 307 Laplace Fact Sheetstephannie montoyaNo ratings yet
- Integrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofDocument5 pagesIntegrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofuditagarwal1997No ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics: (Syllabus 4047)Document12 pagesAdditional Mathematics: (Syllabus 4047)clarissay_1No ratings yet
- ADSP Lab Manual JinishaDocument72 pagesADSP Lab Manual JinishaVIDHI YADAVNo ratings yet
- GATE Signals and Systems by KanodiaDocument128 pagesGATE Signals and Systems by Kanodiakaran11383% (6)
- BiotechDocument112 pagesBiotechMohan Kumar SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Continuous and Discrete Time Signals and Systems Mandal Asif Solutions Chap06 PDFDocument39 pagesContinuous and Discrete Time Signals and Systems Mandal Asif Solutions Chap06 PDFroronoaNo ratings yet
- Materi Matematika Teknik 5Document5 pagesMateri Matematika Teknik 5Maulana HyzbullahNo ratings yet
- C8A Integration Techniques Add Practice (QN)Document3 pagesC8A Integration Techniques Add Practice (QN)wan yangNo ratings yet
- 7 - 4 Partial FractionsDocument16 pages7 - 4 Partial Fractionstinotenda zirevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Modeling in The Frequency Domain Partial Fraction-Expansion Case 1 Ex. 2.3Document4 pagesChapter 2 Modeling in The Frequency Domain Partial Fraction-Expansion Case 1 Ex. 2.3Joy Rizki Pangestu DjuansjahNo ratings yet
- Math-102-Section-8.5-L52-with SolutionDocument16 pagesMath-102-Section-8.5-L52-with SolutionGharsellaoui MuhamedNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics: Reynante T. CiruelaDocument87 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics: Reynante T. CiruelaNoel Saycon Jr.No ratings yet
- 1 - (Partial Fraction)Document7 pages1 - (Partial Fraction)Muhammad RakibNo ratings yet
- The Inverse Z TransformDocument3 pagesThe Inverse Z TransformGuilherme NardezNo ratings yet
- AppendixDocument16 pagesAppendixSushant YadavNo ratings yet
- VCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceDocument17 pagesVCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceMikiNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument6 pagesMATHEMATICSmohitniks1648No ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document8 pagesExperiment 1Ian Arnold FamiNo ratings yet
- Cal Reform 2Document237 pagesCal Reform 2abbas zaidiNo ratings yet
- Scope of Diploma in Mechanical EngineeringDocument160 pagesScope of Diploma in Mechanical Engineeringmohd_irfansalarNo ratings yet
- Unit One Mathematical EconomicsDocument15 pagesUnit One Mathematical EconomicsSitra AbduNo ratings yet
- Expansion Into Partial FractionsDocument6 pagesExpansion Into Partial FractionsMiguel SantillanNo ratings yet
- P3 Classwork Book Session 2020-2021Document314 pagesP3 Classwork Book Session 2020-2021Asad KingNo ratings yet
- BBMP1103 Mathematics For MGT (V Apr18) BookmarkDocument249 pagesBBMP1103 Mathematics For MGT (V Apr18) BookmarkFoo Shu FongNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Transfer Function of Physical SystemsDocument108 pagesControl Systems Theory: Transfer Function of Physical SystemsMelanieNo ratings yet
05 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 5 Mark Scheme
05 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 5 Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
Supreme KingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
05 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 5 Mark Scheme
05 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 5 Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
Supreme KingCopyright:
Available Formats
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
1 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
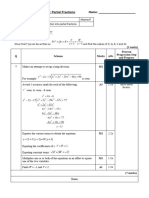
Makes an attempt to factor all the quadratics on the left-hand M1 2.2a 5th
side of the identity.
Simplify
algebraic
Correctly factors each expression on the left-hand side of the A1 2.2a
fractions.
identity:
Successfully cancels common factors: M1 1.1b
M1 1.1b
States that
States or implies that A = 2, B = −9 and C = −18 A1 1.1b
(5 marks)
Notes
Alternative method
Makes an attempt to substitute x = 0 (M1)
Finds C = −18 (A1)
Substitutes x = 1 to give A + B = −7 (M1)
Substitutes x = −1 to give A − B = 11 (M1)
Solves to get A = 2, B = −9 and C = −18 (A1)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 1
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
2 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) Begins the proof by assuming the opposite is true. B1 3.1 7th
‘Assumption: there exists a number n such that n2 is even and n Complete proofs
is odd.’ using proof by
contradiction.
Defines an odd number (choice of variable is not important) and M1 2.2a
successfully calculates n2
Let 2k + 1 be an odd number.
Factors the expression and concludes that this number must be M1 1.1b
odd.
, so n2 is odd.
Makes a valid conclusion. B1 2.4
2 2
This contradicts the assumption n is even. Therefore if n is
even, n must be even.
(4)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 2
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
(b) Begins the proof by assuming the opposite is true. B1 3.1 7th
Complete proofs
‘Assumption: is a rational number.’ using proof by
contradiction.
Defines the rational number: M1 2.2a
for some integers a and b, where a and b have no
common factors.
Squares both sides and concludes that a is even: M1 1.1b
From part a: a2 is even implies that a is even.
Further states that if a is even, then a = 2c. Choice of variable is M1 1.1b
not important.
Makes a substitution and works through to find , M1 1.1b
concluding that b is also even.
From part a: b2 is even implies that b is even.
Makes a valid conclusion. B1 2.4
If a and b are even, then they have a common factor of 2, which
contradicts the statement that a and b have no common factors.
Therefore is an irrational number.
(6)
(10 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 3
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
3 Scheme Marks AOs Pearson
Progression Step
and Progress
descriptor
(a) Correctly states that M1 2.2a 6th
Understand the
binomial theorem
for rational n.
M1 1.1b
Simplifies to obtain …
Deduces that M1 2.2a
Solves to find A1 1.1b
(4)
(b) A1 1.1b 6th
. Award mark for –500 seen.
Understand the
A1 1.1b binomial theorem
. Award mark for 500 seen. for rational n.
(2)
(6 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 4
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
4 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) M1 3.1b 5th
States Differentiate
simple
Makes correct substitutions: M1 1.1b trigonometric
functions.
Uses the appropriate trigonometric addition formula to write M1 2.2a
Groups the terms appropriately A1 2.2a
(4)
(b) M1 3.2b 5th
Explains that as h → 0, and Differentiate
simple
Concludes that this leaves A1 3.2b trigonometric
functions.
So if
(2)
(6 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 5
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
5 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
M1 1.1b 6th
Makes an attempt to find . Raising the power by Integrate using
1 would constitute an attempt. the reverse chain
rule.
A1 2.2a
Correctly states
M1 ft 1.1b
States
Makes an attempt to solve this equation. For example, M1 ft 1.1b
or is seen.
A1 ft 1.1b
Solves to find
(5 marks)
Notes
Student does not need to state ‘+C’ in an answer unless it is the final answer to an indefinite integral.
Award ft marks for a correct answer using an incorrect initial answer.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 6
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
6 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
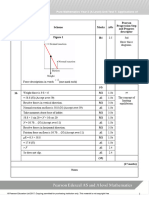
(a) M1 1.1b 5th
Rearranges to find Understand the
concept of roots
A1 1.1b of equations.
States and therefore and or states
(2)
(b) Attempts to use iterative procedure to find subsequent values. M1 1.1b 6th
Solve equations
Correctly finds: A1 1.1b
approximately
using the method
of iteration.
(2)
(c) Demonstrates an understanding that the two values of f(x) to be M1* 2.2a 5th
calculated are for x = –2.7815 and x = –2.7825.
Use a change of
sign to locate
Finds and M1 1.1b
roots.
Change of sign and continuous function in the interval A1 2.4
root
(3)
(7 marks)
Notes
(b) Award M1 if finds at least one correct answer.
(c) Any two numbers that produce a change of sign, where one is greater than –2.782 and one is less than
–2.782, and both numbers round to –2.782 to 3 decimal places, are acceptable. Minimum required is that answer
states there is a sign change in the interval and that this implies a root in the given interval.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 7
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
7 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) Makes an attempt to find . For example, writing M1 2.2a 5th
Find composite
functions.
M1 1.1b
Uses the law of logarithms to write
A1 1.1b
States that
States that the range is or B1 3.2b
(4)
(b) M1 1.1b 5th
States that
Find the domain
Makes an attempt to solve for x, including attempting to take M1 1.1b and range of
the square root of both sides of the equation. For example, composite
functions.
States that x = 8. Does not need to state that , but do A1 3.2b
not award the mark if x = −10 is stated.
(3)
(7 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 8
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
8 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) Forms a pair of simultaneous equations, using the given values M1 2.2a 4th
Understand
simple arithmetic
sequences.
Correctly solves to find d = −6 A1 1.1b
Finds a = 116 A1 1.1b
A1 1.1b
Uses to find
(4)
(b) Uses the sum of an arithmetic series to form the equation M1 ft 2.2a 5th
Understand
simple arithmetic
series.
Successfully multiplies out the brackets and simplifies. Fully M1 ft 1.1b
simplified quadratic of is seen or
is seen.
M1 ft 1.1b
Correctly factorises:
States that n = 39 is the correct answer. A1 1.1b
(4)
(8 marks)
Notes
(a) Can use elimination or substitution to solve the simultaneous equations.
(b) Award method marks for a correct attempt to solve the equation using their incorrect values from part a.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 9
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
9 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
M1 3.1 6th
States that and concludes that Prove
sec2x = 1 + tan2x
M1 3.1 and
cosec2x = 1 + cot2x.
States that and concludes that
States that M1 2.2a
M1 3.1
States that and concludes that oe.
M1 3.1
States that and concludes that oe.
Recognises the need to use Pythagoras’ theorem. For example, M1 2.2a
Makes substitutions and begins to manipulate the equation: M1 1.1b
Uses a clear algebraic progression to arrive at the final answer: A1 1.1b
(8 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 10
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
10 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) Makes an attempt to find the resultant force by adding the three M1 3.1a 6th
force vectors together.
Solve
contextualised
A1 1.1b
Finds problems in
mechanics using
3D vectors.
(2)
(b) M1 3.1a 6th
States or writes
Solve
A1 1.1b contextualised
Finds problems in
mechanics using
3D vectors.
(2)
(c) M1 3.1a 6th
Demonstrates an attempt to find
Solve
contextualised
For example, problems in
mechanics using
A1 1.1b 3D vectors.
Finds m s−2
(2)
(d) M1 3.1a 6th
States Solve
contextualised
Makes an attempt to substitute values into the equation. M1 ft 1.1b problems in
mechanics using
3D vectors.
A1 ft 1.1b
Finds m
(3)
(9 marks)
Notes
(d) Award ft marks for a correct answer to part d using their incorrect answer from part c.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 11
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 12
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
11 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
Equating the coefficients of x4: A = 5 A1 2.2a 6th
Solve problems
Equating the coefficients of x3: B = −4 A1 1.1b
using the
remainder
Equating the coefficients of x2: 2A + C = 17, C = 7 A1 1.1b
theorem linked to
improper
Equating the coefficients of x: 2B + D = −5, D = 3 A1 1.1b
algebraic
fractions.
Equating constant terms: 2C + E = 7, E = −7 A1 1.1b
(5 marks)
Notes
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 13
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
12 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) States that M1 1.1b 6th
Decompose
algebraic
fractions into
Equates the various terms. M1 1.1b
partial fractions −
Equating xs linear factors.
Equating numbers
Multiplies or or both of the equations in an effort to equate one M1 1.1b
of the two variables.
Finds A = 5 A1 1.1b
Find B = 6 A1 1.1b
(5)
(b) M1 ft 2.2a 6th
Integrate
Writes as functions using
the reverse chain
rule.
Makes an attempt to integrate the expression. Attempt would M1 ft 2.2a
constitute the use of logarithms.
A1 ft 1.1b
Integrates the expression to find
Makes an attempt to substitute the limits M1 ft 1.1b
A1 ft 1.1b
Simplifies to find o.e.
(5)
(10 marks)
Notes
Award ft marks for a correct answer to part b using incorrect values from part a.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 14
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 15
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
Pearson
Progression Step
13 Scheme Marks AOs
and Progress
descriptor
(a) Shows or implies that if y = 0, t = 1 M1 1.1b 7th
Solve coordinate
Finds the coordinates of P. A1 1.1b
geometry
problems
involving
parametric
equations.
(2)
(b) Attempts to find a cartesian equation of the curve. For example, M1 2.2a 7th
Solve coordinate
t = x − 2 is substituted into geometry
problems
A1 1.1b involving
parametric
Correctly finds the cartesian equation of the curve
equations.
Accept any equivalent answer. For example,
(2)
(c) M1 2.2a 7th
Finds Solve coordinate
geometry
M1 1.1b problems
involving
Substitutes t = −1 to find x = 1 and parametric
equations.
M1 1.1b
Finds the gradient of the normal
Substitutes t = −1 to find x = 1 and y = −2 A1 1.1b
Makes an attempt to find the equation of the normal. For M1 1.1b
example, is seen.
States fully correct answer A1 1.1b
(6)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 16
A level Pure Maths: Practice Set 5 mark scheme
(d) M1 ft 2.2a 7th
Substitutes and into obtaining Solve coordinate
geometry
problems
involving
parametric
Manipulates and simplifies this equation to obtain M1 ft 1.1b
equations.
Factorises and solves to find t = −1 or t = −11 M1 ft 1.1b
A1 ft 1.1b
Substitutes t = −11 to find x = −9 and , i.e.
(4)
(14 marks)
Notes
(c) Award ft marks for correct answer using incorrect values from part b.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2018 17
You might also like
- A Level Further Mechanics 1 MS 2023Document24 pagesA Level Further Mechanics 1 MS 2023lakhtariyavedNo ratings yet
- MYP M21 Mathematics English MSDocument26 pagesMYP M21 Mathematics English MSJohn100% (1)
- A Level Pure Maths Unit Test 4 Mark SchemeDocument9 pagesA Level Pure Maths Unit Test 4 Mark Schemelauren67% (3)
- AS Pure Unit 2 Coordinate Geometry in The (X, Y) Plane MSDocument7 pagesAS Pure Unit 2 Coordinate Geometry in The (X, Y) Plane MSsaNo ratings yet
- 03 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 3 Mark SchemeDocument21 pages03 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 3 Mark SchemeFox HendersonNo ratings yet
- AL Maths Pure Unit 1 MSDocument11 pagesAL Maths Pure Unit 1 MSjim0% (1)
- Topical Revision Notes Additional Mathematics O Level PDFDocument186 pagesTopical Revision Notes Additional Mathematics O Level PDFShamvil Raza100% (6)
- Y2 Pure Proof by Contradiction Exam Questions MsDocument6 pagesY2 Pure Proof by Contradiction Exam Questions Ms陈家乐No ratings yet
- 07 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 7 Mark SchemeDocument18 pages07 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 7 Mark Schemealexander.tarakanovNo ratings yet
- A Level Mathematics Practice Paper F - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeDocument17 pagesA Level Mathematics Practice Paper F - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeZaka AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Practice Questions Mark Scheme: Pearson Edexcel GCE in Mathematics (9MA0)Document34 pagesPure Mathematics Practice Questions Mark Scheme: Pearson Edexcel GCE in Mathematics (9MA0)james rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Algebraic-and-partial-fractions-MS.docx 3Document10 pagesAlgebraic-and-partial-fractions-MS.docx 3spuddylouNo ratings yet
- GCSE 1MA1 - Algebraic Proof Mark SchemeDocument13 pagesGCSE 1MA1 - Algebraic Proof Mark SchemeArchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark SchemeDocument22 pages06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark Schemealexander.tarakanovNo ratings yet
- 11 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 11 Mark SchemeDocument13 pages11 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 11 Mark Schemealexander.tarakanovNo ratings yet
- 04 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 4 Mark SchemeDocument18 pages04 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 4 Mark SchemeSupreme KingNo ratings yet
- 02 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 2 Mark Scheme 1Document19 pages02 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 2 Mark Scheme 1Supreme KingNo ratings yet
- Alevel Ut m1 U8 MarkschemeDocument6 pagesAlevel Ut m1 U8 Markschemeiwan.fothergillNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Baseline Test Mark Scheme - Non-CalculatorDocument3 pagesYear 9 Baseline Test Mark Scheme - Non-CalculatorMasnoon MorshedNo ratings yet
- A Level Mathematics Practice Paper Q - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeDocument13 pagesA Level Mathematics Practice Paper Q - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeShreyNo ratings yet
- MS Binomial Expansion WSDocument4 pagesMS Binomial Expansion WS11178No ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 21Document5 pages9709 w16 Ms 21yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Mathematics 6360Document4 pagesMark Scheme: Mathematics 6360Özgür Oz Yilmaz MehmetNo ratings yet
- Proof by Contradition (A-Level Only)Document6 pagesProof by Contradition (A-Level Only)/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Supplementary Notes On Partial FractionsDocument10 pagesSupplementary Notes On Partial FractionsMmatshepo Molefe Waha MofokengNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper2Document99 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper2Saket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Mathematics 6360Document5 pagesMark Scheme: Mathematics 6360Ayshy ShuruNo ratings yet
- WME Mathematics Advanced Preliminary Solutions 2019Document32 pagesWME Mathematics Advanced Preliminary Solutions 2019Sebastian YoungNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument5 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International ExaminationsHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- G9 Unit 2 Formative Criteria A Questions and Worked AnswersDocument8 pagesG9 Unit 2 Formative Criteria A Questions and Worked Answersengabd345No ratings yet
- 2023 TRIAL SMKJT Math (T) P2 QADocument8 pages2023 TRIAL SMKJT Math (T) P2 QAChin Ling ChiengNo ratings yet
- Sample MSDocument16 pagesSample MShasantheboss9No ratings yet
- Practice Paper C MsDocument17 pagesPractice Paper C MsKostas KostaNo ratings yet
- MAT Paper 1 Mark SchemeDocument31 pagesMAT Paper 1 Mark Schememiatomlin93No ratings yet
- Note 6Document7 pagesNote 6Jiasheng NiNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper1Document124 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper1ishaanNo ratings yet
- CRW 5. Factors and Polynomials MarkSchemeDocument8 pagesCRW 5. Factors and Polynomials MarkSchemeMahdi TasninNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 22Document7 pages9709 w16 Ms 22yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Vectors (H) MSDocument9 pagesVectors (H) MSPujan PatelNo ratings yet
- 01b A Level Mathematics Practice Paper A - Pure Mathematics Mark SchemeDocument17 pages01b A Level Mathematics Practice Paper A - Pure Mathematics Mark Schemejotpalak5No ratings yet
- 2306 8FM0-23 AS Further Statistics 1 - June 2023 Mark Scheme PDFDocument11 pages2306 8FM0-23 AS Further Statistics 1 - June 2023 Mark Scheme PDFsol.proctertarabanovNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument12 pagesMark SchemeChanYuYanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Practice Feb 2Document5 pagesMark Scheme Practice Feb 2Owin Nolan GunawanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Forces MSDocument7 pagesApplications of Forces MSjunkthingsandspamandstuffNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument7 pagesMark SchemenazmulNo ratings yet
- PSM1 - Jan 2019 MS PDFDocument14 pagesPSM1 - Jan 2019 MS PDFTae Young ChoiNo ratings yet
- 04b Angles Proof - H - Mark SchemeDocument6 pages04b Angles Proof - H - Mark SchemeAbhinNo ratings yet
- 01.unit-Test 2 MSDocument2 pages01.unit-Test 2 MS185359No ratings yet
- Rev Vectors Paper 1 MSDocument13 pagesRev Vectors Paper 1 MSmac richNo ratings yet
- Y8 End of Year Mark Scheme - Non-CalculatorDocument4 pagesY8 End of Year Mark Scheme - Non-CalculatorKateNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Mid Year 2017 P1Document14 pagesYear 1 Mid Year 2017 P1Viet Quoc HoangNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper 9709Document9 pagesExam Paper 9709MayaNo ratings yet
- A-Levels Mathematics 2004 AnswersDocument20 pagesA-Levels Mathematics 2004 Answersalexiowellington1No ratings yet
- Eecs 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2019 Exam Location: Cory 144MA (DSP)Document46 pagesEecs 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2019 Exam Location: Cory 144MA (DSP)Annabel YauNo ratings yet
- February Mock Decision Exam Mark Scheme 1Document8 pagesFebruary Mock Decision Exam Mark Scheme 1kayef26110No ratings yet
- 4 Maths MsDocument3 pages4 Maths MsAbhay KaushalNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 MATH EASTER Mid Term Worksheet 2023Document2 pagesGRADE 10 MATH EASTER Mid Term Worksheet 2023Elena LoveNo ratings yet
- 8FM0-22 AS Further Pure Mathematics 2 Mark Scheme (Student-Friendly)Document6 pages8FM0-22 AS Further Pure Mathematics 2 Mark Scheme (Student-Friendly)ArjanSSNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Part 2 MSDocument53 pagesTopic 10 Part 2 MSHAN SEUL SHIMNo ratings yet
- 06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark SchemeDocument22 pages06 9MA0 01 9MA0 02 A Level Pure Mathematics Practice Set 6 Mark Schemealexander.tarakanovNo ratings yet
- BA 501 Chapter 4 Partial FractionsDocument24 pagesBA 501 Chapter 4 Partial FractionsUdin AnuarNo ratings yet
- M 307 Laplace Fact SheetDocument3 pagesM 307 Laplace Fact Sheetstephannie montoyaNo ratings yet
- Integrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofDocument5 pagesIntegrals: Definitions Definite Integral: Suppose Anti-Derivative: An Anti-Derivative ofuditagarwal1997No ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics: (Syllabus 4047)Document12 pagesAdditional Mathematics: (Syllabus 4047)clarissay_1No ratings yet
- ADSP Lab Manual JinishaDocument72 pagesADSP Lab Manual JinishaVIDHI YADAVNo ratings yet
- GATE Signals and Systems by KanodiaDocument128 pagesGATE Signals and Systems by Kanodiakaran11383% (6)
- BiotechDocument112 pagesBiotechMohan Kumar SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Continuous and Discrete Time Signals and Systems Mandal Asif Solutions Chap06 PDFDocument39 pagesContinuous and Discrete Time Signals and Systems Mandal Asif Solutions Chap06 PDFroronoaNo ratings yet
- Materi Matematika Teknik 5Document5 pagesMateri Matematika Teknik 5Maulana HyzbullahNo ratings yet
- C8A Integration Techniques Add Practice (QN)Document3 pagesC8A Integration Techniques Add Practice (QN)wan yangNo ratings yet
- 7 - 4 Partial FractionsDocument16 pages7 - 4 Partial Fractionstinotenda zirevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Modeling in The Frequency Domain Partial Fraction-Expansion Case 1 Ex. 2.3Document4 pagesChapter 2 Modeling in The Frequency Domain Partial Fraction-Expansion Case 1 Ex. 2.3Joy Rizki Pangestu DjuansjahNo ratings yet
- Math-102-Section-8.5-L52-with SolutionDocument16 pagesMath-102-Section-8.5-L52-with SolutionGharsellaoui MuhamedNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics: Reynante T. CiruelaDocument87 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics: Reynante T. CiruelaNoel Saycon Jr.No ratings yet
- 1 - (Partial Fraction)Document7 pages1 - (Partial Fraction)Muhammad RakibNo ratings yet
- The Inverse Z TransformDocument3 pagesThe Inverse Z TransformGuilherme NardezNo ratings yet
- AppendixDocument16 pagesAppendixSushant YadavNo ratings yet
- VCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceDocument17 pagesVCE Unit 1 Specialist Maths Bound ReferenceMikiNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument6 pagesMATHEMATICSmohitniks1648No ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document8 pagesExperiment 1Ian Arnold FamiNo ratings yet
- Cal Reform 2Document237 pagesCal Reform 2abbas zaidiNo ratings yet
- Scope of Diploma in Mechanical EngineeringDocument160 pagesScope of Diploma in Mechanical Engineeringmohd_irfansalarNo ratings yet
- Unit One Mathematical EconomicsDocument15 pagesUnit One Mathematical EconomicsSitra AbduNo ratings yet
- Expansion Into Partial FractionsDocument6 pagesExpansion Into Partial FractionsMiguel SantillanNo ratings yet
- P3 Classwork Book Session 2020-2021Document314 pagesP3 Classwork Book Session 2020-2021Asad KingNo ratings yet
- BBMP1103 Mathematics For MGT (V Apr18) BookmarkDocument249 pagesBBMP1103 Mathematics For MGT (V Apr18) BookmarkFoo Shu FongNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Transfer Function of Physical SystemsDocument108 pagesControl Systems Theory: Transfer Function of Physical SystemsMelanieNo ratings yet