Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integumentary System
Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Jhana SamsonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Integumentary System
Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Jhana SamsonCopyright:
Available Formats
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LEC:
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
MAGALLANES JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- TERM 02- MIDTERMS
CONTENT 4. Excretion – releases small
amounts of waste products with
LESSON 06: INTEGUMENTARY sweat.
SYSTEM 5. Vitamin D Production – important
regulator of calcium homeostasis.
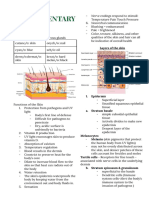
- Integumentary System
and its Functions PARTS OF THE SKIN
- The skin
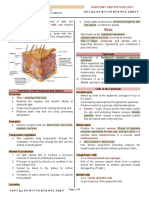
A. Layers of the skin - Epidermis + Dermis
B. Cells found in the - Hypodermis is not part of the skin
Dermis - Derm means skin
C. Layers of the Epidermis
D. Layer of the Dermis LAYERS OF THE SKIN
- Accessory of the Skin
Structure
- Skin Pathologies
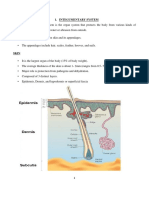
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
- Includes the skin and accessory
organs such as the hair, nails, and
glands.
- Integument means covering.
- The appearance of the
Integumentary System can Epidermis
determine or indicate physiological - It is the superficial layer of the skin
imbalances in the body. that prevents later loss and resists
- Skin – Largest organ of the body in abrasions.
terms of weight - above the Dermis
Functions - Avascular (no blood vessels)
1. Protection against abrasions, - Stratified squamous epithelium
ultraviolet rays, and - Keratinization – cells become filled
microorganisms from entering the with keratin protein that makes
body. them more rigid and durable.
2. Sensation – Detect heat, cold, pain, - Strata – layers of the skin
pressure, touch.
3. Temperature Regulation – activity Cells found in the Epidermis
of sweat glands and blood flow 1. Keratinocytes
help in regulating body - 90% of epidermal cells
- Produces keratin
temperature.
MAGALLANES, JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- BSMT MED212
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LEC:
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
MAGALLANES JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- TERM 02- MIDTERMS
- Releases Lamellar granules – 3. Stratum Granulosum
water repellant and prevents - 3 to 5 layers of flattened
dehydration keratinocytes
2. Melanocytes - Under Apoptosis – programed cell
- Produces Melanin – color pigment, death
protection against UV rays - Contains Lamellar granules and
- Albinism – recessive genetic trait keratohyalin-intermediate
that causes deficiency or absence filaments.
of melanin. 4. Stratum Lucidum
- Melasma – a skin condition, - 4 to 6 layers of keratinocytes
usually during pregnancy, - Thick and hairless skin
characterized by brown or blue- 5. Stratum Corneum
gray patches or freckle-like spots - Most superficial layer
caused by overproduction of cells. - Aka “horny cells”
- Cyanosis – decrease in blood - 25 to 30 layers of dead squamous
oxygen producing an bluish color cells
on the skin • Carotene – lipid - Examples: callus, dandruff, corns –
soluble yellow pigment callus on top of bony prominences
3. Epidermal Macrophages / Langerhans
Cells
- Responsible for immune response
- Act as the outermost guard of the
cutaneous immune system and
are likely to induce the first
reactions against pathogens
encountered via the skin.
4. Tactile Epithelial Cells / Merkel Cells
- Tactile – touch
- Cells responsible for detecting
sensations.
Layers of the Epidermis Dermis
1. Stratum Basale - Composed of dense collagenous
- Deepest layer connective tissues that contains
- Cuboidal to columnar in shape fibroblasts, adipocytes, and
- Cells that are the most mitotically macrophages.
active. - Structural strength – collagen and
- Contains melanocytes and keratin elastic fibers
filaments - Cleavage / Tension Lines
2. Stratum Spinosum - fibers that are oriented in many
- 8 to 10 layers of flattened directions causing them to resist
keratinocytes stretching
- Contains intermediate filaments
and desmosomes.
MAGALLANES, JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- BSMT MED212
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LEC:
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
MAGALLANES JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- TERM 02- MIDTERMS
Layers of the Dermis Intravenous Injection
1. Papillary Layer / Dermal Papillae - Insertion of a thin tube, catheter,
- Contains many blood vessels that or needle into a vein and directly
supplies nutrients and removes to the bloodstream.
waste products. - IV Administration
- Ridges that cause finger and foot Subcutaneous Injection
prints. - Pinching the skin to form a tent
- Meissner Corpuscles – free nerve and inserting a short needle into
endings the adipose tissue.
2. Reticular Layer - Insulin Injection
- Contains collagen and elastic Intramuscular Injection
fibers that helps in resisting - Inserting a long needle at a 90-
stretch. degree angle to the skin into the
- Stretch marks – breakdown of muscle.
collagen - Most vaccine and antibiotics
- Sun-damaged Wrinkles
Hair
Hypodermis (Subcutaneous Layer) - Found everywhere on the skin
- Loosely arranged tissue that except the palms, soles, lips,
attaches the skin to the underlying nipples, parts of the genitals, and
bone. distal segments of the fingers and
- Contains Adipose tissues – storage toes.
of body’s lipids - Hair color is determined by varying
- Functions as padding and amounts of melanin.
insulation - Alopecia – is an autoimmune
disorder that causes your hair to
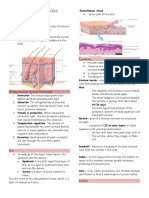
DIFFERENT TYPES OF INJECTIONS come out, often in clumps the size
and shape of a quarter. Can be
caused by: medication, stress, and
infections.
Parts
1. Hair Follicle – holds the hair (in place
2. Shaft
3. Root
4. Hair Bulb
5. Cortex
6. Medulla
7. Cuticle
Intradermal Injection
8. Hair Papilla – supply hair with
- Administered by inserting a needle nutrients needed to produce hair
at a shallow angle into the dermis
- Tuberculin skin test
MAGALLANES, JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- BSMT MED212
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LEC:
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
MAGALLANES JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- TERM 02- MIDTERMS
Glands
Sebaceous Glands
- Branched acinar glands that
produces sebum – oily, white
substance rich in lipids.
- The Sebum lubricates the hair and
surface of the skin, which prevents
drying and protects against some
bacteria.
Sweat Glands
1. Eccrine Sweat Glands
- Tubular
- Empties directly to the
Nail epidermis − Water with a
- It is a thin plate that consists of few salts
layers of dead stratum corneum - Palms and sole
cells that contains a very hard 2. Apocrine Sweat Glands
type of keratin - Produce a thick secretion
rich in organic substances.
Parts
- Protein sweat
1. Nail plate / Nail body – visible - Empties in the hair follicle
part of the nail - Groin, underarm, etc. −
2. Nail root puberty
3. Nail groove Manner of Secretion of Glands
4. Cuticle / Eponychium – stratum 1. Merocrine
corneum that extends onto the - Exocytosis
nail body. 2. Apocrine
5. Nail matrix - Apical portion gets pinched out
6. Nail Bed - Apo: A portion
7. Lunula – moon like, white part of 3. Holocrine
the nail - Entire cell rupture
- Hollo: whole
Skin Pathologies
Infections Fungal Infections
1. Superficial mycoses
a. Seborrheic Dermatitis
(Malassezia globosa) - dandruff
b. Tinea versicolor / Pityriasis – An-
an
c. Tinea nigra – mukhang dark spots
MAGALLANES, JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- BSMT MED212
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LEC:
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
MAGALLANES JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- TERM 02- MIDTERMS
2. Cutaneous mycoses 2 nd degree burn
a. Tinea pedis – althlete’s foot - Both the epidermis and dermis are
(alipunga) damaged
b. Tinea corporis – ringworm - Redness, pain, edema, and blisters
c. Tinea curis – jock itch (hadhad) 3 rd degree burn
d. Tinea capitis – ringworm of scalp - Epidermis and dermis are
e. Tinea unguium (onychomycosis) – completely destroyed
finger and toenails - Painless because sensory
3. Subcutaneous mycoses receptors are damaged
a. Sporotrichosis – cigar shaped - May appear white, brown, black,
yeast in tissue (causes by soil
tan, or deep cherry red
eme)
Skin Cancer
Bacterial Infection
- ABCD Rule
1. Acne – hair follicles become clogged - Asymmetry
with sebum - Border irregularity
2. Impetigo – reddish sores in face - Color
3. Carbuncle – boils and pus-filled - Diameter
bumps Basal Cell Carcinoma
4. Decubitus ulcer – pressure sore areas
- Least malignant
Viral Infection
- Stratum basale
1. Herpes Simplex virus – cold sores - Areas of skin exposed to the sun
2. Human Papilloma virus – causes Squamous Cell Carcinoma
warts
- Areas of the body damaged by UV
3. Measles – morbillivirus
rays
4. Varicella zoster – causes chicken pox
- Benign
Allergies - Can be metastasized via lymph
1. Contact Dermatitis – follow the shape Malignant Melanoma
of the allergy causing material. - Worst prognosis
2. Psoriasis – auto immune disease - Can metastasized easily through
Burns the veins and lymphatic system.
- Rule of Nines
- Burn unit – one way ventilation
room, removes contaminants from
air.
1 st degree burn
- Only the epidermis is damaged
- Most painful
- May cause slight edema
- Swelling may be present
MAGALLANES, JULIETA GWENDOLIN A.- BSMT MED212
You might also like
- Dermoscopy Pathology Correlation in MelanomaDocument8 pagesDermoscopy Pathology Correlation in MelanomaDaniela SerbanNo ratings yet
- Exsc 223 Practice Exam 2Document11 pagesExsc 223 Practice Exam 2kimber brownNo ratings yet
- Aquaxyl: Hydraconcept: An Innovative Moisturizing and Restructuring TechnologyDocument38 pagesAquaxyl: Hydraconcept: An Innovative Moisturizing and Restructuring TechnologyMihaNo ratings yet
- 5 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pages5 Integumentary SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Integumentary System?Document6 pagesWhat Is The Integumentary System?Jerneth Nyka FloresNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesIntegumentary SystemChan TalNo ratings yet
- Chap5 - Integument TransesDocument4 pagesChap5 - Integument TransesSophia Margarette CawalingNo ratings yet
- Cells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDocument5 pagesCells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDimple Lexiry GloriaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument8 pagesAnaphy ReviewerMark GonzalesNo ratings yet
- IntegumentaryDocument15 pagesIntegumentaryhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- 5 - IntegDocument8 pages5 - IntegGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- MOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Document41 pagesMOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Suez AyomNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Analysis of The Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesMicroscopic Analysis of The Integumentary SystemAgatha joy MadrazoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy MidtermsDocument28 pagesAnaphy MidtermsxeanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab IntegDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lab IntegPhoemela Reign GregorioNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument8 pagesIntegumentary SystemEunice TungNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument8 pagesSkin and Body MembranesVincent AlgarmeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument10 pagesSkinKaren Mae AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body Membranes HahaDocument6 pagesSkin and Body Membranes Hahaقى قىNo ratings yet
- Intergumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntergumentary SystemAkihiro FurukawaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System PDF 2Document8 pagesIntegumentary System PDF 2thyezlianNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Class - The Integumentary SystemDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Class - The Integumentary SystemChristina MarkwartNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemOddysa EstorqueNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1 - Integumentary System (Review Material)Document13 pagesGROUP 1 - Integumentary System (Review Material)SALGIE SERNALNo ratings yet
- S4 Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesS4 Integumentary Systemcam broquelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 IntegumentaryDocument2 pagesChapter 5 IntegumentaryElle UgaddanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerDocument27 pagesAnaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerFAITH EFONDONo ratings yet
- Nursing AnaPhy Integumentary SystemDocument22 pagesNursing AnaPhy Integumentary SystemGail Chantel Spring PerlasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - Integumentary SystemLora Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- 4 Ntegumentary SystemDocument8 pages4 Ntegumentary SystemAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument8 pagesIntegumentary Systemnero.keishareignc17No ratings yet
- Anaphy - IntegumentaryDocument4 pagesAnaphy - IntegumentaryYo1No ratings yet
- 24 Urological Trauma LRDocument67 pages24 Urological Trauma LRManushi HenadeeraNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument18 pagesIntegumentary SystemRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- 420-510chapter 1 (5) Introduction To The Integumentary SystemDocument6 pages420-510chapter 1 (5) Introduction To The Integumentary Systemtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System ReviewerDocument6 pagesIntegumentary System ReviewerKrize Colene dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Skin and Body Membranes: Body MembranesDocument16 pagesIntegumentary System: Skin and Body Membranes: Body MembranesIvan LimNo ratings yet
- Skin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPDocument59 pagesSkin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPJosephine SNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemCarmela Cordon FelixNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 & 6Document18 pagesTopic 5 & 6PhoebeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Document4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Millen ArenasNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 2 Main Regions: Human Anatomy & Physiology Kylie Jan C. SilvaDocument4 pagesIntegumentary System 2 Main Regions: Human Anatomy & Physiology Kylie Jan C. SilvaKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Integumentary NotesDocument13 pagesIntegumentary Noteslovj melNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Review MaterialDocument11 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Review MaterialSALGIE SERNALNo ratings yet
- P-Integumentary Sytem - AnaphyDocument3 pagesP-Integumentary Sytem - AnaphyQueen RiquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: The Skin: Keratins Thickest Layer Stratum Germinativum TonofibrilsDocument3 pagesChapter 18: The Skin: Keratins Thickest Layer Stratum Germinativum TonofibrilsjajaNo ratings yet
- Schwartz's Principles of Surgery: CH16: Page 1Document13 pagesSchwartz's Principles of Surgery: CH16: Page 1Kathryn ReunillaNo ratings yet
- Geraldine Sagun Rose Ann Wamil Trina de Guzman Vladimir TacmoDocument42 pagesGeraldine Sagun Rose Ann Wamil Trina de Guzman Vladimir TacmoShon ShimaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument46 pagesIntegumentary SystemDainah ArticuloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy&Physiology of SkinDocument45 pagesAnatomy&Physiology of Skinpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Skinbody MemranesDocument3 pagesModule 3 Skinbody MemranesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- The Dermis: LocationDocument3 pagesThe Dermis: LocationJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- Zoology 100 Notes 1Document8 pagesZoology 100 Notes 1Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroNo ratings yet
- SKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Document40 pagesSKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Sadia SohailNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-NotesDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-NotesAkirah Jewelle JaenNo ratings yet
- Skin ShortDocument10 pagesSkin ShortKashar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Midterm AnaphyDocument19 pagesMidterm AnaphywannabeeurzNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System - ANAPHYDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System - ANAPHYmariaNo ratings yet
- 1styear Physiology of Excercise Module 4Document16 pages1styear Physiology of Excercise Module 4zedy gullesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3-4Document13 pagesAnatomy 3-4Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- MLSHUHIC - Lesson 3 - The Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesMLSHUHIC - Lesson 3 - The Integumentary SystemJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and VariabilityDocument4 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and VariabilityJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Parasitology-Summary NotesDocument15 pagesParasitology-Summary NotesJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- MLSHUHIC - Lesson 2 - Fundamental Types of TissuesDocument14 pagesMLSHUHIC - Lesson 2 - Fundamental Types of TissuesJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Nematodes LabDocument12 pagesNematodes LabJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Histo Compiled 1Document82 pagesHisto Compiled 1Jhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- MED227Samson LabQuiz2Document2 pagesMED227Samson LabQuiz2Jhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- 6.introduction To Laboratory Services-Student'sDocument36 pages6.introduction To Laboratory Services-Student'sJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- FinalOutput AnachemDocument2 pagesFinalOutput AnachemJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Midterm Lab Part 1Document6 pagesMidterm Lab Part 1Jhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- 5.non Blood Samples - Other Body FluidsDocument41 pages5.non Blood Samples - Other Body FluidsJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 17 - Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesLesson 17 - Reproductive SystemJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 PROTEINDocument15 pagesLesson 3 PROTEINJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Special SensesDocument6 pagesLesson 9 - Special SensesJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - ENZYMESDocument10 pagesLesson 4 - ENZYMESJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Pmls Lec CompiledDocument23 pagesPmls Lec CompiledJhana SamsonNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck OncologyDocument361 pagesHead and Neck OncologyDino Alberto MurilloNo ratings yet
- ENERPEEL - The Technology Rev - 2 - 2011Document48 pagesENERPEEL - The Technology Rev - 2 - 2011CHONG WEI SHENGNo ratings yet
- Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 Notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue StructureDocument8 pagesBiology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 Notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue StructureDrGeorge Saad AbdallaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Book 1-1228Document158 pagesMCQ Book 1-1228Yasser ezzatNo ratings yet
- Ichthyosis VulgarisDocument18 pagesIchthyosis VulgarisYudi SupartaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Lab ExerciseDocument12 pagesIntegumentary System Lab Exercisekams sardinesNo ratings yet
- Vikas H.V PDFDocument139 pagesVikas H.V PDFRajesh RajendranNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Anti Emetic Patch Comprising On Dan Set Ron Hydro ChlorideDocument107 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Anti Emetic Patch Comprising On Dan Set Ron Hydro ChlorideuduriskNo ratings yet
- Seed Morphology and Histology of Some ParonychiaDocument6 pagesSeed Morphology and Histology of Some ParonychiaAngrainiNo ratings yet
- Interface Dermatitis: Rajendra Singh, MDDocument97 pagesInterface Dermatitis: Rajendra Singh, MDsatkriti100% (3)
- Dactylos PDFDocument151 pagesDactylos PDFZenny Jabuen100% (2)
- IJPC 13 5 Veterinary CompoundingDocument100 pagesIJPC 13 5 Veterinary CompoundingMatiasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy&Physiology of SkinDocument45 pagesAnatomy&Physiology of Skinpreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Webquest - HistologyDocument6 pagesWebquest - HistologyicdjpNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesLab 5 - Integumentary Systemsidro123No ratings yet
- XBHA2103 Human Anatomy and Physiology Capr14 (RS) (M) PDFDocument8 pagesXBHA2103 Human Anatomy and Physiology Capr14 (RS) (M) PDFbell mailNo ratings yet
- InTech-Split Thickness Skin GraftsDocument15 pagesInTech-Split Thickness Skin GraftsAnonymous LnWIBo1GNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument31 pagesIntegumentary Systemjcali06No ratings yet
- Skin LayersDocument3 pagesSkin LayersCrackmcat CrackmcatNo ratings yet
- Biology 2: CH 5 - The Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesBiology 2: CH 5 - The Integumentary SystemNicole Athena CruzNo ratings yet
- Wound Management ManualDocument81 pagesWound Management ManualBrian Harris100% (2)
- AP 5 Integumentary SystemDocument120 pagesAP 5 Integumentary SystemIkhsan HidayatNo ratings yet
- The American Naturol: MuseumDocument76 pagesThe American Naturol: Museumraheema tahirNo ratings yet
- Niacinamide A4 8pp 2020Document8 pagesNiacinamide A4 8pp 2020Joatan de SousaNo ratings yet
- Microneedling Percutaneous Collagen Induction (PCI) TherapyDocument13 pagesMicroneedling Percutaneous Collagen Induction (PCI) Therapyangela TavaresNo ratings yet
- The Essential Review Guide For Passing The Mblex Licensing Exam 2017 EditionDocument192 pagesThe Essential Review Guide For Passing The Mblex Licensing Exam 2017 EditionSabrina Marie100% (3)
- Argan Vitalisation of Dermal Stem Cells For Skin Rejuvenation Personal Care 07 2011Document3 pagesArgan Vitalisation of Dermal Stem Cells For Skin Rejuvenation Personal Care 07 2011Steve D'HamsNo ratings yet