Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsPulse Oximetry NCM 112 SL
Pulse Oximetry NCM 112 SL
Uploaded by
Rose Ann BollerosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Pulse OximetryDocument38 pagesPulse OximetryJoanna Jauculan Albaño100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Occlusion in FPDDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Occlusion in FPDVishal Reddy100% (2)
- Monitoring Intra Operatif: Mindi Widayani NRP 122.022.1115 FK UPN "Veteran" JakartaDocument21 pagesMonitoring Intra Operatif: Mindi Widayani NRP 122.022.1115 FK UPN "Veteran" Jakartaputri wulandariNo ratings yet
- MonitoringDocument45 pagesMonitoringضبيان فرحانNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument3 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromechoobiNo ratings yet
- Standard Monitors in AnaesthesiaDocument70 pagesStandard Monitors in AnaesthesiaAFOLAYAN OLUWAJUWON PRAISENo ratings yet
- Postoperative HypoxiaDocument33 pagesPostoperative HypoxiasrinidhiNo ratings yet
- Pulse OximetryDocument9 pagesPulse OximetryACOB, Jamil C.No ratings yet
- DX & MX of Limb Ischemia NewDocument51 pagesDX & MX of Limb Ischemia NewVape OutNo ratings yet
- Shock Syndrome: Clinical Signs Common To All Types of Shock Critically Ill Patient MonitoringDocument24 pagesShock Syndrome: Clinical Signs Common To All Types of Shock Critically Ill Patient MonitoringCamelia A. ParuschiNo ratings yet
- Monitoring PerioperatipDocument54 pagesMonitoring Perioperatipjavajavu100% (1)
- Xducers & P-MonitorsDocument22 pagesXducers & P-MonitorschanlalNo ratings yet
- Monitoring During AnaesthesiaDocument17 pagesMonitoring During AnaesthesiaSummaiyya FazalNo ratings yet
- Physiomonitoring TransDocument4 pagesPhysiomonitoring TransAimie DagaleaNo ratings yet
- MonitoringDocument16 pagesMonitoringLawrence WanderiNo ratings yet
- Acute Chest SyndromeDocument28 pagesAcute Chest SyndromeJohn OkidiNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument10 pagesOxygen TherapyRunel PabloNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure: Dr. Mullasari Ajit S. Director - Cardiology Madras Medical MissionDocument40 pagesBlood Pressure: Dr. Mullasari Ajit S. Director - Cardiology Madras Medical MissionChristine GraceNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MonitoringDocument138 pagesCardiac Monitoringanjanar26No ratings yet
- Plethysmography: Biosensors & TransducersDocument66 pagesPlethysmography: Biosensors & TransducersmeharNo ratings yet
- Pulse OximeterDocument17 pagesPulse OximeterΑнмєɒ FσυαɒNo ratings yet
- RT 312 Prelim NotesDocument20 pagesRT 312 Prelim NotesGiralph NikkoNo ratings yet
- Shock: & Metabolic Response To SurgeryDocument20 pagesShock: & Metabolic Response To SurgeryFemale calmNo ratings yet
- Post Anesthesia RecoveryDocument63 pagesPost Anesthesia RecoverypaulaNo ratings yet
- Anticancer MOADocument36 pagesAnticancer MOADrNorNo ratings yet
- Basics of AnaesthesiaDocument34 pagesBasics of Anaesthesiadremad1974No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular 4416Document5 pagesCardiovascular 4416api-3703191No ratings yet
- Post Anesthesia RecoveryDocument69 pagesPost Anesthesia RecoverypaulaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument1 pageRespiratory Acidosis and AlkalosisKenric DavidNo ratings yet
- (Anes) 3 - Monitoring of Anesthetized Patient (Dra. Mendoza) ?Document4 pages(Anes) 3 - Monitoring of Anesthetized Patient (Dra. Mendoza) ?NoreenNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument40 pagesBlood PressureImran KhanNo ratings yet
- GUIDELINES FOR THE USE OF PULSE OXIMETRY IN MONITORING COVID-19 PATIENTS IN HBIC - EnglishDocument3 pagesGUIDELINES FOR THE USE OF PULSE OXIMETRY IN MONITORING COVID-19 PATIENTS IN HBIC - EnglishThanh NamNo ratings yet
- Pulse OximetryDocument2 pagesPulse OximetryNiño Robert RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Curs 3 ShockDocument78 pagesCurs 3 ShockIoana CNo ratings yet
- Shock: Curs Studenti An ViDocument78 pagesShock: Curs Studenti An ViAnonymous dKiLqVS3L5No ratings yet
- MonitoringDocument50 pagesMonitoringfadil85No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of AnaestheticsDocument28 pagesPharmacology of AnaestheticsRahaf AliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PediaDocument18 pagesDrug Study PediaCyx17No ratings yet
- OxygenDocument34 pagesOxygenSamson AyalewNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation ReviewerDocument9 pagesOxygenation Reviewerlaarns.manalo04No ratings yet
- Transoperative 812217287Document27 pagesTransoperative 812217287Pepe PeñaNo ratings yet
- ABC - Pulmonary Contusion and Penetrating TraumaDocument19 pagesABC - Pulmonary Contusion and Penetrating TraumaSHANIA HASEENAH SALAZARNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument53 pagesShockVarsini C PNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument37 pagesHemodynamic MonitoringStephy Sojan50% (2)
- Pulse Oximetry 2Document38 pagesPulse Oximetry 2Hcu RSTDDNo ratings yet
- Handout 5 CardioVascular System Overview PDFDocument7 pagesHandout 5 CardioVascular System Overview PDFGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- MI-I Pulse Oximeter PPDocument10 pagesMI-I Pulse Oximeter PPanwar1971No ratings yet
- Pulse OximetryDocument17 pagesPulse OximetryAndrei-Botnari Kristina100% (1)
- Buerger's Disease: By:-Dr - Mohit Singhania (Intern)Document33 pagesBuerger's Disease: By:-Dr - Mohit Singhania (Intern)MohitNo ratings yet
- Shock: Erdiansyah Zulyadaini, MD, FIHA FK Universitas Muhammadiyah Purwokerto/ RSUD Dr. Soeselo Kabupaten TegalDocument47 pagesShock: Erdiansyah Zulyadaini, MD, FIHA FK Universitas Muhammadiyah Purwokerto/ RSUD Dr. Soeselo Kabupaten TegalFarah AkhwanisNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia MonitoringDocument69 pagesAnesthesia MonitoringCzar SyNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia MonitoringDocument14 pagesAnesthesia MonitoringIga Bagus Suastika100% (3)
- Handout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Document7 pagesHandout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Orlyn Joy TanaweNo ratings yet
- CBR Midterms: Assessment of Vital Signs Key TermsDocument4 pagesCBR Midterms: Assessment of Vital Signs Key TermsFlint RockNo ratings yet
- Final Project On Pulse OximeterDocument17 pagesFinal Project On Pulse OximeterDwayne Coelho100% (1)
- OxygenationDocument57 pagesOxygenationassumptaNo ratings yet
- Finger Pulse Oximetry InserviceDocument22 pagesFinger Pulse Oximetry InserviceagainesNo ratings yet
- MODULE G2 - Pulse OximetryDocument40 pagesMODULE G2 - Pulse OximetryShanu Kumar100% (1)
- Cardiogenic and Septic Shock LectureDocument27 pagesCardiogenic and Septic Shock LectureMohd EdieNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument35 pagesShockAbdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State University College of Nursing City of Malolos, BulacanDocument2 pagesBulacan State University College of Nursing City of Malolos, BulacanMia PascualNo ratings yet
- Therapy of Bedridden PatientsDocument7 pagesTherapy of Bedridden PatientsKapil LakhwaraNo ratings yet
- Superior Orbital Fissure Aka Tolosa Hunt SyndromeDocument5 pagesSuperior Orbital Fissure Aka Tolosa Hunt SyndromeKalpana GunasekarNo ratings yet
- Heartbeat HomeostasisDocument1 pageHeartbeat Homeostasisapi-296692561No ratings yet
- PLASMAPHERESISDocument18 pagesPLASMAPHERESISmuhammad24fayazNo ratings yet
- Hemochroma PLUSDocument2 pagesHemochroma PLUSsatujuli23No ratings yet
- Bertram FlehmigDocument50 pagesBertram FlehmigAnum FaheemNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudyLauren HollidgeNo ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbations of Pulmonary DiseasesDocument258 pagesAcute Exacerbations of Pulmonary DiseasesOxana TurcuNo ratings yet
- FW - Plea For 2nd Dose VaccineDocument2 pagesFW - Plea For 2nd Dose VaccineLJNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Dental Assisting 6th Edition by RobinsonDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Dental Assisting 6th Edition by Robinsonnoticehyoideal.iyjt100% (49)
- Why Is Development of New Treatments Necessary For Myasthenia Gravis? Recent Advances in Clinical TrialsDocument5 pagesWhy Is Development of New Treatments Necessary For Myasthenia Gravis? Recent Advances in Clinical TrialsRameshKrishnanNo ratings yet
- 2020 Journal Basic and Clinical Physiology and PharmacologyDocument10 pages2020 Journal Basic and Clinical Physiology and PharmacologytsamoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Word Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesUnit 4 Word Circulatory SystemChandan Shah100% (2)
- Fitzpatrick 1992Document4 pagesFitzpatrick 1992Nursyafiq Ali ShibramulisiNo ratings yet
- Conduct-Of-Normal-Labor - LABISDocument2 pagesConduct-Of-Normal-Labor - LABISDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- Measures in Meeting The Needs of Clients With Alteration in Visual and AuditoryDocument13 pagesMeasures in Meeting The Needs of Clients With Alteration in Visual and AuditoryJan Federick BantayNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka: Pharmacology (RS3 & RS4) Q.P. CODE: 2710Document1 pageRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka: Pharmacology (RS3 & RS4) Q.P. CODE: 2710Nuhman Abdu RahmanNo ratings yet
- Torsion of HematosalpinxDocument3 pagesTorsion of HematosalpinxKartikaningtyas KusumastutiNo ratings yet
- Systems Review MnemonicsDocument4 pagesSystems Review MnemonicsNatasha JuchkovNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive EmergenciesDocument49 pagesHypertensive EmergenciesSafa Abdualrahaman Ali HamadNo ratings yet
- SHIROVASTIDocument3 pagesSHIROVASTINatseenNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Table of Bacteria: CLSI 2017Document16 pagesAntimicrobial Table of Bacteria: CLSI 2017behzad bm0% (1)
- 10 Antibiotics Protein Synthesis Inhibitors PhenicolsDocument11 pages10 Antibiotics Protein Synthesis Inhibitors PhenicolsIdrissou FmsbNo ratings yet
- Novel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudyDocument9 pagesNovel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudymarcelodentNo ratings yet
- CHARTINGDocument5 pagesCHARTINGGIG OCA ROBLES SEAMEN'S HOSPITALNo ratings yet
- Initial Resuscitation Algorithm For ChildrenDocument2 pagesInitial Resuscitation Algorithm For ChildrenDalia GomNo ratings yet
- Dr. Gupta Says, No One Must Die of Cancer Except Out of CarelessnessDocument2 pagesDr. Gupta Says, No One Must Die of Cancer Except Out of CarelessnessMyrelle Da Jose Sario0% (1)
- Adejoke 2019Document10 pagesAdejoke 2019claraNo ratings yet
Pulse Oximetry NCM 112 SL
Pulse Oximetry NCM 112 SL
Uploaded by
Rose Ann Bolleros0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pagePulse Oximetry NCM 112 SL
Pulse Oximetry NCM 112 SL
Uploaded by
Rose Ann BollerosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
NCM 112 SL Specific Health Conditions
Pulse Oximetry • Heart Attack
• Most essential monitors for routine use in • Heart Failure
anesthesia and intensive care. • Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
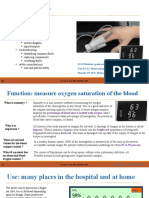
• An EASY and PAINLESS test measuring the oxygen ( COPD )
level ( Oxygen Saturation 5th vital sign ) of the • Anemia
blood, heart rate and gives an idea of tissue • Lung Cancer
perfusion by pulse wave form • Asthma
• A clip like device called probe placed on the body • Pneumonia
part ( Finger or Ear Lobe ) LIMITATIONS OF PULSE OXIMETRY ( Inaccurate or
• Probe : uses light to measure oxygen in the blood unreliable reading )
• Information indicator if patient needs extra oxygen • Poor Circulation
Parts of the Oximetry • Cool Skin Temperature
• Dark Nail Polish
• Low Perfusion State
• Anemia
• Tobacco Usage
• Patient Motion
How Does a Pulse Oximeter
1. Infrared light is absorbed by the oxyhemoglobin
while the red light is absorbed by the reduced
hemoglobin
2. Amount and type of light transmitted through the
tissue is converted to a digital value representing the
percentage of hemoglobin saturated with oxygen.
3. Detect HYPOXIA ( too little oxygen to fulfill the needs
of the brain and body ) before cyanosis ( bluish
discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes )
Indications for Pulse Oximetry
• Undergoing surgical procedure under general
anesthesia
• Undergoing surgical procedure under conscious
sedation
• Emergency situations : loss of consciousness, trauma
• After surgery during recovery phase
Types of Pulse Oximetry
TRANSMISSIVE APPLICATION MODE
• Most common application mode
• Sensor device placed on the thin part of patient’s
body : fingertip or earlobe
REFLECTANCE PULSE OXIMETRY
• Less common alternative eto transmissive pulse
oximetry
• Does not require a thin section of the body
• Universal application : feet, forehead and chest
You might also like
- Pulse OximetryDocument38 pagesPulse OximetryJoanna Jauculan Albaño100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Occlusion in FPDDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Occlusion in FPDVishal Reddy100% (2)
- Monitoring Intra Operatif: Mindi Widayani NRP 122.022.1115 FK UPN "Veteran" JakartaDocument21 pagesMonitoring Intra Operatif: Mindi Widayani NRP 122.022.1115 FK UPN "Veteran" Jakartaputri wulandariNo ratings yet
- MonitoringDocument45 pagesMonitoringضبيان فرحانNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument3 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromechoobiNo ratings yet
- Standard Monitors in AnaesthesiaDocument70 pagesStandard Monitors in AnaesthesiaAFOLAYAN OLUWAJUWON PRAISENo ratings yet
- Postoperative HypoxiaDocument33 pagesPostoperative HypoxiasrinidhiNo ratings yet
- Pulse OximetryDocument9 pagesPulse OximetryACOB, Jamil C.No ratings yet
- DX & MX of Limb Ischemia NewDocument51 pagesDX & MX of Limb Ischemia NewVape OutNo ratings yet
- Shock Syndrome: Clinical Signs Common To All Types of Shock Critically Ill Patient MonitoringDocument24 pagesShock Syndrome: Clinical Signs Common To All Types of Shock Critically Ill Patient MonitoringCamelia A. ParuschiNo ratings yet
- Monitoring PerioperatipDocument54 pagesMonitoring Perioperatipjavajavu100% (1)
- Xducers & P-MonitorsDocument22 pagesXducers & P-MonitorschanlalNo ratings yet
- Monitoring During AnaesthesiaDocument17 pagesMonitoring During AnaesthesiaSummaiyya FazalNo ratings yet
- Physiomonitoring TransDocument4 pagesPhysiomonitoring TransAimie DagaleaNo ratings yet
- MonitoringDocument16 pagesMonitoringLawrence WanderiNo ratings yet
- Acute Chest SyndromeDocument28 pagesAcute Chest SyndromeJohn OkidiNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument10 pagesOxygen TherapyRunel PabloNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure: Dr. Mullasari Ajit S. Director - Cardiology Madras Medical MissionDocument40 pagesBlood Pressure: Dr. Mullasari Ajit S. Director - Cardiology Madras Medical MissionChristine GraceNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MonitoringDocument138 pagesCardiac Monitoringanjanar26No ratings yet
- Plethysmography: Biosensors & TransducersDocument66 pagesPlethysmography: Biosensors & TransducersmeharNo ratings yet
- Pulse OximeterDocument17 pagesPulse OximeterΑнмєɒ FσυαɒNo ratings yet
- RT 312 Prelim NotesDocument20 pagesRT 312 Prelim NotesGiralph NikkoNo ratings yet
- Shock: & Metabolic Response To SurgeryDocument20 pagesShock: & Metabolic Response To SurgeryFemale calmNo ratings yet
- Post Anesthesia RecoveryDocument63 pagesPost Anesthesia RecoverypaulaNo ratings yet
- Anticancer MOADocument36 pagesAnticancer MOADrNorNo ratings yet
- Basics of AnaesthesiaDocument34 pagesBasics of Anaesthesiadremad1974No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular 4416Document5 pagesCardiovascular 4416api-3703191No ratings yet
- Post Anesthesia RecoveryDocument69 pagesPost Anesthesia RecoverypaulaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument1 pageRespiratory Acidosis and AlkalosisKenric DavidNo ratings yet
- (Anes) 3 - Monitoring of Anesthetized Patient (Dra. Mendoza) ?Document4 pages(Anes) 3 - Monitoring of Anesthetized Patient (Dra. Mendoza) ?NoreenNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument40 pagesBlood PressureImran KhanNo ratings yet
- GUIDELINES FOR THE USE OF PULSE OXIMETRY IN MONITORING COVID-19 PATIENTS IN HBIC - EnglishDocument3 pagesGUIDELINES FOR THE USE OF PULSE OXIMETRY IN MONITORING COVID-19 PATIENTS IN HBIC - EnglishThanh NamNo ratings yet
- Pulse OximetryDocument2 pagesPulse OximetryNiño Robert RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Curs 3 ShockDocument78 pagesCurs 3 ShockIoana CNo ratings yet
- Shock: Curs Studenti An ViDocument78 pagesShock: Curs Studenti An ViAnonymous dKiLqVS3L5No ratings yet
- MonitoringDocument50 pagesMonitoringfadil85No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of AnaestheticsDocument28 pagesPharmacology of AnaestheticsRahaf AliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PediaDocument18 pagesDrug Study PediaCyx17No ratings yet
- OxygenDocument34 pagesOxygenSamson AyalewNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation ReviewerDocument9 pagesOxygenation Reviewerlaarns.manalo04No ratings yet
- Transoperative 812217287Document27 pagesTransoperative 812217287Pepe PeñaNo ratings yet
- ABC - Pulmonary Contusion and Penetrating TraumaDocument19 pagesABC - Pulmonary Contusion and Penetrating TraumaSHANIA HASEENAH SALAZARNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument53 pagesShockVarsini C PNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument37 pagesHemodynamic MonitoringStephy Sojan50% (2)
- Pulse Oximetry 2Document38 pagesPulse Oximetry 2Hcu RSTDDNo ratings yet
- Handout 5 CardioVascular System Overview PDFDocument7 pagesHandout 5 CardioVascular System Overview PDFGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- MI-I Pulse Oximeter PPDocument10 pagesMI-I Pulse Oximeter PPanwar1971No ratings yet
- Pulse OximetryDocument17 pagesPulse OximetryAndrei-Botnari Kristina100% (1)
- Buerger's Disease: By:-Dr - Mohit Singhania (Intern)Document33 pagesBuerger's Disease: By:-Dr - Mohit Singhania (Intern)MohitNo ratings yet
- Shock: Erdiansyah Zulyadaini, MD, FIHA FK Universitas Muhammadiyah Purwokerto/ RSUD Dr. Soeselo Kabupaten TegalDocument47 pagesShock: Erdiansyah Zulyadaini, MD, FIHA FK Universitas Muhammadiyah Purwokerto/ RSUD Dr. Soeselo Kabupaten TegalFarah AkhwanisNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia MonitoringDocument69 pagesAnesthesia MonitoringCzar SyNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia MonitoringDocument14 pagesAnesthesia MonitoringIga Bagus Suastika100% (3)
- Handout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Document7 pagesHandout 5 CardioVascular System Overview (Recovered)Orlyn Joy TanaweNo ratings yet
- CBR Midterms: Assessment of Vital Signs Key TermsDocument4 pagesCBR Midterms: Assessment of Vital Signs Key TermsFlint RockNo ratings yet
- Final Project On Pulse OximeterDocument17 pagesFinal Project On Pulse OximeterDwayne Coelho100% (1)
- OxygenationDocument57 pagesOxygenationassumptaNo ratings yet
- Finger Pulse Oximetry InserviceDocument22 pagesFinger Pulse Oximetry InserviceagainesNo ratings yet
- MODULE G2 - Pulse OximetryDocument40 pagesMODULE G2 - Pulse OximetryShanu Kumar100% (1)
- Cardiogenic and Septic Shock LectureDocument27 pagesCardiogenic and Septic Shock LectureMohd EdieNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument35 pagesShockAbdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State University College of Nursing City of Malolos, BulacanDocument2 pagesBulacan State University College of Nursing City of Malolos, BulacanMia PascualNo ratings yet
- Therapy of Bedridden PatientsDocument7 pagesTherapy of Bedridden PatientsKapil LakhwaraNo ratings yet
- Superior Orbital Fissure Aka Tolosa Hunt SyndromeDocument5 pagesSuperior Orbital Fissure Aka Tolosa Hunt SyndromeKalpana GunasekarNo ratings yet
- Heartbeat HomeostasisDocument1 pageHeartbeat Homeostasisapi-296692561No ratings yet
- PLASMAPHERESISDocument18 pagesPLASMAPHERESISmuhammad24fayazNo ratings yet
- Hemochroma PLUSDocument2 pagesHemochroma PLUSsatujuli23No ratings yet
- Bertram FlehmigDocument50 pagesBertram FlehmigAnum FaheemNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudyLauren HollidgeNo ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbations of Pulmonary DiseasesDocument258 pagesAcute Exacerbations of Pulmonary DiseasesOxana TurcuNo ratings yet
- FW - Plea For 2nd Dose VaccineDocument2 pagesFW - Plea For 2nd Dose VaccineLJNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Dental Assisting 6th Edition by RobinsonDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Dental Assisting 6th Edition by Robinsonnoticehyoideal.iyjt100% (49)
- Why Is Development of New Treatments Necessary For Myasthenia Gravis? Recent Advances in Clinical TrialsDocument5 pagesWhy Is Development of New Treatments Necessary For Myasthenia Gravis? Recent Advances in Clinical TrialsRameshKrishnanNo ratings yet
- 2020 Journal Basic and Clinical Physiology and PharmacologyDocument10 pages2020 Journal Basic and Clinical Physiology and PharmacologytsamoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Word Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesUnit 4 Word Circulatory SystemChandan Shah100% (2)
- Fitzpatrick 1992Document4 pagesFitzpatrick 1992Nursyafiq Ali ShibramulisiNo ratings yet
- Conduct-Of-Normal-Labor - LABISDocument2 pagesConduct-Of-Normal-Labor - LABISDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- Measures in Meeting The Needs of Clients With Alteration in Visual and AuditoryDocument13 pagesMeasures in Meeting The Needs of Clients With Alteration in Visual and AuditoryJan Federick BantayNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka: Pharmacology (RS3 & RS4) Q.P. CODE: 2710Document1 pageRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka: Pharmacology (RS3 & RS4) Q.P. CODE: 2710Nuhman Abdu RahmanNo ratings yet
- Torsion of HematosalpinxDocument3 pagesTorsion of HematosalpinxKartikaningtyas KusumastutiNo ratings yet
- Systems Review MnemonicsDocument4 pagesSystems Review MnemonicsNatasha JuchkovNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive EmergenciesDocument49 pagesHypertensive EmergenciesSafa Abdualrahaman Ali HamadNo ratings yet
- SHIROVASTIDocument3 pagesSHIROVASTINatseenNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Table of Bacteria: CLSI 2017Document16 pagesAntimicrobial Table of Bacteria: CLSI 2017behzad bm0% (1)
- 10 Antibiotics Protein Synthesis Inhibitors PhenicolsDocument11 pages10 Antibiotics Protein Synthesis Inhibitors PhenicolsIdrissou FmsbNo ratings yet
- Novel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudyDocument9 pagesNovel Approach For Treating Challenging Implant-Borne Maxillary Dental Rehabilitation Cases of Cleft Lip and Palate: A Retrospective StudymarcelodentNo ratings yet
- CHARTINGDocument5 pagesCHARTINGGIG OCA ROBLES SEAMEN'S HOSPITALNo ratings yet
- Initial Resuscitation Algorithm For ChildrenDocument2 pagesInitial Resuscitation Algorithm For ChildrenDalia GomNo ratings yet
- Dr. Gupta Says, No One Must Die of Cancer Except Out of CarelessnessDocument2 pagesDr. Gupta Says, No One Must Die of Cancer Except Out of CarelessnessMyrelle Da Jose Sario0% (1)
- Adejoke 2019Document10 pagesAdejoke 2019claraNo ratings yet