Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Switchgear Building Ventilation
Switchgear Building Ventilation
Uploaded by
vlAnandCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Operator Manual - ClimaAIRE II - ENGDocument2 pagesOperator Manual - ClimaAIRE II - ENG2ndpostaNo ratings yet
- RR Trent 60Document39 pagesRR Trent 60Ricardo Cabrera Osinaga100% (6)
- Chigo Service-manual-CS25-35 PDFDocument32 pagesChigo Service-manual-CS25-35 PDFabloemenveldNo ratings yet
- Sequence of Operations For Hvac ControlsDocument4 pagesSequence of Operations For Hvac Controlsmacanipharoldf6220No ratings yet
- Liebert MC Condensers Guide SpecificationsDocument5 pagesLiebert MC Condensers Guide SpecificationsDavid SoaresNo ratings yet
- Standards and Labeling ProgramDocument9 pagesStandards and Labeling ProgramhimanshuNo ratings yet
- MC Quay Chiller 2Document44 pagesMC Quay Chiller 2naikNo ratings yet
- 空调Document16 pages空调HayLenLeeNo ratings yet
- Ewa (H) (D) - TZ C Data Books Eeden21 EnglishDocument255 pagesEwa (H) (D) - TZ C Data Books Eeden21 EnglishDiego Navarro PinoNo ratings yet
- EWYD-BZ Data-Books EEDEN21!10!27 EnglishDocument44 pagesEWYD-BZ Data-Books EEDEN21!10!27 EnglishMiquel BallesterNo ratings yet
- 90 Updated ELECTROMECHANICAL TRAINING MANUAL GENERATORS, UPS AND AIR CONDITIONINGDocument19 pages90 Updated ELECTROMECHANICAL TRAINING MANUAL GENERATORS, UPS AND AIR CONDITIONINGyalewlet tarekeggnNo ratings yet
- ComPacAVPAPDS 020509Document12 pagesComPacAVPAPDS 020509Anthony OrendainNo ratings yet
- Specification For Air-Cooled Packaged Computer Ac UnitDocument7 pagesSpecification For Air-Cooled Packaged Computer Ac Unitmihai_serban13No ratings yet
- Technical Specification For Air Conditioning System: GeneralDocument2 pagesTechnical Specification For Air Conditioning System: GeneralSaptarshi ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Air Con Ventilation and AccessoriesDocument52 pagesAir Con Ventilation and AccessoriesBala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Thyvent BroDocument6 pagesThyvent BroAlev AktürkNo ratings yet
- Liebert Intelecool2: 1.0 GeneralDocument5 pagesLiebert Intelecool2: 1.0 GeneraljairofgfNo ratings yet
- MRBT 075 CW D SpecificationsDocument19 pagesMRBT 075 CW D SpecificationsJorge Bravo100% (1)
- Chapter12 Water and DX SystemDocument32 pagesChapter12 Water and DX SystemNurhidayat NurhidayatNo ratings yet
- SASO2663Document19 pagesSASO2663damaso taracenaNo ratings yet
- AFPC Electrical ProceduresDocument4 pagesAFPC Electrical Proceduresapi-3697472100% (1)
- Brochure Air Cooled With ChillerDocument63 pagesBrochure Air Cooled With ChillerFrancisco BelloNo ratings yet
- VRVII Cooling Only Specification SMC 1-8-03 - TestDocument7 pagesVRVII Cooling Only Specification SMC 1-8-03 - TestAlexOdarteyBannermanNo ratings yet
- 1370 000DuMDocument13 pages1370 000DuMdrago.andres9No ratings yet
- Opa 116-201 TD 0521Document12 pagesOpa 116-201 TD 05217tddprzxbbNo ratings yet
- AVN 204 To 904 EVN/CVN 204 To 904: Vertical Packaged and Split Air ConditionersDocument32 pagesAVN 204 To 904 EVN/CVN 204 To 904: Vertical Packaged and Split Air ConditionersJoseLuisMuñozMuñozNo ratings yet
- Teh 12.530 60 0220Document46 pagesTeh 12.530 60 0220سعد الجهنيNo ratings yet
- Electronics Cooling TermsDocument13 pagesElectronics Cooling TermscristianNo ratings yet
- Inverter Air Cooled Screw Chillers: Product ManualDocument52 pagesInverter Air Cooled Screw Chillers: Product ManualKyaw San OoNo ratings yet
- VRVII Cooling Only Specification SMC 1-8-03Document7 pagesVRVII Cooling Only Specification SMC 1-8-03mohamed mansyNo ratings yet
- Saudi Exhaust FanDocument40 pagesSaudi Exhaust FanBasheer MohammedNo ratings yet
- ML13073A698Document9 pagesML13073A698Dexter BothaNo ratings yet
- G2 Spec Mechanical Air CondDocument5 pagesG2 Spec Mechanical Air Condsyahirah natasyaNo ratings yet
- DBR PDDDocument13 pagesDBR PDDMEERANo ratings yet
- Micro Extension TSGDocument28 pagesMicro Extension TSGeng-ashraf abdullahNo ratings yet
- HVAC Guide Specifications Commercial Air-Cooled Condensing UnitsDocument4 pagesHVAC Guide Specifications Commercial Air-Cooled Condensing UnitsHazemNo ratings yet
- Ewyq FDocument54 pagesEwyq FRicardo Molina SánchezNo ratings yet
- Letter of AssociationDocument25 pagesLetter of AssociationluluNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER23PT2Document12 pagesCHAPTER23PT2dustinmoateNo ratings yet
- Eastman Industries SpecificationDocument47 pagesEastman Industries SpecificationcivilNo ratings yet
- McQuay McEnergy HPI Technical Manual EngDocument48 pagesMcQuay McEnergy HPI Technical Manual EngZhenqian HNo ratings yet
- Appendix a - ComplianceDocument1 pageAppendix a - CompliancePråðèép Thê PërfömèrNo ratings yet
- CSRAT-Y Air Cooled Chiller - R134aDocument36 pagesCSRAT-Y Air Cooled Chiller - R134aLeed ENNo ratings yet
- Databook - EWA (Y) T-CZ (N-P-H) Daikin EN - Rev6Document64 pagesDatabook - EWA (Y) T-CZ (N-P-H) Daikin EN - Rev6kevin.sparks.isoenergyNo ratings yet
- Cooling For Mobile Base Stations and Cell TowersDocument7 pagesCooling For Mobile Base Stations and Cell TowersRaed Al-HajNo ratings yet
- Hvac Technical SpecificationsDocument6 pagesHvac Technical SpecificationsAbdul JabbarNo ratings yet
- Ferroli Hot Oil HTR (GB)Document30 pagesFerroli Hot Oil HTR (GB)RodNo ratings yet
- Especification Guide Serie 9Document12 pagesEspecification Guide Serie 9menmsisNo ratings yet
- Vitocal 100-Aw Am2v TDMDocument44 pagesVitocal 100-Aw Am2v TDMerugazeroNo ratings yet
- 1391 1Document26 pages1391 1Aaron AngNo ratings yet
- 42BJ ICM LEC 1.9 - 2.9 - 4.9: Individual Comfort Module For Variable Air Volume SystemsDocument20 pages42BJ ICM LEC 1.9 - 2.9 - 4.9: Individual Comfort Module For Variable Air Volume SystemsBulat IııNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones Tecnicas Apc Aa InrowDocument6 pagesEspecificaciones Tecnicas Apc Aa InrowWilder Phill Arzapalo GinesNo ratings yet
- EN WPE0063 Choosing Cooling IT CabinetDocument5 pagesEN WPE0063 Choosing Cooling IT CabinetabudisNo ratings yet
- Mechanical - Hvac SystemsDocument11 pagesMechanical - Hvac SystemsWahyudi HardyNo ratings yet
- SUNLINE 2000-: Single Package Gas / Electric Units and Single Package Air ConditionersDocument16 pagesSUNLINE 2000-: Single Package Gas / Electric Units and Single Package Air ConditionersBernardo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Opa 465-960 Uc8 Eco TD 0322Document24 pagesOpa 465-960 Uc8 Eco TD 03227tddprzxbbNo ratings yet
- Acson Lexus ChillersDocument59 pagesAcson Lexus ChillersKardos Zoltan100% (1)
- AHUs 2020Document36 pagesAHUs 2020Technical OfficeNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Built-In Thermal Protection For - !elbctric Motors Rated Up To 660 V Ac - SpecificationDocument14 pagesIndian Standard: Built-In Thermal Protection For - !elbctric Motors Rated Up To 660 V Ac - Specificationkushal_lonareNo ratings yet
- Mep LayoutsDocument3 pagesMep LayoutsvlAnandNo ratings yet
- Sofilair H13/H14: AdvantagesDocument1 pageSofilair H13/H14: AdvantagesvlAnandNo ratings yet
- Production SystemDocument58 pagesProduction SystemvlAnandNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3: Advances in MetrologyDocument42 pagesUNIT-3: Advances in MetrologyMebinNo ratings yet
- Delta Ia-Dpm DPM C en 20160914Document7 pagesDelta Ia-Dpm DPM C en 20160914CLAUDIONo ratings yet
- Air Handling Unit - Definition and Configuration TypesDocument6 pagesAir Handling Unit - Definition and Configuration TypesAhmad HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Abbattitore Di Temperatura Mod. BE-R151 - UKDocument3 pagesAbbattitore Di Temperatura Mod. BE-R151 - UKConrado TangariNo ratings yet
- Manual Mcquay M4RT250ARDocument207 pagesManual Mcquay M4RT250ARalextermotecNo ratings yet
- Guidehouse S.E PDFDocument43 pagesGuidehouse S.E PDFJuan Amilcar Pedraza PachecoNo ratings yet
- NRC ProposedChanges 2022 NBC NFC NPC NECB Combined 2022-10-24Document345 pagesNRC ProposedChanges 2022 NBC NFC NPC NECB Combined 2022-10-24AliNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration 22.1Document29 pagesRefrigeration 22.1preceiuxNo ratings yet
- Catalog F-1 PRV Adrp SporlanDocument16 pagesCatalog F-1 PRV Adrp Sporlancafreita0No ratings yet
- Trane 2TTB0060Document16 pagesTrane 2TTB0060Daniel Viñas B100% (1)
- Air-conditionSystems and VFDDocument5 pagesAir-conditionSystems and VFDAntonio PiagentiniNo ratings yet
- Damvent ENG BrochureDocument10 pagesDamvent ENG BrochureDamVent DamVentNo ratings yet
- Acc SVN25C en - 02082011Document68 pagesAcc SVN25C en - 02082011Mark Izsm AmersonNo ratings yet
- Basic Guide To Fire Alarm InstallationDocument12 pagesBasic Guide To Fire Alarm InstallationCatrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant CompressorDocument6 pagesRefrigerant CompressorLeonardo PerezNo ratings yet
- Thermal 10Document2 pagesThermal 10Rommel AunarioNo ratings yet
- Definition of Intelligent BuildingsDocument7 pagesDefinition of Intelligent BuildingsEmpress Vanessa TuticaNo ratings yet
- Compressor SpecificationsDocument1 pageCompressor SpecificationsSilas NjueNo ratings yet
- Saso-2874 2016Document34 pagesSaso-2874 2016Anand GkNo ratings yet
- FXMQ-NVE6 Data BookDocument36 pagesFXMQ-NVE6 Data BookmohamedroyaleyeuaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systems 2Document17 pagesLecture 3 Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systems 2Meftah ElfituriNo ratings yet
- Liebert Chilled Water Air Handler Data SheetDocument2 pagesLiebert Chilled Water Air Handler Data Sheetho luongNo ratings yet
- LG Um42r.n20Document1 pageLG Um42r.n20ΠΟΤΕΤΣΙΑΝΑΚΗ ΑΣΗΜΟΜΥΤΗΣNo ratings yet
- 42C&D FCU Series Catalogue-1-10Document10 pages42C&D FCU Series Catalogue-1-10KyawtNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled chiller-OQDocument2 pagesAir Cooled chiller-OQYu-Chih PuNo ratings yet
- What Are Double Pipe Heat Exchangers and Their Working PrinciplesDocument8 pagesWhat Are Double Pipe Heat Exchangers and Their Working PrinciplesAngel RatuNo ratings yet
- 201.28-EG1Document56 pages201.28-EG1Time To Use BrainNo ratings yet
- Audi q5 2008 Heating Ventilation Air Conditioner EngDocument728 pagesAudi q5 2008 Heating Ventilation Air Conditioner EngGiovanni L MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chiller Surge - The Engineering MindsetDocument4 pagesChiller Surge - The Engineering MindsetmuthuveerNo ratings yet
- HEATING - PRICE - LIST - September 2022 - ISSUE - 2Document36 pagesHEATING - PRICE - LIST - September 2022 - ISSUE - 2Mihaela ClaudiaNo ratings yet
Switchgear Building Ventilation
Switchgear Building Ventilation
Uploaded by
vlAnandOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Switchgear Building Ventilation
Switchgear Building Ventilation
Uploaded by
vlAnandCopyright:
Available Formats
U.S.
EPR FINAL SAFETY ANALYSIS REPORT
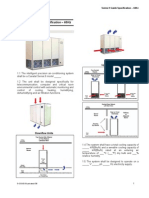
9.4.10 Switchgear Building Ventilation System
The switchgear building ventilation system (SGBVS) provides ventilation to the
station blackout diesel generator (SBODG) divisions 1 and 2 located inside the
Switchgear Building, including the diesel hall, fuel tank room, and associated electrical
rooms. The SGBVS is available to operate during all plant operating conditions, and
provides ventilation to remove heat generated by the SBODGs and associated electrical
equipment when in operation. During normal operation, the SBODGs are in standby.
9.4.10.1 Design Bases
The SGBVS does not perform any safety-related function. All components of the
SGBVS are non-safety related and Non-Seismic. The SBODGs are required only for
beyond design basis events (BDBEs).
The SGBVS maintains acceptable ambient temperatures and air renewals in the station
blackout (SBO) divisions to support operation of the SBODGs and associated electrical
equipment which provide an onsite alternate AC (AAC) emergency power source to
achieve and maintain the plant in a safe shutdown condition following a BDBE (refer
to Section 8.4). The SGBVS maintains the following ambient conditions inside the
SBO diesel divisions:
● Diesel hall and fuel tank room:
− 50°F to 115°F.
− No humidity control.
● Electric room:
− 59°F to 95°F.
− 35 to 70 percent humidity.
9.4.10.2 System Description
9.4.10.2.1 General Description
The SGBVS includes ventilation of the SBODG divisions 1 and 2. Each division has its
own independent and identical heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC)
system. The SGBVS provides ventilation of the diesel hall, fuel tank room, and
associated electrical rooms using outside air as the cooling medium.
The SGBVS consists of following subsystems for each SBODG division:
● Ventilation of diesel hall and fuel tank room.
● Ventilation of electrical rooms.
Tier 2 Revision 1 Page 9.4-103
U.S. EPR FINAL SAFETY ANALYSIS REPORT
Ventilation of Diesel Hall and Fuel Tank Room
The outside air is drawn to the SBODG division through an air intake screen and grill,
which prevents large objects from entering the air intake. The screen and grill are
heated during cold weather to prevent ice buildup. The outside air is supplied through
supply fans which are designed to provide the required air delivery flow rates. During
winter conditions, when the SBODGs are not in operation, the air in the diesel hall is
recirculated through the electric fan heaters to maintain the required minimum
temperature. The exhaust air from the diesel hall and fuel tank room is exhausted
outside the building.
Ventilation of Electrical Room
The inlet air supply for the electrical room is drawn from a common air supply shared
with the diesel hall. The inlet air is then directed through an air conditioning unit.
The conditioned air is supplied to the electrical room. The electric heaters increase the
supply air temperature during cold weather conditions. The exhaust air from the
electrical room is recirculated back through the air conditioning unit.
9.4.10.2.2 Component Description
The major components of the SGBVS are listed as follows, along with the applicable
codes and standards. Refer to Section 3.2 for the seismic and system quality group
classification of these components.
Ductwork and Accessories
The supply and exhaust air ducts are constructed of sheet steel and are structurally
designed for fan shutoff pressures. The ductwork meets the design, testing and
construction specifications of ASME AG-1-2003 (Reference 1).
Electric Heaters
The electric heaters are installed to maintain room ambient conditions, which are
controlled by local room temperature sensors. The electric heaters are designed to
commercial standards.
Prefilters
The prefilters are located upstream of the fans to prevent large particles from entering
the system. The prefilters meet the specifications of ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 52.2-
1999 (Reference 2).
Tier 2 Revision 1 Page 9.4-104
U.S. EPR FINAL SAFETY ANALYSIS REPORT
Fans
The supply and exhaust fans include electric motor drivers. Fan performance is rated
in accordance with ANSI/AMCA-210-99 (Reference 3), ANSI/AMCA-211-1987
(Reference 4), and ANSI/AMCA-300-1985 (Reference 5).
Isolation dampers
Manual dampers are adjusted during initial plant testing to establish accurate flow
balance between the rooms. The motor-operated dampers fail to “close” or “open”
position in case of power loss, depending on the safety function of the dampers. The
performance and testing requirements of the dampers are per Reference 1.
Fire Dampers
Fire dampers are installed where ductwork penetrates a fire barrier. Fire damper
design meets the requirements of UL 555 (Reference 6) and the damper fire rating is
commensurate with the fire rating of the barrier penetrated.
Cooling Coils
The cooling coils are installed in the supply train for cooling the electrical room. The
cooling coils are designed in accordance with Reference 1. A packaged chiller
provides a cooling medium of cold water to the cooling coils.
Humidifiers
Humidifiers are installed to maintain ambient humidity conditions in the electrical
room. Humidity levels are controlled by the humidity sensors in the room.
9.4.10.2.3 System Operation
Normal Plant Operation
The SGBVS maintains the required ambient conditions in the diesel hall, fuel tank
room and electrical room of each of the SBODG divisions, 1 and 2. During normal
plant operation, the SBODGs are in standby. However, outside air is supplied to the
diesel hall to prepare for startup of the SBODGs and for personnel comfort. During
cold weather conditions, the fan heaters are available to maintain the required
minimum temperature. When the SBODGs are in operation, the exhaust air removes
the excess heat generated in the diesel hall.
The electrical components are located in a separate room that has a separate air supply
train. The electrical room air supply provides conditioned air to maintain the required
ambient temperature and humidity. The outside air is mixed with the recycled air
from the electrical room, and the mixed air is then processed through the air
Tier 2 Revision 1 Page 9.4-105
U.S. EPR FINAL SAFETY ANALYSIS REPORT
conditioning train. The mixed air supply temperature and humidity are maintained by
the electrical heater, cooling coils, and humidifier located in the air conditioning train.
The exhaust air is discharged through the duct to an exhaust fan, then exhausted from
the Switchgear Building. Air renewals for the electrical room, diesel hall, and fuel
tank room are maintained as needed to obtain the required ambient temperatures.
Fire dampers are located in the ventilation system to avoid fire propagation within the
SBODG divisions. These rooms are completely isolated from each other in case of a
fire in an individual room. Fire is detected by a fire alarm system, which automatically
closes the corresponding fire damper.
Abnormal Operating Conditions
Failure of a Component
If one or more components of the SBODG division fail, the SGBVS is not able to
maintain the required ambient conditions in the affected SBO diesel division. Because
there are two redundant divisions, the failure of a component in one division does not
affect the other division.
Station Blackout
In the event of SBO, the SBODGs are started. Each of the two SGBVS divisions
receives power from its associated SBODG.
9.4.10.3 Safety Evaluation
There are no safety-related components for the SGBVS. The SBODGs are required
only for BDBEs.
9.4.10.4 Inspection and Testing Requirements
Refer to Section 14.2 (test abstract #086) for initial plant startup test program.
9.4.10.5 Instrumentation Requirements
Indication of the operational status of the equipment, position of dampers, instrument
indications and alarms are provided in the main control room (MCR). Fans, motor-
operated dampers, heaters and cooling units are operable from the MCR. Local
instruments are provided to measure differential pressure across filters, flow,
temperature and pressure. The fire detection and sensors information is delivered to
the fire detection system.
Tier 2 Revision 1 Page 9.4-106
U.S. EPR FINAL SAFETY ANALYSIS REPORT
9.4.10.6 References
1. ASME AG-1-2003, “Code on Nuclear Air and Gas Treatment,” The American
Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2003 (including the AG-1a, 2004 Addenda).
2. ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 52.2-1999, “Method of Testing General Ventilation Air-
Cleaning Devices for Removal Efficiency by Particle Size,” ANSI/American Society
of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers, 1999.
3. ANSI/AMCA-210-99, “Laboratory Methods of Testing Fans for Aerodynamic
Performance Rating,” American National Standards Institute/Air Movement and
Control Association International, December 1999.
4. ANSI/AMCA-211-1987, “Certified Ratings Program–Air Performance,” American
National Standards Institute/Air Movement and Control Association International,
1987.
5. ANSI/AMCA-300-1985, “Reverberant Room Method of Testing Fans for Rating
Purposes,” American National Standards Institute/Air Movement and Control
Association International, 1985.
6. UL 555, “Standard for Fire Dampers,” Underwriter’s Laboratories, Sixth Edition,
June 1999.
Next File
Tier 2 Revision 1 Page 9.4-107
You might also like
- Operator Manual - ClimaAIRE II - ENGDocument2 pagesOperator Manual - ClimaAIRE II - ENG2ndpostaNo ratings yet
- RR Trent 60Document39 pagesRR Trent 60Ricardo Cabrera Osinaga100% (6)
- Chigo Service-manual-CS25-35 PDFDocument32 pagesChigo Service-manual-CS25-35 PDFabloemenveldNo ratings yet
- Sequence of Operations For Hvac ControlsDocument4 pagesSequence of Operations For Hvac Controlsmacanipharoldf6220No ratings yet
- Liebert MC Condensers Guide SpecificationsDocument5 pagesLiebert MC Condensers Guide SpecificationsDavid SoaresNo ratings yet
- Standards and Labeling ProgramDocument9 pagesStandards and Labeling ProgramhimanshuNo ratings yet
- MC Quay Chiller 2Document44 pagesMC Quay Chiller 2naikNo ratings yet
- 空调Document16 pages空调HayLenLeeNo ratings yet
- Ewa (H) (D) - TZ C Data Books Eeden21 EnglishDocument255 pagesEwa (H) (D) - TZ C Data Books Eeden21 EnglishDiego Navarro PinoNo ratings yet
- EWYD-BZ Data-Books EEDEN21!10!27 EnglishDocument44 pagesEWYD-BZ Data-Books EEDEN21!10!27 EnglishMiquel BallesterNo ratings yet
- 90 Updated ELECTROMECHANICAL TRAINING MANUAL GENERATORS, UPS AND AIR CONDITIONINGDocument19 pages90 Updated ELECTROMECHANICAL TRAINING MANUAL GENERATORS, UPS AND AIR CONDITIONINGyalewlet tarekeggnNo ratings yet
- ComPacAVPAPDS 020509Document12 pagesComPacAVPAPDS 020509Anthony OrendainNo ratings yet
- Specification For Air-Cooled Packaged Computer Ac UnitDocument7 pagesSpecification For Air-Cooled Packaged Computer Ac Unitmihai_serban13No ratings yet
- Technical Specification For Air Conditioning System: GeneralDocument2 pagesTechnical Specification For Air Conditioning System: GeneralSaptarshi ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Air Con Ventilation and AccessoriesDocument52 pagesAir Con Ventilation and AccessoriesBala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Thyvent BroDocument6 pagesThyvent BroAlev AktürkNo ratings yet
- Liebert Intelecool2: 1.0 GeneralDocument5 pagesLiebert Intelecool2: 1.0 GeneraljairofgfNo ratings yet
- MRBT 075 CW D SpecificationsDocument19 pagesMRBT 075 CW D SpecificationsJorge Bravo100% (1)
- Chapter12 Water and DX SystemDocument32 pagesChapter12 Water and DX SystemNurhidayat NurhidayatNo ratings yet
- SASO2663Document19 pagesSASO2663damaso taracenaNo ratings yet
- AFPC Electrical ProceduresDocument4 pagesAFPC Electrical Proceduresapi-3697472100% (1)
- Brochure Air Cooled With ChillerDocument63 pagesBrochure Air Cooled With ChillerFrancisco BelloNo ratings yet
- VRVII Cooling Only Specification SMC 1-8-03 - TestDocument7 pagesVRVII Cooling Only Specification SMC 1-8-03 - TestAlexOdarteyBannermanNo ratings yet
- 1370 000DuMDocument13 pages1370 000DuMdrago.andres9No ratings yet
- Opa 116-201 TD 0521Document12 pagesOpa 116-201 TD 05217tddprzxbbNo ratings yet
- AVN 204 To 904 EVN/CVN 204 To 904: Vertical Packaged and Split Air ConditionersDocument32 pagesAVN 204 To 904 EVN/CVN 204 To 904: Vertical Packaged and Split Air ConditionersJoseLuisMuñozMuñozNo ratings yet
- Teh 12.530 60 0220Document46 pagesTeh 12.530 60 0220سعد الجهنيNo ratings yet
- Electronics Cooling TermsDocument13 pagesElectronics Cooling TermscristianNo ratings yet
- Inverter Air Cooled Screw Chillers: Product ManualDocument52 pagesInverter Air Cooled Screw Chillers: Product ManualKyaw San OoNo ratings yet
- VRVII Cooling Only Specification SMC 1-8-03Document7 pagesVRVII Cooling Only Specification SMC 1-8-03mohamed mansyNo ratings yet
- Saudi Exhaust FanDocument40 pagesSaudi Exhaust FanBasheer MohammedNo ratings yet
- ML13073A698Document9 pagesML13073A698Dexter BothaNo ratings yet
- G2 Spec Mechanical Air CondDocument5 pagesG2 Spec Mechanical Air Condsyahirah natasyaNo ratings yet
- DBR PDDDocument13 pagesDBR PDDMEERANo ratings yet
- Micro Extension TSGDocument28 pagesMicro Extension TSGeng-ashraf abdullahNo ratings yet
- HVAC Guide Specifications Commercial Air-Cooled Condensing UnitsDocument4 pagesHVAC Guide Specifications Commercial Air-Cooled Condensing UnitsHazemNo ratings yet
- Ewyq FDocument54 pagesEwyq FRicardo Molina SánchezNo ratings yet
- Letter of AssociationDocument25 pagesLetter of AssociationluluNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER23PT2Document12 pagesCHAPTER23PT2dustinmoateNo ratings yet
- Eastman Industries SpecificationDocument47 pagesEastman Industries SpecificationcivilNo ratings yet
- McQuay McEnergy HPI Technical Manual EngDocument48 pagesMcQuay McEnergy HPI Technical Manual EngZhenqian HNo ratings yet
- Appendix a - ComplianceDocument1 pageAppendix a - CompliancePråðèép Thê PërfömèrNo ratings yet
- CSRAT-Y Air Cooled Chiller - R134aDocument36 pagesCSRAT-Y Air Cooled Chiller - R134aLeed ENNo ratings yet
- Databook - EWA (Y) T-CZ (N-P-H) Daikin EN - Rev6Document64 pagesDatabook - EWA (Y) T-CZ (N-P-H) Daikin EN - Rev6kevin.sparks.isoenergyNo ratings yet
- Cooling For Mobile Base Stations and Cell TowersDocument7 pagesCooling For Mobile Base Stations and Cell TowersRaed Al-HajNo ratings yet
- Hvac Technical SpecificationsDocument6 pagesHvac Technical SpecificationsAbdul JabbarNo ratings yet
- Ferroli Hot Oil HTR (GB)Document30 pagesFerroli Hot Oil HTR (GB)RodNo ratings yet
- Especification Guide Serie 9Document12 pagesEspecification Guide Serie 9menmsisNo ratings yet
- Vitocal 100-Aw Am2v TDMDocument44 pagesVitocal 100-Aw Am2v TDMerugazeroNo ratings yet
- 1391 1Document26 pages1391 1Aaron AngNo ratings yet
- 42BJ ICM LEC 1.9 - 2.9 - 4.9: Individual Comfort Module For Variable Air Volume SystemsDocument20 pages42BJ ICM LEC 1.9 - 2.9 - 4.9: Individual Comfort Module For Variable Air Volume SystemsBulat IııNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones Tecnicas Apc Aa InrowDocument6 pagesEspecificaciones Tecnicas Apc Aa InrowWilder Phill Arzapalo GinesNo ratings yet
- EN WPE0063 Choosing Cooling IT CabinetDocument5 pagesEN WPE0063 Choosing Cooling IT CabinetabudisNo ratings yet
- Mechanical - Hvac SystemsDocument11 pagesMechanical - Hvac SystemsWahyudi HardyNo ratings yet
- SUNLINE 2000-: Single Package Gas / Electric Units and Single Package Air ConditionersDocument16 pagesSUNLINE 2000-: Single Package Gas / Electric Units and Single Package Air ConditionersBernardo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Opa 465-960 Uc8 Eco TD 0322Document24 pagesOpa 465-960 Uc8 Eco TD 03227tddprzxbbNo ratings yet
- Acson Lexus ChillersDocument59 pagesAcson Lexus ChillersKardos Zoltan100% (1)
- AHUs 2020Document36 pagesAHUs 2020Technical OfficeNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Built-In Thermal Protection For - !elbctric Motors Rated Up To 660 V Ac - SpecificationDocument14 pagesIndian Standard: Built-In Thermal Protection For - !elbctric Motors Rated Up To 660 V Ac - Specificationkushal_lonareNo ratings yet
- Mep LayoutsDocument3 pagesMep LayoutsvlAnandNo ratings yet
- Sofilair H13/H14: AdvantagesDocument1 pageSofilair H13/H14: AdvantagesvlAnandNo ratings yet
- Production SystemDocument58 pagesProduction SystemvlAnandNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3: Advances in MetrologyDocument42 pagesUNIT-3: Advances in MetrologyMebinNo ratings yet
- Delta Ia-Dpm DPM C en 20160914Document7 pagesDelta Ia-Dpm DPM C en 20160914CLAUDIONo ratings yet
- Air Handling Unit - Definition and Configuration TypesDocument6 pagesAir Handling Unit - Definition and Configuration TypesAhmad HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Abbattitore Di Temperatura Mod. BE-R151 - UKDocument3 pagesAbbattitore Di Temperatura Mod. BE-R151 - UKConrado TangariNo ratings yet
- Manual Mcquay M4RT250ARDocument207 pagesManual Mcquay M4RT250ARalextermotecNo ratings yet
- Guidehouse S.E PDFDocument43 pagesGuidehouse S.E PDFJuan Amilcar Pedraza PachecoNo ratings yet
- NRC ProposedChanges 2022 NBC NFC NPC NECB Combined 2022-10-24Document345 pagesNRC ProposedChanges 2022 NBC NFC NPC NECB Combined 2022-10-24AliNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration 22.1Document29 pagesRefrigeration 22.1preceiuxNo ratings yet
- Catalog F-1 PRV Adrp SporlanDocument16 pagesCatalog F-1 PRV Adrp Sporlancafreita0No ratings yet
- Trane 2TTB0060Document16 pagesTrane 2TTB0060Daniel Viñas B100% (1)
- Air-conditionSystems and VFDDocument5 pagesAir-conditionSystems and VFDAntonio PiagentiniNo ratings yet
- Damvent ENG BrochureDocument10 pagesDamvent ENG BrochureDamVent DamVentNo ratings yet
- Acc SVN25C en - 02082011Document68 pagesAcc SVN25C en - 02082011Mark Izsm AmersonNo ratings yet
- Basic Guide To Fire Alarm InstallationDocument12 pagesBasic Guide To Fire Alarm InstallationCatrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant CompressorDocument6 pagesRefrigerant CompressorLeonardo PerezNo ratings yet
- Thermal 10Document2 pagesThermal 10Rommel AunarioNo ratings yet
- Definition of Intelligent BuildingsDocument7 pagesDefinition of Intelligent BuildingsEmpress Vanessa TuticaNo ratings yet
- Compressor SpecificationsDocument1 pageCompressor SpecificationsSilas NjueNo ratings yet
- Saso-2874 2016Document34 pagesSaso-2874 2016Anand GkNo ratings yet
- FXMQ-NVE6 Data BookDocument36 pagesFXMQ-NVE6 Data BookmohamedroyaleyeuaeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systems 2Document17 pagesLecture 3 Vapour Compression Refrigeration Systems 2Meftah ElfituriNo ratings yet
- Liebert Chilled Water Air Handler Data SheetDocument2 pagesLiebert Chilled Water Air Handler Data Sheetho luongNo ratings yet
- LG Um42r.n20Document1 pageLG Um42r.n20ΠΟΤΕΤΣΙΑΝΑΚΗ ΑΣΗΜΟΜΥΤΗΣNo ratings yet
- 42C&D FCU Series Catalogue-1-10Document10 pages42C&D FCU Series Catalogue-1-10KyawtNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled chiller-OQDocument2 pagesAir Cooled chiller-OQYu-Chih PuNo ratings yet
- What Are Double Pipe Heat Exchangers and Their Working PrinciplesDocument8 pagesWhat Are Double Pipe Heat Exchangers and Their Working PrinciplesAngel RatuNo ratings yet
- 201.28-EG1Document56 pages201.28-EG1Time To Use BrainNo ratings yet
- Audi q5 2008 Heating Ventilation Air Conditioner EngDocument728 pagesAudi q5 2008 Heating Ventilation Air Conditioner EngGiovanni L MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chiller Surge - The Engineering MindsetDocument4 pagesChiller Surge - The Engineering MindsetmuthuveerNo ratings yet
- HEATING - PRICE - LIST - September 2022 - ISSUE - 2Document36 pagesHEATING - PRICE - LIST - September 2022 - ISSUE - 2Mihaela ClaudiaNo ratings yet