Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dytdytyd
Dytdytyd
Uploaded by
amanrathor96310 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageOriginal Title
dytdytyd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageDytdytyd
Dytdytyd
Uploaded by
amanrathor9631Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
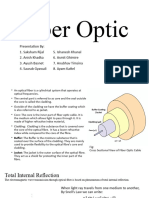
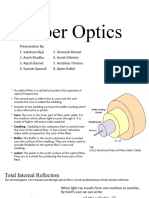
Attenuation is a measure of decay of signal strength or
loss of light power that occurs as light pulses
propagate through the length of the fiber. Mie scattering is elastic scattered light of particles that
have a diameter similar to or larger than the
wavelength of the incident light. The Mie signal is
proportional to the square of the particle diameter.
Types of non-linear scattering losses 1. Stimulated
Brillonin Scattering (SBS) 2. Raman Scattering (SRS)
Brillonin Scattering (SBS) • The SBS exists when light
is modulated through the thermal molecular vibrations
Basic Attenuation Mechanisms 2. Scattering ( Linear within fiber. • The scattered light is observed as both
and Non-linear) 3. Bending loss 1. Material Absorption upper and lower sidebands separated from incident
(Intrinsic and Extrinsic).
Material absorption is caused by absorption of light by modulation frequency. Raman Scattering
photons within the fiber.When a material is (SRS) • SRS is stimulated with a high frequency
illuminated, photons can make the valence electrons optical photon generated in scattering phenomena. •
of an atom transition to higher energy levels Photon is SRS may exist both in forward and backward
destroyed, and the radiant energy is transformed into directions in optical fibers. • The optical power
threshold is three times higher than SBS threshold.
electric potential energy. This energy can then• Be re-
Bending Loss an optical fiber introduces a loss in light
emitted (scattering)• Frees the electron (photoelectric
power Microbending - Result of microscopic
effects) (not in fibers)• Dissipated to the rest of the
imperfections in the geometry of the fiber
material (transformed into heat).In an optical fiber
Macrobending - Fiber bending with diameters on the
Material Absorption is the optical power that is order of centimeters (usually if the radius of the bend is
effectively converted to heat dissipation within the larger than 10cm.
fiber.
• Two types of absorption exist:
Intrinsic Absorption, caused by interaction with one or
more of the components of the glass.
Extrinsic Absorption, caused by impurities within the
glass.
• Intrinsic Absorption is caused by basic fiber material
properties. If an optical fiber is absolutely pure, with
no imperfections or impurities, ten all absorption will
be intrinsic. Intrinsic absorption in the ultraviolet
region is caused by electronic absorption bands. Pulse Broadening In the ray model there are a
Intrinsic Absorption occurs when a light particle continuum of ray directions between the axial ray and
(photon) interacts with an electron and excites it to a the critical angle ac The axial ray takes the shortest
higher energy level. route and arrives at the far end first, whereas the ray at
the critical angle takes the longest route and arrives
Extrinsic Absorption is caused by impurities caused by
impurities introduced into the fiber material. The
metal impurities such as iron, nickel and chromium are
introduced into the fiber during fabrication. Extrinsic
Absorption is caused by the electronic transition of
these metal ions from one energy level to another
energy level. last. A short input pulse will be broadened by the
range of paths travelled
Dispersion • Dispersion effects broaden the pulse as it
propagates along the fibre • The broadening is
measured in nsec/km • After large distance the pulses
overlap (intersymbol interference-ISI) and become
indistinguishable – electrical dispersion
Dispersion types 2. Intermodal (Modal) dispersion 1.
Intramodal (Chromatic) dispersion i) Material
dispersion ii) Waveguide dispersion
Intramodal dispersion
Scattering LossesLight scattering is a form of scattering An optical signal can have different wavelengths that
in which light in the form of propagating energy is travels at a slightly different speed and arrive at the
scattered.Light scattering can be thought of as the receiver at different times within the mode causing the
deflection of a ray from a straight path, for example by signal to spread out and become distorted. This type
irregularities in the propagation medium, particles, or of dispersion is called Intramodal dispersion and
in the interface between two media.Deviations from occurs in both single and multimode fibers.
the law of reflection due to irregularities on a surface The dispersion which is caused by the delay between
are also usually considered to be a form of scattering. different modes is called inter model dispersion.
When these irregularities are considered to be random It is dispersion between the modes, caused by
and dense enough that their individual effects average difference in propagation time for different modes.
out, this kind of scattered reflection is commonly
referrec to as diffuse reflection.
Linear Scattering may be of two types
1.Rayleigh Scattering2. Mie Scattering
Rayleigh scattering is the scattering of light by the
particles present in the atmosphere. According to
Rayleigh's scattering law, the amount of scattering of
the light is inversely proportional to the fourth power
of the wavelength. From the relation between
scattering and wavelength, we understand that shorter
wavelengths scatter more. Since blue light has a lesser
wavelength than red light it scatters more. Rayleigh
scattering component can be reduced by operating at
the longest possible wavelength.
You might also like
- Loss Characteristics of Optical FiberDocument9 pagesLoss Characteristics of Optical FiberShuvodip Das93% (15)
- Losses in Optical FiberDocument8 pagesLosses in Optical FiberthatoneJgd100% (8)
- Raman Scattering BasicsDocument11 pagesRaman Scattering BasicsAnkita RajputNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument86 pagesFiber OpticsChristopher Oares100% (1)
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneFrom EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- YORK Price ListDocument4 pagesYORK Price ListKoekie67% (3)
- Attenuation Is A Measure of Decay of Signal Strength or Loss of Light Power That Occurs As Light Pulses Propagate Through The Length of The FiberDocument1 pageAttenuation Is A Measure of Decay of Signal Strength or Loss of Light Power That Occurs As Light Pulses Propagate Through The Length of The Fiberamanrathor9631No ratings yet
- Unit2 Trail OcDocument22 pagesUnit2 Trail OcAnonymous 1DK1jQgAGNo ratings yet
- through mirror and prisms frequency and very short λ photo electric effectDocument2 pagesthrough mirror and prisms frequency and very short λ photo electric effectRaymie A RahmanNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument8 pagesFiber Optics CommunicationsKuronix ArcayaNo ratings yet
- Brillouin Scattering Is Caused by The Non Linearity of A MediumDocument3 pagesBrillouin Scattering Is Caused by The Non Linearity of A Mediummus4allNo ratings yet
- ch3 - Fiber - Signal DegradationDocument23 pagesch3 - Fiber - Signal Degradationjitendra chaudhariNo ratings yet
- Light Notes 1Document31 pagesLight Notes 1api-233194737No ratings yet
- Optical Communication and NetworkDocument44 pagesOptical Communication and Networkkumarnath jNo ratings yet
- Ocn Unit 2Document41 pagesOcn Unit 2rohityaduvanshirrNo ratings yet
- OC Unit 2 - PPTDocument51 pagesOC Unit 2 - PPTRajeswariNo ratings yet
- 4th Attenuation and DispersionDocument45 pages4th Attenuation and DispersionSahmi Abdulqahar NizoriNo ratings yet
- Lec11 ES475 2023 Upload PDFDocument28 pagesLec11 ES475 2023 Upload PDFEmad RazaNo ratings yet
- MMC403 Lecture 06Document14 pagesMMC403 Lecture 06tridibkuiry116No ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Intro: - Presentor Muhammad JawadDocument59 pagesOptical Fiber Intro: - Presentor Muhammad JawadMuhammad JawadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 7Document12 pagesChemistry Chapter 7Heather KieferNo ratings yet
- Fors211 Photo Lesson 3 (Light)Document34 pagesFors211 Photo Lesson 3 (Light)Almar MamarintaNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Intro PDFDocument35 pagesSpectroscopy Intro PDFonyxNo ratings yet
- Wave Behavior of LightDocument20 pagesWave Behavior of LightrafaNo ratings yet
- Signal DegradationDocument33 pagesSignal Degradationmukhsin 98No ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument29 pagesOptical Fiberakanskah kumariNo ratings yet
- Interference Diffraction PolarizationDocument45 pagesInterference Diffraction Polarizationloharnikhil309No ratings yet
- Losses in OfcDocument26 pagesLosses in OfcdharaniNo ratings yet
- OPTICAL FIBRE COMMUNICATION Notes PDFDocument18 pagesOPTICAL FIBRE COMMUNICATION Notes PDFAkhil RajuNo ratings yet
- UNIT II 2 MarksDocument5 pagesUNIT II 2 MarksMaster SINIVASANNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Pertama - PPTX (Autosaved)Document66 pagesPertemuan Pertama - PPTX (Autosaved)VickyodianaNo ratings yet
- Laser Model 2Document182 pagesLaser Model 2vipinNo ratings yet
- Light Waves (Science)Document43 pagesLight Waves (Science)Aurish Bang-asanNo ratings yet
- Optical PropertiesDocument27 pagesOptical PropertiespotterheadNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing and GisDocument17 pagesRemote Sensing and Gismd khajaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics and Laser Instrumentation - Module 1Document35 pagesFiber Optics and Laser Instrumentation - Module 1maheshnaikm143No ratings yet
- Transmission Characteristics of Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument16 pagesTransmission Characteristics of Optical Fiber CommunicationanjaliNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticDocument14 pagesFiber Optic080bei010.asmitNo ratings yet
- Scattering LossDocument13 pagesScattering LossRidhima Mamnani100% (2)
- Phys 3616e Chap7Document21 pagesPhys 3616e Chap7johnNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticDocument18 pagesFiber Optic080bei010.asmitNo ratings yet
- LightDocument14 pagesLightmarinellearbisNo ratings yet
- LightDocument68 pagesLightAmita MaddhesiyaNo ratings yet
- 411 SydDocument159 pages411 SydUtsho DasNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties & CharacteristicsDocument21 pagesOptical Properties & CharacteristicsRogelyn JosolNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument4 pagesLIGHTNerrio Christian Art NerioNo ratings yet
- LightDocument12 pagesLightapi-3703711100% (1)
- IR/UV Spectroscopy: U. Mall Lindau, 28.10.2010Document54 pagesIR/UV Spectroscopy: U. Mall Lindau, 28.10.2010Trishna paulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document28 pagesLecture 2Md. Rakibul IslamNo ratings yet
- The Nature of LightDocument15 pagesThe Nature of LightPrince SumanNo ratings yet
- Lec 07Document32 pagesLec 07Jonald CastañedaNo ratings yet
- CHM556/ CHM557 Organic Chemistry Ii/ Organic Chemistry: Spectroscopy of Carbon CompoundsDocument200 pagesCHM556/ CHM557 Organic Chemistry Ii/ Organic Chemistry: Spectroscopy of Carbon CompoundsnanaNo ratings yet
- Electrotherapy 2Document138 pagesElectrotherapy 2nagyrashad123No ratings yet
- Introduction To Spectroscopy: I Spectroscopy and The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Spectroscopy: I Spectroscopy and The Electromagnetic Spectrumbinfa kashafNo ratings yet
- Nature of Light PPT FinalDocument58 pagesNature of Light PPT FinalMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Optical PropertiesDocument31 pagesOptical PropertiesAhmed MalikNo ratings yet
- Attenuation Losses by MAMCEDocument9 pagesAttenuation Losses by MAMCEDhalal AsmiNo ratings yet
- Spectro Photo Me TryDocument3 pagesSpectro Photo Me TryAshley Nicole DelizoNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 Spectroscopy 1Document93 pagesChap 3 Spectroscopy 1Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- Remote SensingDocument24 pagesRemote Sensingsom ranaNo ratings yet
- Chew 2011Document14 pagesChew 2011sooommmNo ratings yet
- 6-9660-F (DD320-40) PDFDocument4 pages6-9660-F (DD320-40) PDFlorenzo henerNo ratings yet
- Stefanos Manias: Power Electronics Motor Drive Systems Renewable Energy SourcesDocument2 pagesStefanos Manias: Power Electronics Motor Drive Systems Renewable Energy SourcesmizraimNo ratings yet
- Experimental Stress Analysis (ME412) - PPTclass3Document14 pagesExperimental Stress Analysis (ME412) - PPTclass3Ssh keys JoshNo ratings yet
- Disconnectors Reliability On The French Grid and Means To Reduce The Consequences of Their FailuresDocument7 pagesDisconnectors Reliability On The French Grid and Means To Reduce The Consequences of Their Failureskushwah9kpriyaNo ratings yet
- Retrofitting Works at Khurja Dehat (Zone-1 Nehrupur, Zone-2 Qila Mawai) Village Water Supply SchemeDocument8 pagesRetrofitting Works at Khurja Dehat (Zone-1 Nehrupur, Zone-2 Qila Mawai) Village Water Supply Schemeankur yadavNo ratings yet
- Tatad vs. Secretary of EnergyDocument7 pagesTatad vs. Secretary of EnergySGTNo ratings yet
- Satish CVDocument3 pagesSatish CVmesattyNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: C-Mag Hs 7Document2 pagesData Sheet: C-Mag Hs 7SarahBlueGazitanNo ratings yet
- Mypyn Ta7-SnrDocument2 pagesMypyn Ta7-SnrJ.l. AlemanNo ratings yet
- PM3 Owners ManualDocument4 pagesPM3 Owners ManualHeather Stephanie SchweitzerNo ratings yet
- Transient Conduction: Spatial Effects, Semi-Infinite Solids, and Finite-Difference MethodsDocument58 pagesTransient Conduction: Spatial Effects, Semi-Infinite Solids, and Finite-Difference MethodsJkun gamingNo ratings yet
- CGP30, DGP30: Vishay General SemiconductorDocument4 pagesCGP30, DGP30: Vishay General SemiconductorTuribio Almeida BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Indian National Astronomy Olympiad (Inao) - 2016: Questions Paper With SoluionDocument9 pagesIndian National Astronomy Olympiad (Inao) - 2016: Questions Paper With SoluionDwiNo ratings yet
- Cabinet Cooler SystemsDocument18 pagesCabinet Cooler SystemsRoberto Renato Castro VergaraNo ratings yet
- 3M 8810 Thermal AdhesiveDocument8 pages3M 8810 Thermal Adhesivecsanders7No ratings yet
- Chilled Water DistibutionDocument56 pagesChilled Water DistibutionorganicspolybondNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Srk40hd-s ManualDocument22 pagesMitsubishi Srk40hd-s Manualdingeo11No ratings yet
- Hsu 07.09.Cc - HC.CH - HHDocument114 pagesHsu 07.09.Cc - HC.CH - HHHenry Colmenares0% (1)
- Polygeneration of Electricity, Heat and Ultra Pure Water For Semiconductor IndustryDocument16 pagesPolygeneration of Electricity, Heat and Ultra Pure Water For Semiconductor IndustrybillNo ratings yet
- LCM & LEM 320 Control and Expander Modules Data SheetDocument2 pagesLCM & LEM 320 Control and Expander Modules Data SheetGabriel OsorioNo ratings yet
- Steven Greer TranscriptDocument44 pagesSteven Greer Transcriptpgeorg100% (1)
- Appropriate TechnologyDocument16 pagesAppropriate Technologydpka85No ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 4: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsDocument16 pagesICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 4: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsArijit Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- Braun Hallprobe A5s Series Data SheetDocument6 pagesBraun Hallprobe A5s Series Data SheetsrinuvoodiNo ratings yet
- Highlights of Union Budget 2019-20Document26 pagesHighlights of Union Budget 2019-20Sunil SaharanNo ratings yet
- MA010 ManualDocument2 pagesMA010 ManualJOSE SALAZARNo ratings yet
- Mic 1462 1/4 Din Setpoint Programmer Reference Manual: REV. 10-07 E-91 P.N. 136109Document112 pagesMic 1462 1/4 Din Setpoint Programmer Reference Manual: REV. 10-07 E-91 P.N. 136109kmpoulosNo ratings yet
- Sinvert - 600 SiemensDocument2 pagesSinvert - 600 SiemensLuis Álvarez JátivaNo ratings yet