Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HRT-8 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid
HRT-8 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid
Uploaded by
AakankshaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HRT-6 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidDocument3 pagesHRT-6 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidAakankshaNo ratings yet
- HRT-3 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidDocument4 pagesHRT-3 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidAakankshaNo ratings yet
- HRT-5 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidDocument3 pagesHRT-5 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidAakankshaNo ratings yet
- HRT-7 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidDocument4 pagesHRT-7 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidAakankshaNo ratings yet
- CHM222 Ch.8 (Ch.20) MCQDocument22 pagesCHM222 Ch.8 (Ch.20) MCQlianahajjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4Haseeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ester EnolatesDocument10 pagesEster EnolatesJunior GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQ XiiDocument53 pagesChemistry MCQ XiiHassan RedaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 OchemII QuizDocument13 pagesChapter 19 OchemII QuizPriyanka SaxenaNo ratings yet
- KetonesDocument13 pagesKetonesPriyanka SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 12 ComoleteDocument1 page12 ComoleteSheraz ShahNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry EM - Public Exam 2022 - Model Question Paper - English Medium PDF DownloadDocument4 pages12th Chemistry EM - Public Exam 2022 - Model Question Paper - English Medium PDF DownloadThenmozh iNo ratings yet
- Paper Class XDocument3 pagesPaper Class XHaiderNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SET C QPDocument9 pagesChemistry SET C QPowenknight3456No ratings yet
- Do Not Open This Booklet Until Told To Do SoDocument18 pagesDo Not Open This Booklet Until Told To Do SoNasyaNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Compounds Will Have Highest Boiling Point?Document4 pagesWhich of The Following Compounds Will Have Highest Boiling Point?reham khaledNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Carboxylic AcidDocument1 pageQuiz 2 Carboxylic AcidYousef AminNo ratings yet
- 1694692263SAT Chemistry Practice - Paper 38Document6 pages1694692263SAT Chemistry Practice - Paper 38agyeimalvin29No ratings yet
- Set 2Document6 pagesSet 2sanjith4arisNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE 2012 FST1 P2 QnsDocument25 pagesIIT-JEE 2012 FST1 P2 QnsShivamGoyalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10Document14 pagesChemistry 10BehruzNo ratings yet
- All Boards Full Book McqsDocument9 pagesAll Boards Full Book Mcqsbebetterpls3No ratings yet
- KVS Lucknow XII CHE QP & MS Pre-Board (23-24)Document11 pagesKVS Lucknow XII CHE QP & MS Pre-Board (23-24)GuestNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Questions Chapter Wise Upsc Capf Ac ExamDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRY Questions Chapter Wise Upsc Capf Ac Exambnnews2019100% (1)
- Chem 10 Ch#9,10,11,13Document3 pagesChem 10 Ch#9,10,11,13Zeeshan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQDocument11 pagesHalogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQParshantKumarBajaj92% (13)
- 116180HSSC IichemistryDocument2 pages116180HSSC IichemistryMughal usmanNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-III-CHE-PaperDocument6 pagesMock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-III-CHE-PaperHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- SIET CHEM Mock 2 PDFDocument7 pagesSIET CHEM Mock 2 PDFVikashNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Jee: Objective QuestionsDocument44 pagesQuestion Bank For Jee: Objective QuestionsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model Paper XIIDocument10 pagesChemistry Model Paper XIImoonmehar2240No ratings yet
- D) 3 AlcoholDocument9 pagesD) 3 AlcoholJessicaNo ratings yet
- Test 9Document1 pageTest 9Sheraz ShahNo ratings yet
- PUC II EXPERT CHEMISTRY 12 Set of MODEL QUESTION PAPERDocument46 pagesPUC II EXPERT CHEMISTRY 12 Set of MODEL QUESTION PAPERShreyasNo ratings yet
- FORM TP 2007061: Caribbean Examinations Council Secondary Education Certificate Examination ChemistryDocument8 pagesFORM TP 2007061: Caribbean Examinations Council Secondary Education Certificate Examination ChemistryJennifer ElliottNo ratings yet
- Kedah Chemistry Trial 2010 (NO BAHASA MELAYU)Document27 pagesKedah Chemistry Trial 2010 (NO BAHASA MELAYU)plouffleNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument5 pagesAssignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesREGINE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- Excel Educational Centre, Villa #25, Street #818, Al Thumama, Doha, QatarDocument7 pagesExcel Educational Centre, Villa #25, Street #818, Al Thumama, Doha, QatarteenaNo ratings yet
- CHEM W.S For G-9&10Document5 pagesCHEM W.S For G-9&10Chernet AhmedNo ratings yet
- CHM222 Ch.9 (Ch.21) MCQDocument44 pagesCHM222 Ch.9 (Ch.21) MCQlianahajjNo ratings yet
- Maritime Engineering Exam EthiopiaDocument7 pagesMaritime Engineering Exam EthiopiaLemi Chala Beyene95% (37)
- Alkynes and Aromatic CompoundsDocument4 pagesAlkynes and Aromatic Compounds22071a6652No ratings yet
- IIT JEE Main Sample Paper Set2 QuestionsDocument45 pagesIIT JEE Main Sample Paper Set2 QuestionsaskiitianNo ratings yet
- Chem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)Document4 pagesChem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)fahadmustafa100% (1)
- Test 12Document2 pagesTest 12Sheraz ShahNo ratings yet
- Trial p3 2016 Q (Johor-Sekolah Tinggi Muar)Document8 pagesTrial p3 2016 Q (Johor-Sekolah Tinggi Muar)Chan Yek FungNo ratings yet
- Diwali Assignment 12thDocument19 pagesDiwali Assignment 12thNishantPlayz YtNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Assignment No. 3 Chapters 11 12 (AY2021-2022 (2nd Sem)Document8 pagesAnswer Key Assignment No. 3 Chapters 11 12 (AY2021-2022 (2nd Sem)REGINE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- 12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument23 pages12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsBedosi Bidita PandaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry MCQDocument19 pagesClass 12 Chemistry MCQTayseer SaudiaNo ratings yet
- (ACOT'22) Part 1 - Bronze Tier SolnsDocument12 pages(ACOT'22) Part 1 - Bronze Tier SolnsAnju GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chem 17 LE 2 2nd SemDocument3 pagesChem 17 LE 2 2nd SemMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Practice Chapter 2 Hydrocarbon Frameworks - AlkanesDocument22 pagesPractice Chapter 2 Hydrocarbon Frameworks - AlkanesNadzirah ZaimNo ratings yet
- Application of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchFrom EverandApplication of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchRajmund MichalskiNo ratings yet
- AGARBATTI処方2Document16 pagesAGARBATTI処方2cobianNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet Alkanes Sbi 09Document6 pagesWork Sheet Alkanes Sbi 09neneng rohayatiNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionDocument15 pagesName Reactionnirbhay shukla100% (1)
- Analysis of Oxygen-Bearing Organic CompoundsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Oxygen-Bearing Organic CompoundsJudith Eliza MarianoNo ratings yet
- 2-328 Physical and Chemical Data: TABLE 2-371 Diffusivities of Pairs of Gases and Vapors (1 Atm)Document5 pages2-328 Physical and Chemical Data: TABLE 2-371 Diffusivities of Pairs of Gases and Vapors (1 Atm)opinion surNo ratings yet
- Drawing Haworth ProjectionsDocument4 pagesDrawing Haworth ProjectionsDoris GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Glove SafetyDocument2 pagesChemical Glove SafetynootsamNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 231111 210733Document3 pagesAssignment-1 231111 210733mamon137No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesCarbohydrates: Organic Chemistryistri kyungsoNo ratings yet
- Alcohols - Nomenclature and Classification: Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesAlcohols - Nomenclature and Classification: Learning ObjectivesDionisio BrinosaNo ratings yet
- CHIMICA PANZIERI Industrial-CatalogueDocument28 pagesCHIMICA PANZIERI Industrial-CatalogueJose E BatistaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Derivatives and NitrilesDocument23 pagesAcids, Derivatives and NitrilesLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- CarbenesDocument4 pagesCarbenesDr_GSNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xii NAME: - : Alcohol, Phenol & EtherDocument1 pageChemistry Xii NAME: - : Alcohol, Phenol & EtherSahir Hemnani100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - Benzene and AromaticityDocument38 pagesChapter 6 - Benzene and AromaticityS JNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Protecting GroupDocument39 pagesTopic 4 - Protecting Groupzatty kimNo ratings yet
- Oc02 Alkenesalkynesandcyclichydrocarbons WorksheetDocument5 pagesOc02 Alkenesalkynesandcyclichydrocarbons WorksheetEnma MaradiagaNo ratings yet
- Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal As A Building Block in Heterocyclic SynthesisDocument27 pagesDimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal As A Building Block in Heterocyclic SynthesisWalid Ebid ElgammalNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and Alkynes: Lesson 3Document21 pagesAlkenes and Alkynes: Lesson 3AlbaraaAliNo ratings yet
- Nomen 1st Day Quiz Key 2 PDFDocument16 pagesNomen 1st Day Quiz Key 2 PDFUday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations II - V 3 (Carbon With One Heteroatom Attached by A Multiple Bond)Document748 pagesComprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations II - V 3 (Carbon With One Heteroatom Attached by A Multiple Bond)Marlos BayerNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 DipadDocument4 pagesExp 4 DipadGrace HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument114 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryJoefrance MayagmaNo ratings yet
- Amines and Amides AnswersDocument2 pagesAmines and Amides AnswersKristine Sumalinog0% (1)
- Che102 Likely Qs and AnsDocument13 pagesChe102 Likely Qs and AnsAlexander GeorgeNo ratings yet
- NET-REAGENTS OlaxDocument5 pagesNET-REAGENTS Olaxraghava123456No ratings yet
- Mock Exam 2-AnswersDocument8 pagesMock Exam 2-AnswersKhaledEl-MaghallawyNo ratings yet
- Chapter36 - BiomoleculesDocument19 pagesChapter36 - BiomoleculesAkash GoelNo ratings yet
- Apch11 EstersDocument2 pagesApch11 Estersloly62006No ratings yet
- 2.24 Pyrans and Fused Pyrans: (Iii) Synthesis and ApplicationsDocument1 page2.24 Pyrans and Fused Pyrans: (Iii) Synthesis and ApplicationsscadvijayNo ratings yet
HRT-8 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid
HRT-8 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid
Uploaded by
AakankshaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HRT-8 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid
HRT-8 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic Acid
Uploaded by
AakankshaCopyright:
Available Formats
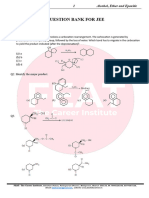
PARA CLASSES
IIT–JEE/NEET/FOUNDATION
CHEMISTRY BY ARUN DIXIT SIR
CLASS - XII
gj jkst VsLV&8 (HRT-8) (SYLLABUS COVERED–ALDEHYDES, KETONS AND CARBOXYLIC ACID)
TIME : 20 MINUTES M.M. 80
Important Instructions:
1. The test is for 20 Minutes duration and contains 20 multiple choice questions
2. Each Question carries 4 marks. For each correct response, the candidate will get 4 marks. For each incorrect response one mark will be deducted from the
total scores. The maximum marks are 80.
3. Use Blue /Black Point Pen only for writing particulars on this page/marking responses on Answer Sheet.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1. Two mole of acetic acid are heated with P2 O5. The product formed is:
a) 2 mole of ethyl alcohol
b) Formic anhydride
c) Acetic anhydride
d) 2 mole of methyl cyanide
2. The nitrogen content in the proteins can be quantitatively estimated by:
a) Carius method
b) Kjeldahl’s method
c) Victor Meyer’s method
d) Rast method
3. Correct order of reducing power of the following carbonyl compounds
a) HCHO > 𝐶H3 COCH3 > 𝜙𝐶𝐻𝑂 b) CH3 COCH3 > 𝜙𝐶𝐻𝑂 > 𝐻𝐶𝐻𝑂
c) HCHO > 𝜙𝐶𝐻𝑂 > 𝐶H3 COCH3 d) CH3 COCH3 > 𝐻𝐶𝐻𝑂 > 𝜙𝐶𝐻𝑂
4. Cyanohydrin of which of the following forms lactic acid?
a) HCHO b) CH3 COCH3 c) CH3 CHO d) CH3 CH2 CHO
5. Ethyl acetate on reaction with a Grignard reagent gives,
a) Alcohol b) Aldehyde c) Acid d) Ketone
6. Acetaldehyde reacts with HCN followed by hydrolysis forms a compound which shows:
a) Optical isomerism
b) Geometrical isomerism
c) Metamerism
d) Tautomerism
7. Carboxylic acids dissolve in 𝑎𝑞. NaOH because the acids undergo:
a) Protonation b) Deprotonation c) Carboxylation d) Decarboxylation
8. Which of the acids cannot be prepared by Grignard reagent?
a) Acetic acid b) Succinic acid c) Formic acid d) All of these
9. Compound 𝐴 when treated with ethyl magnesim iodide in dry ether forms an addition compound which on
hydrolysis form compound 𝐵. The compound 𝐵 on oxidation form 3-pentanone. Hence, the compound 𝐴 and
𝐵 are
a) Propanol, 3-pentanol b) Pentanol, 3-pentanol c) Ethanal, pentanal d) Acetone, 3-pentanol
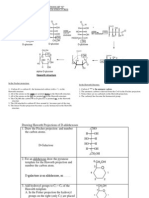
10. Suggest appropriate structures for the missing final compound. (The number of carbon atom remains the
same throughout the reaction.)
BRANCH – 1 : SIS – 130, FIRST FLOOR, HUDA MARKET, SECTOR-3, FARIDABAD
BRANCH – 2 : SCF-126, ABOVE ANDHRA BANK, FIRST FLOOR, HUDA MARKET, SECTOR-17, FARIDABAD
MOB. NO. 8505883137, 9625245071
a) b) c) d)
11. Lactic acid on heating with conc. H2 SO4 gives
a) Acetic acid b) Formic acid c) Acrylic acid d) Propionic acid
12. Urea can be detected by
a) Benedict test b) Molisch test c) Ninhydrine test d) Biurate test
13. Which of the following does not give brick red precipitate with Fehling’s solution?
a) Acetaldehyde b) Formalin c) D-glucose d) Acetone
14. Which of the following statements is wrong?
a) Formic acid is stronger than acetic acid
b) 𝑜-bromobenzoic acid is weaker than 𝑜-chlorobenzoic acid
c) Lactic acid does not answer the silver mirror test
d) Benzaldehyde does not reduce Fehling’s solution
15. Pick out the reaction in which formic and acetic acid differs from each other:
a) Sodium replaces hydrogen from the compound
b) Forms esters with alcohols
c) Reduces solution of ammoniacal silver nitrate or Fehling’s solution of dil. acid KMnO4
d) Turns red litmus blue
16. An organic substance from its aqueous solution can be separated by:
a) Solvent extraction b) Steam distillation c) Distillation d) Fractional distillation
17. The strongest acid amongst the following compounds is
a) CH3 COOH b) HCOOH c) CH3 CH2 CH(Cl)CO2 H d) ClCH2 CH2 CH2 COOH
18. What is obtained what acetyl chloride is heated with benzene in presence of anhydrous AlCl3
a) Acetyl benzoic acid b) Anisol c) Acetonephenone d) Chlolorobenzene
19. Reaction of formaldehyde and ammonia gives
a) Hexamethylene tetramine b) Bakelite
c) Urea d) Triethylene tetramine
20. 4-methyl benzene sulphonic acid reacts with sodium acetate to give
a) b) c) d)
BRANCH – 1 : SIS – 130, FIRST FLOOR, HUDA MARKET, SECTOR-3, FARIDABAD
BRANCH – 2 : SCF-126, ABOVE ANDHRA BANK, FIRST FLOOR, HUDA MARKET, SECTOR-17, FARIDABAD
MOB. NO. 8505883137, 9625245071
ANSWER-KEY
Q. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
A. C B C C D A B C A A
Q. 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
A. C D D C C A C C A A
BRANCH – 1 : SIS – 130, FIRST FLOOR, HUDA MARKET, SECTOR-3, FARIDABAD
BRANCH – 2 : SCF-126, ABOVE ANDHRA BANK, FIRST FLOOR, HUDA MARKET, SECTOR-17, FARIDABAD
MOB. NO. 8505883137, 9625245071
You might also like
- HRT-6 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidDocument3 pagesHRT-6 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidAakankshaNo ratings yet
- HRT-3 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidDocument4 pagesHRT-3 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidAakankshaNo ratings yet
- HRT-5 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidDocument3 pagesHRT-5 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidAakankshaNo ratings yet
- HRT-7 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidDocument4 pagesHRT-7 - Aldehydes, Ketons and Carboxylic AcidAakankshaNo ratings yet
- CHM222 Ch.8 (Ch.20) MCQDocument22 pagesCHM222 Ch.8 (Ch.20) MCQlianahajjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4Haseeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ester EnolatesDocument10 pagesEster EnolatesJunior GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQ XiiDocument53 pagesChemistry MCQ XiiHassan RedaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 OchemII QuizDocument13 pagesChapter 19 OchemII QuizPriyanka SaxenaNo ratings yet
- KetonesDocument13 pagesKetonesPriyanka SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 12 ComoleteDocument1 page12 ComoleteSheraz ShahNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry EM - Public Exam 2022 - Model Question Paper - English Medium PDF DownloadDocument4 pages12th Chemistry EM - Public Exam 2022 - Model Question Paper - English Medium PDF DownloadThenmozh iNo ratings yet
- Paper Class XDocument3 pagesPaper Class XHaiderNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SET C QPDocument9 pagesChemistry SET C QPowenknight3456No ratings yet
- Do Not Open This Booklet Until Told To Do SoDocument18 pagesDo Not Open This Booklet Until Told To Do SoNasyaNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Compounds Will Have Highest Boiling Point?Document4 pagesWhich of The Following Compounds Will Have Highest Boiling Point?reham khaledNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Carboxylic AcidDocument1 pageQuiz 2 Carboxylic AcidYousef AminNo ratings yet
- 1694692263SAT Chemistry Practice - Paper 38Document6 pages1694692263SAT Chemistry Practice - Paper 38agyeimalvin29No ratings yet
- Set 2Document6 pagesSet 2sanjith4arisNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE 2012 FST1 P2 QnsDocument25 pagesIIT-JEE 2012 FST1 P2 QnsShivamGoyalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10Document14 pagesChemistry 10BehruzNo ratings yet
- All Boards Full Book McqsDocument9 pagesAll Boards Full Book Mcqsbebetterpls3No ratings yet
- KVS Lucknow XII CHE QP & MS Pre-Board (23-24)Document11 pagesKVS Lucknow XII CHE QP & MS Pre-Board (23-24)GuestNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Questions Chapter Wise Upsc Capf Ac ExamDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRY Questions Chapter Wise Upsc Capf Ac Exambnnews2019100% (1)
- Chem 10 Ch#9,10,11,13Document3 pagesChem 10 Ch#9,10,11,13Zeeshan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQDocument11 pagesHalogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQParshantKumarBajaj92% (13)
- 116180HSSC IichemistryDocument2 pages116180HSSC IichemistryMughal usmanNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-III-CHE-PaperDocument6 pagesMock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-III-CHE-PaperHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- SIET CHEM Mock 2 PDFDocument7 pagesSIET CHEM Mock 2 PDFVikashNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Jee: Objective QuestionsDocument44 pagesQuestion Bank For Jee: Objective QuestionsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model Paper XIIDocument10 pagesChemistry Model Paper XIImoonmehar2240No ratings yet
- D) 3 AlcoholDocument9 pagesD) 3 AlcoholJessicaNo ratings yet
- Test 9Document1 pageTest 9Sheraz ShahNo ratings yet
- PUC II EXPERT CHEMISTRY 12 Set of MODEL QUESTION PAPERDocument46 pagesPUC II EXPERT CHEMISTRY 12 Set of MODEL QUESTION PAPERShreyasNo ratings yet
- FORM TP 2007061: Caribbean Examinations Council Secondary Education Certificate Examination ChemistryDocument8 pagesFORM TP 2007061: Caribbean Examinations Council Secondary Education Certificate Examination ChemistryJennifer ElliottNo ratings yet
- Kedah Chemistry Trial 2010 (NO BAHASA MELAYU)Document27 pagesKedah Chemistry Trial 2010 (NO BAHASA MELAYU)plouffleNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument5 pagesAssignment No. 6 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesREGINE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- Excel Educational Centre, Villa #25, Street #818, Al Thumama, Doha, QatarDocument7 pagesExcel Educational Centre, Villa #25, Street #818, Al Thumama, Doha, QatarteenaNo ratings yet
- CHEM W.S For G-9&10Document5 pagesCHEM W.S For G-9&10Chernet AhmedNo ratings yet
- CHM222 Ch.9 (Ch.21) MCQDocument44 pagesCHM222 Ch.9 (Ch.21) MCQlianahajjNo ratings yet
- Maritime Engineering Exam EthiopiaDocument7 pagesMaritime Engineering Exam EthiopiaLemi Chala Beyene95% (37)
- Alkynes and Aromatic CompoundsDocument4 pagesAlkynes and Aromatic Compounds22071a6652No ratings yet
- IIT JEE Main Sample Paper Set2 QuestionsDocument45 pagesIIT JEE Main Sample Paper Set2 QuestionsaskiitianNo ratings yet
- Chem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)Document4 pagesChem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)fahadmustafa100% (1)
- Test 12Document2 pagesTest 12Sheraz ShahNo ratings yet
- Trial p3 2016 Q (Johor-Sekolah Tinggi Muar)Document8 pagesTrial p3 2016 Q (Johor-Sekolah Tinggi Muar)Chan Yek FungNo ratings yet
- Diwali Assignment 12thDocument19 pagesDiwali Assignment 12thNishantPlayz YtNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Assignment No. 3 Chapters 11 12 (AY2021-2022 (2nd Sem)Document8 pagesAnswer Key Assignment No. 3 Chapters 11 12 (AY2021-2022 (2nd Sem)REGINE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- 12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument23 pages12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsBedosi Bidita PandaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry MCQDocument19 pagesClass 12 Chemistry MCQTayseer SaudiaNo ratings yet
- (ACOT'22) Part 1 - Bronze Tier SolnsDocument12 pages(ACOT'22) Part 1 - Bronze Tier SolnsAnju GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chem 17 LE 2 2nd SemDocument3 pagesChem 17 LE 2 2nd SemMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Practice Chapter 2 Hydrocarbon Frameworks - AlkanesDocument22 pagesPractice Chapter 2 Hydrocarbon Frameworks - AlkanesNadzirah ZaimNo ratings yet
- Application of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchFrom EverandApplication of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchRajmund MichalskiNo ratings yet
- AGARBATTI処方2Document16 pagesAGARBATTI処方2cobianNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet Alkanes Sbi 09Document6 pagesWork Sheet Alkanes Sbi 09neneng rohayatiNo ratings yet
- Name ReactionDocument15 pagesName Reactionnirbhay shukla100% (1)
- Analysis of Oxygen-Bearing Organic CompoundsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Oxygen-Bearing Organic CompoundsJudith Eliza MarianoNo ratings yet
- 2-328 Physical and Chemical Data: TABLE 2-371 Diffusivities of Pairs of Gases and Vapors (1 Atm)Document5 pages2-328 Physical and Chemical Data: TABLE 2-371 Diffusivities of Pairs of Gases and Vapors (1 Atm)opinion surNo ratings yet
- Drawing Haworth ProjectionsDocument4 pagesDrawing Haworth ProjectionsDoris GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Glove SafetyDocument2 pagesChemical Glove SafetynootsamNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 231111 210733Document3 pagesAssignment-1 231111 210733mamon137No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesCarbohydrates: Organic Chemistryistri kyungsoNo ratings yet
- Alcohols - Nomenclature and Classification: Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesAlcohols - Nomenclature and Classification: Learning ObjectivesDionisio BrinosaNo ratings yet
- CHIMICA PANZIERI Industrial-CatalogueDocument28 pagesCHIMICA PANZIERI Industrial-CatalogueJose E BatistaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Derivatives and NitrilesDocument23 pagesAcids, Derivatives and NitrilesLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- CarbenesDocument4 pagesCarbenesDr_GSNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xii NAME: - : Alcohol, Phenol & EtherDocument1 pageChemistry Xii NAME: - : Alcohol, Phenol & EtherSahir Hemnani100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - Benzene and AromaticityDocument38 pagesChapter 6 - Benzene and AromaticityS JNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Protecting GroupDocument39 pagesTopic 4 - Protecting Groupzatty kimNo ratings yet
- Oc02 Alkenesalkynesandcyclichydrocarbons WorksheetDocument5 pagesOc02 Alkenesalkynesandcyclichydrocarbons WorksheetEnma MaradiagaNo ratings yet
- Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal As A Building Block in Heterocyclic SynthesisDocument27 pagesDimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal As A Building Block in Heterocyclic SynthesisWalid Ebid ElgammalNo ratings yet
- Alkenes and Alkynes: Lesson 3Document21 pagesAlkenes and Alkynes: Lesson 3AlbaraaAliNo ratings yet
- Nomen 1st Day Quiz Key 2 PDFDocument16 pagesNomen 1st Day Quiz Key 2 PDFUday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations II - V 3 (Carbon With One Heteroatom Attached by A Multiple Bond)Document748 pagesComprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations II - V 3 (Carbon With One Heteroatom Attached by A Multiple Bond)Marlos BayerNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 DipadDocument4 pagesExp 4 DipadGrace HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument114 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryJoefrance MayagmaNo ratings yet
- Amines and Amides AnswersDocument2 pagesAmines and Amides AnswersKristine Sumalinog0% (1)
- Che102 Likely Qs and AnsDocument13 pagesChe102 Likely Qs and AnsAlexander GeorgeNo ratings yet
- NET-REAGENTS OlaxDocument5 pagesNET-REAGENTS Olaxraghava123456No ratings yet
- Mock Exam 2-AnswersDocument8 pagesMock Exam 2-AnswersKhaledEl-MaghallawyNo ratings yet
- Chapter36 - BiomoleculesDocument19 pagesChapter36 - BiomoleculesAkash GoelNo ratings yet
- Apch11 EstersDocument2 pagesApch11 Estersloly62006No ratings yet
- 2.24 Pyrans and Fused Pyrans: (Iii) Synthesis and ApplicationsDocument1 page2.24 Pyrans and Fused Pyrans: (Iii) Synthesis and ApplicationsscadvijayNo ratings yet