Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tut 1 Ah
Tut 1 Ah
Uploaded by
sunnybhosale2259Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ProblemsDocument14 pagesProblemsSophia VarshiniNo ratings yet
- MT Assignment - IDocument2 pagesMT Assignment - IDeneshVijayNo ratings yet
- 07M305 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery: Question BankDocument7 pages07M305 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery: Question BankAmarkarthik ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech ProblemsDocument2 pagesFluid Mech ProblemsMarky SantosNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Now That You Review The Most Essential Principles in Fluid Properties, PressureDocument1 pageActivity 1: Now That You Review The Most Essential Principles in Fluid Properties, PressureAllaizaNo ratings yet
- AssignDocument2 pagesAssignlaudaNo ratings yet
- FM QB At-2Document3 pagesFM QB At-2Tarini DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Laminar FlowDocument2 pagesLaminar Flowpyp_pypNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesMechanics of Fluids Question Bank PDFSuresh Raju100% (2)
- Unit IDocument5 pagesUnit IJackson ..No ratings yet
- Sheet 10Document1 pageSheet 10Hussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment EME 4350 FLUID IDocument2 pagesAssignment EME 4350 FLUID ISylvester WasongaNo ratings yet
- Ce8 PS1Document2 pagesCe8 PS1Yedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 1Document2 pagesIndividual Assignment 1Syazwani SallehNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Ayush ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1 cmt460Document2 pagesExercise Chapter 1 cmt460Nurin AidaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Topic 2 - Fluid PropertiesDocument2 pagesPractice Problems - Topic 2 - Fluid PropertiesAnonymous LDvhURRXmNo ratings yet
- FP 1 Objective QuestionsDocument16 pagesFP 1 Objective Questionsbachayadav0% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics - Problems - Solutions July 4 - EducspaceDocument19 pagesFluid Mechanics - Problems - Solutions July 4 - EducspaceAdrian SelgasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1.docx (ME-102)Document13 pagesAssignment 1.docx (ME-102)umair rasheedNo ratings yet
- Example ProblemsDocument5 pagesExample ProblemsSam OmpadNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Question Bank @Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics Question Bank @AnujNo ratings yet
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- B Tech Mechanical QuestionsDocument11 pagesB Tech Mechanical QuestionsAnkita VermaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1nexowa9068No ratings yet
- Assignment 1-AFM-FLUID MECHANICSDocument2 pagesAssignment 1-AFM-FLUID MECHANICSEcneicsNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesFluid MechanicsjsivabharathyNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment No 1 Properties of Fluid (3)Document3 pagesGroup Assignment No 1 Properties of Fluid (3)Bridget Nicole BordeosNo ratings yet
- Mto Problem Sheets 1 2 3Document5 pagesMto Problem Sheets 1 2 3Prakash DoliyaNo ratings yet
- Ha 5Document2 pagesHa 5PRIYANSHU VATSNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics QtnsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics QtnsAnonymous NV1AeWXEo100% (1)
- Tutorial Chapter1Document3 pagesTutorial Chapter1prakash ChapagainNo ratings yet
- Tutorial # 2Document2 pagesTutorial # 2sunnybhosale2259No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Problems - July 4Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics - Problems - July 4John Paul JacalanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - Laminar and Turbulent Flow in Circular Pipes.Document2 pagesTutorial 5 - Laminar and Turbulent Flow in Circular Pipes.afifiNo ratings yet
- Mto Problem Sheets 1Document4 pagesMto Problem Sheets 1Chandrapal Singh SolankiNo ratings yet
- Important 2 MarksDocument4 pagesImportant 2 MarksPandiya Rajan100% (1)
- Suresh SirDocument5 pagesSuresh SirPruthvi PrakashaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Set 2 of CE (ES) 401 2023Document7 pagesAssignment Set 2 of CE (ES) 401 2023Kausik BeraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial of 2nd Year Civil HydraulicDocument2 pagesTutorial of 2nd Year Civil HydraulicPankaj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment WTDocument1 pageAssignment WTTadesse MegersaNo ratings yet
- Agustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW3Document20 pagesAgustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW3mark agustinNo ratings yet
- Assisgnment - 1Document1 pageAssisgnment - 1File SharingNo ratings yet
- Fundmental Concepts - ProblemsDocument2 pagesFundmental Concepts - Problemsadharb21No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Unit 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1 - Unit 1Kiran Babu100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment 4Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics Assignment 4Rojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Flid Mechanics AssignmentDocument2 pagesFlid Mechanics AssignmentAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1Marie Angeline BautistaNo ratings yet
- AIr NummericalDocument2 pagesAIr NummericalArnav TiwariNo ratings yet
- MEC241 Assignment 1Document1 pageMEC241 Assignment 1Shahrul EdeezaNo ratings yet
- Problems Ch01 Ch02.2015 IDocument16 pagesProblems Ch01 Ch02.2015 ISalvador Vargas-Diaz0% (1)
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document6 pagesTutorial Chapter 1dhiauddinfarhiNo ratings yet
- 3 Me 20me303 QB1Document5 pages3 Me 20me303 QB1Dhanush kumar NNo ratings yet
- Principle of Working of Grit ChamberDocument11 pagesPrinciple of Working of Grit ChamberAhmed Amedi100% (3)
- Assignment Set 3 of CE (ES) 401 2023Document7 pagesAssignment Set 3 of CE (ES) 401 2023Kausik BeraNo ratings yet
- Phy 210Document2 pagesPhy 210nadiaNo ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXXII, June, 1911 Water Purification Plant, Washington, D. C. Results of Operation.From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXXII, June, 1911 Water Purification Plant, Washington, D. C. Results of Operation.No ratings yet
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsFrom EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168No ratings yet
Tut 1 Ah
Tut 1 Ah
Uploaded by
sunnybhosale2259Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tut 1 Ah
Tut 1 Ah
Uploaded by
sunnybhosale2259Copyright:
Available Formats
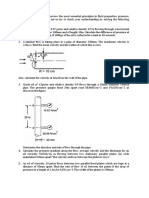
Tutorial # 1- Laminar Flow
1. A horizontal pipe 50 mm diameter carrying glycerin has shear stress at the pipe boundary
as 196.2 N/m2 [20 kg (f)/m2]. Determine the pressure gradient, mean velocity and
Reynolds number. Take for glycerin 𝜌 = 1275.3 kg/m3 (130 msl/m3) and μ = 80.442 ×
10–2N.s/m3 [8.20 × 10–2kg(f)–s/m2].
2. Two parallel plates kept 0.1 m apart have laminar flow of oil between them with a
maximum velocity of 1.5 m/s. Calculate the discharge per meter width, the shear stress at
the plates, the difference in pressure in pascals between two points 20 m apart, the
velocity gradient at the plates and velocity at 0.02 m from the plate. Take viscosity of oil
to be 2.453 N.s/m .
3. A small glass sphere of specific gravity 2.65 has a diameter of 3 mm. If the sphere falls
0.6 m in 30 seconds through a liquid of specific gravity 0.85, what is the absolute
viscosity of the liquid?
4. Find the radial location in a steady, fully developed, laminar flow in a circular horizontal
pipe where the local velocity is equal to the average velocity.
You might also like
- ProblemsDocument14 pagesProblemsSophia VarshiniNo ratings yet
- MT Assignment - IDocument2 pagesMT Assignment - IDeneshVijayNo ratings yet
- 07M305 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery: Question BankDocument7 pages07M305 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery: Question BankAmarkarthik ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech ProblemsDocument2 pagesFluid Mech ProblemsMarky SantosNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Now That You Review The Most Essential Principles in Fluid Properties, PressureDocument1 pageActivity 1: Now That You Review The Most Essential Principles in Fluid Properties, PressureAllaizaNo ratings yet
- AssignDocument2 pagesAssignlaudaNo ratings yet
- FM QB At-2Document3 pagesFM QB At-2Tarini DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Laminar FlowDocument2 pagesLaminar Flowpyp_pypNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesMechanics of Fluids Question Bank PDFSuresh Raju100% (2)
- Unit IDocument5 pagesUnit IJackson ..No ratings yet
- Sheet 10Document1 pageSheet 10Hussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment EME 4350 FLUID IDocument2 pagesAssignment EME 4350 FLUID ISylvester WasongaNo ratings yet
- Ce8 PS1Document2 pagesCe8 PS1Yedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 1Document2 pagesIndividual Assignment 1Syazwani SallehNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Ayush ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1 cmt460Document2 pagesExercise Chapter 1 cmt460Nurin AidaNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - Topic 2 - Fluid PropertiesDocument2 pagesPractice Problems - Topic 2 - Fluid PropertiesAnonymous LDvhURRXmNo ratings yet
- FP 1 Objective QuestionsDocument16 pagesFP 1 Objective Questionsbachayadav0% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics - Problems - Solutions July 4 - EducspaceDocument19 pagesFluid Mechanics - Problems - Solutions July 4 - EducspaceAdrian SelgasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1.docx (ME-102)Document13 pagesAssignment 1.docx (ME-102)umair rasheedNo ratings yet
- Example ProblemsDocument5 pagesExample ProblemsSam OmpadNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Question Bank @Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics Question Bank @AnujNo ratings yet
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- B Tech Mechanical QuestionsDocument11 pagesB Tech Mechanical QuestionsAnkita VermaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1nexowa9068No ratings yet
- Assignment 1-AFM-FLUID MECHANICSDocument2 pagesAssignment 1-AFM-FLUID MECHANICSEcneicsNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesFluid MechanicsjsivabharathyNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment No 1 Properties of Fluid (3)Document3 pagesGroup Assignment No 1 Properties of Fluid (3)Bridget Nicole BordeosNo ratings yet
- Mto Problem Sheets 1 2 3Document5 pagesMto Problem Sheets 1 2 3Prakash DoliyaNo ratings yet
- Ha 5Document2 pagesHa 5PRIYANSHU VATSNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics QtnsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics QtnsAnonymous NV1AeWXEo100% (1)
- Tutorial Chapter1Document3 pagesTutorial Chapter1prakash ChapagainNo ratings yet
- Tutorial # 2Document2 pagesTutorial # 2sunnybhosale2259No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Problems - July 4Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics - Problems - July 4John Paul JacalanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - Laminar and Turbulent Flow in Circular Pipes.Document2 pagesTutorial 5 - Laminar and Turbulent Flow in Circular Pipes.afifiNo ratings yet
- Mto Problem Sheets 1Document4 pagesMto Problem Sheets 1Chandrapal Singh SolankiNo ratings yet
- Important 2 MarksDocument4 pagesImportant 2 MarksPandiya Rajan100% (1)
- Suresh SirDocument5 pagesSuresh SirPruthvi PrakashaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Set 2 of CE (ES) 401 2023Document7 pagesAssignment Set 2 of CE (ES) 401 2023Kausik BeraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial of 2nd Year Civil HydraulicDocument2 pagesTutorial of 2nd Year Civil HydraulicPankaj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment WTDocument1 pageAssignment WTTadesse MegersaNo ratings yet
- Agustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW3Document20 pagesAgustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW3mark agustinNo ratings yet
- Assisgnment - 1Document1 pageAssisgnment - 1File SharingNo ratings yet
- Fundmental Concepts - ProblemsDocument2 pagesFundmental Concepts - Problemsadharb21No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Unit 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1 - Unit 1Kiran Babu100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment 4Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics Assignment 4Rojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Flid Mechanics AssignmentDocument2 pagesFlid Mechanics AssignmentAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document1 pageProblem Set 1Marie Angeline BautistaNo ratings yet
- AIr NummericalDocument2 pagesAIr NummericalArnav TiwariNo ratings yet
- MEC241 Assignment 1Document1 pageMEC241 Assignment 1Shahrul EdeezaNo ratings yet
- Problems Ch01 Ch02.2015 IDocument16 pagesProblems Ch01 Ch02.2015 ISalvador Vargas-Diaz0% (1)
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document6 pagesTutorial Chapter 1dhiauddinfarhiNo ratings yet
- 3 Me 20me303 QB1Document5 pages3 Me 20me303 QB1Dhanush kumar NNo ratings yet
- Principle of Working of Grit ChamberDocument11 pagesPrinciple of Working of Grit ChamberAhmed Amedi100% (3)
- Assignment Set 3 of CE (ES) 401 2023Document7 pagesAssignment Set 3 of CE (ES) 401 2023Kausik BeraNo ratings yet
- Phy 210Document2 pagesPhy 210nadiaNo ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXXII, June, 1911 Water Purification Plant, Washington, D. C. Results of Operation.From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXXII, June, 1911 Water Purification Plant, Washington, D. C. Results of Operation.No ratings yet
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsFrom EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168No ratings yet