Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 42
Table 42
Uploaded by
Emon Faiz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
TABLE 42_
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesTable 42
Table 42
Uploaded by
Emon FaizCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Huppert’s Notes: Pathophysiology and Clinical Pearls for Internal Medicine >Diagnostics in
Gastroenterology
Laura A. Huppert, Timothy G. Dyster, (Lead Contributing Editor)+
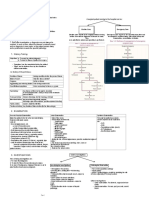
TABLE 4.2Diagnostic Tests in Gastroenterology
Study Indication Procedure Details
•Diagnosis: Upper GI bleed (UGIB), iron-deficiency anemia,
diarrhea with features of small bowel disease (e.g., celiac),
refractory GERD, dysphagia, odynophagia, upper abdominal •Prep: NPO for >8 hr
symptoms with alarm features (e.g., unintentional weight loss, •Sedation: Options include moderate sedation, monitored
early satiety) anesthesia care, general anesthesia
•Treatment: •Procedure: Endoscope inserted through the mouth and advanced
through the esophagus, stomach, and as far as to the second
Upper endoscopy (EGD)
•- UGIB: Injections, thermals/cautery, mechanical clipping portion of duodenum. Biopsies and therapeutics can be performed
•- Varices: Variceal banding as indicated.
•- Achalasia, stenosis, strictures •Push enteroscopy: Variation of an EGD that utilizes a longer
•- Pneumatic dilation, stent placement endoscope, which makes it possible to advance beyond the
•- Malignancy: Stent placement, resection ligament of Treitz and into the jejunum.
•Screening: Barrett’s esophagus, upper GI malignancies in high-
risk patients
•Diagnosis: Lower GI bleed (LGIB), iron-deficiency anemia, lower
•Prep: Clear liquids × 1 day prior with bowel prep, NPO at least 2
GI symptoms (e.g., chronic diarrhea), evaluation for IBD
hr
•Treatment:
•Sedation: Options include no sedation, moderate sedation,
monitored anesthesia care, general anesthesia
Colonoscopy •- LGIB: Injections, thermals/cautery, mechanical clipping
•Procedure: Colonoscope inserted through the anus and advanced
•- Polyp removal
through the rectum, large bowel, and small bowel up to the
•- Decompression of sigmoid volvulus/colonic pseudo-obstruction
cecum/terminal ileum. Biopsies and therapeutics can be
•- Balloon dilation of strictures
performed as indicated.
•Screening: Colorectal cancer (CRC)
•Prep: Less involved than colonoscopy: Enemas × 2
•Diagnosis: LGIB, iron-deficiency anemia, lower GI symptoms
•Sedation: None (benefit over colonoscopy)
(e.g., chronic diarrhea), surveillance for IBD.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy •Procedure: Colonoscope inserted through the anus and advanced
•Treatment: Polyp removal
through the rectum and up to the distal 60 cm of the colon (up to
•Screening: CRC (alternative to colonoscopy, q5yr)
the splenic flexure). Misses proximal/right-sided lesions. Thus,
colonoscopy is preferred for CRC screening.
•Prep: NPO for 12 hr
•Procedure: The patient swallows a video capsule. An external
•Diagnosis only: Iron-deficiency anemia with normal
Capsule endoscopy wireless recorder captures images of the entire GI tract while the
EGD/colonoscopy, small bowel tumor, Crohn’s disease.
capsule is in transit, and then the footage is analyzed. Capsules
are disposable and excreted with a bowel movement.
•Diagnosis/Treatment: Typically performed when both a
diagnostic/therapeutic indication are present, such as to evaluate •Prep: Pregnancy testing, coagulation studies, NPO for 8 hr
and possibly treat the following conditions: •Sedation: Monitored anesthesia care or general anesthesia
•Procedure: Combined endoscopic/fluoroscopic procedure.
•- Suspected biliary obstruction Duodenoscope is advanced through the mouth and to the
•- Suspected pancreatic/biliary malignancy duodenum. A catheter is then inserted into the papilla of Vater
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopan-creatography (ERCP)
•- Acute pancreatitis with cholangitis or biliary obstruction and contrast is injected. X-rays are taken of the biliary tree and
•- Choledocholithiasis pancreatic duct. May perform sphincterotomy, stent placement,
•- Biliary dyskinesia CBD stone extraction, and/or dilation of strictures.
•- Biliary strictures •Complications: >5% risk: Acute pancreatitis, bleeding,
•- Pancreatic pseudocyst drainage cholangitis/sepsis, perforation
•Limitation: Difficult to perform in Roux-en-Y anatomy
•Prep: NPO for 8 hr
•Diagnosis: Pancreatic cancer with FNA, choledocholithiasis,
•Sedation: Monitored anesthesia care, general anesthesia
submucosal masses of stomach, duodenum, rectum.
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) •Procedure: Endoscope with an ultrasound transducer is advanced
•Treatment: Pancreatic fluid collection drainage, celiac plexus
through the mouth and down to the duodenum. Enables clearer
neurolysis (improves pain control in pancreatic cancer)
view of the pancreas. Can be done in conjunction with FNA.
•Diagnosis only: Choledocholithiasis, biliary strictures, chronic •Prep: NPO for 4 hr
Magnetic resonance cholangiopan-creatography (MRCP) pancreatitis, suspected congenital anomaly of pancreaticobiliary •Procedure: Same as MRI scan. Allows for better visualization of
tract, preop/postop evaluation of biliary abnormalities pancreaticobiliary tract
•Procedure: The patient is put in a prone or supine position with tilt
and then instructed to rapidly swallow barium contrast (100-200
•Diagnosis only: Dysphagia, esophageal perforation, hiatal hernia, cc). X-ray or fluoroscopy is used to evaluate the patient’s swallow,
Barium swallow malignancy, diverticula, esophageal motility disorders (e.g., enabling the localization of lesions and the initial identification of
achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm) some esophageal pathologies.
•Classic findings: “Bird beak” appearance of achalasia, “corkscrew
sign” in diffuse esophageal spasm
•Procedure: Can be conventional or high resolution (more pressure
sensors). A long tube is positioned in the esophagus terminating
•Diagnosis only: Esophageal motility disorders (e.g., achalasia,
Esophageal manometry in the stomach. The patient is instructed to swallow, and then the
hypercontractile esophagus, distal esophageal spasm)
system detects pressure changes generated by the esophagus or
the upper/lower esophageal sphincter.
•Procedure: Options include a transnasally placed catheter or a
Ambulatory pH monitoring •Diagnosis only: GERD wireless capsule that is fixed to the distal mucosa. pH sensor
results are analyzed after 24 hr to 4 days.
Date of download: 09/13/21 from AccessMedicine: accessmedicine.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw Hill. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- The Complete Family Guide To SchizophreniaDocument497 pagesThe Complete Family Guide To Schizophreniaaganayan100% (1)
- Overview of Lower GastroIntestinal Bleeding 1.1Document42 pagesOverview of Lower GastroIntestinal Bleeding 1.1Raja Ain100% (1)
- The Eyelids and The OrbitDocument7 pagesThe Eyelids and The OrbitRawana AliNo ratings yet
- GI Liver PerceptionDocument9 pagesGI Liver PerceptionJUDE ARIZALANo ratings yet
- Causes of Acute PeritonitisDocument6 pagesCauses of Acute PeritonitisYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- 116 - Alterations in GI EliminationDocument12 pages116 - Alterations in GI EliminationGino-o, KyleNo ratings yet
- Emergenze Addome RXDocument9 pagesEmergenze Addome RXBrovazzo PieroNo ratings yet
- LEC 08-Hernia-Collective NotesDocument36 pagesLEC 08-Hernia-Collective NotesAmira NabilNo ratings yet
- GIT Fully DoneDocument14 pagesGIT Fully DoneTirtha Taposh100% (1)
- UntitledDocument44 pagesUntitledKaye A. JardinicoNo ratings yet
- 02 ConstipationDocument11 pages02 ConstipationYunus AmmarieNo ratings yet
- Common Causes of PUD: Duodenal Ulcer: A Peptic Ulcer of TheDocument8 pagesCommon Causes of PUD: Duodenal Ulcer: A Peptic Ulcer of Thestudy mailNo ratings yet
- Ileus & ObstructionDocument3 pagesIleus & ObstructionYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Gep MidtermDocument20 pagesNCM 116 Gep MidtermKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Protocol-ABDOMINAL DISTENTION-ServandoDocument4 pagesProtocol-ABDOMINAL DISTENTION-ServandoAllison Eunice ServandoNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Concept MapDocument17 pagesPeptic Ulcer Concept Mappotchistroberri100% (1)
- Duodenal PerforationDocument20 pagesDuodenal PerforationarbindraNo ratings yet
- Surgery ReviewerDocument21 pagesSurgery ReviewerHarissa Katrina De LaraNo ratings yet
- Surgical Specialties DR - PaghubasanDocument11 pagesSurgical Specialties DR - PaghubasanRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Diseases Part2Document8 pagesGastrointestinal Diseases Part2sarguss14No ratings yet
- Liver Biopsy: Mary Raina Angeli Fujiyoshi, MDDocument10 pagesLiver Biopsy: Mary Raina Angeli Fujiyoshi, MDRaina FujiyoshiNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument26 pagesPerioperative NursingTine Guibao100% (1)
- Cancer of The Stomach Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesCancer of The Stomach Stomach CancerCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- 2015 Colectomy Brochure FINALDocument8 pages2015 Colectomy Brochure FINALAnghelo Aldair Velásquez CarrilloNo ratings yet
- KKKKDocument22 pagesKKKKMARY CLAIRE SUMILHIGNo ratings yet
- Investigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceDocument38 pagesInvestigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceUjas PatelNo ratings yet
- Funda D2 by Prof Melody BautistaDocument3 pagesFunda D2 by Prof Melody BautistaGeraldine MaeNo ratings yet
- 227 Ramirez, Diana Rose S. August 3, 2022Document1 page227 Ramirez, Diana Rose S. August 3, 2022Diana Rose RamirezNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing Day2Document15 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Day2lindzy.amurao01No ratings yet
- Git Radiology 160216093600 1Document39 pagesGit Radiology 160216093600 1Wangju Sumnyan100% (1)
- Peritonitis Sek UnderDocument2 pagesPeritonitis Sek UnderAnonymous eF8cmVvJaNo ratings yet
- Anorexia: Basic InformationDocument34 pagesAnorexia: Basic InformationcarlosNo ratings yet
- RanitidineDocument2 pagesRanitidineHarvey BanagNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm MidconDocument1 pageAneurysm MidconVamshi TejavathNo ratings yet
- Week 11: Nursing Care of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal Disorders Abnormalities of Fecal EliminationDocument9 pagesWeek 11: Nursing Care of Patients With Intestinal and Rectal Disorders Abnormalities of Fecal Eliminationeliza luisNo ratings yet
- Renal and Urinary DisordersDocument11 pagesRenal and Urinary DisordersChristian Espanilla100% (4)
- Nursing Management of Git Problems: Oral and Esophageal DisordersDocument18 pagesNursing Management of Git Problems: Oral and Esophageal Disorderslcpot_se7en7505100% (2)
- Presenting Problems in Gastrointestinal Disease:: DysphagiaDocument9 pagesPresenting Problems in Gastrointestinal Disease:: DysphagiaMohamed AlsaabNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 GIT RKDocument46 pagesLecture-3 GIT RKmuhammadameerhamza4786No ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet, Small and Large Bowel ObstructionDocument16 pagesGastric Outlet, Small and Large Bowel ObstructionGoodone OneNo ratings yet
- Powrerpoint: Gastro-Duodenal Surgical DiseasesDocument45 pagesPowrerpoint: Gastro-Duodenal Surgical Diseasesj.doe.hex_870% (1)
- GASTRODocument11 pagesGASTRONatricia TrondilloNo ratings yet
- Elec 3 GIT Sem 5Document79 pagesElec 3 GIT Sem 5Ebraheem NegmNo ratings yet
- Therapeutics in Biliary DiseasesDocument37 pagesTherapeutics in Biliary DiseasesLucy LimNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument31 pagesAcute AbdomenWildan AngelouNo ratings yet
- GI ReviewDocument44 pagesGI Reviews129682No ratings yet
- Presentation 24 - Copy Intestinal ObstructionDocument11 pagesPresentation 24 - Copy Intestinal Obstructionrbawa0800No ratings yet
- Surgery EORDocument76 pagesSurgery EORAndrew BowmanNo ratings yet
- Lower GIT 1Document15 pagesLower GIT 1Zuhra JabeenNo ratings yet
- Presentation From Today's Meeting !Document67 pagesPresentation From Today's Meeting !chaitanya varmaNo ratings yet
- General Surgery IntroductionDocument1 pageGeneral Surgery IntroductionAndrew BonusNo ratings yet
- Atlas FK UnairDocument45 pagesAtlas FK UnairMITHANo ratings yet
- ARenalDocument8 pagesARenalf14chrisNo ratings yet
- PathopysiologyDocument14 pagesPathopysiologyAbigail Faith PretestoNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For Endoscopic Procedures: What Goes In, Must Come Out (Or Call A Surgeon)Document26 pagesAnesthesia For Endoscopic Procedures: What Goes In, Must Come Out (Or Call A Surgeon)dpeka dpekaNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Jaundice: Endoscopic ManagementDocument51 pagesObstructive Jaundice: Endoscopic ManagementTopher ReyesNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary Notes 2.0Document18 pagesHepatobiliary Notes 2.0Sri VathanahNo ratings yet
- Home Care RN Skills ChecklistDocument2 pagesHome Care RN Skills ChecklistGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- GASTROINTESTINALDocument9 pagesGASTROINTESTINALjsreyes.402No ratings yet
- The Perfect Ic Diet Cookbook The Complete Nutrition Guide To Healing Chronic Pelvic Pain And Managing Symptoms Of Interstitial Cystitis With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Ic Diet Cookbook The Complete Nutrition Guide To Healing Chronic Pelvic Pain And Managing Symptoms Of Interstitial Cystitis With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- "Azithromycin": Bachelor of PharmacyDocument36 pages"Azithromycin": Bachelor of Pharmacydeepak_143No ratings yet
- Vaccination Schedule of Small and Large Animals NewDocument5 pagesVaccination Schedule of Small and Large Animals NewMahnoor ArshadNo ratings yet
- Loneliness & IsolationDocument31 pagesLoneliness & Isolationnadzirah ruslanNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Butterfly Innovative Entrepren - Yaniv IzakiDocument39 pagesThe Carbon Butterfly Innovative Entrepren - Yaniv IzakifabchatNo ratings yet
- Hyper Hyponatremia LERMADocument8 pagesHyper Hyponatremia LERMAJINYVEV APARICINo ratings yet
- 2-Downer Cow and HypoMgDocument13 pages2-Downer Cow and HypoMgY.rajuNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Manifestation of HIVDocument16 pagesGastrointestinal Manifestation of HIVashuNo ratings yet
- Drugs 2018 FebDocument143 pagesDrugs 2018 FebTuliNo ratings yet
- Find Out The Lack of Healthcare Concerns of Mass Populations and The Local Government During The Epidemic in Rural Area: A Study On Basail Upazila, Tangail, BangladeshDocument6 pagesFind Out The Lack of Healthcare Concerns of Mass Populations and The Local Government During The Epidemic in Rural Area: A Study On Basail Upazila, Tangail, BangladeshMuhammad Al AminNo ratings yet
- Fix JurnalDocument12 pagesFix JurnalYolanda Qonita ShalihatNo ratings yet
- CESU ORD DRAFT EDITED Sent To Dr. AlfieDocument7 pagesCESU ORD DRAFT EDITED Sent To Dr. AlfieDulce TomotorgoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Veruka VulgarisDocument3 pagesJurnal Veruka Vulgariscitra annisa fitriNo ratings yet
- HES 032 BSN - Lecture Comprehensive ExamDocument47 pagesHES 032 BSN - Lecture Comprehensive ExamDIAZ, GIANNA D.No ratings yet
- ST 9 PDFDocument2 pagesST 9 PDFsorinNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry: Psychology-Psychiatric Evaluation - 1 (Medical Transcription Sample Report)Document7 pagesPsychiatry: Psychology-Psychiatric Evaluation - 1 (Medical Transcription Sample Report)Nguyên VũNo ratings yet
- Fimmu 09 00328Document11 pagesFimmu 09 00328miss betawiNo ratings yet
- TB ArticleDocument2 pagesTB ArticlePinpin Jao SerraNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 NotesDocument6 pagesNCM 112 NotesKatrina Jhane MercadoNo ratings yet
- MHN Ii Unit 2Document33 pagesMHN Ii Unit 2Blessing GloriaNo ratings yet
- GreatAuPair Medical Evaluation Form 01012014Document4 pagesGreatAuPair Medical Evaluation Form 01012014EhickyyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular MCQsDocument23 pagesCardiovascular MCQssb medexNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument8 pagesBronchial AsthmaSiti HalijahNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy in ChildrenDocument7 pagesCerebral Palsy in ChildrenKelvin FundiNo ratings yet
- Tetanus, Botulisn, Gas GangreneDocument87 pagesTetanus, Botulisn, Gas GangreneTarik100% (1)
- s12904 022 01101 4Document9 pagess12904 022 01101 4Gabriel MoraguesNo ratings yet
- Nimesulide BrandsDocument1 pageNimesulide BrandsKimberly RiceNo ratings yet
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: Review of The Literature: Stitt CarolinaDocument4 pagesStevens-Johnson Syndrome: Review of The Literature: Stitt CarolinaNurul AfiahNo ratings yet
- Pharma - SkinDocument8 pagesPharma - Skinreference books100% (1)